| Citation: |
Dan Lu, Yiming He, Zhaosong Li, Lingjuan Zhao, Wei Wang. InP-based monolithically integrated few-mode devices[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2018, 39(10): 101001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/10/101001
****
D Lu, Y M He, Z S Li, L J Zhao, W Wang, InP-based monolithically integrated few-mode devices[J]. J. Semicond., 2018, 39(10): 101001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/10/101001.
|
InP-based monolithically integrated few-mode devices
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/10/101001
More Information
-
Abstract
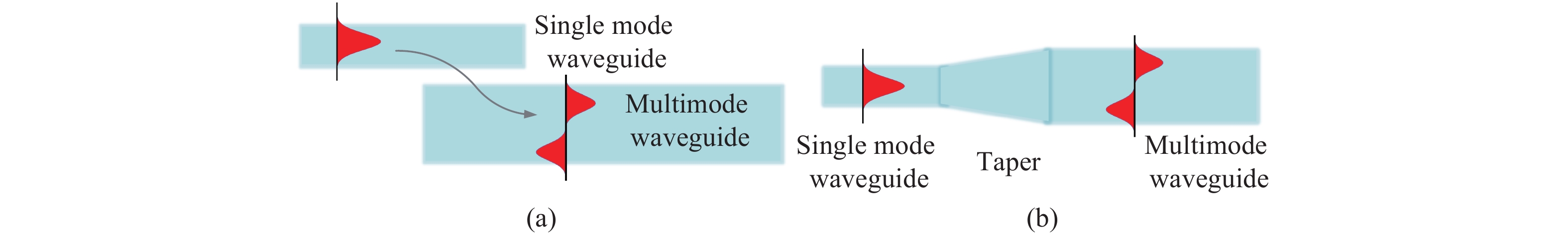
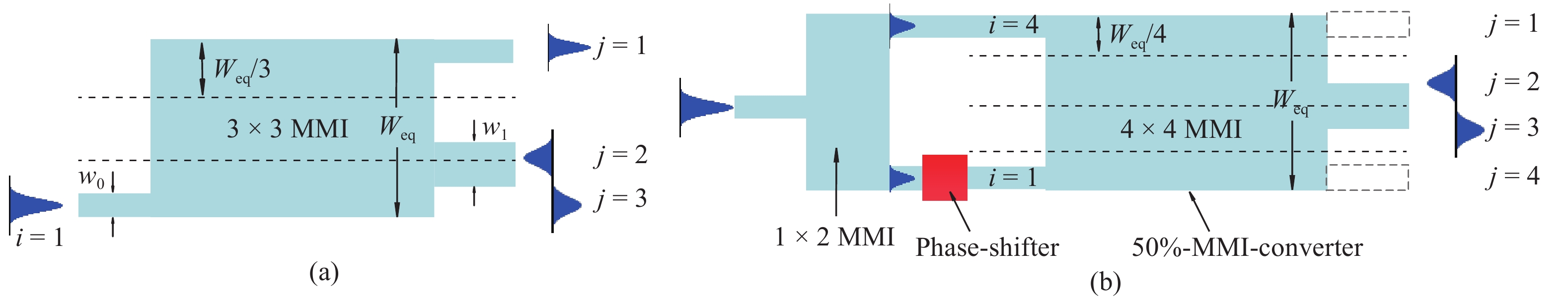
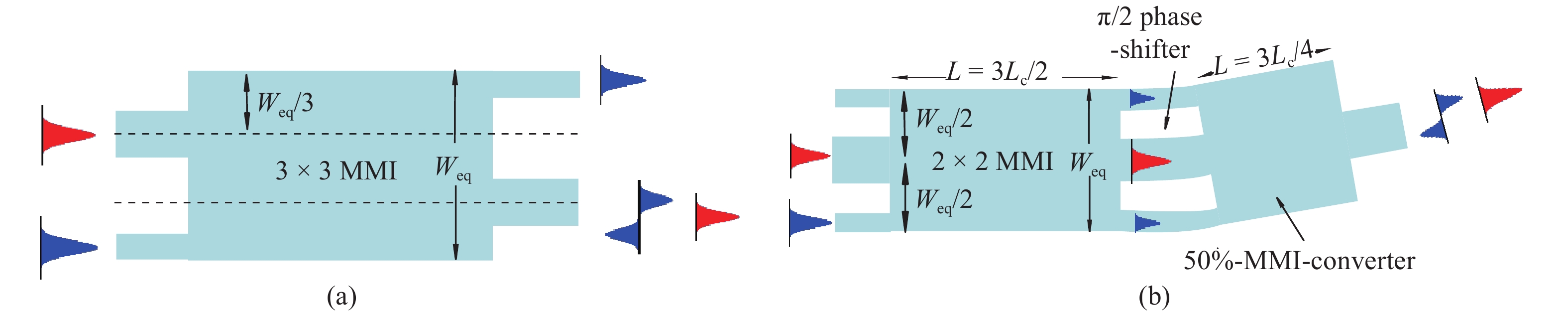
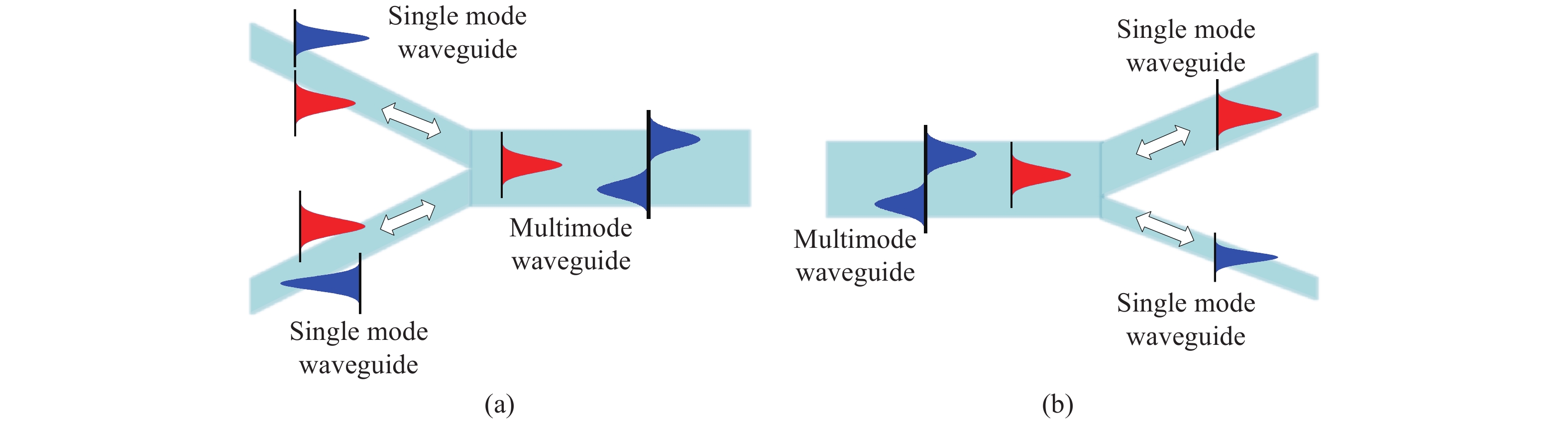
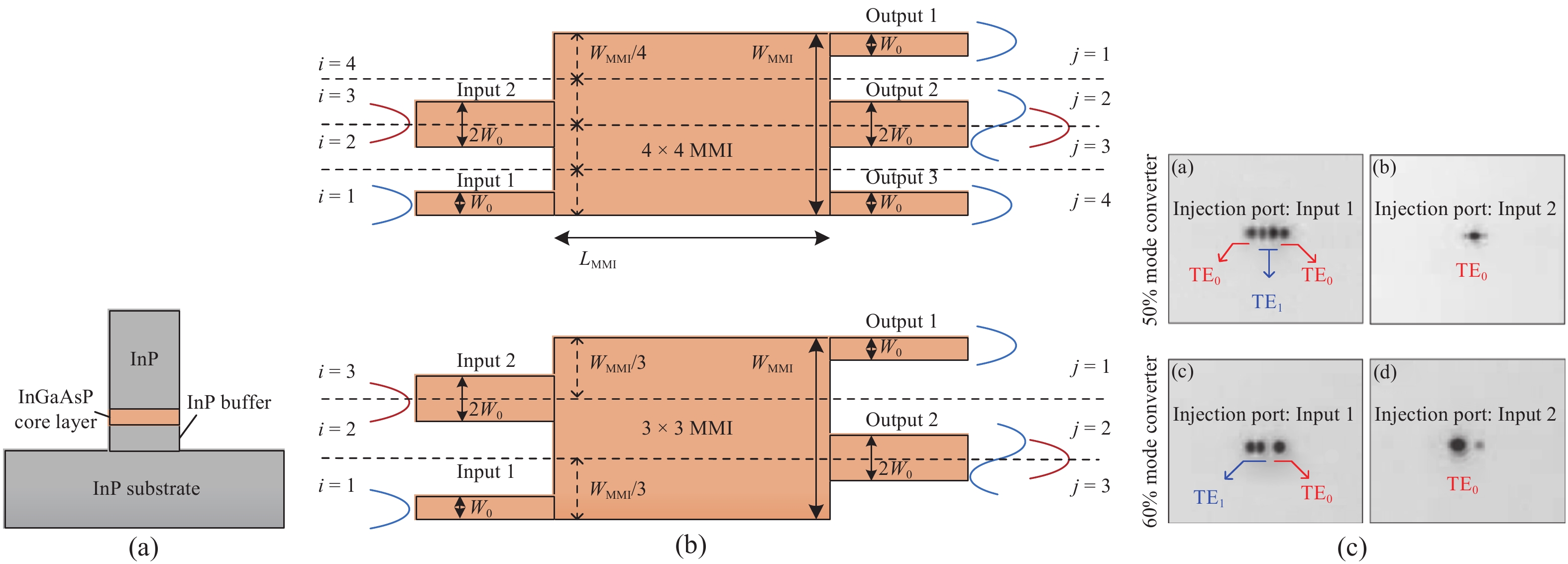
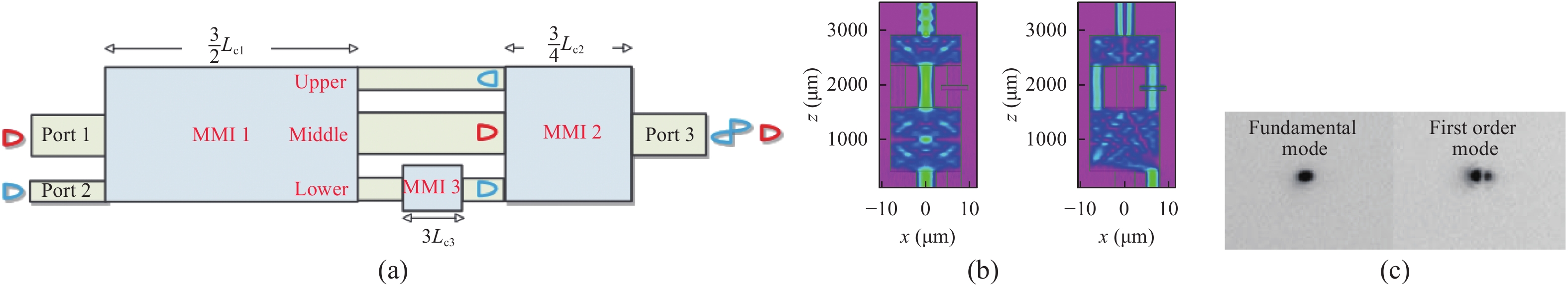
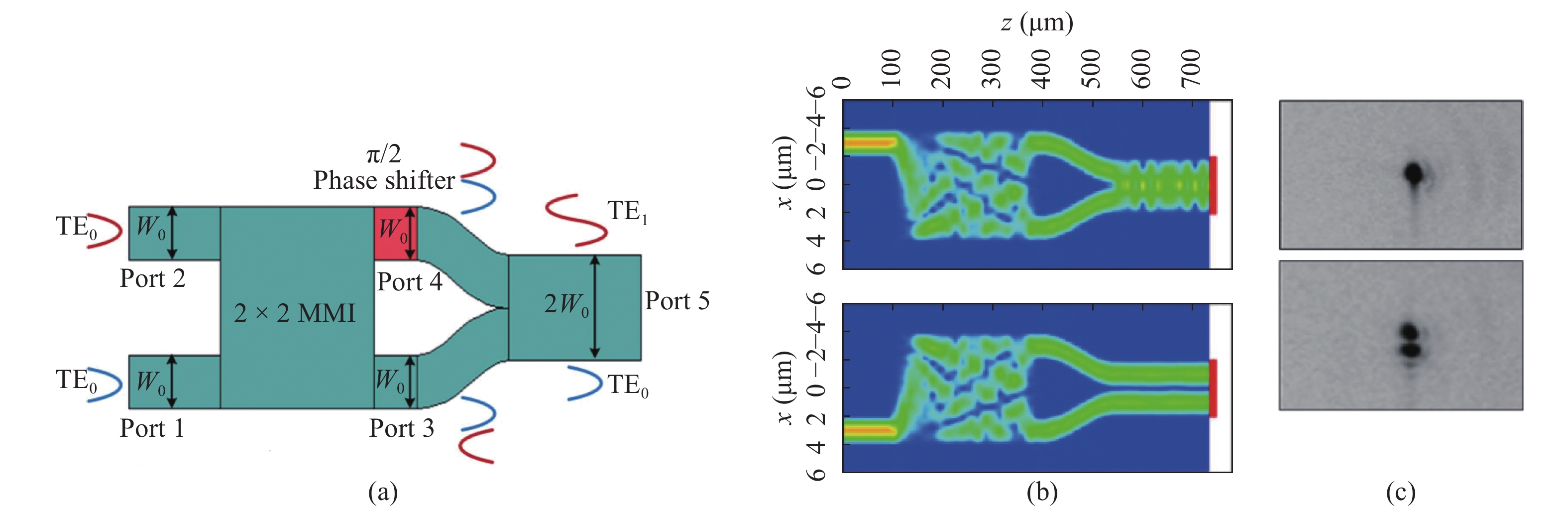
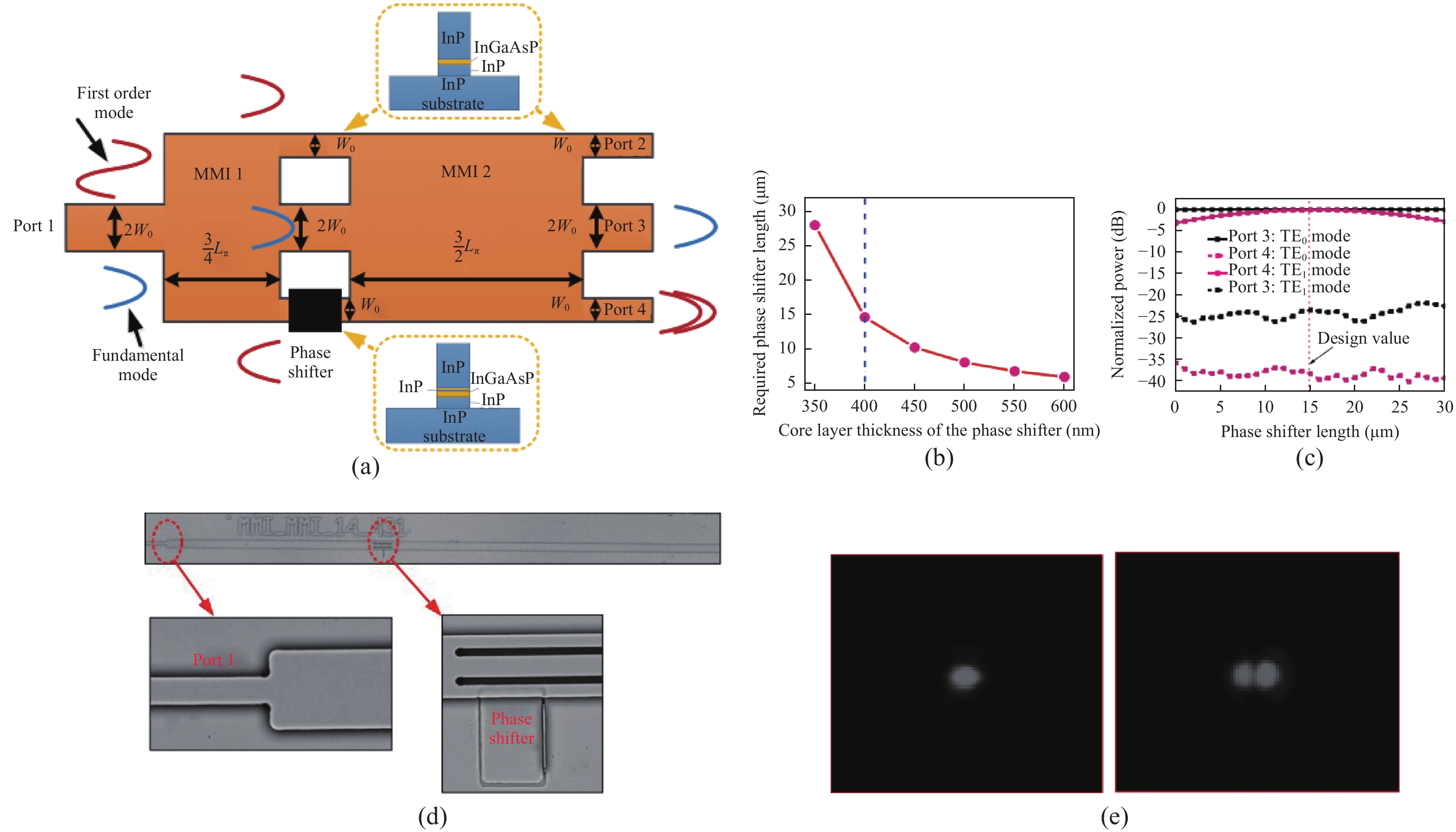
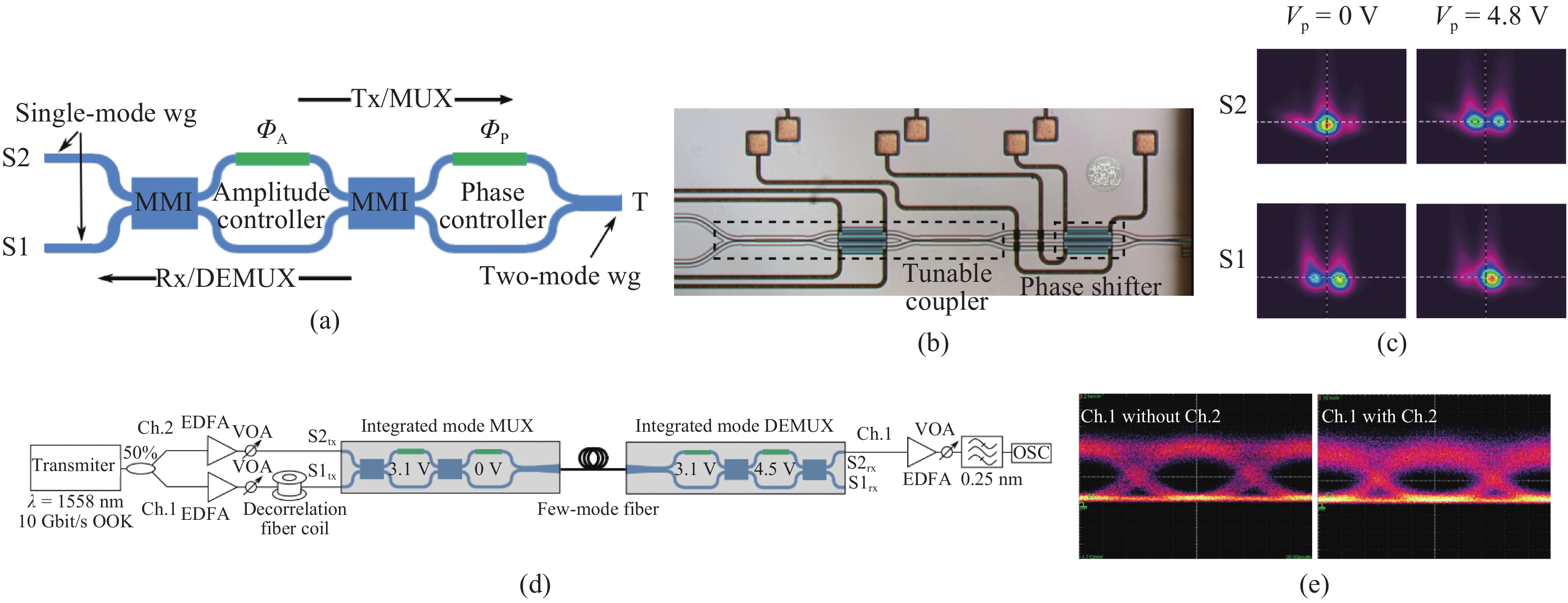
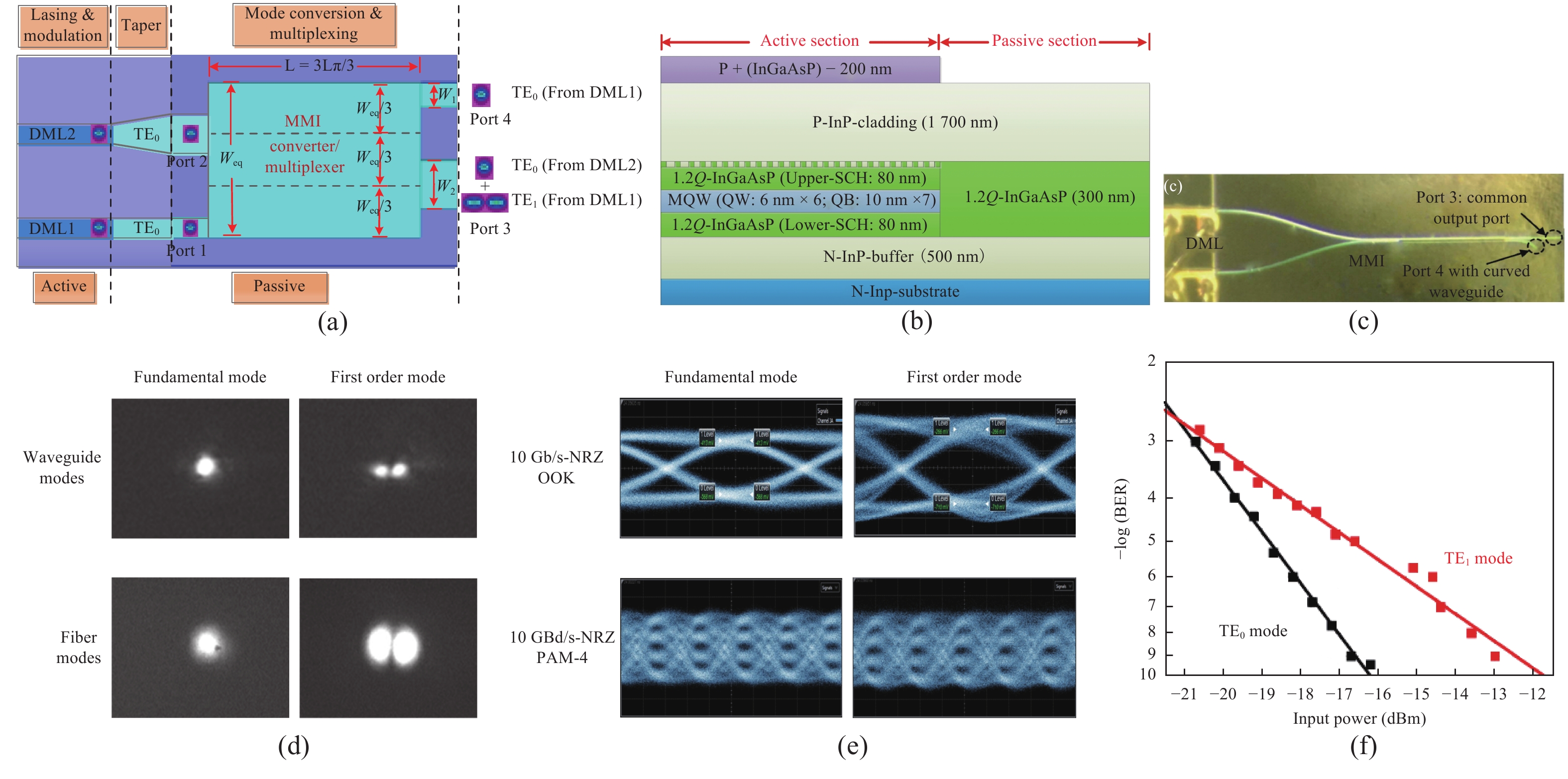
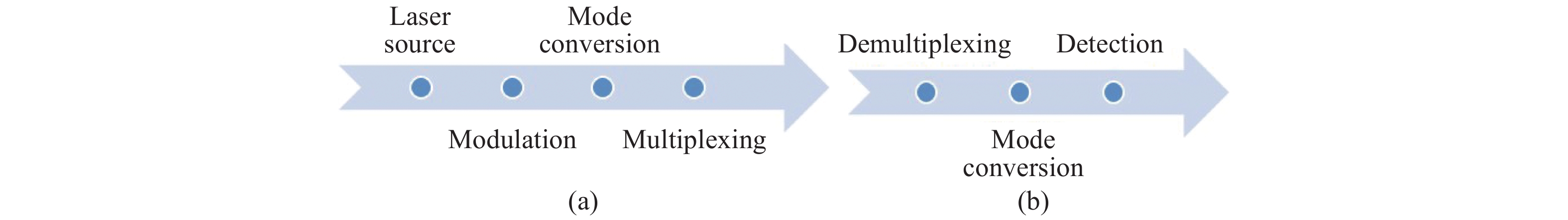
Mode-division multiplexing (MDM) has become an increasingly important technology to further increase the transmission capacity of both optical-fiber-based communication networks, data centers and waveguide-based on-chip optical interconnects. Mode manipulation devices are indispensable in MDM system and have been widely studied in fiber, planar lightwave circuits, and silicon and InP based platforms. InP-based integration technology provides the easiest accessibility to bring together the functions of laser sources, modulators, and mode manipulation devices into a single chip, making it a promising solution for fully integrated few-mode transmitters in the MDM system. This paper reviews the recent progress in InP-based mode manipulation devices, including the few-mode converters, multiplexers, demultiplexers, and transmitters. The working principle, structures, and performance of InP-based few-mode devices are discussed. -
References
[1] Soma D, Wakayama Y, Beppu S, et al. 10.16-Peta-bit/s dense SDM/WDM transmission over 6-mode 19-core fiber across the C + L band. J Light Technol, 2018, 36(6): 2799380[2] Greenberg M, Orenstein M. Multimode add-drop multiplexing by adiabatic linearly tapered coupling. Opt Express, 2005, 13(23): 009381 doi: 10.1364/OPEX.13.009381[3] Uematsu T, Ishizaka Y, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Design of a compact two-mode multi/demultiplexer consisting of multimode interference waveguides and a wavelength-insensitive phase shifter for mode-division multiplexing transmission. J Light Technol, 2012, 30(15): 2199961[4] Ding Y, Xu J, Ros F Da, et al. On-chip two-mode division multiplexing using tapered directional coupler-based mode multiplexer and demultiplexer. Opt Express, 2013, 21(8): 010376 doi: 10.1364/OE.21.010376[5] Xing J, Li Z, Xiao X, et al. Two-mode multiplexer and demultiplexer based on adiabatic couplers. Opt Lett, 2013, 38(17): 003468 doi: 10.1364/OL.38.003468[6] Luo L W, Ophir N, Chen C P, et al. WDM-compatible mode-division multiplexing on a silicon chip. Nat Commun, 2014, 5: 4069 doi: 10.1038/ncomms5069[7] Dai D, Mao M. Mode converter based on an inverse taper for multimode silicon nanophotonic integrated circuits. Opt Express, 2015, 23(22): 028376 doi: 10.1364/OE.23.028376[8] Qiu J, Zhou D, Tian Y, et al. Performance analysis of a broadband second-order mode converter based on multimode interference coupler and phase shifter. IEEE Photonics J, 2015, 7(5): 2486719[9] Leuthold J, Eckner J, Gamper E, et al. Multimode interference couplers for the conversion and combining of zero- and first-order modes. J Light Technol, 1998, 16(7): 701401[10] Guo F, Lu D, Zhang R, et al. An MMI-based mode (DE)MUX by varying the waveguide thickness of the phase shifter. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2016, 28(21): 2599934[11] Guo F, Lu D, Zhang R, et al. Two-mode converters at 1.3 μm based on multimode interference couplers on inp substrates. Chin Phys Lett, 2016, 33(2): 024203 doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/33/2/024203[12] Zhang L M, Lu D, Li Z S, et al. C-band fundamental/first-order mode converter based on multimode interference coupler on InP substrate. J Semicond, 2016, 37(12): 124005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/12/124005[13] Li Z, Lu D, Zuo B, et al. Proposal of an InP-based few-mode transmitter based on multimode interference couplers for wavelength division multiplexing and mode division multiplexing applications. Chine Opt Lett, 2016, 14(8): 080601 doi: 10.3788/COL[14] Li Z, Lu D, Zhao L, et al. An InP-based two-mode converter/(de) multiplexer with 100% mode conversion efficiency by using multimode interference couplers as the building blocks. Conf Lasers Electr-Optics, 2016: JW2A.123[15] Guo F, Lu D, Zhang R, et al. Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on MMI couplers with different core thickness on InP. SPIE Photonics West, 2016: 97500Z[16] Melati D, Alippi A, Melloni A. Reconfigurable photonic integrated mode (de)multiplexer for SDM fiber transmission. Opt Express, 2016, 24(12): 012625 doi: 10.1364/OE.24.012625[17] Li Z, Lu D, He Y, et al. An InP-based directly modulated monolithic integrated few-mode transmitter. Photonics Res, 2018, 6(5): 000463 doi: 10.1364/PRJ.6.000463[18] Dai D, Wang J, He S. Silicon multimode photonic integrated devices for on-chip mode-division-multiplexed optical interconnects. Prog Electromagn Res, 2013, 143: 13111003[19] Dai D, Wang J, Shi Y. Silicon mode (de)multiplexer enabling high capacity photonic networks-on-chip with a single-wavelength-carrier light. Opt Lett, 2013, 38(9): 001422 doi: 10.1364/OL.38.001422[20] Dai D, Tang Y, Bowers J E. Mode conversion in tapered submicron silicon ridge optical waveguides. Opt Express, 2012, 20(12): 013425 doi: 10.1364/OE.20.013425[21] Schmid J H, Lamontagne B, Cheben P, et al. Mode converters for coupling to high aspect ratio silicon-on-insulator channel waveguides. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2007, 19(11): 897461[22] Driscoll J B, Grote R R, Souhan B, et al. Asymmetric Y junctions in silicon waveguides for on-chip mode-division multiplexing. Opt Lett, 2013, 38(11): 001854 doi: 10.1364/OL.38.001854[23] Riesen N, Love J D. Design of mode-sorting asymmetric Y-junctions. Appl Opt, 2012, 51(15): 002778 doi: 10.1364/AO.51.002778[24] Li Y, Li C, Li C, et al. Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and multimode interference waveguides. Opt Express, 2014, 22(5): 005781 doi: 10.1364/OE.22.005781[25] Guo F, Lu D, Zhang R, et al. A two-mode (de)multiplexer based on multimode interferometer coupler and Y-junction on InP substrate. IEEE Photonics J, 2016, 8(1): 2523986[26] Bachmann M, Besse P, Melchior H. General self-imaging properties in N × N multimode interference couplers including phase relations. Appl Opt, 1994, 33(18): 003905 doi: 10.1364/AO.33.003905[27] Izutsu M, Nakai Y, Sueta T. Operation mechanism of the single-mode optical-waveguide Y junction. Opt Lett, 1982, 7(3): 000136 doi: 10.1364/OL.7.000136[28] Van der Tol J J G M, Pedersen J W, Metaal E G, et al. Mode evolution type polarization splitter on InGaAsP/InP. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 1993, 5(12): 262558[29] Han L, Liang S, Zhu H, et al. Two-mode de/multiplexer based on multimode interference couplers with a tilted joint as phase shifter. Opt Lett, 2015, 40(4): 000518 doi: 10.1364/OL.40.000518[30] Smit M, Leijtens X, Ambrosius H, et al. An introduction to InP-based generic integration technology. Semicond Sci Technol, 2014, 29(8): 083001 doi: 10.1088/0268-1242/29/8/083001 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: