| Citation: |
Shaoxi Wang, Dan Feng, Chenxia Hu, P. Rezai. The simple two-step polydimethylsiloxane transferring process for high aspect ratio microstructures[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2018, 39(8): 086001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/8/086001
****
S X Wang, D Feng, C X Hu, P Rezai, The simple two-step polydimethylsiloxane transferring process for high aspect ratio microstructures[J]. J. Semicond., 2018, 39(8): 086001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/8/086001.
|
The simple two-step polydimethylsiloxane transferring process for high aspect ratio microstructures
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/8/086001
More Information
-
Abstract
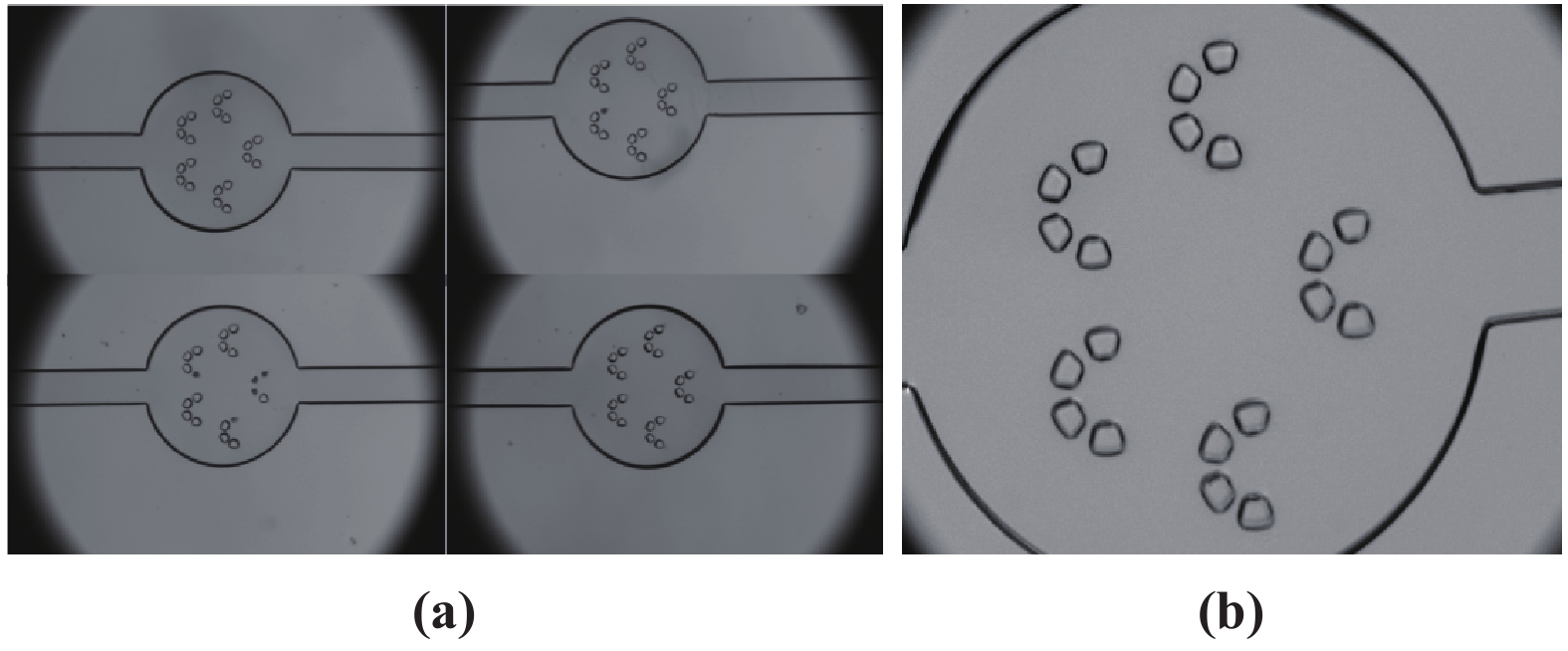
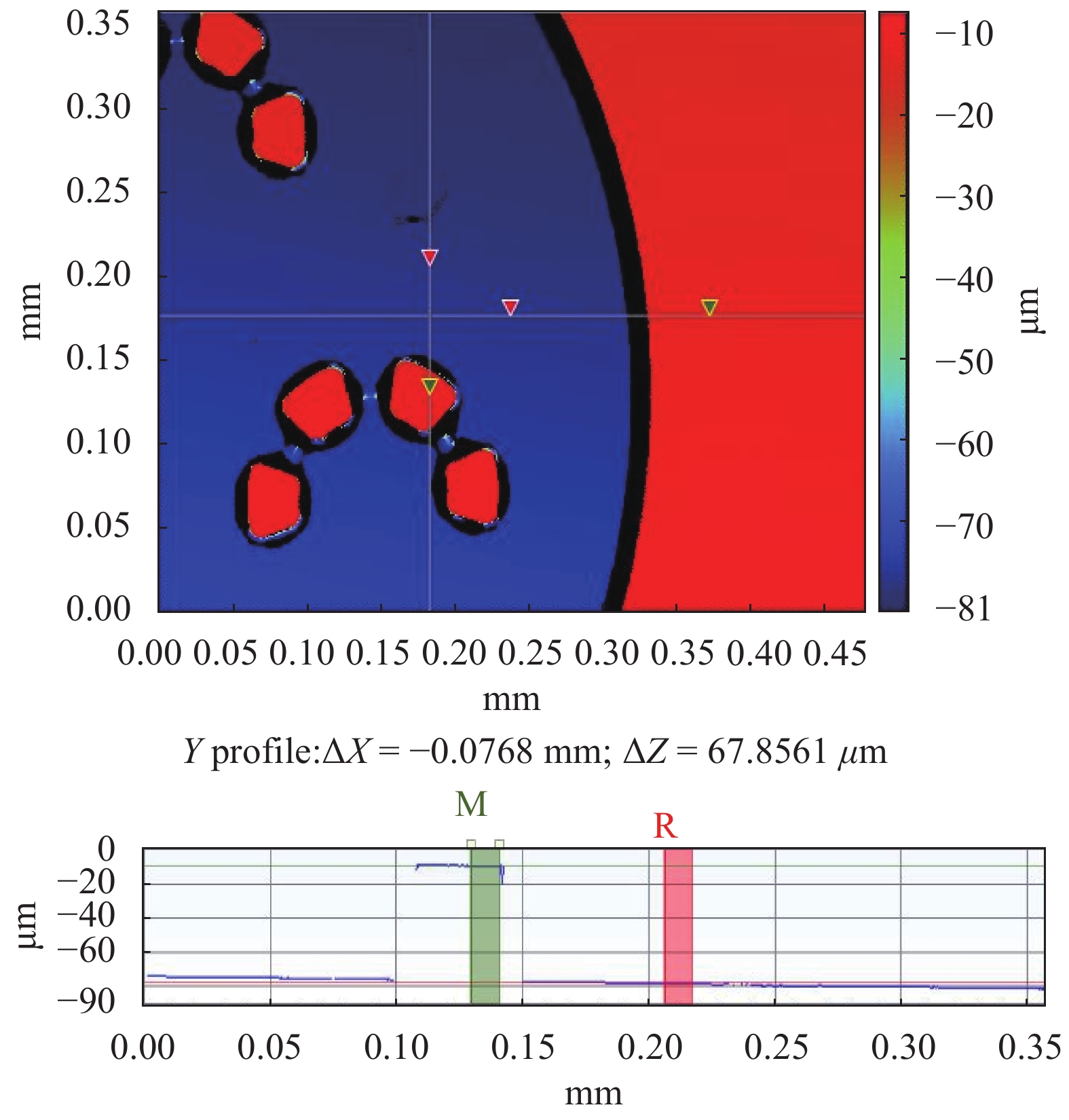
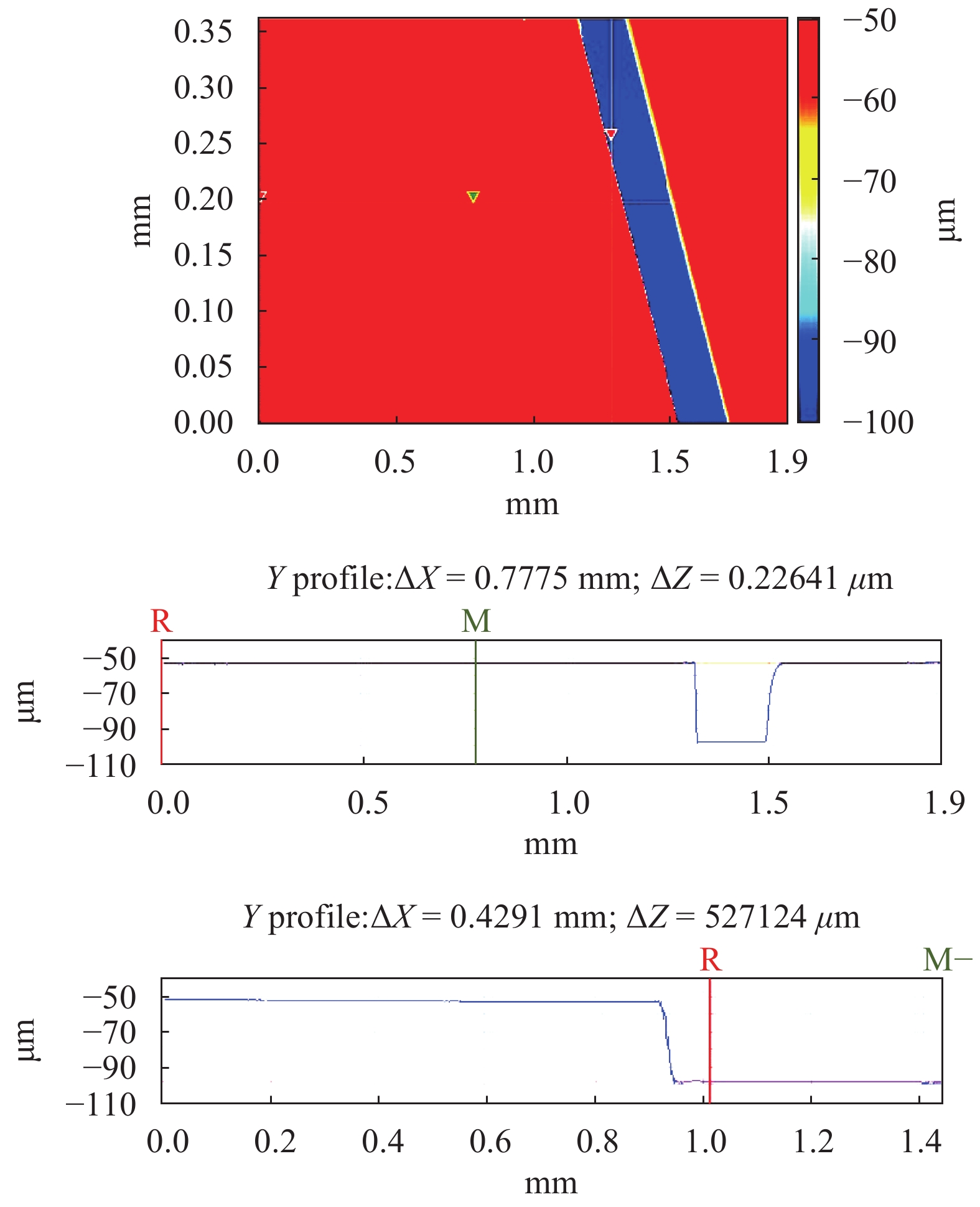
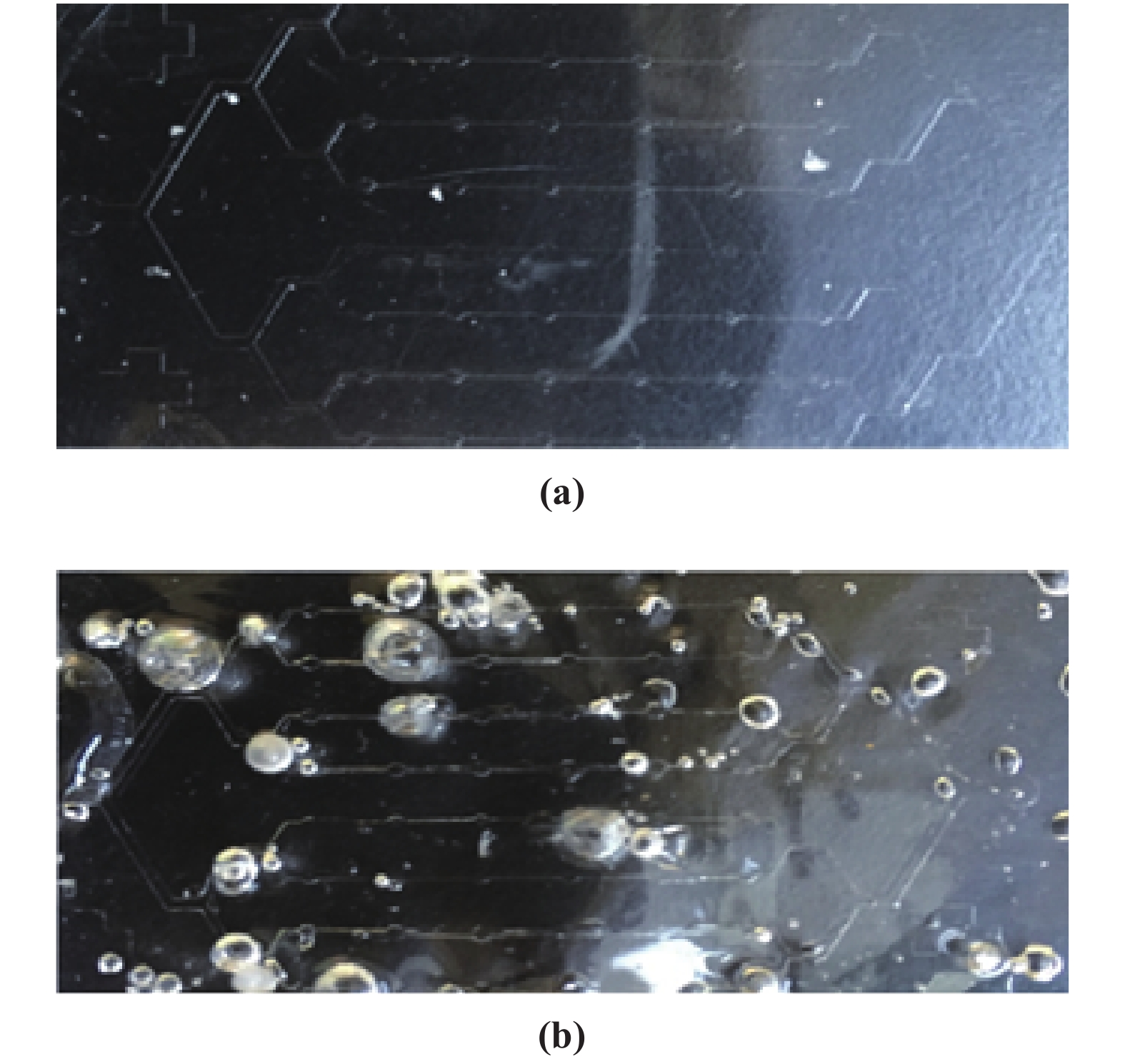
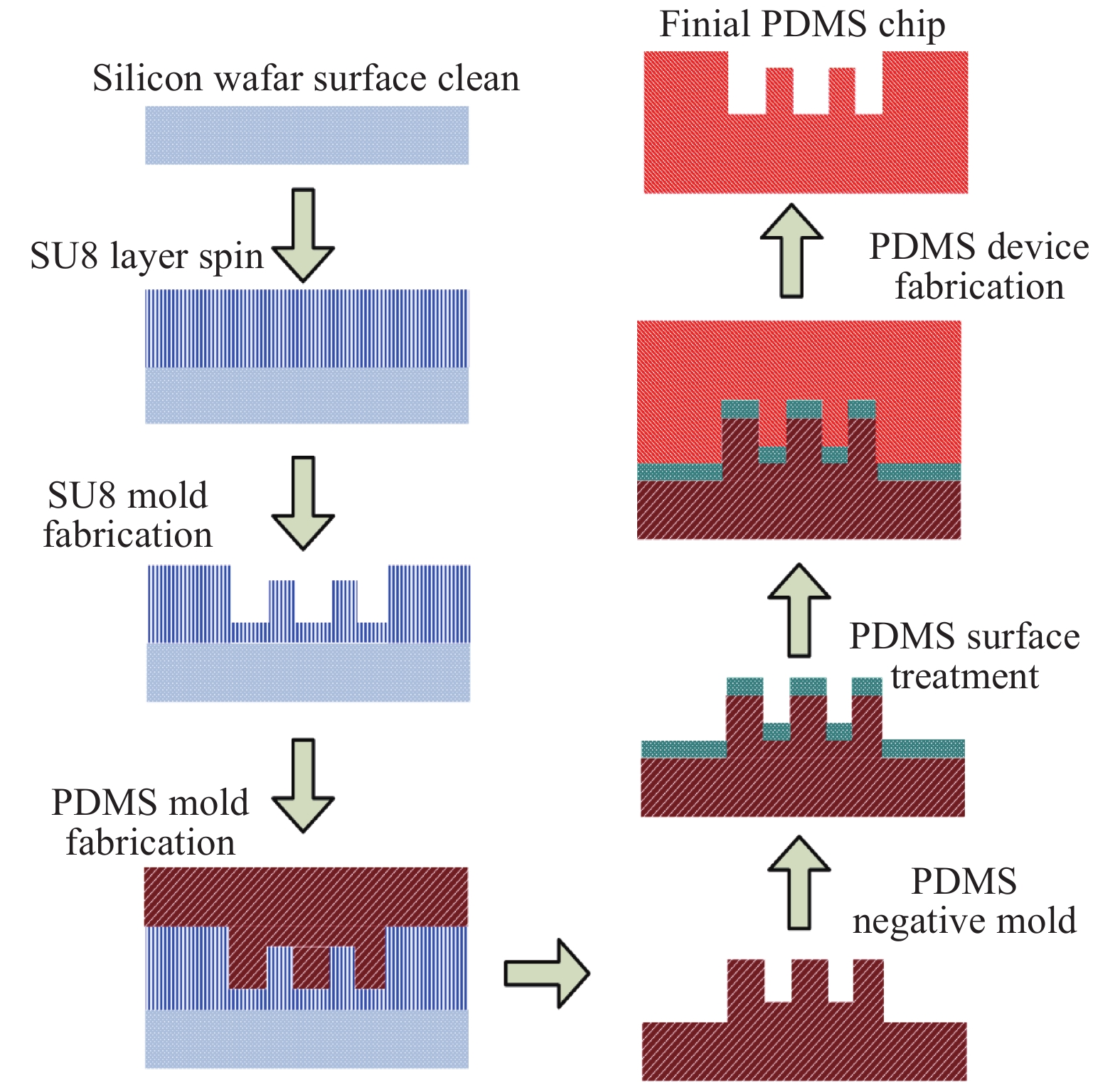
High aspect ratio units are necessary parts of complex microstructures in microfluidic devices. Some methods that are available to achieve a high aspect ratio require expensive materials or complex chemical processes; for other methods it is difficult to reach simple high aspect ratio structures, which need supporting structures. The paper presents a simple and cheap two-step Polydimethylsioxane (PDMS) transferring process to get high aspect ratio single pillars, which only requires covering the PDMS mold with a Brij@52 surface solution after getting a relative PDMS mold based on an SU8 mold. The experimental results demonstrate the method efficiency and effectiveness.-
Keywords:
- high aspect,
- microfluidic chip,
- microstructures
-
References
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polydimethylsiloxane[2] McDonald J C, Whitesides G M. Polydimethylsiloxane as a material for fabricating microfluidic devices. Acc Chem Res, 2002, 35(7): 491 doi: 10.1021/ar010110q[3] Friese C, Werber A, Krogmann F, et al. Materials effects and components for tunable micro-optics. IEEE Trans Electr Electron Eng, 2007, 2(3): 232 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1931-4981[4] Nguyen N T. Micro-optofluidic lenses: a review. Biomicrofluidics, 2010, 4(3): 031501 doi: 10.1063/1.3460392[5] Shao G C, Wu J H, Cai Z L, et al. Fabrication of elastomeric high-aspect-ratio microstructures using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) double casting technique. Sens Actuators A, 2012, 178(5): 230[6] Lee T R, Chung K O, Chang Y S, et al. Resonant behavior and microfluidic manipulation of silicone cilia due to an added mass effect. Soft Matter, 2011, 7(9): 4325 doi: 10.1039/c0sm01294g[7] Sun M, Luo C, Xu L, et al. Artificial lotus leaf by nanocasting. Langmuir, 2005, 21(19): 8978 doi: 10.1021/la050316q[8] Gitlin L, Schulze P, Belder D. Rapid replication of master structures by double casting with PDMS. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9(20): 3000 doi: 10.1039/b904684d[9] Natarajan S, Chang-yen D A, Gale B L. Large-area, high aspect ratio SU-8 molds for the fabrication of PDMS microfluidic devices. J Micromechan Microeng, 2008, 18(4): 045021 doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/18/4/045021[10] Paek J, Kim J. Microsphere assisted fabrication of high aspect ratio elastomeric micropillars and waveguides. Nat Commun, 2014, 5(5): 3324[11] Sasoglu F M, Bohl A J, Layton B E. Design and microfabrication of a high aspect ratio PDMS microbeam array for parallel nanonewton force measurement and protein printing. J Micromechan Microeng, 2007, 17(3): 623 doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/17/3/027[12] vanKan J A, Wang L P, Shao P G, et al. High aspect ratio PDMS replication through proton beam fabricated Ni masters. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B, 2007, 260(1): 353 doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2007.02.046[13] Sitti M. High aspect ratio polymer micro/nano-structure manufacturing using nanoembossing, nanomolding and directed self-assembly. IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, 2003, 2(2): 886[14] Chandra D, Taylor J A, Yang S. Replica molding of high aspect ratio (sub-) micro hydrogel pillar arrays and their stability in air and solvents. Soft Matter, 2008, 4(5): 979 doi: 10.1039/b717711a[15] Hung P J, Lee P J, Sabounchi P, et al. A novel high aspect ratio microfluidic degsin to provide a stable and uniform microenviroment for cell growth in a high throughput mammalian cell culture array. Lab on a Chip, 2005, 5: 44 doi: 10.1039/b410743h[16] Kung Y C, Huang K W, Fan Y J, et al. Fabrication of 3D high aspect ratio PDMS microfluidic networks with a hybrid stamp. Lab on a Chip, 2015, 15(8): 1861 doi: 10.1039/C4LC01211A[17] Cusachs P R, Rico F, Martinez E, et al. Stability of microfabricated high aspect ratio structures in Poly(dimethylsiloxane). Langmuir, 2005, 21(12): 5524 doi: 10.1021/la050252j[18] Sia S K, Whitesides G M. Microfluidic devices fabricated in poly (dimethylsiloxane) for biological studies. Electrophoresis, 2003, 24(21): 3563-3576 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1522-2683[19] McDonald J C, Whitesides G M. Poly (dimethylsiloxane) as a material for fabricating microfluidic devices. Acc Chem Res, 2002, 35(7): 491 doi: 10.1021/ar010110q -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: