| Citation: |
A. K. Mishra, S. K. Mishra, S. P. Pandey, Kshama Lakshmi Mishra. Thermally stimulated properties in ZnSe:Tb and ZnSe:(Mn, Tb) phosphors[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2018, 39(2): 022001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/2/022001
****
A. K. Mishra, S. K. Mishra, S. P. Pandey, K L Mishra. Thermally stimulated properties in ZnSe:Tb and ZnSe:(Mn, Tb) phosphors[J]. J. Semicond., 2018, 39(2): 022001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/2/022001.
|
Thermally stimulated properties in ZnSe:Tb and ZnSe:(Mn, Tb) phosphors
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/2/022001
More Information
-
Abstract
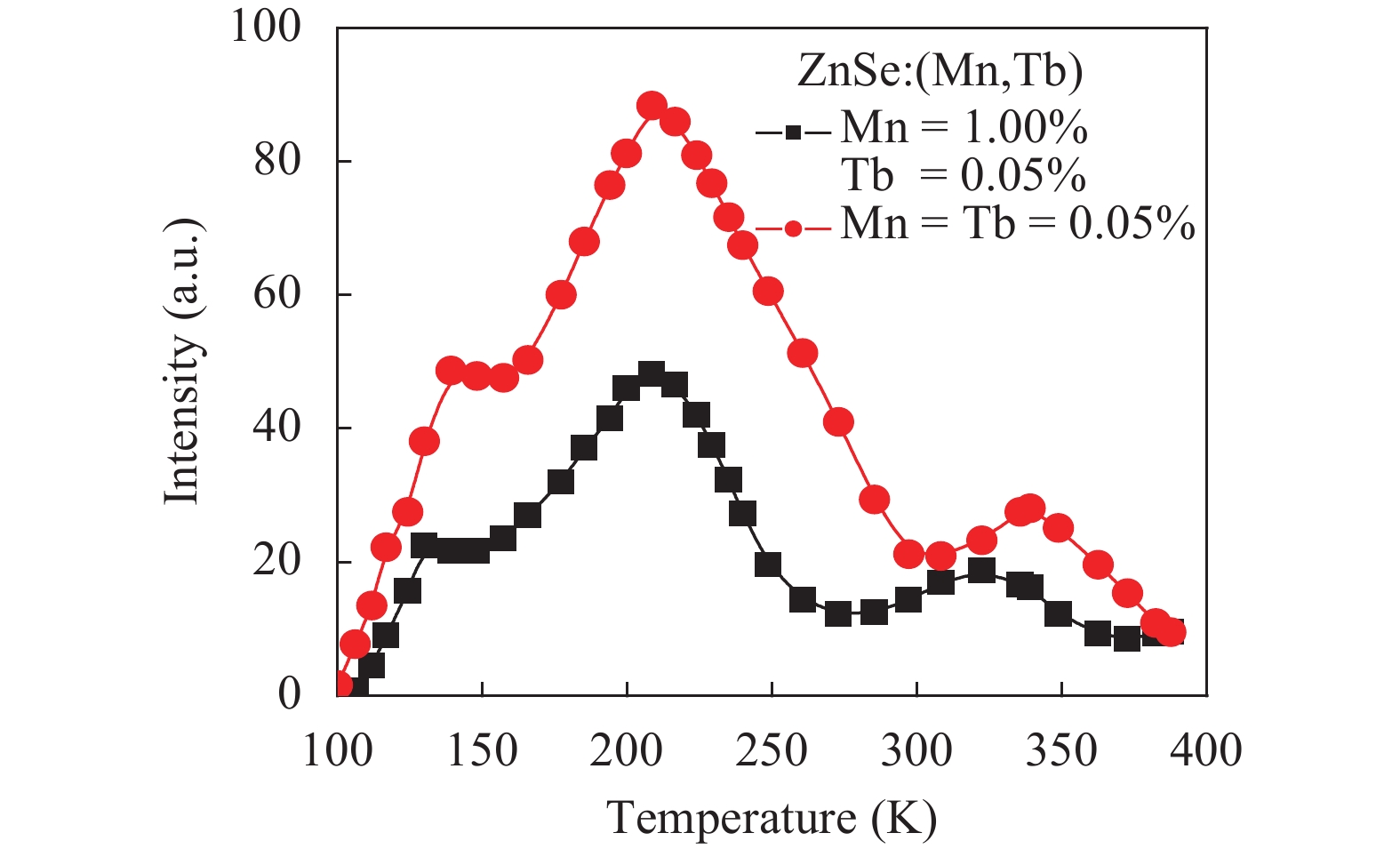
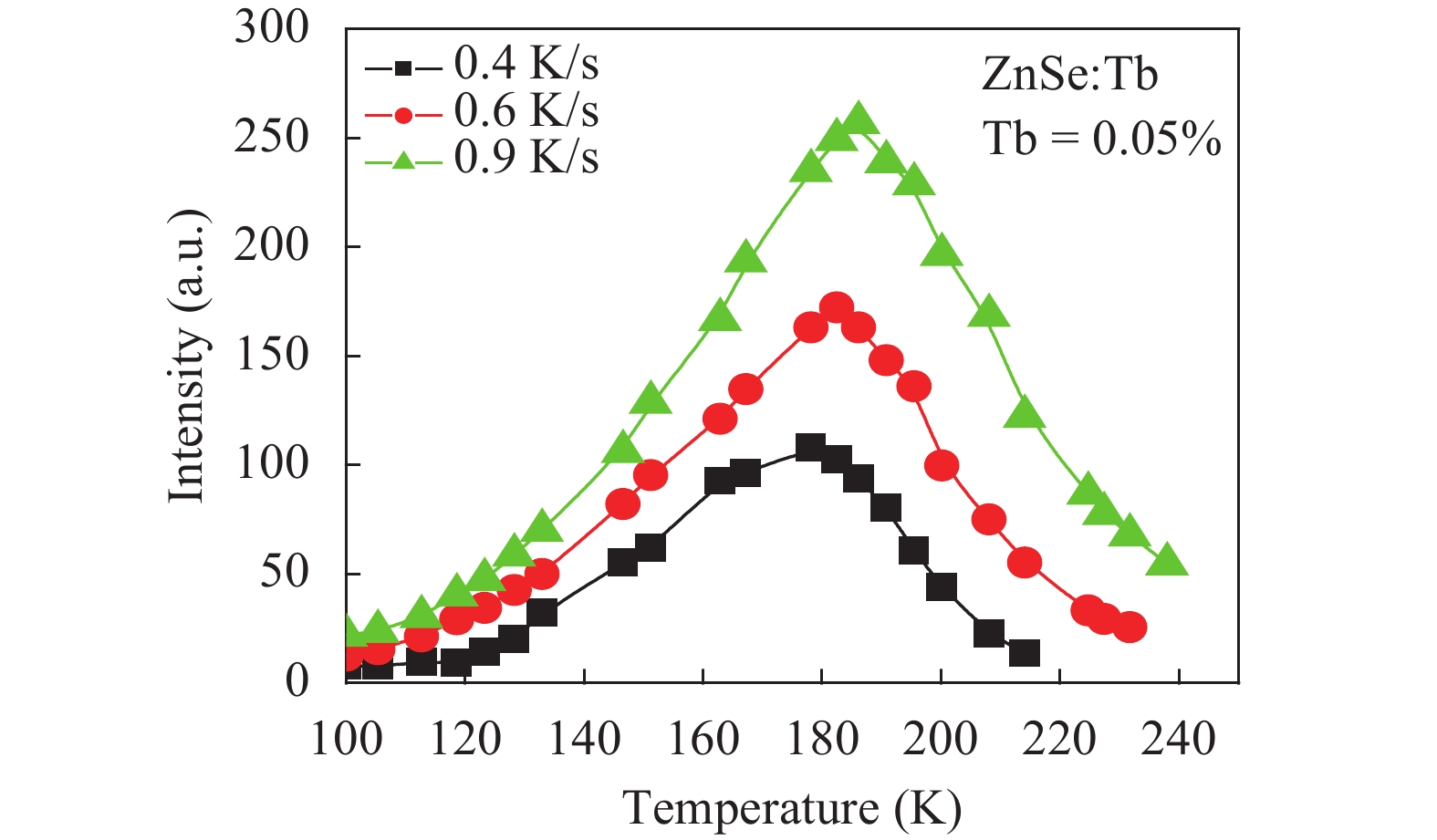
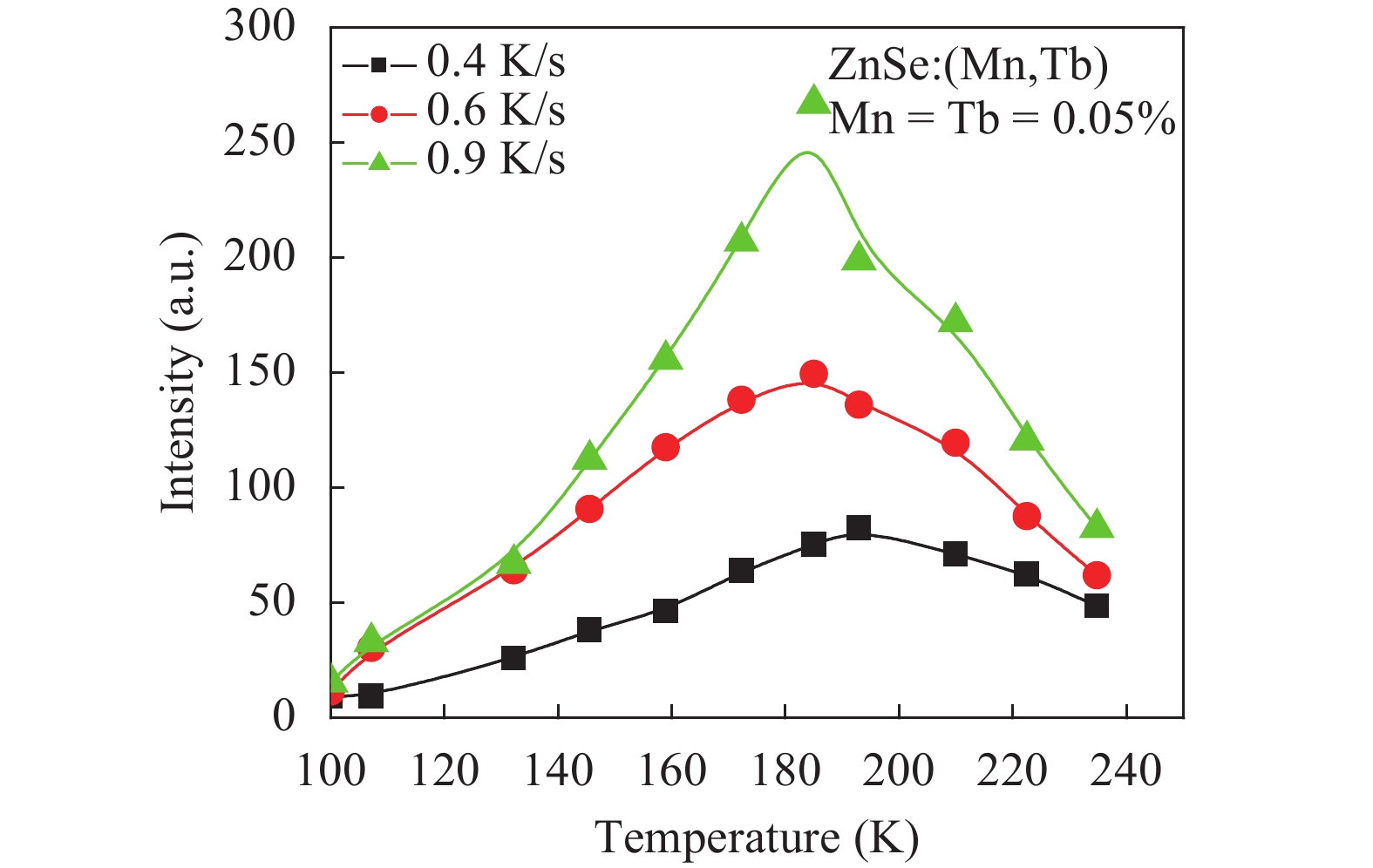
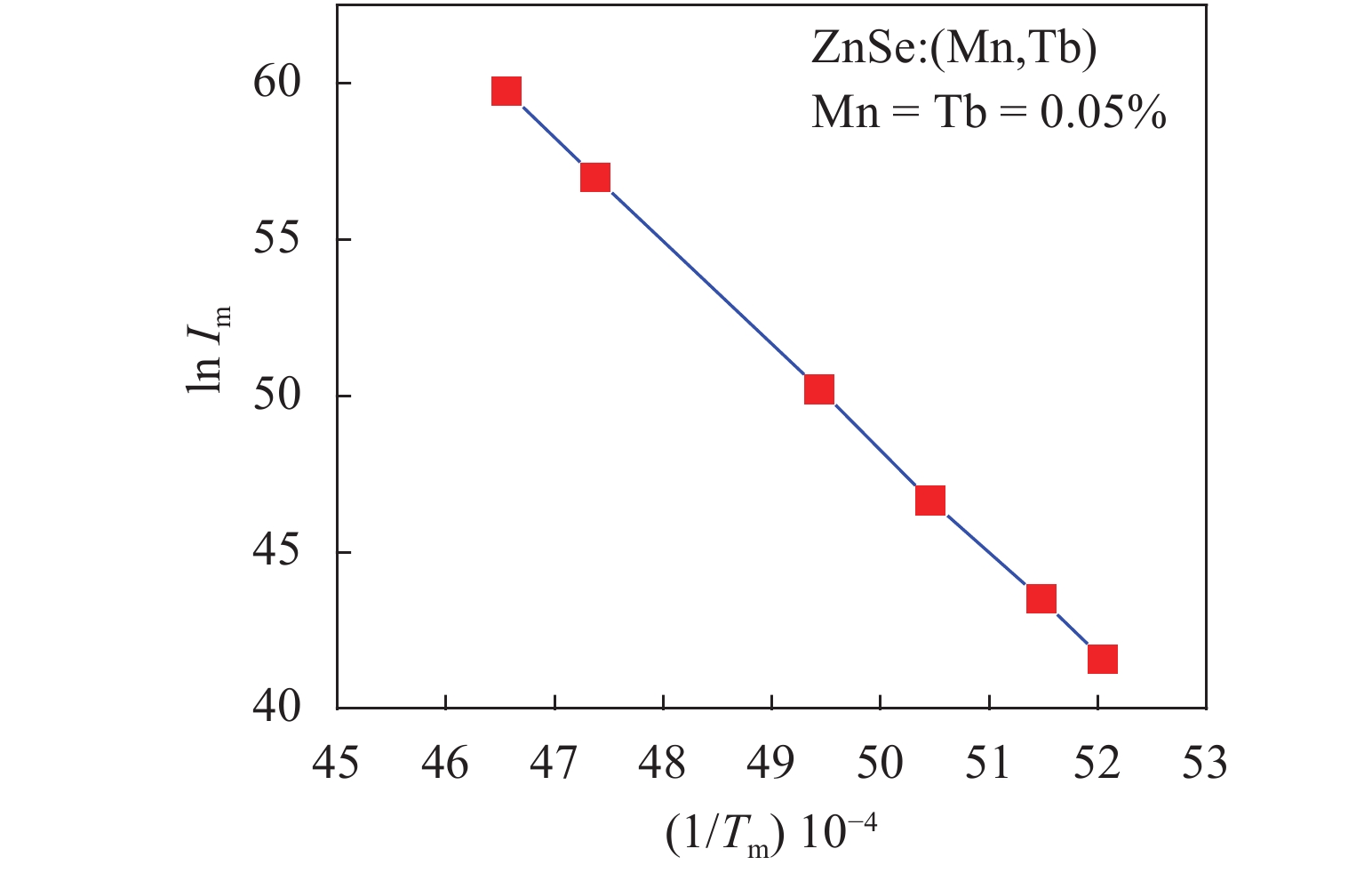
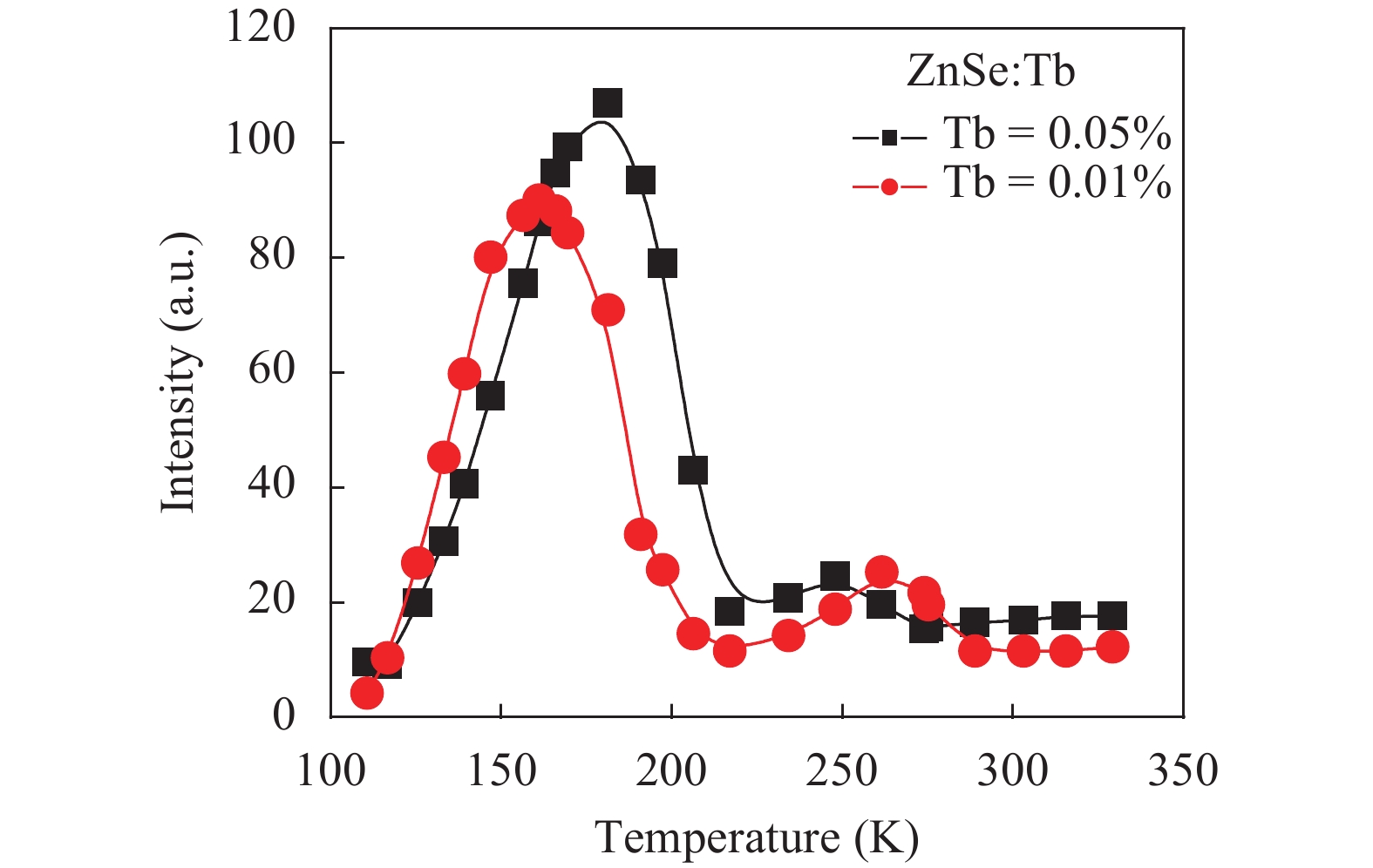
Thermoluminescence studies were performed of ZnSe:Tb and ZnSe:(Mn, Tb) phosphors. A method of preparation for ZnSe phosphors doped with Tb and (Mn, Tb) has been discussed. The thermoluminescence (TL) properties of these phosphors have been studied from 100 to 370 K temperature after exciting by UV radiation (365 nm) at three uniform heating rates 0.4, 0.6 and 0.9 K/s. The trapping parameters like trap depth, lifetime of electrons and capture cross-section have also been determined using various methods. -
References
[1] Green A G J, Ray B, Viney I V F, et al. Luminescence studies of CaS phosphors doped with cerium and copper. Phys Stat Sol A, 1988, 110: 269 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-396X[2] Tripathi L N, Mishra Sanjaya K, Pandey U N. Thermoluminescence of ZnS doped with Dy and Mn. Phys Lett A, 1991, 154(5/6): 312[3] Pillai S M, Vallabhan C P J. A study on the electroluminescence spectrum of samarium and dysprosium doped calcium sulfide. Phys Stat Sol B, 1986, 134(1): 383 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3951[4] Tripathi L N, Mishra S K, Raj N S. Luminescence in ZnSe doped with Pr and (Sn, Pr) phosphors. Int J Pure Appl Phys, 1993, 31(2): 899[5] Tripathi L N, Sinha S K, Mishra Sanjaya K. Thermoluminescence in ZnS:Ag and (Ag, Gd) phosphors. Proc Nat Symp on Some Auspects of Mod Phys at Dibrugarh Univ Dibrugarh, May, 1994: 27[6] Tripathi L N, Pandey U N, Mishra Sanjaya K, et al. Thermoluminescence and phosphorescence decay in ZnS:(Cu, Dy). Proc Nat Sem on TL & Its Appl at M.S. Univ Barauda Publ Tata Mc-Graw Hill, 1990: P-95-100.[7] Mishra A K, Tripathi L N, Pandey U N, et al. Thermoluminescence in ZnS doped Pr and (Cu, Pr) phosphors. Ind J Pure Appl Phys, 2002, 40: 337[8] Chen R, Kirsh Y. Analysis of thermally stimulated process. Pargamon Press, 1981, 15: 148[9] Mott N F, Gurney R W. Electronic Process in ionic crystals. Oxford Univ Press, 1940[10] Randall J T, Wilkins M H F. Phosphorescence of electron traps. 1945, A-184: 366[11] Mishra S K. Luminescence in some inorganic phosphors. LAP Lambert Publisher, 2012[12] Das S, Mandal K C. Optical down conversion in rare earth (Tb3+ and Yb3+) doped CdS nanocrystal. Mater Lett, 2012, 66: 46 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2011.08.034[13] Reddy J A, Kokila M K, Nagabhushana H. Structural, EPR, photo and thermoluminescence properties of ZnO doped Fe nanoparticles. Spectroshimica Acta A, 2011, 133(2): 876[14] Sharma R, Bisen D P, Dhole J J, et al. Mechno-luminescence and thermoluminescence of Mn doped ZnS Crystal. J Lumin, 2011, 131(10): 2089 doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2011.05.020[15] Tiwari R, Balatraunk P, Tamarkar R K, et al. Synthesis, characterization and thermoluminescence behavior of (Cd,Zn)S mixed phosphors doped with Ag. Chalcogenide Lett, 2014, 11(3): 141[16] Tu D, Xu C N, Fujio Y, et al. Phosphorescence quenching by mechanical stimulus in CaZnOS:Cu. App Phy Lett, 2014, 105: 605[17] Chandra B P, Chandra P K, Jha P. Piezoelectrically-induced trap-depth reduction model of elastico-mechanoluminescent materials. Physica B, 2015, 461: 38 doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2014.12.007[18] Curie D. Luminescence in crystal. London: Methuen Co. Ltd, 1963: 162[19] Khan F, Baek S H, Kim J H. Investigation of the surface passivation mechanism through an Ag-doped Al-rich film using a solution process. Nanoscale, 2016, 8: 1007 doi: 10.1039/C5NR06883E -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: