| Citation: |
Yong Sun, Xiujuan Miao, Zhaohua Ding, Jinglin Xiao. The properties of an asymmetric Gaussian potential quantum well qubit in RbCl crystal[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(4): 042002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/4/042002
****
Y Sun, X J Miao, Z H Ding, J L Xiao. The properties of an asymmetric Gaussian potential quantum well qubit in RbCl crystal[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(4): 042002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/4/042002.
|
The properties of an asymmetric Gaussian potential quantum well qubit in RbCl crystal
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/4/042002
More Information
-
Abstract
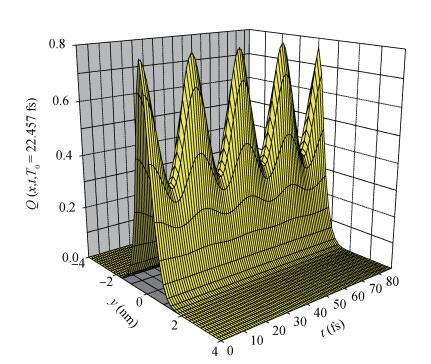
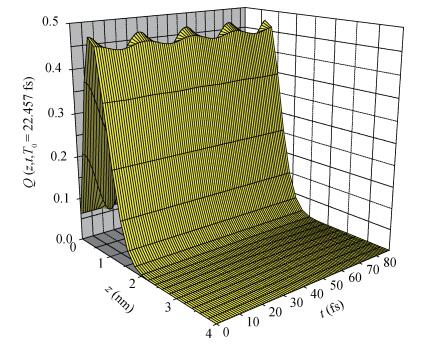
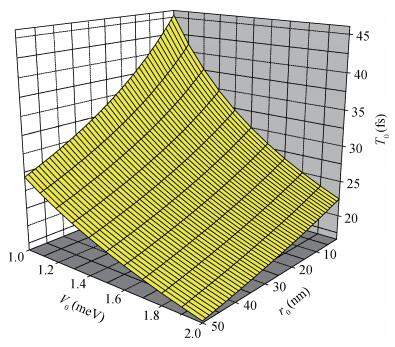
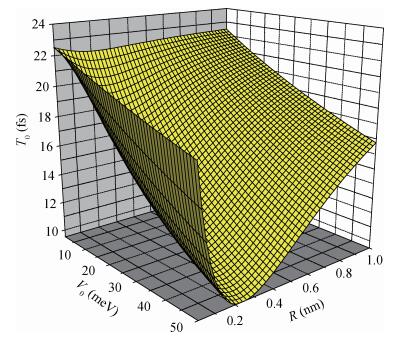
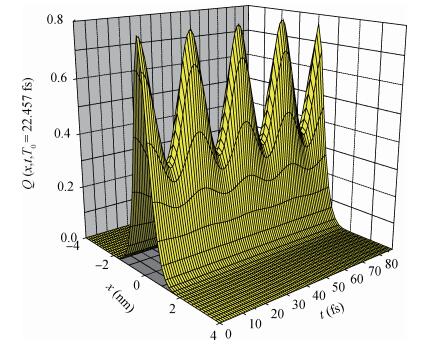
With the circumstance of the electron strongly coupled to LO-phonon and using the variational method of Pekar type (VMPT), we study the eigenenergies and the eigenfunctions (EE) of the ground and the first excited states (GFES) in a RbCl crystal asymmetric Gaussian potential quantum well (AGPQW). It concludes: (i) Two-energy-level of the AGPQW may be seen as a qubit. (ii) When the electron located in the superposition state of the two-energy-level system, the time evolution and the coordinate changes of the electron probability density oscillated periodically in the AGPQW with every certain period T0=22.475 fs. (iii) Due to the confinement that is a two dimensional x-y plane symmetric structure in the AGPQW and the asymmetrical Gaussian potential (AGP) in the AGPQW growth direction, the electron probability density presents only one peak configuration located in the coordinate of z>0, whereas it is zero in the range of z < 0. (iv) The oscillatory period is a decreasing function of the AGPQW height and the polaron radius. (v) The oscillating period is a decreasing one in the confinement potential R < 0.24 nm, whereas it is an increasing one in the confinement potential R>0.24 nm and it takes a minimum value in R=0.24 nm. -
References
[1] Cho A Y, Arthur J R. Molecular beam epitaxy. Prog Solid State Chem, 1975, 10: 157 doi: 10.1016/0079-6786(75)90005-9[2] Dupuis R D, Dapkus P D, Holonyak N Jr, et al. Room temperature laser operation of quantum well Ga1-xAlxAsGaAs laser diodes grown by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. Appl Phys Lett, 1978, 32(5): 295 doi: 10.1063/1.90026[3] Vargo T G, Thompson P M, Gerenser L J, et al. Monolayer chemical lithography and characterization of fluoropolymer films. Langmuir, 1992, 8(1): 130 doi: 10.1021/la00037a025[4] Negoita V, Snoke D W, Eberl K. Harmonic-potential traps for indirect excitons in coupled quantum wells. Phys Rev B, 1999, 60(4): 2661 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.60.2661[5] Nomura S, Nakanishi T, Aoyagi Y. Fermi-edge singularities in photoluminescence spectra of n-type modulation-doped quantum wells with a lateral periodic potential. Phys Rev B, 2001, 63(16): 165330 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.63.165330[6] Alsina F, Stotz J A H, Hey R, et al. Acoustically induced potential dots in GaAs quantum wells. Solid State Commun, 2004, 129(7): 453 doi: 10.1016/j.ssc.2003.11.014[7] Clausen C, Usmani I, Bussiéres F, et al. Quantum storage of photonic entanglement in a crystal. Nature, 2011, 469(7331): 508 doi: 10.1038/nature09662[8] Weitenberg C, Kuhr S, Molmer K, et al. Quantum computation architecture using optical tweezers. Phys Rev A, 2011, 84(3): 032322 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.84.032322[9] Alicea J, Oreg Y, Refael G, et al. Non-Abelian statistics and topological quantum information processing in 1D wire networks. Nat Phys, 2011, 7(5): 412 doi: 10.1038/nphys1915[10] Ferrón A, Serra P, Osenda O. Quantum control of a model qubit based on a multi-layered quantum dot. J Appl Phys, 2013, 113(13): 134304 doi: 10.1063/1.4795608[11] Jordan S P, Lee K S M, Preskill J. Quantum algorithms for quantum field theories. Science, 2012, 336(6085): 1130 doi: 10.1126/science.1217069[12] Zhang L, Luo J W, Saraiva A, et al. Genetic design of enhanced valley splitting towards a spin qubit in silicon. Nat Commun, 2012, 4: 2396 http://www.colorado.edu/zunger-materials-by-design/sites/default/files/attached-files/640.pdf[13] Zhai W. A study of electric-field-induced second-harmonic generation in asymmetrical Gaussian potential quantum wells. Physica B, 2014, 454: 50 doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2014.07.030[14] Wu J, Guo K, Liu G. Polaron effects on nonlinear optical rectification in asymmetrical Gaussian potential quantum wells with applied electric fields. Physica B, 2014, 446: 59 doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2014.04.013[15] Ma X J, Xiao B Y, Sun Y, et al. Effects of magnetic field on the polaron in an asymmetrical Gaussian confinement potential quantum well. J Semicond, 2015, 36(10): 102004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/10/102004[16] Xiao W, Qi B, Xiao J L. Impurity effect of asymmetric Gaussian potential quantum well qubit. J Low Temp Phys, 2015, 179(3/4): 166 doi: 10.1007/s10909-015-1276-z[17] Xiao J L. The effect of electric field on RbCl asymmetric Gaussian potential quantum well qubit. Int J Theor Phys, 2016, 55(1): 147 doi: 10.1007/s10773-015-2644-9[18] Cai C Y, Zhao C L, Xiao J L. The effect of magnetic field on an asymmetrical Gaussian potential quantum well qubit. Commun Theor Phys, 2015, 63(2): 159 doi: 10.1088/0253-6102/63/2/07[19] Landau L D, Pekar S I. Effective mass of the polaron. J Exp Theor Phys, 1948, 18: 419 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780080105864500729[20] Pekar S I. Dispersion of light in the exciton absorption region of crystals. Zh Eksp Teor Fiz, 1958, 34(7): 1189 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/245263078_Dispersion_of_light_in_the_exciton_resonance_region_in_crystals[21] Pekar S I. Untersuchungen über die Elektronen-theorie der Kristalle. Berlin: Akademie Verlag, 1954[22] Sun Y, Ding Z H, Xiao J L. State energies and transition frequency of strong-coupling polaron in an anisotropic quantum dot. J At Mol Sci, 2013, 4: 176 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271351486_State_Energies_and_transition_frequency_of_strong-coupling_polaron_in_an_anisotropic_quantum_dot[23] Ding Z H, Sun Y, Xiao J L. Optical phonon effect in an asymmetric quantum dot qubit. Int J Quantum Inf, 2012, 10(07): 1250077 doi: 10.1142/S0219749912500773[24] Li W P, Yin J W, Yu Y F, et al. The effect of magnetic on the properties of a parabolic quantum dot qubit. J Low Temp Phys, 2010, 160(3/4): 112 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265911246_Effects_of_Magnetic_Field_on_the_Coherence_Time_of_a_Parabolic_Quantum_Dot_Qubit[25] Wang Z W, Xiao J L. Parabolic linear bound potential quantum dot qubit and its optical phonon effect. Acta Phys Sinica, 2007, 56: 0678 http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-WLXB200702012.htm -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: