| Citation: |
Vipul Bhatnagar, Pradeep Kumar, Neeta Pandey, Sujata Pandey. A dual Vt disturb-free subthreshold SRAM with write-assist and read isolation[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2018, 39(2): 025002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/2/025002
****
V Bhatnagar, P Kumar, Neeta Pandey, Sujata Pandey. A dual Vt disturb-free subthreshold SRAM with write-assist and read isolation[J]. J. Semicond., 2018, 39(2): 025002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/2/025002.
|
A dual Vt disturb-free subthreshold SRAM with write-assist and read isolation
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/2/025002
More Information
-
Abstract
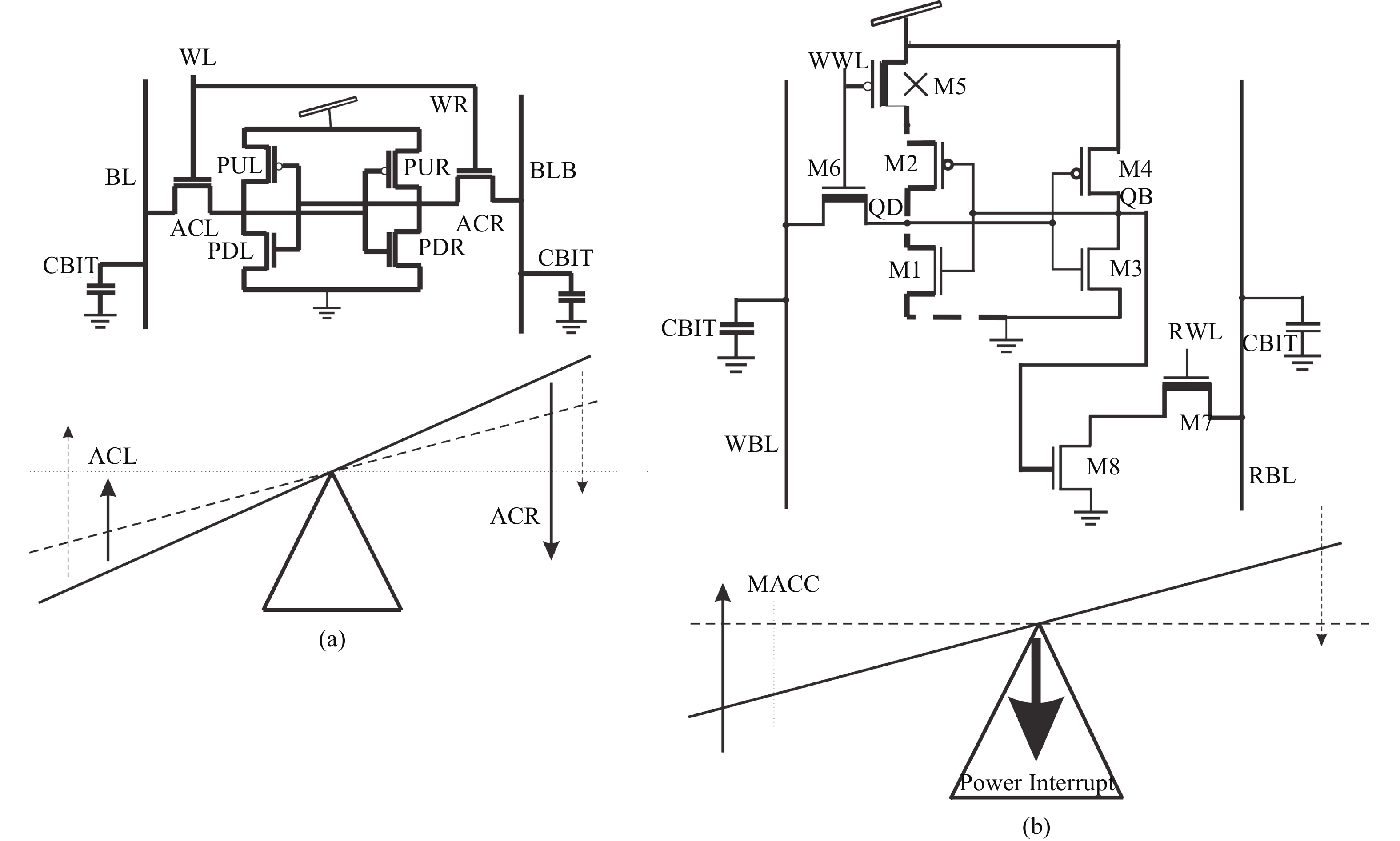
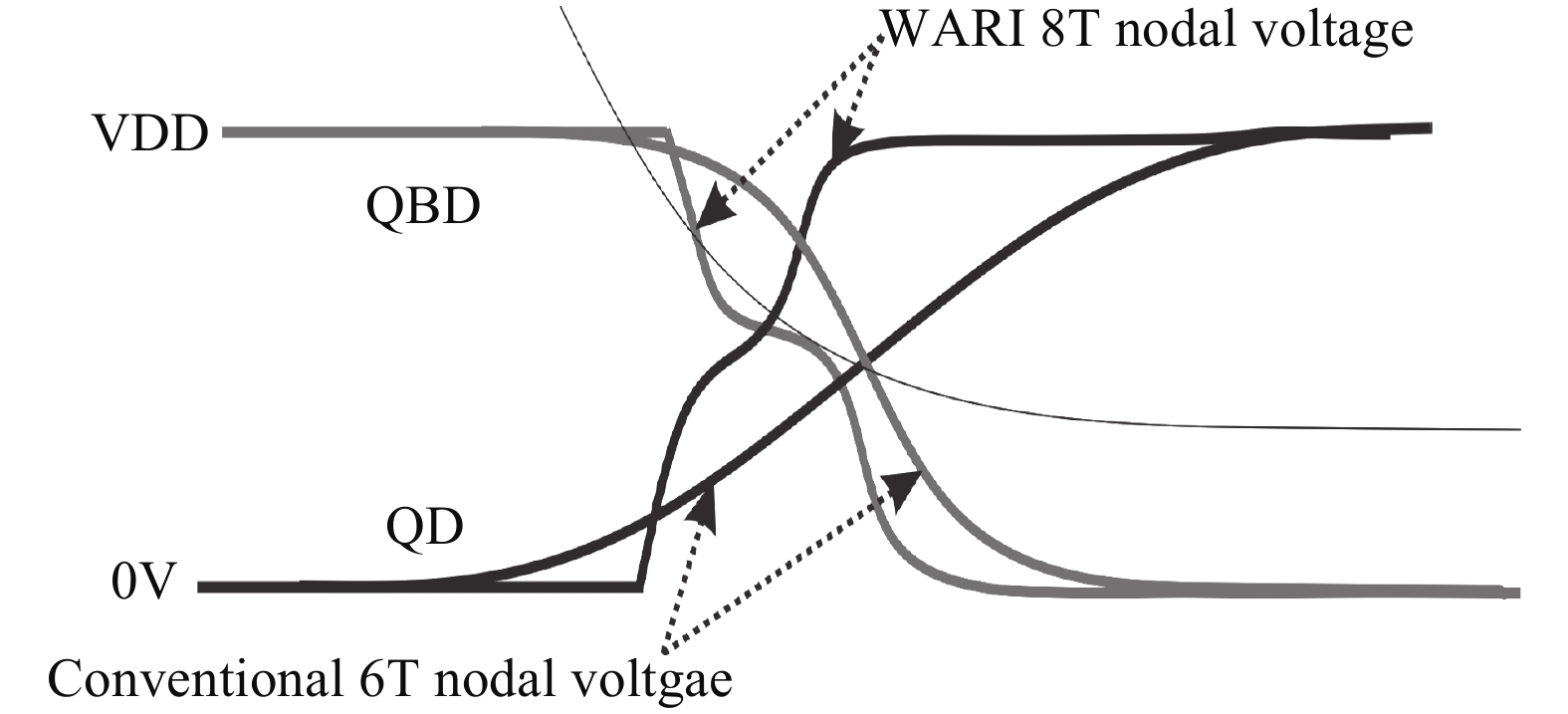
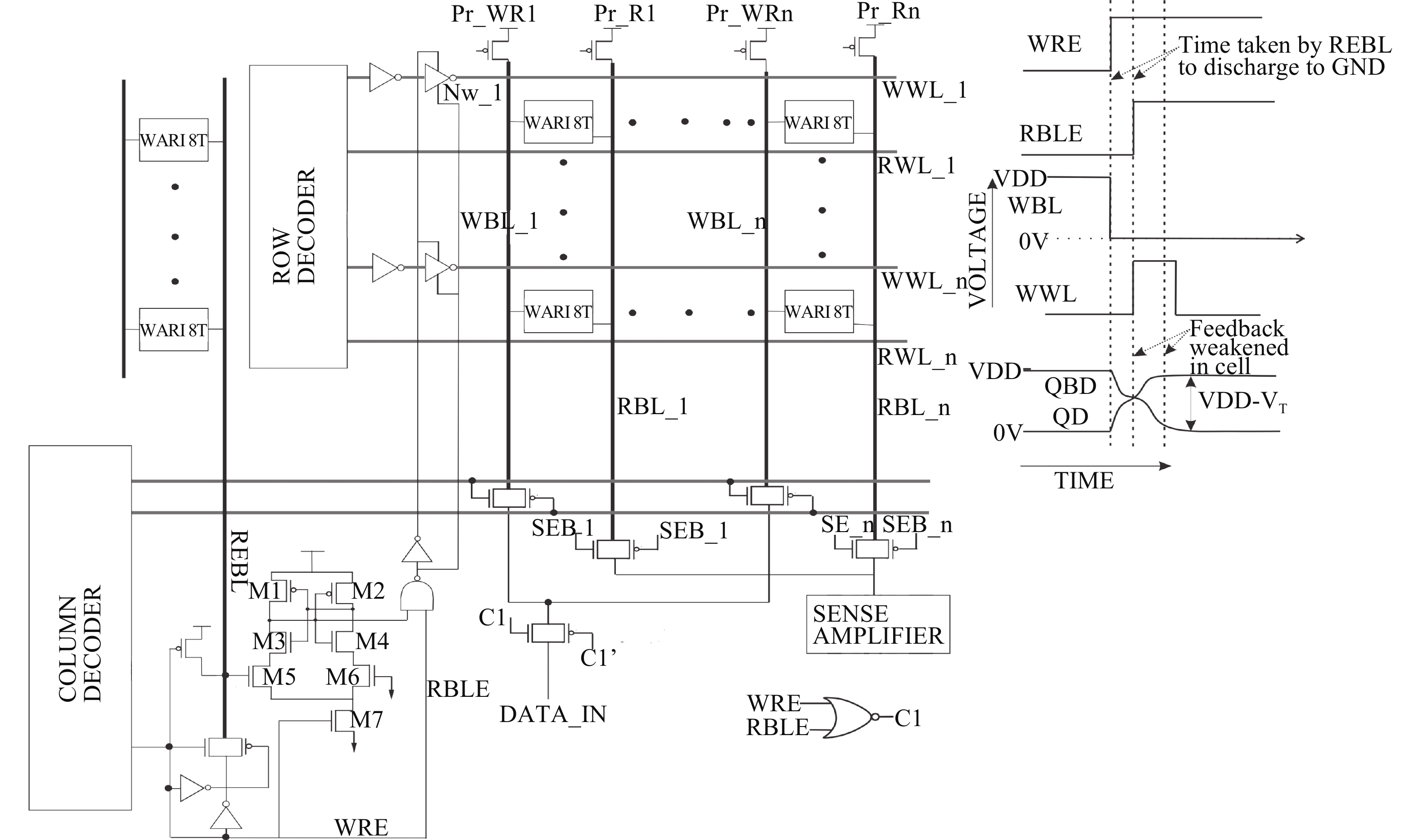
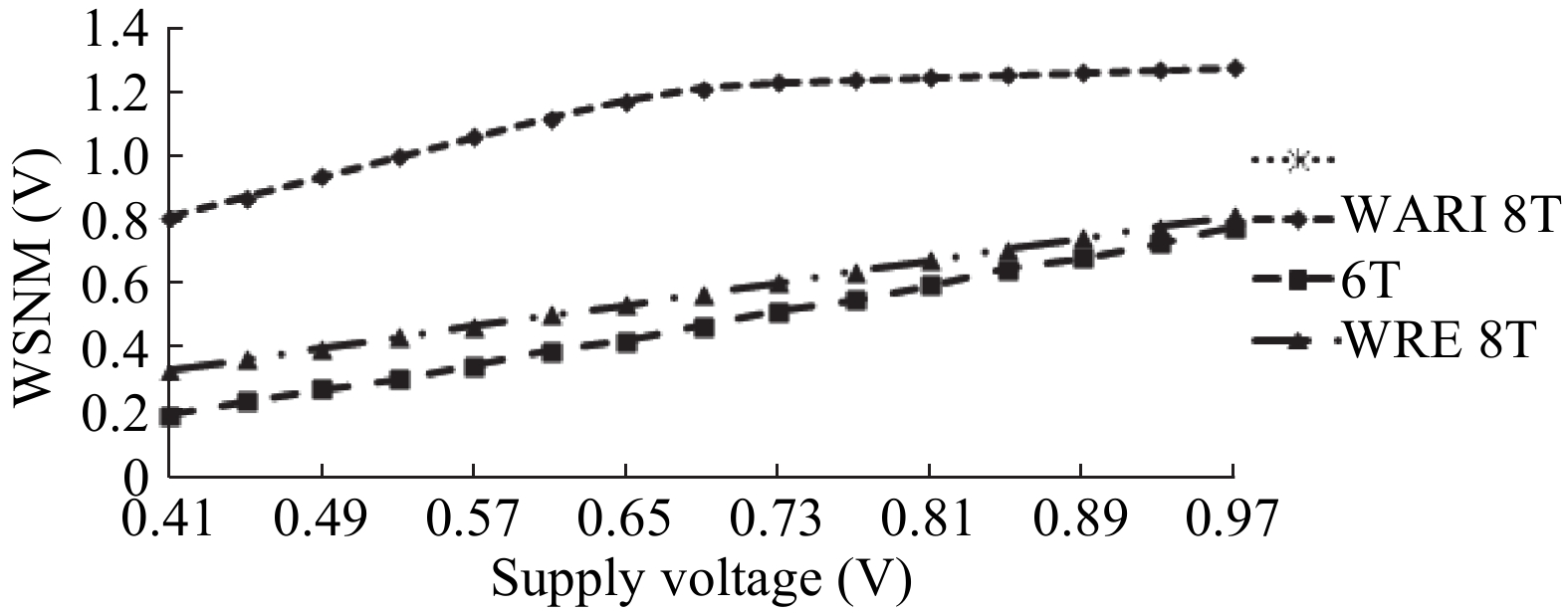
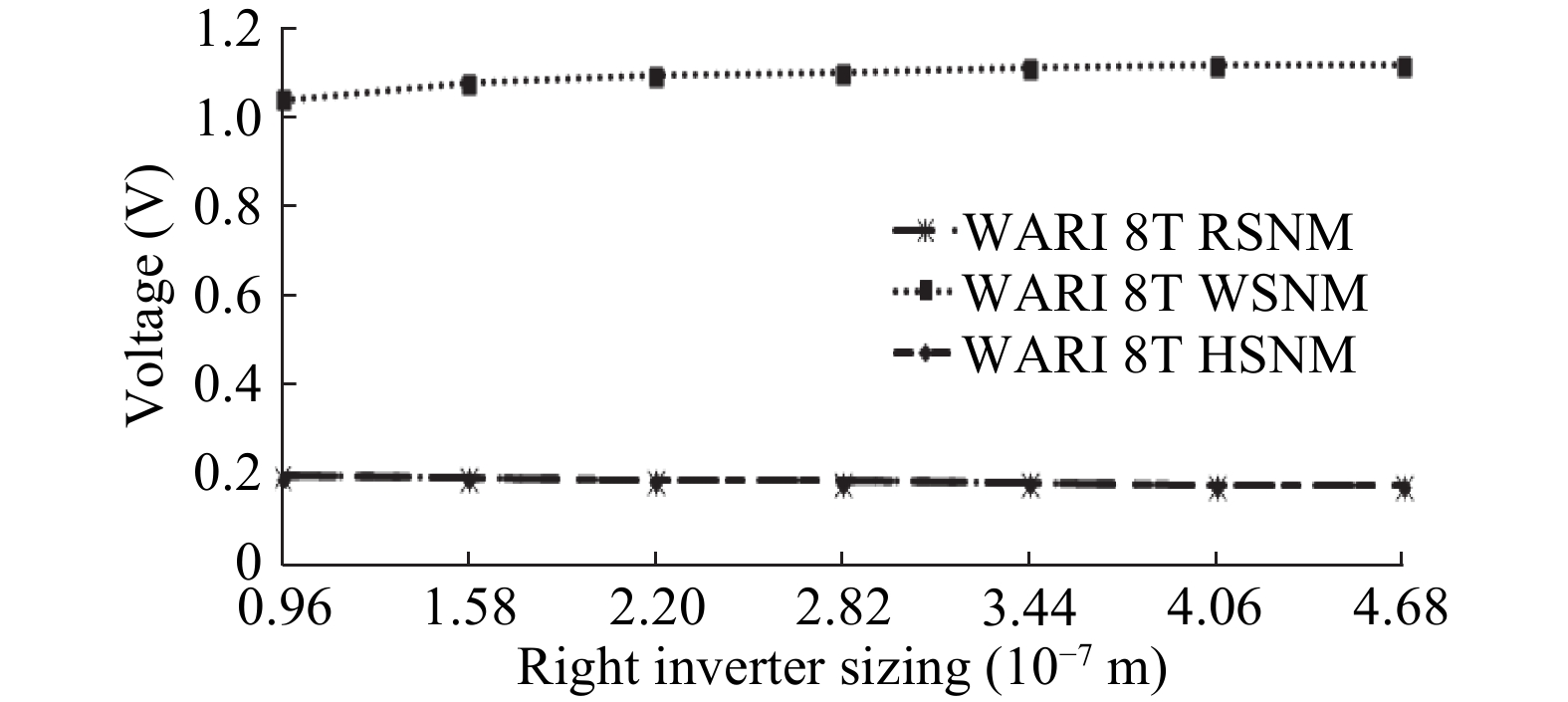
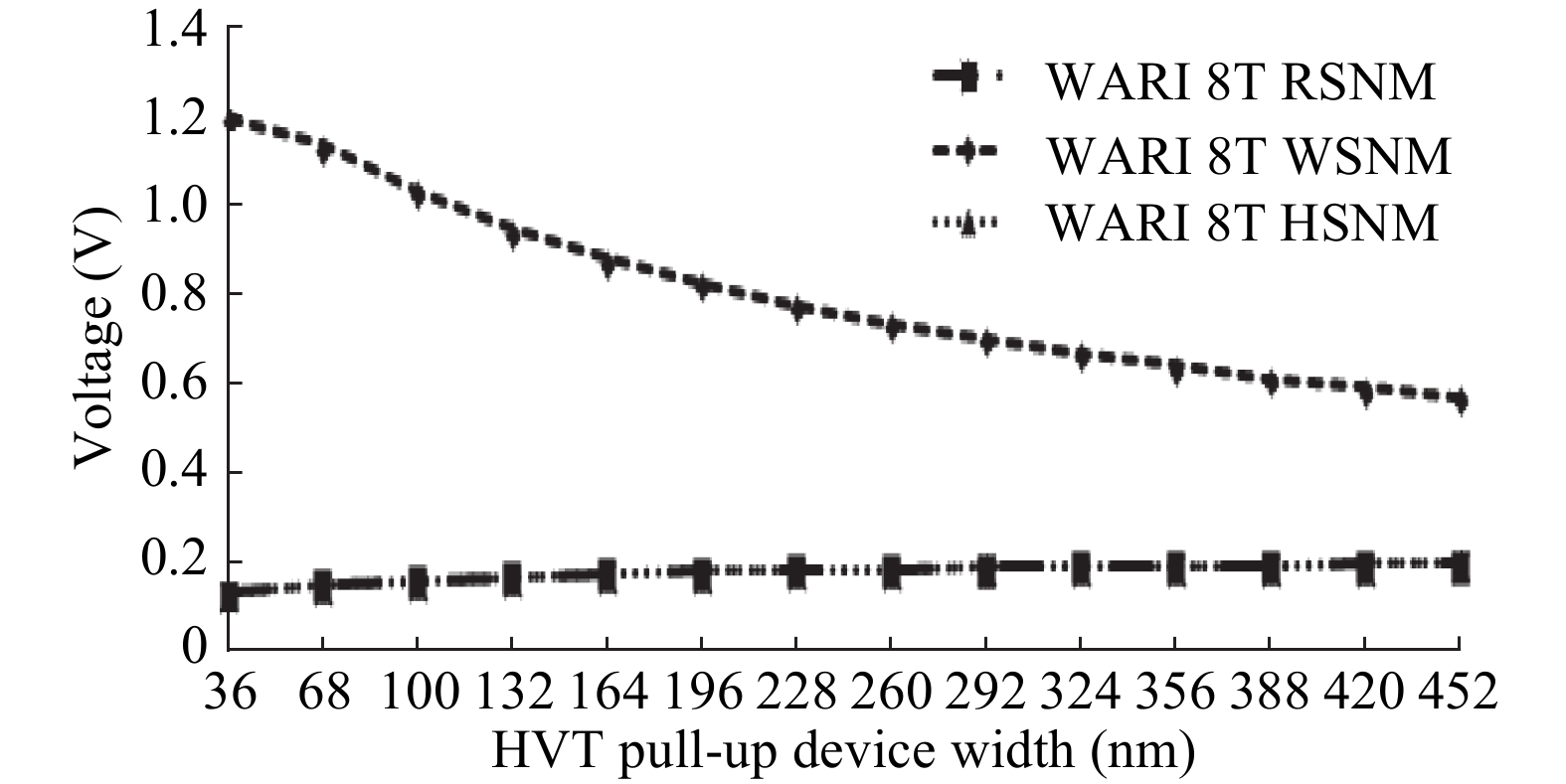
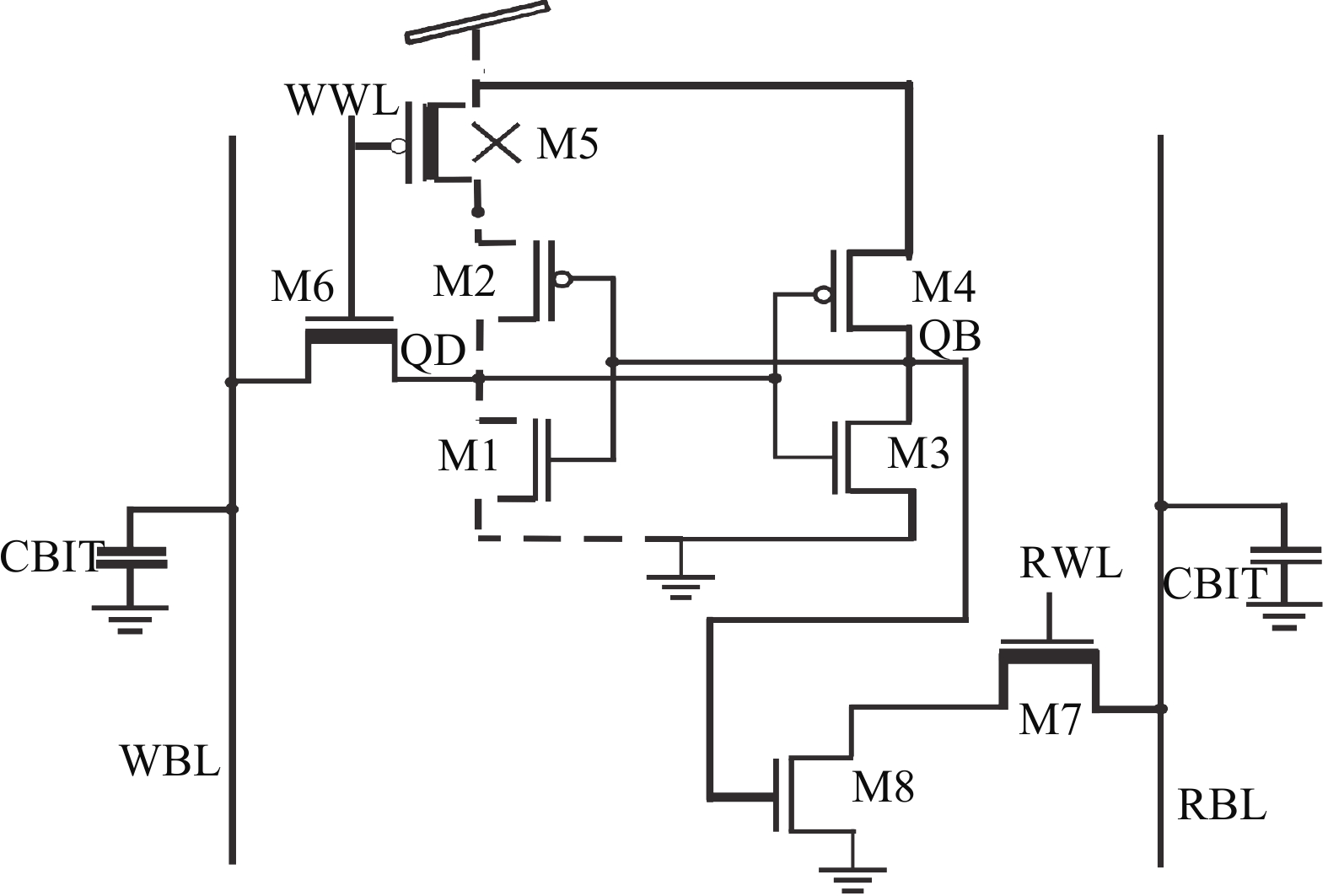
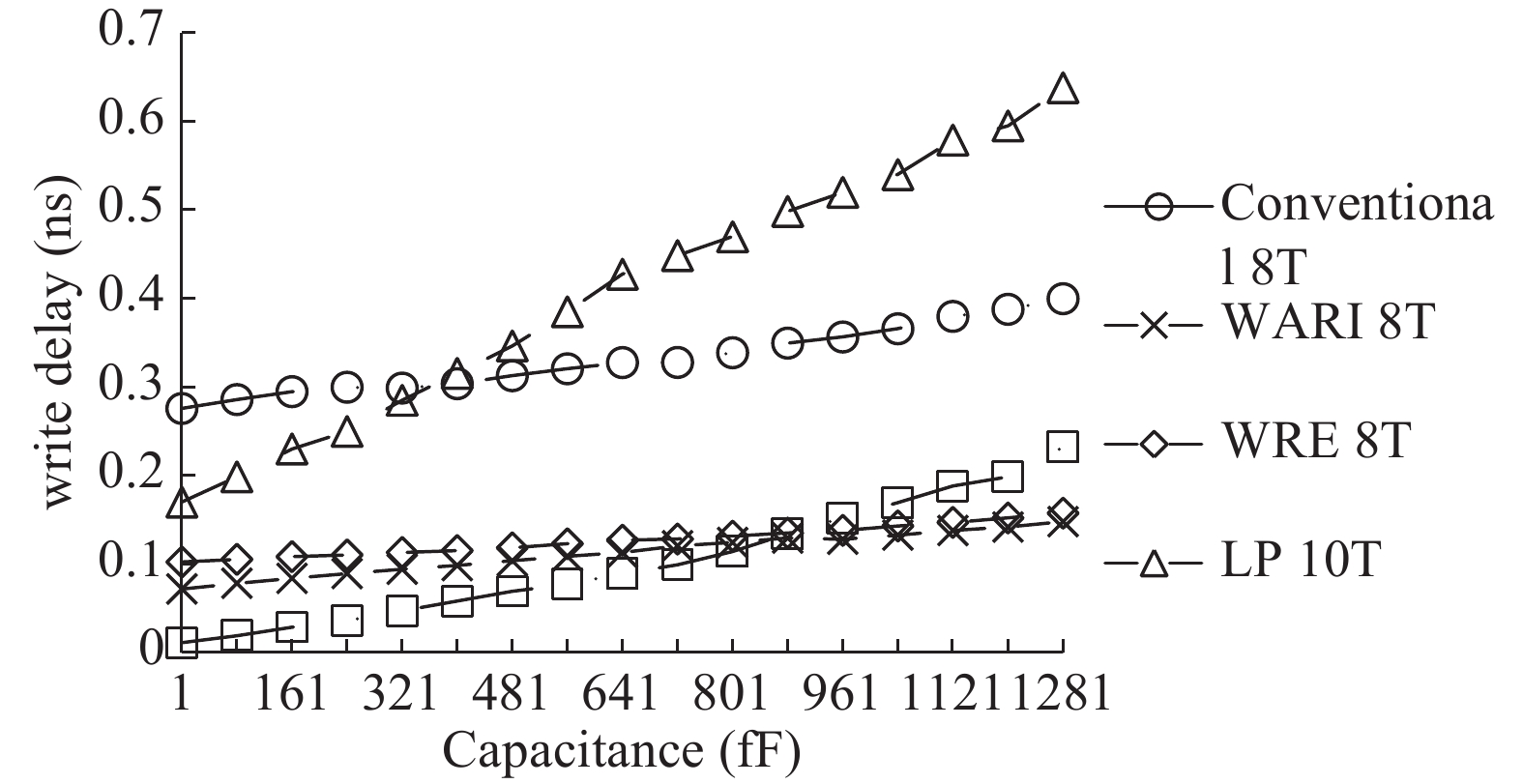
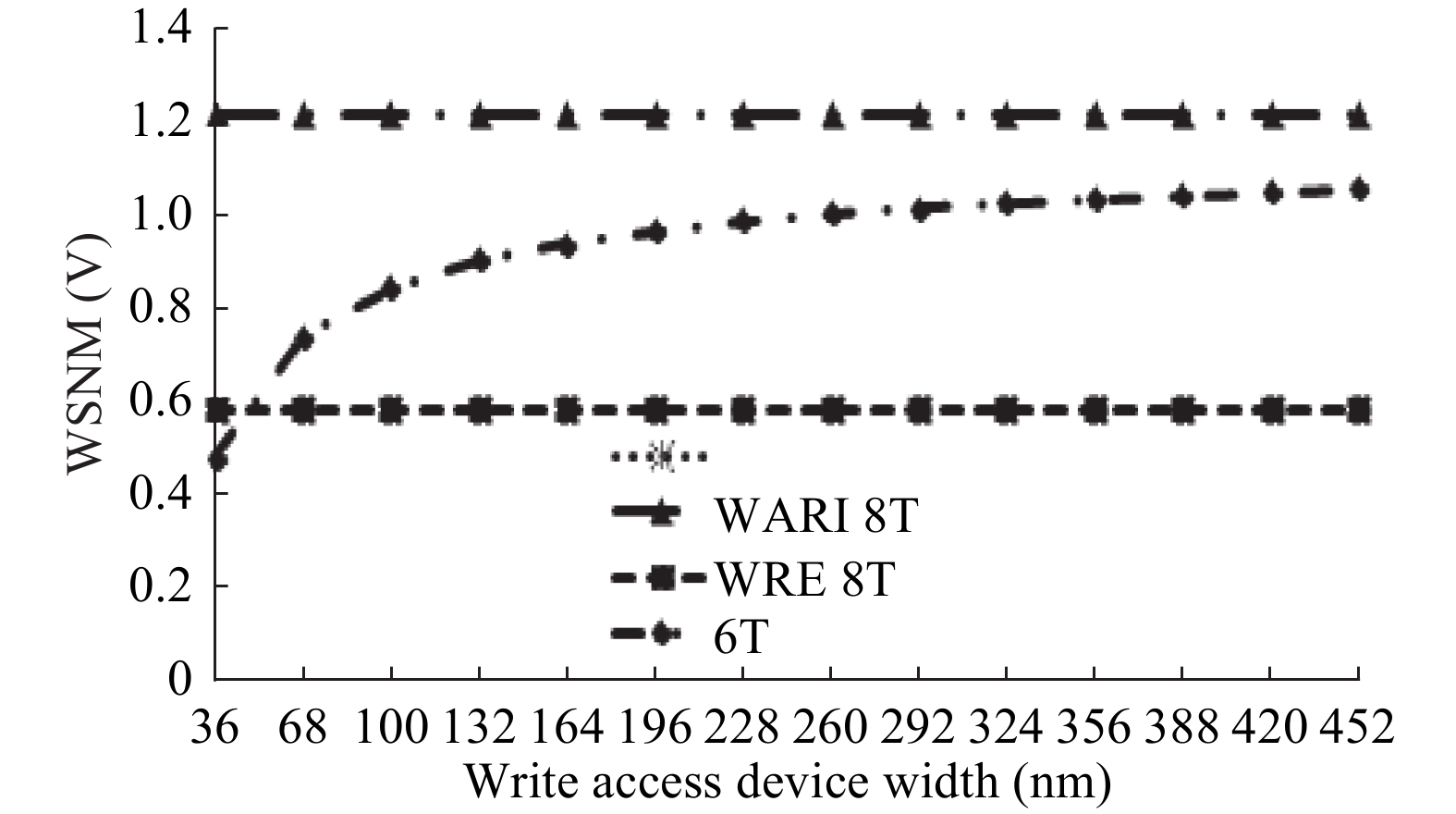
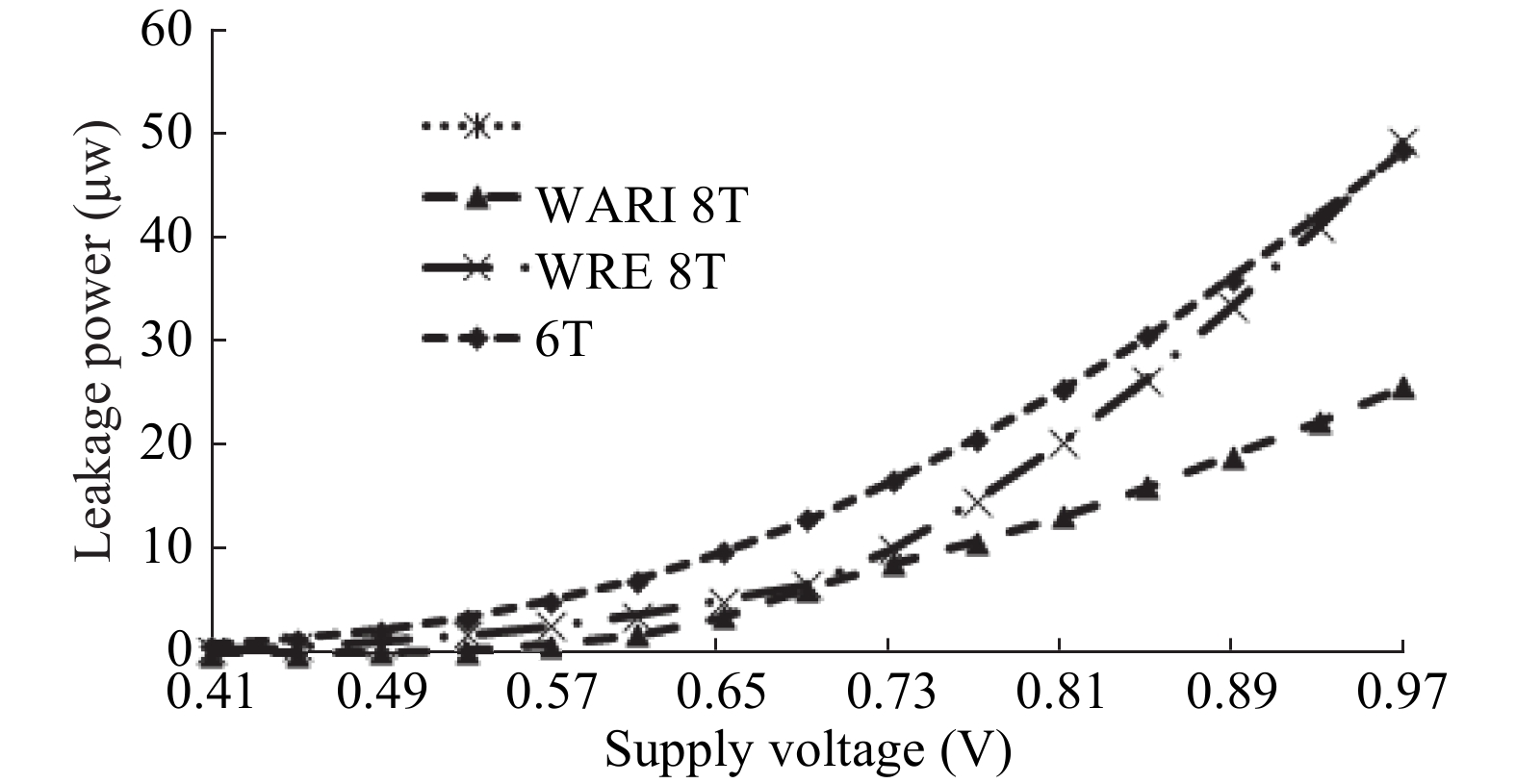
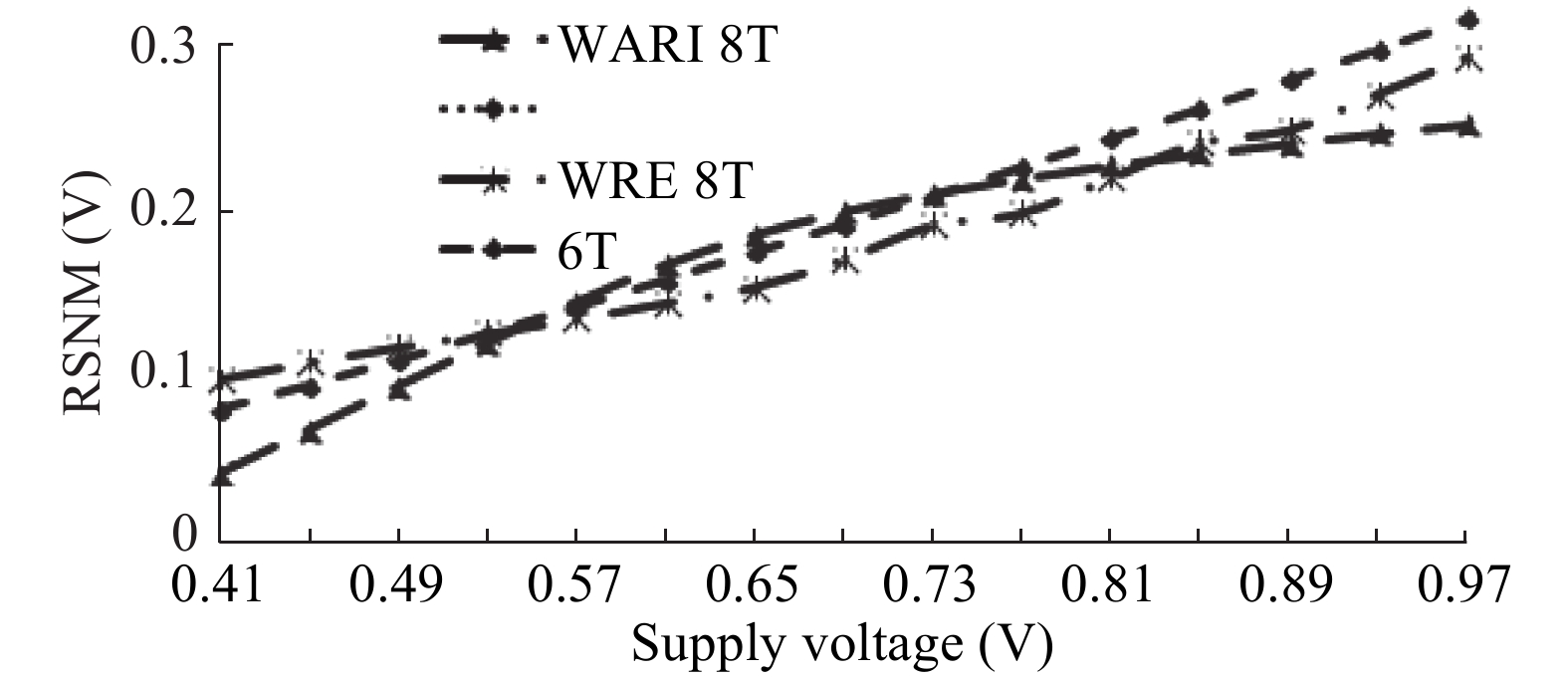
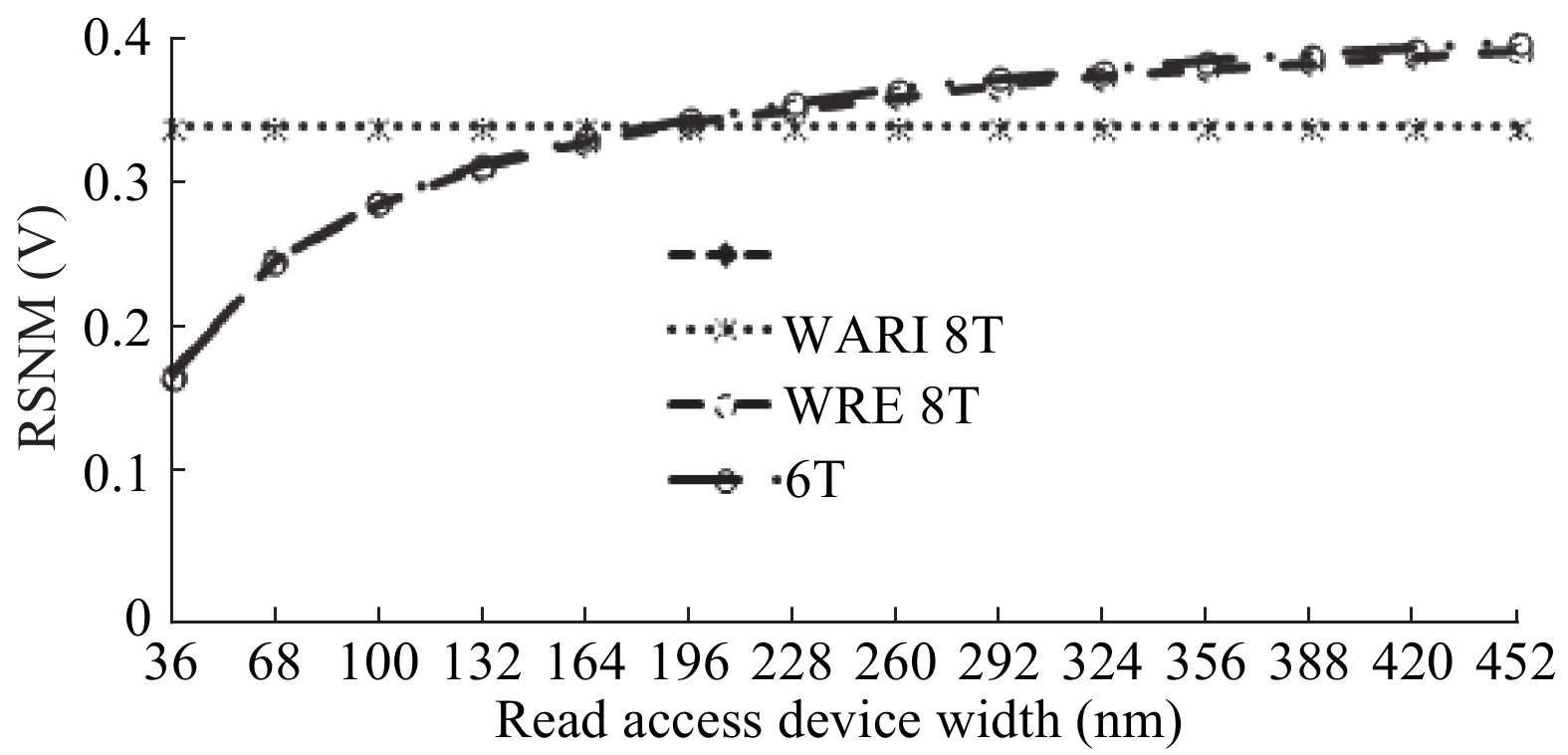
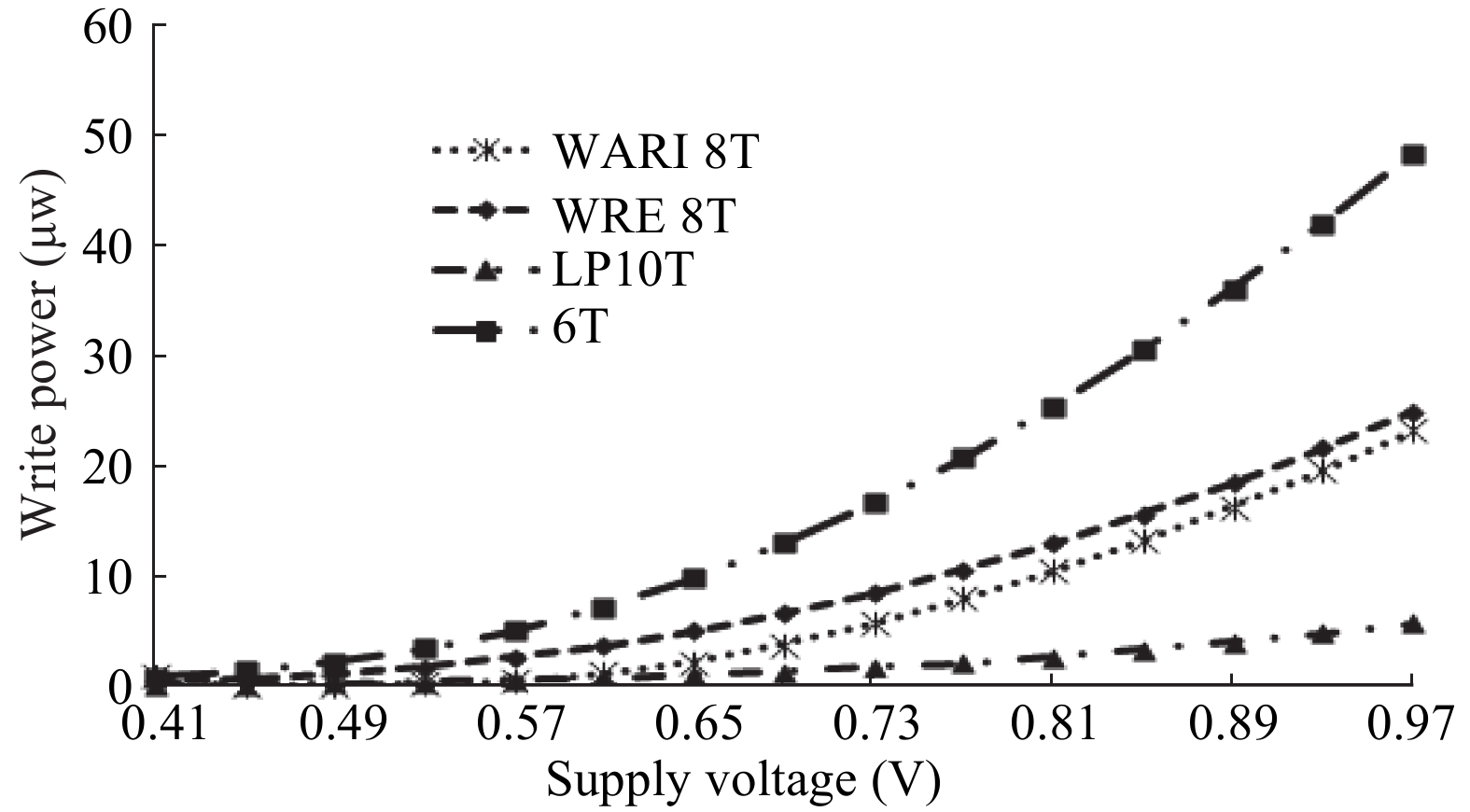
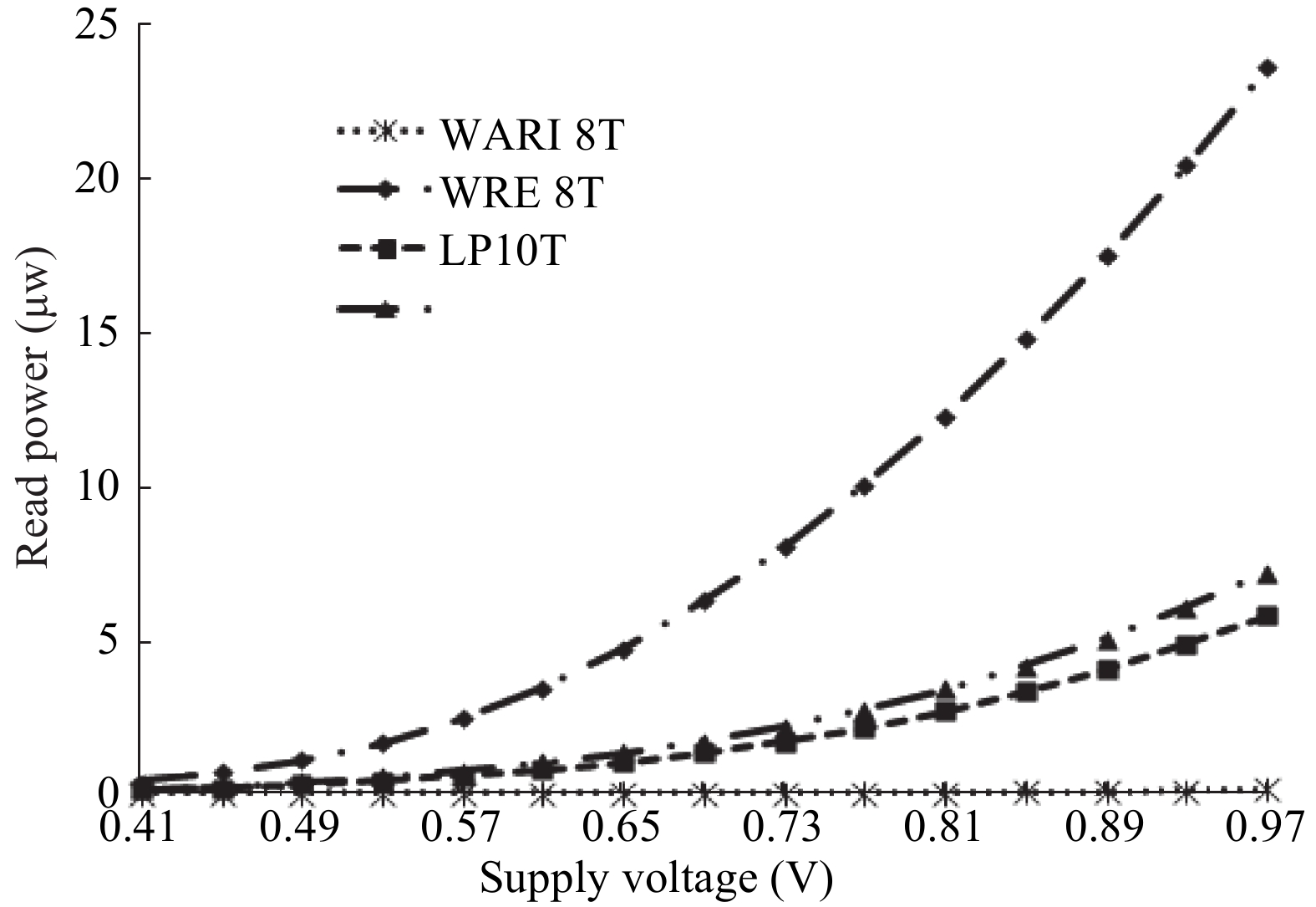
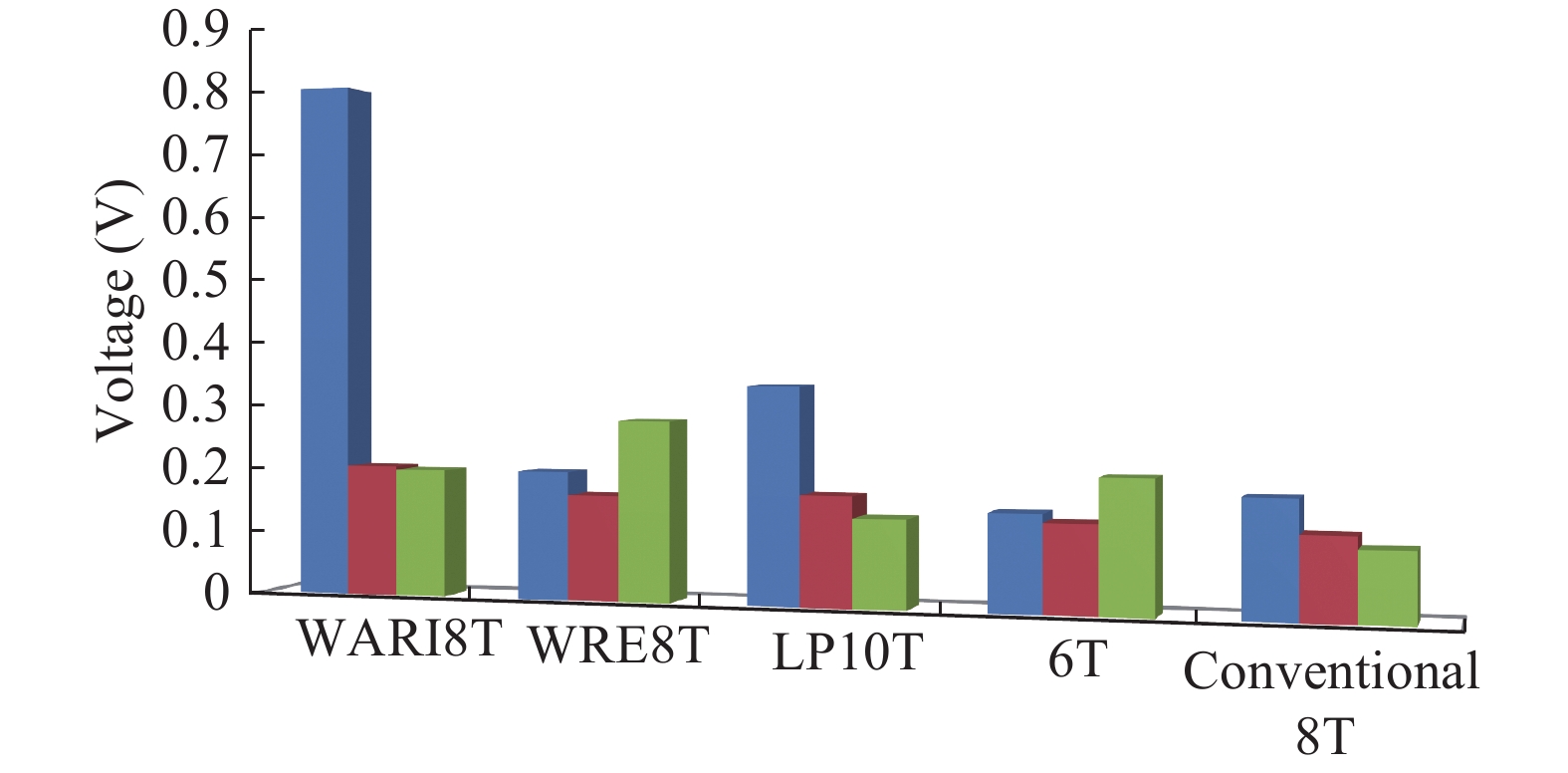
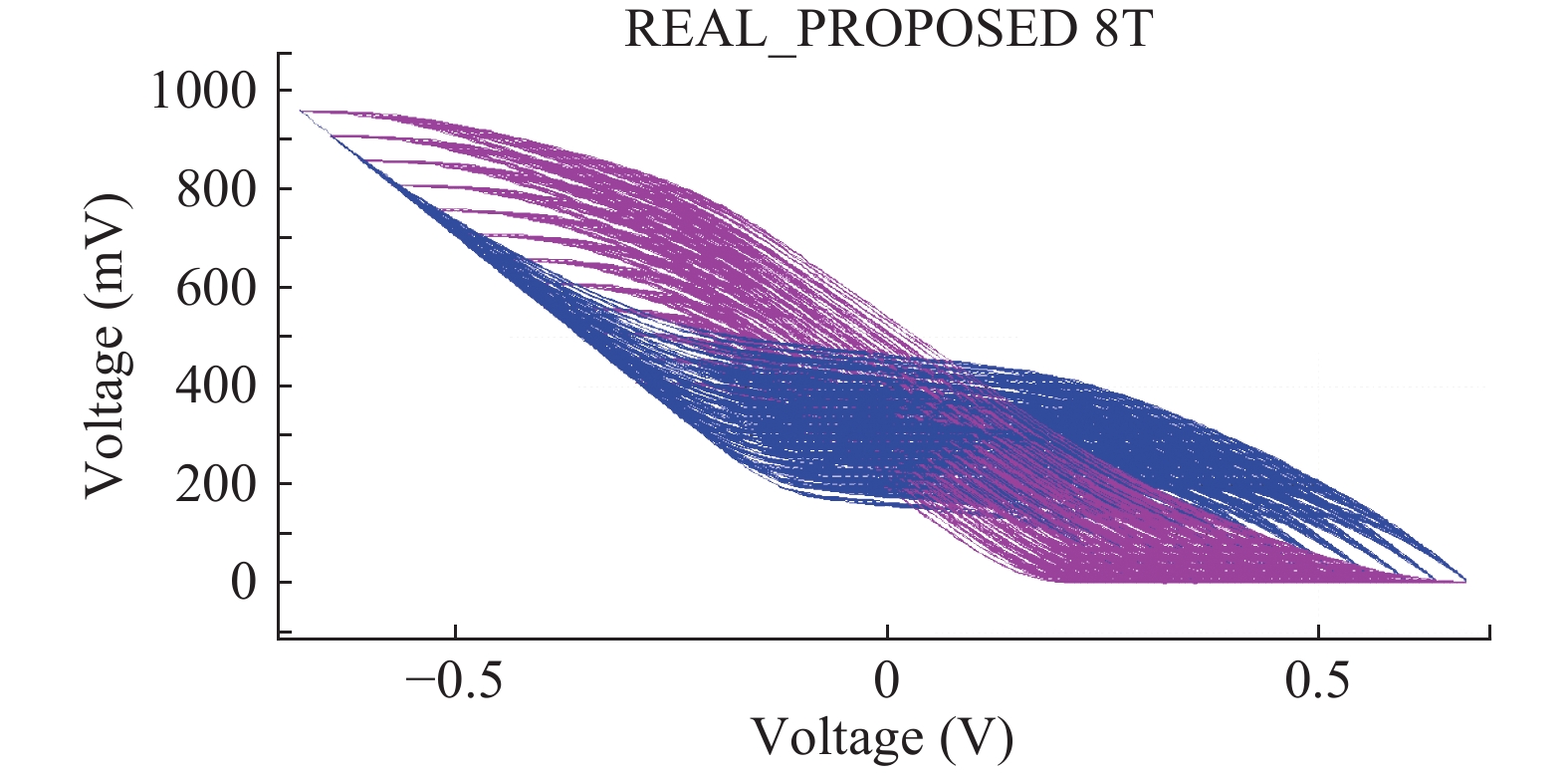
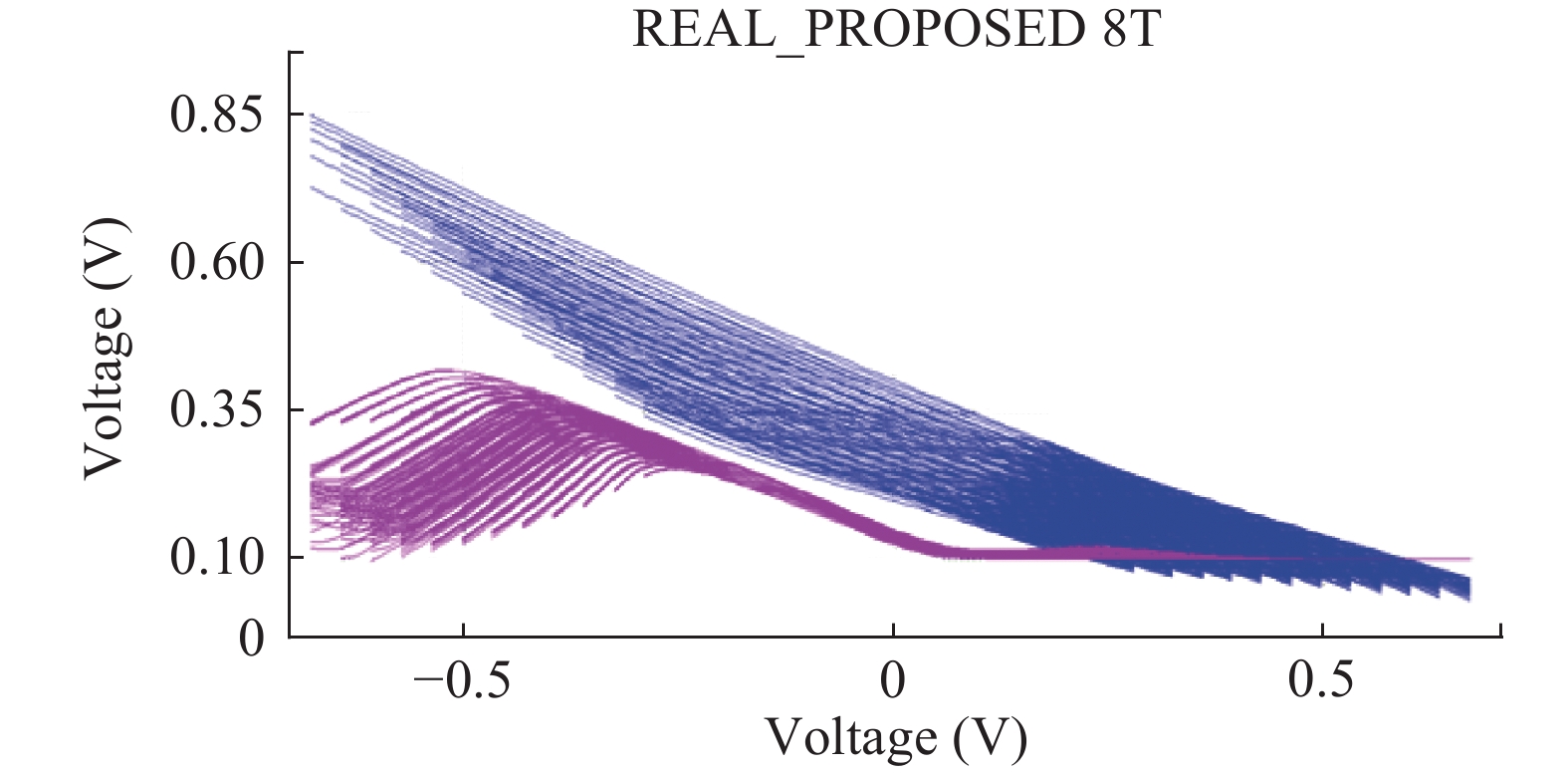
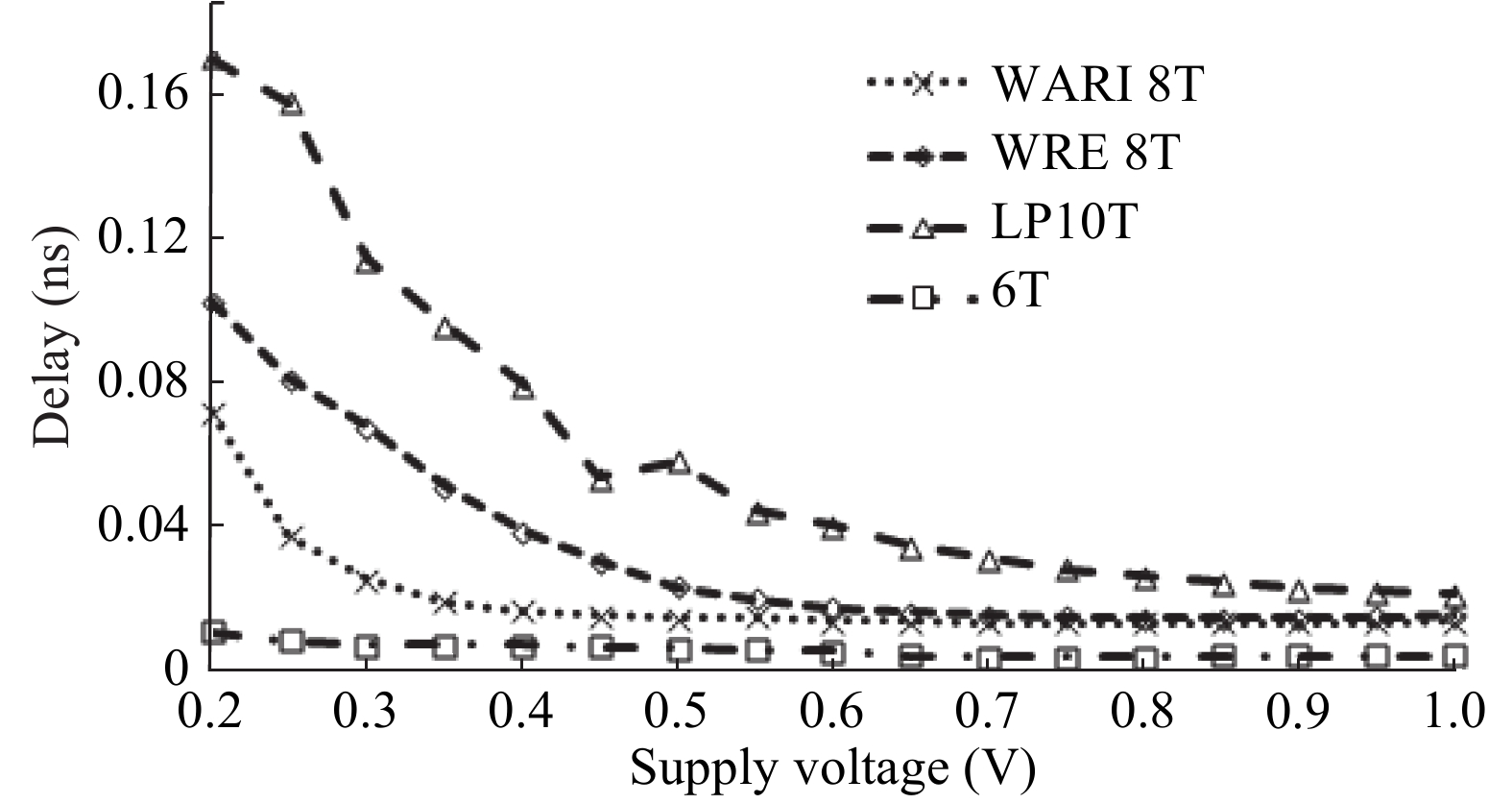
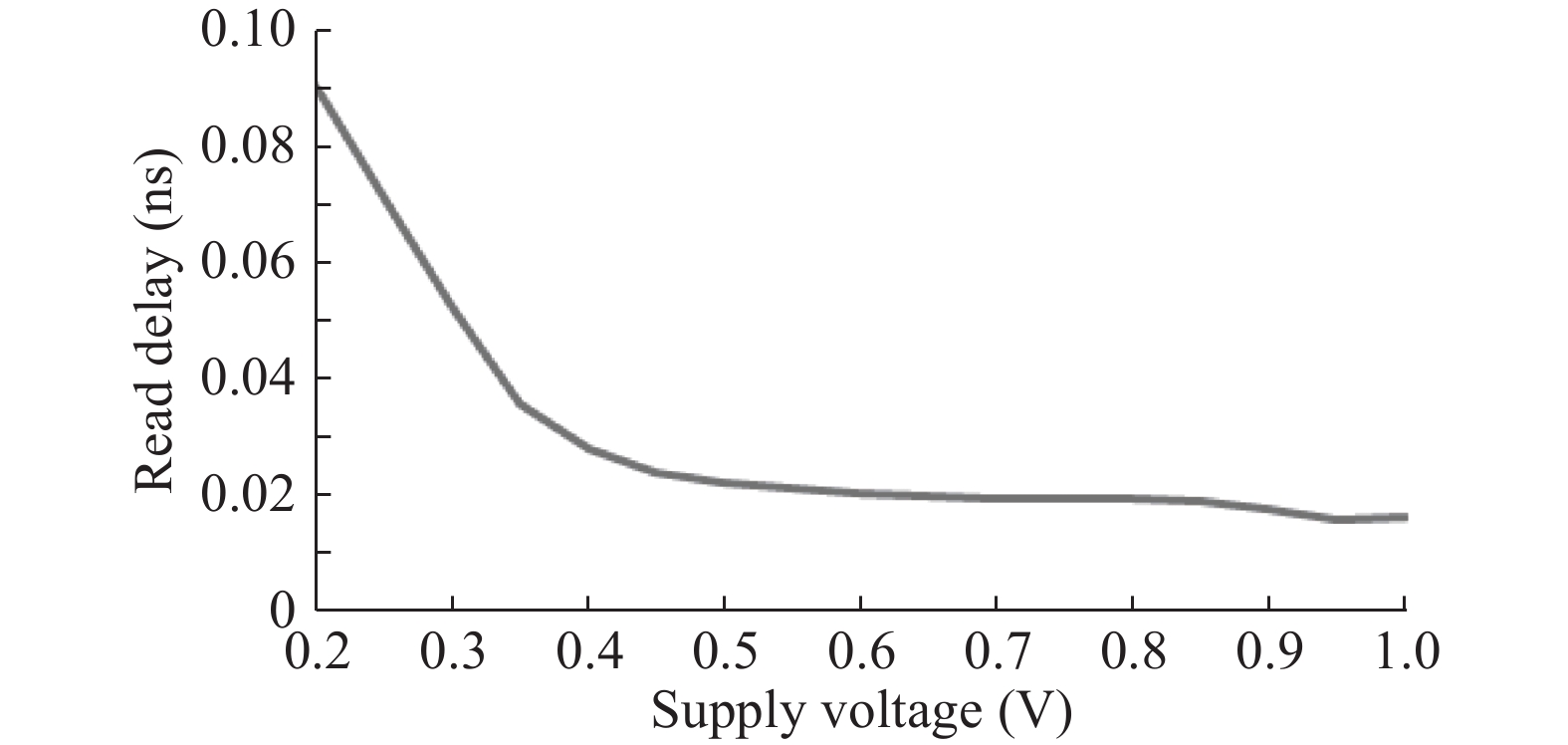
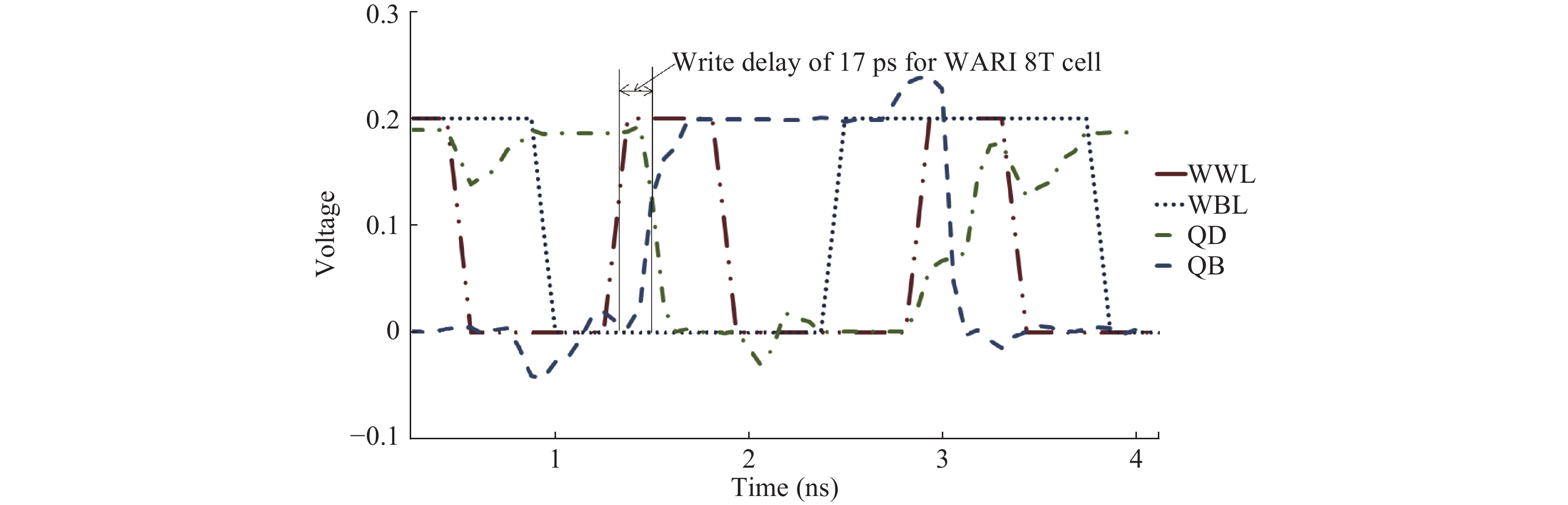
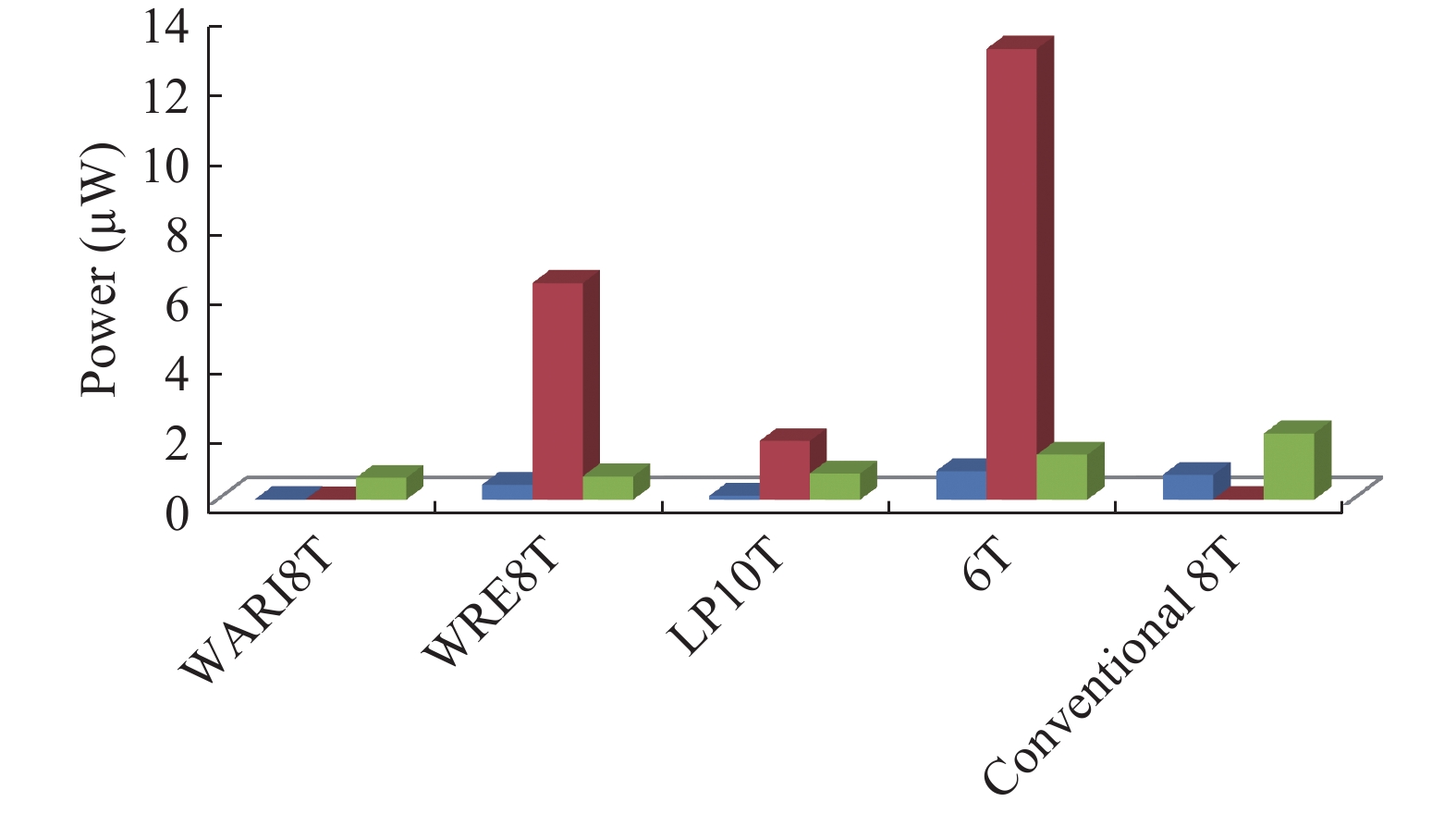
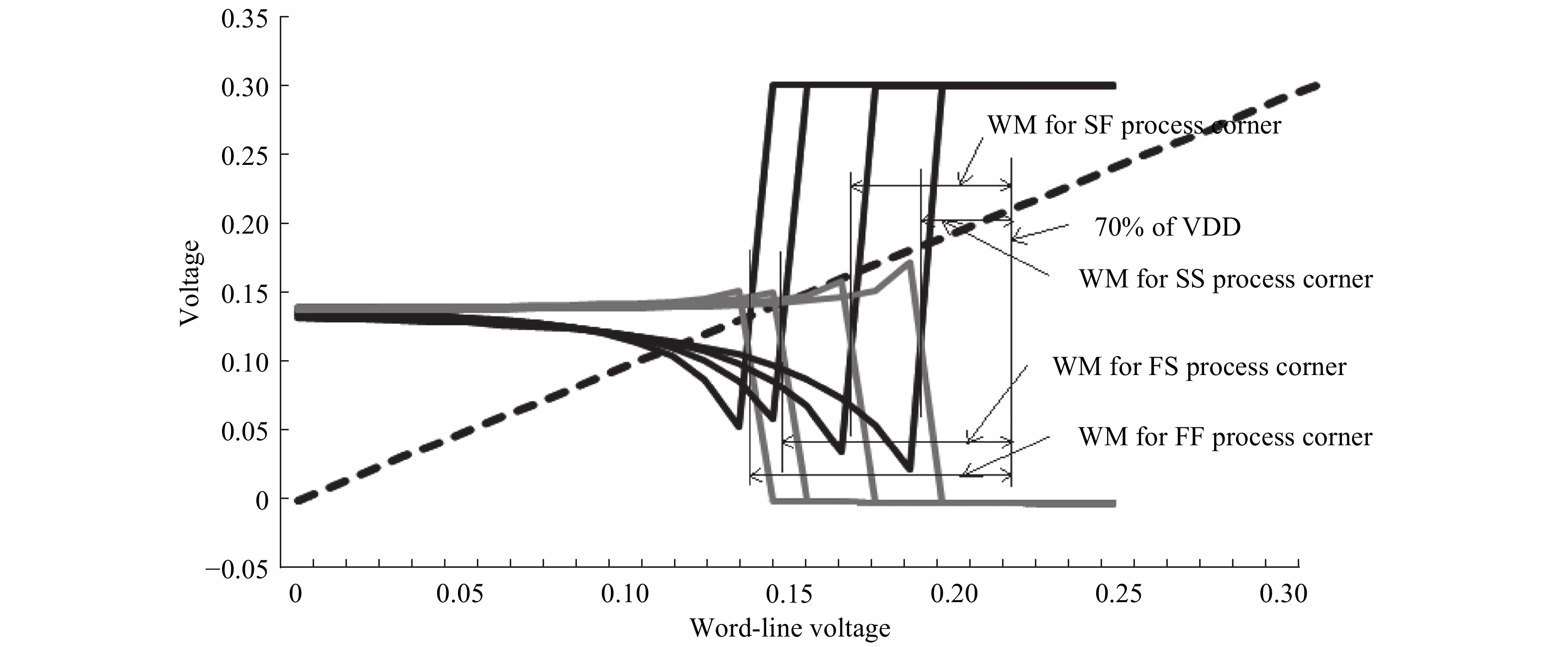
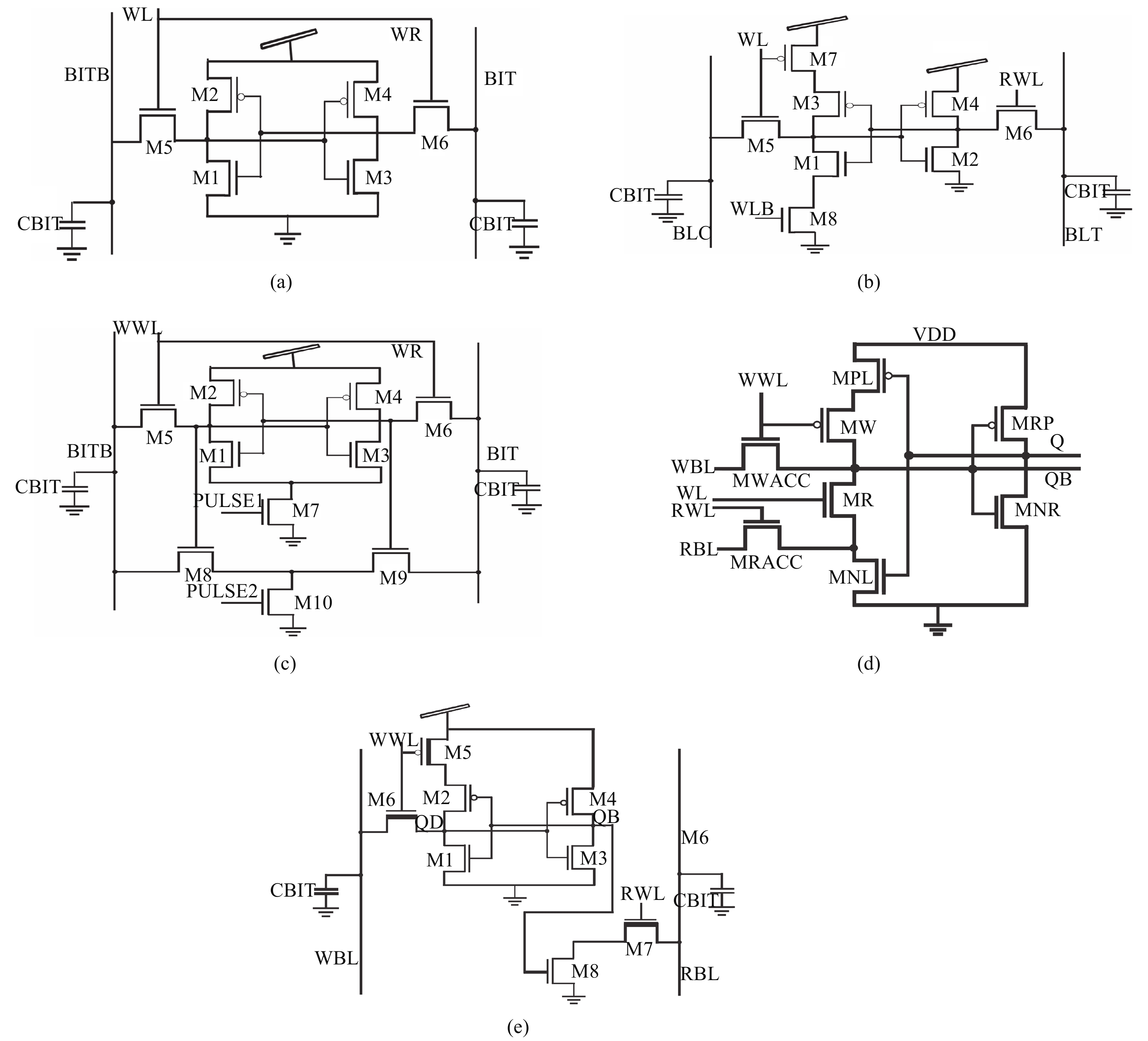
This paper presents a new dual Vt 8T SRAM cell having single bit-line read and write, in addition to Write Assist and Read Isolation (WARI). Also a faster write back scheme is proposed for the half selected cells. A high Vt device is used for interrupting the supply to one of the inverters for weakening the feedback loop for assisted write. The proposed cell provides an improved read static noise margin (RSNM) due to the bit-line isolation during the read. Static noise margins for data read (RSNM), write (WSNM), read delay, write delay, data retention voltage (DRV), leakage and average powers have been calculated. The proposed cell was found to operate properly at a supply voltage as small as 0.41 V. A new write back scheme has been suggested for half-selected cells, which uses a single NMOS access device and provides reduced delay, pulse timing hardware requirements and power consumption. The proposed new WARI 8T cell shows better performance in terms of easier write, improved read noise margin, reduced leakage power, and less delay as compared to the existing schemes that have been available so far. It was also observed that with proper adjustment of the cell ratio the supply voltage can further be reduced to 0.2 V.-
Keywords:
- dual Vt,
- disturb free,
- write assist,
- read isolation,
- half selected cells
-
References
[1] Mooney V. Research trends in hardware/software codesign of embedded operating systems for FPGAs. FPGA Worlds, 2007[2] Chandrakasan A P, Daly D C, Finchelstein D F. Technologies for ultradynamic voltage scaling. Proc IEEE, 2010, 98(2): 191 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2009.2033621[3] Zhang K, Hamzaoglu F, Wang Y. Low-power SRAMs in nanoscale CMOS technologies. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2008, 55(1): 145 doi: 10.1109/TED.2007.911356[4] Gottscho, Banaiyanmofrad A, Dutt N, et al. DPCS: dynamic power/capacity scaling for SRAM caches in the nanoscale era. ACM Trans Architect Code Optim, 2015, 12(3): 27[5] Fan M L, Wu Y S, Hu V H, et al. Investigation of cell stability and write ability of FinFET subthreshold SRAM using analytical SNM model. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2010, 57(6): 1375 doi: 10.1109/TED.2010.2046988[6] Bansal A, Mukhopadhyay S, Roy K. Device-optimization technique for robust and low-power FinFET SRAM design in nanoscale era. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2007, 54(6): 1409 doi: 10.1109/TED.2007.895879[7] Rabaey J M. Low power design essentials. NY: Springer-Verlag, 2009[8] Islam S, Hasan M. Variability aware low leakage reliable SRAM cell design technique. Microelectron Reliab, 2012, 52(6): 1247 doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2012.01.003[9] Pasandi G, Fakhraie S M. A new sub-threshold 7T SRAM cell design with capability of bit-interleaving in 90 nm CMOS. Proc 21st ICEE , 2013: 1[10] Aly R, Bayoumi M. Low-power cache design using 7T SRAM cell. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II, 2007, 54(4): 318 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2006.877276[11] Zhai B, Hanson S, Blaauw D, et al. A variation-tolerant sub-200 mV 6-T subthreshold SRAM. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(10): 2338 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.2001903[12] Wen L, Li Z T, Li Y. Single-ended, robust 8T SRAM cell for low-voltage operation. Microelectron J, 2013, 44(8): 718 doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2013.04.007[13] Gupta P, Gupta N, Asati A. Leakage immune modified pass transistor based 8T SRAM cell in subthreshold Region. Int J Reconfig Comput, 2015, 2015: 749816[14] Sharifkhani M, Sachdev M. Segmented virtual ground architecture for low-power embedded SRAM. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr (VLSI) Syst, 2007, 15(2): 196 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2007.893584[15] Kulkarni K K, Roy K. A 160 mV robust Schmitt trigger based subthreshold SRAM. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42(10): 2303 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2007.897148[16] Islam A, Hasan M. Leakage characterization of 10T SRAM cell. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2012, 59(3): 631 doi: 10.1109/TED.2011.2181387[17] Liu Z, Kursun V. Characterization of a novel nine-transistor SRAM cell. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr (VLSI) Syst, 2008, 16(4): 488 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2007.915499[18] Wen L, Duan Z K, Li Y, et al. Analysis of a read disturb-free 9T SRAM cell with bit-interleaving capability. Microelectron J, 2014, 45(6): 815 doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2014.02.020[19] Wang B, Zhou J, Kim T T H. SRAM devices and circuits optimization toward energy efficiency in multi-Vth CMOS. Microelectron J, 2015, 46(3): 265 doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2014.12.003[20] Morifuji E, Patil D, Horowitz, et al. Power optimization for SRAM and its scaling. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2007, 54(4): 715 doi: 10.1109/TED.2007.891869[21] Roy K, Mak T M, Cheng K T. Test consideration for nanoscale scale CMOS circuits. IEEE Des Test J, 2006, 23: 128 doi: 10.1109/MDT.2006.52[22] Roy K, Mukhopadhyay S, Mahmoodi-Meimand H. Leakage current mechanisms and leakage reduction techniques in deep-submicronmeter CMOS circuits. Proc IEEE, 2003, 91(2): 305 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2002.808156[23] Lee D W, Kwong W, Blaauw S, et al. Analysis and minimization techniques for total leakage considering gate oxide leakage. 40th Annual Design and Automation Conference, 2003: 175[24] Kulkarni J, Kim K, Roy K. A 160 mV robust Schmitt trigger based subthreshold SRAM. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42(10): 2303 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2007.897148[25] Wang J, Singhee A, Rutenbar R, et al. Statistical modeling for minimum standby supply voltage of a full SRAM array. 33rd Proc ESSCIRC, 2007: 400[26] Yashimoto M, Anami K, Shinohara H, et al. A divided word line structure in the static RAM and its application to a 64K full CMOS SRAM. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1983, 18(5): 479 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.1983.1051981[27] Honda K, Miyaji K, Tanakamaru S, et al. Elimination of half select disturb in 8T-SRAM by local injected electron asymmetric pass gate transistor. Proc IEEE CICC, 2010: 1[28] Pasandi G, Fakhraie S M. An 8T low-voltage and low-leakage half-selection disturb-free SRAM using bulk-CMOS and FinFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2014, 61(7): 2357 doi: 10.1109/TED.2014.2321295[29] Kim T H, Liu J, Keane J, et al. A 0.2 V, 480 Kb subthreshold SRAM with 1 k cells per bitline for ultra-low-voltage computing. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(2): 518 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2007.914328 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: