| Citation: |
Tianxiao Fang, Bifeng Cui, Shuai Hao, Yang Wang. The simulation of thermal characteristics of 980 nm vertical cavity surface emitting lasers[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2018, 39(2): 024001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/2/024001
****
T X Fang, B F Cui, S Hao, Y Wang. The simulation of thermal characteristics of 980 nm vertical cavity surface emitting lasers[J]. J. Semicond., 2018, 39(2): 024001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/2/024001.
|
The simulation of thermal characteristics of 980 nm vertical cavity surface emitting lasers
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/2/024001
More Information
-
Abstract
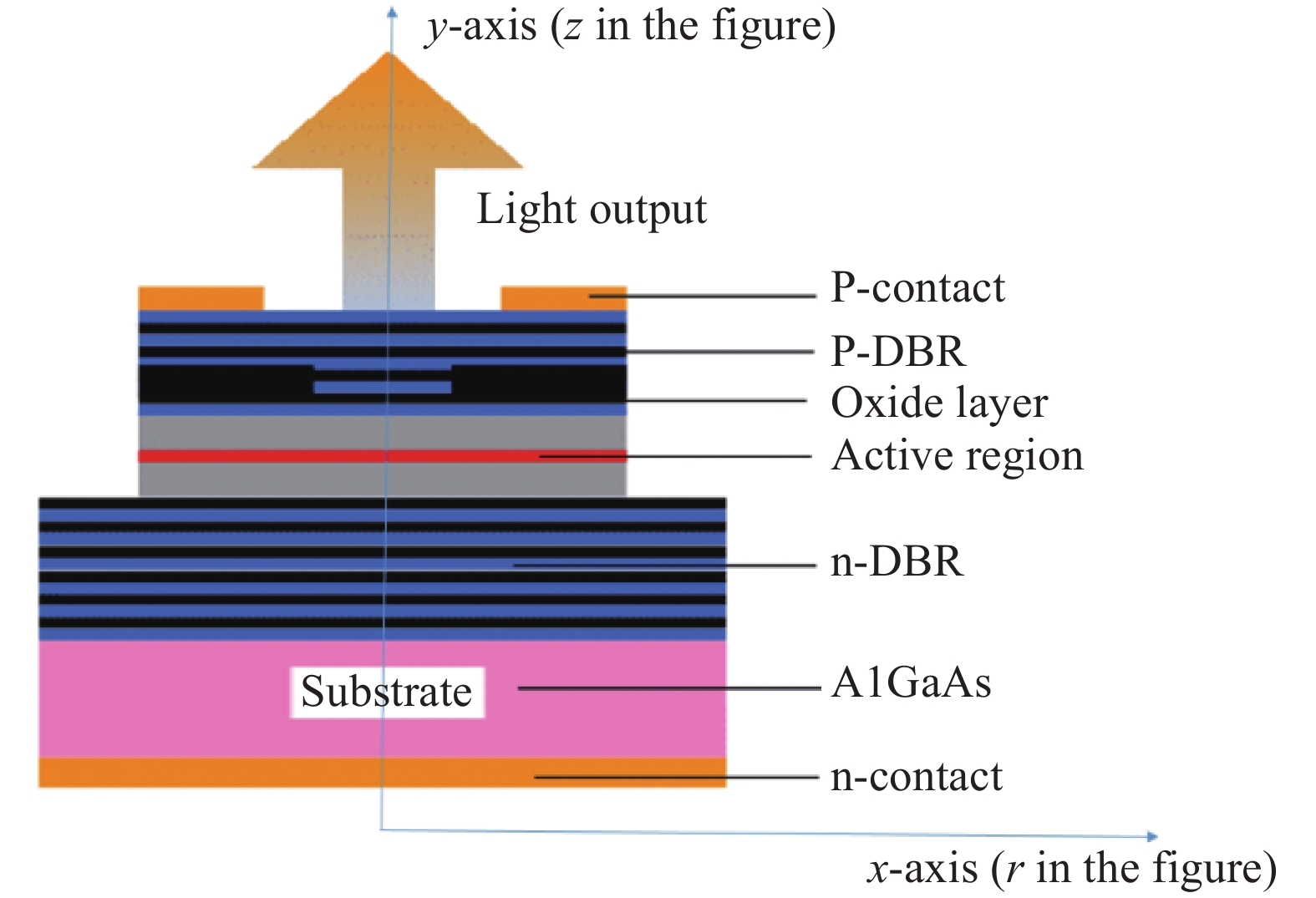
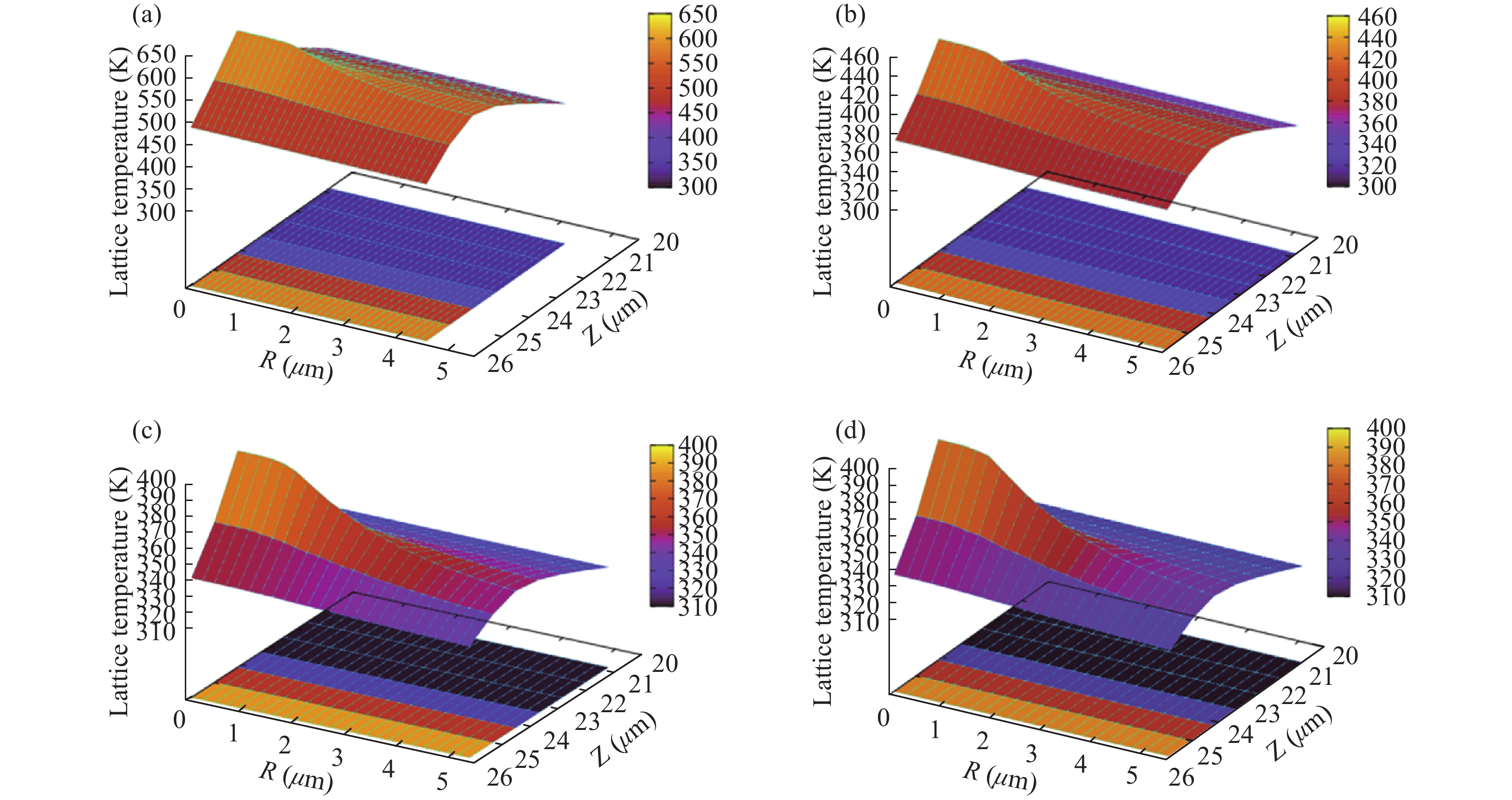
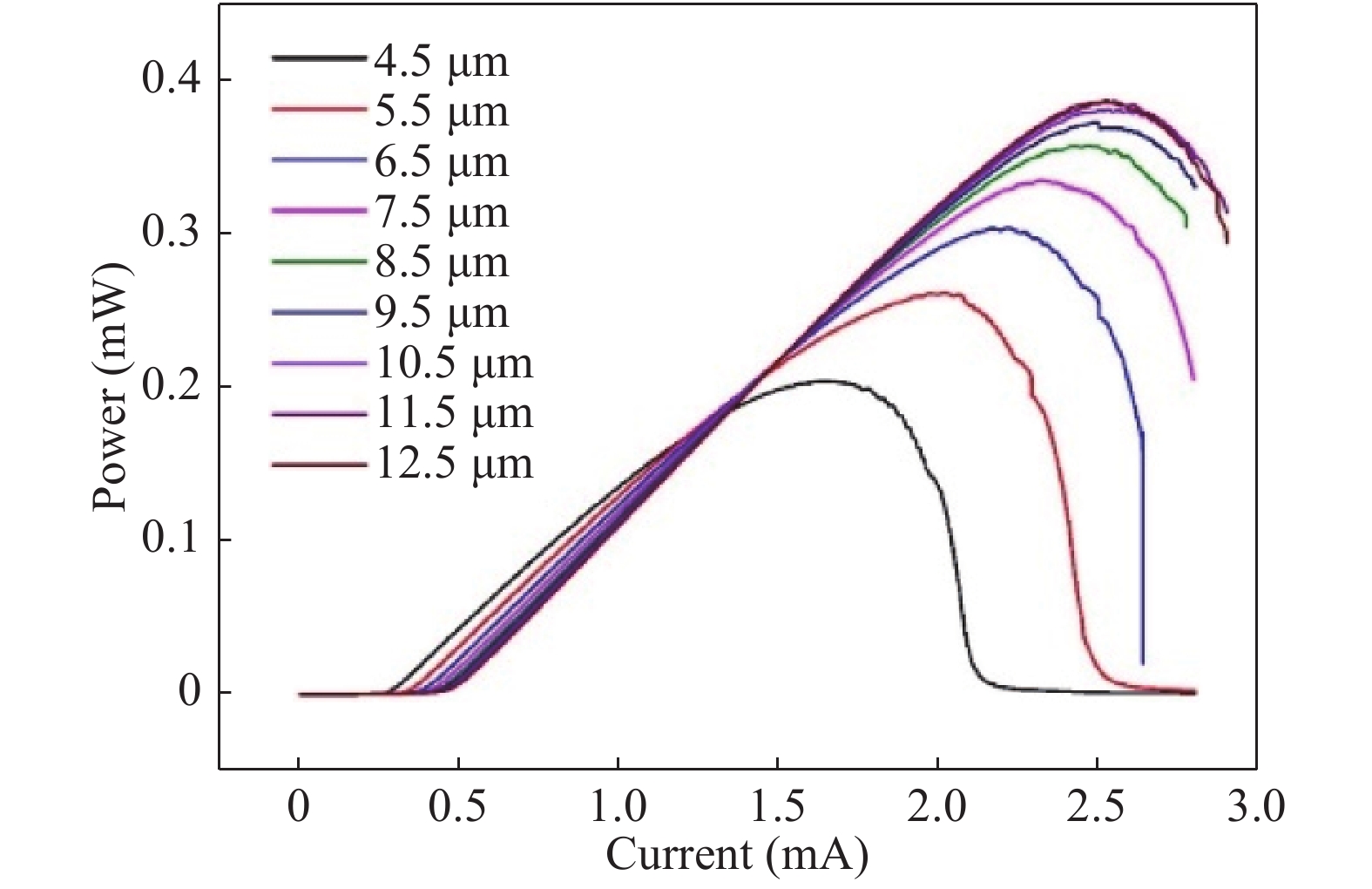
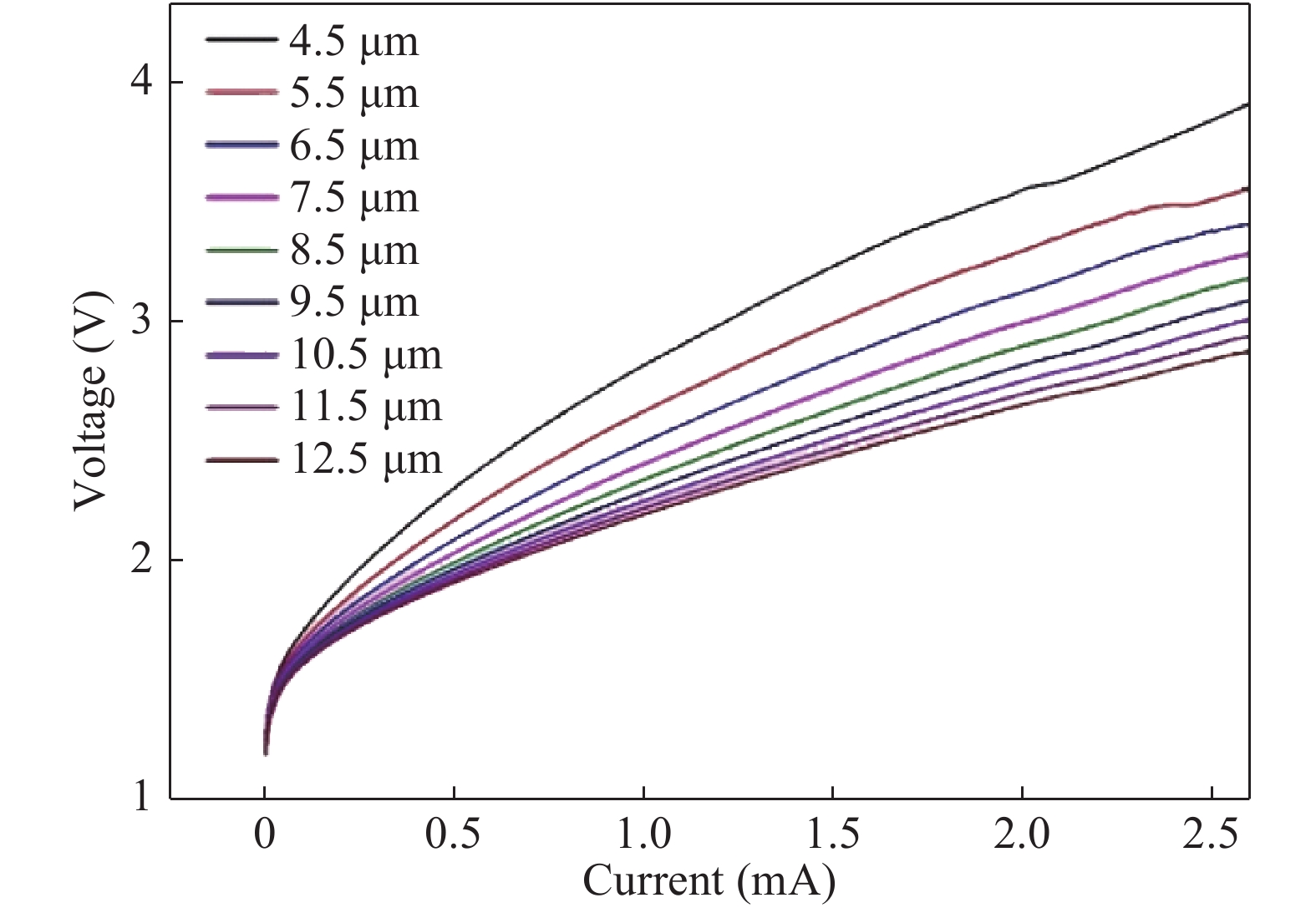
In order to design a single mode 980 nm vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL), a 2 μm output aperture is designed to guarantee the single mode output. The effects of different mesa sizes on the lattice temperature, the output power and the voltage are simulated under the condition of continuous working at room temperature, to obtain the optimum process parameters of mesa. It is obtained by results of the crosslight simulation software that the sizes of mesa radius are between 9.5 to 12.5 μm, which cannot only obtain the maximum output power, but also improve the heat dissipation of the device.-
Keywords:
- 980 nm,
- laser,
- mesa sizes
-
References
[1] Cui J J, Ning Y Q, Zhang Y, et al. Design and characterization of a nonuniform linear vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser array with a Gaussian far-filed distribution. Appl Opt, 2009, 48(18): 3317 doi: 10.1364/AO.48.003317[2] Calciati M, Tibaldi A, Bertazzi F, et al. Many-valley electron transport in AlGaAs VCSELs. Semicond Sci Technol, 2017, 32(5): 055007 doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/aa66bb[3] Zhao Y J, Hao Y Q, Li G J, et al. Fabrication of new structure vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser. Chin J Lasers, 2009, 36: 1946 doi: 10.3788/JCL[4] Islam S I, Islam A, Islam S, et al. Integrated duo wavelength VCSEL using an electrically pumped GaInAs/AlGaAs 980 nm cavity at the bottom and an pptically pumped GaInAs/AlGaInAs 1550 nm cavity on the top. Int Scholy Res Notices, 2014, 2014: 627165[5] Vladimirov A G, Pimenov A, Gurevich S V, et al. Cavity solitons in vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers. Philosophical Trans Royal Soc A, 2014, 372(2027): 1[6] Vanzi M, Mura G, Marcello G, et al. ESD tests on 850 nm GaAs-based VCSELs. Microelectron Reliab, 2016, 64: 617 doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2016.07.023[7] Shi G Z, Guan B L, Li S, et al. Power dissipation in oxide-confined 980-nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers. Chin Phys B, 2013, 22(1): 014206 doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/22/1/014206[8] Yan C L, Ning Y Q, Qin L, et al. High-power vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser with an extra Au layer. IEEE Photon Technol Lett, 2005, 17: 1599 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2005.850903[9] Zhao Y G, Mclnerney J G. Transverse-mode control of vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers. IEEE Quantum Electron, 1996, 32(11): 1950 doi: 10.1109/JQE.1996.541681[10] Choquette K D. Vertical cavity surface emitting lasers (VCSELs). Elsevier Inc, 2013[11] Calciati M, Tibaldi A, Bertazzi F, et al. Many-valley electron transport in AlGaAs VCSELs. Semicond Sci Technol, 2017, 32(5): 055007 doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/aa66bb[12] Khreis O M. Modeling and analysis of smoothly diffused vertical cavity surface emitting lasers. Comput Conden Matter, 2016, 9: 56 doi: 10.1016/j.cocom.2016.09.005[13] Bajaj R, Mishra H K, Goyal P, et al. Design of oxide-confined and temperature stable long wavelength vertical cavity surface emitting laser for optical interconnects. Optik-Int J Light Electron Opt, 2017, 131: 506 doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.10.129[14] Nakwaski W. VCSEL structures used to suppress higher-order transverse modes. Opto-Electron Rev, 2011, 19(1): 119[15] Zhang L, Cui B F, Gao X, et al. Temperature distribution changes of tunnel regeneration semiconductor laser caused by solder void. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2008(10): 1038 -
Proportional views






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: