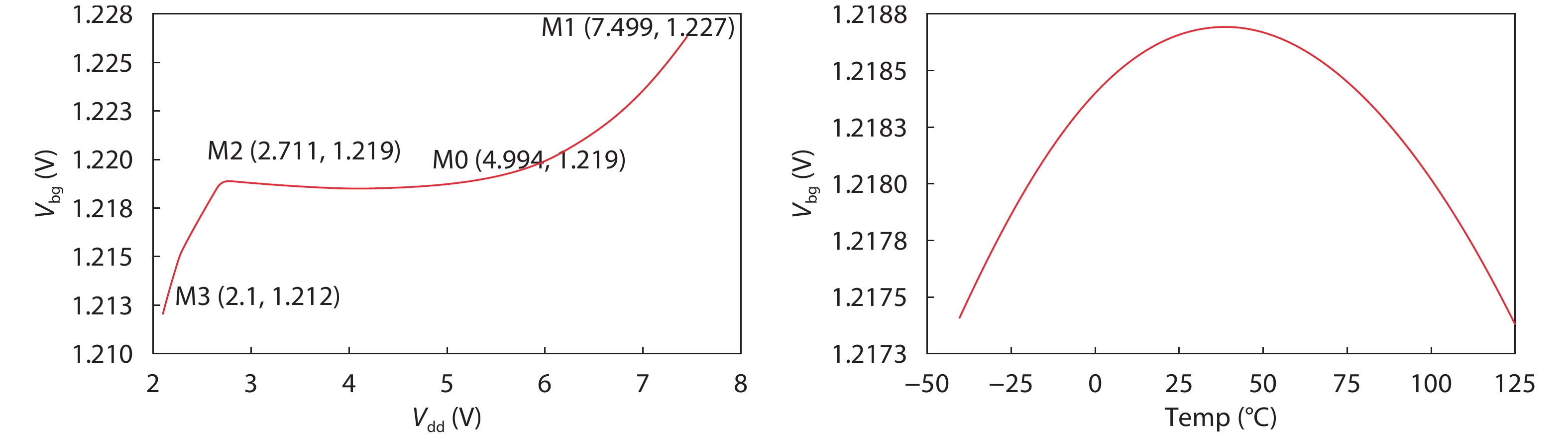| Citation: |
Guiping Cao, Ning Dong. An 18-bit sigma –delta switched-capacitor modulator using 4-order single-loop CIFB architecture[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2020, 41(6): 062404. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/6/062404
****
G P Cao, N Dong, An 18-bit sigma –delta switched-capacitor modulator using 4-order single-loop CIFB architecture[J]. J. Semicond., 2020, 41(6): 062404. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/6/062404.
|
An 18-bit sigma –delta switched-capacitor modulator using 4-order single-loop CIFB architecture
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/6/062404
More Information
-
Abstract
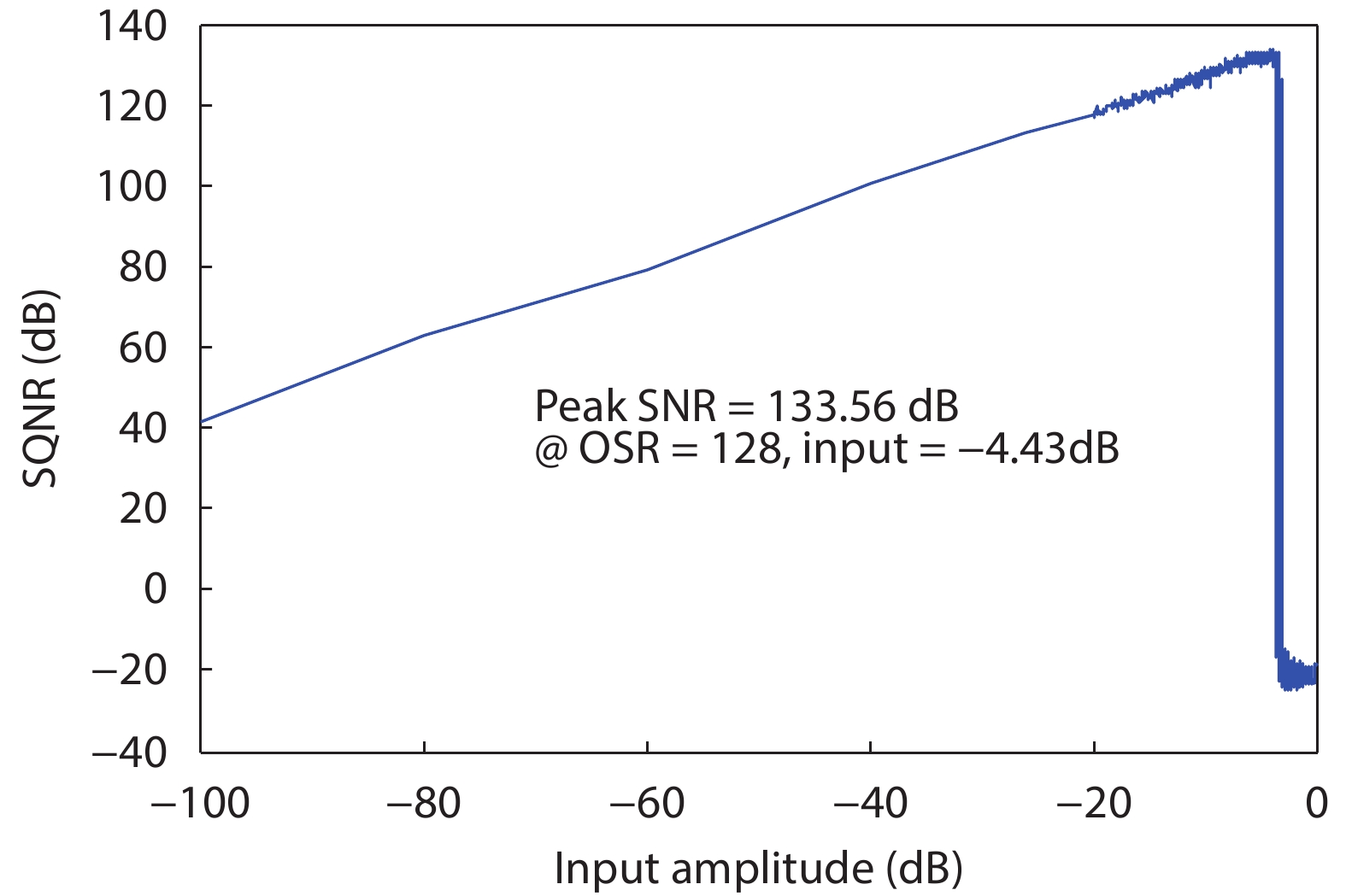
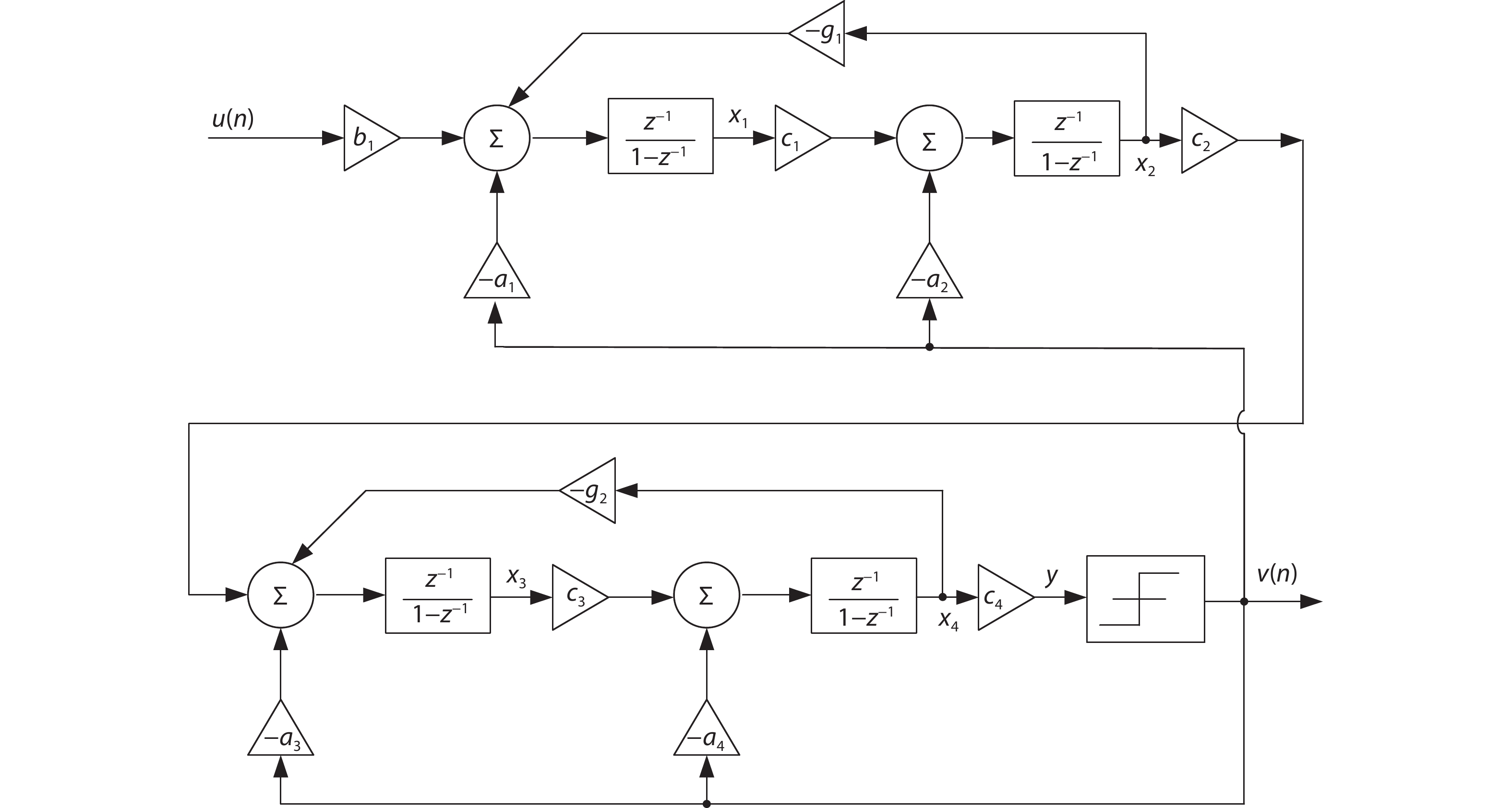
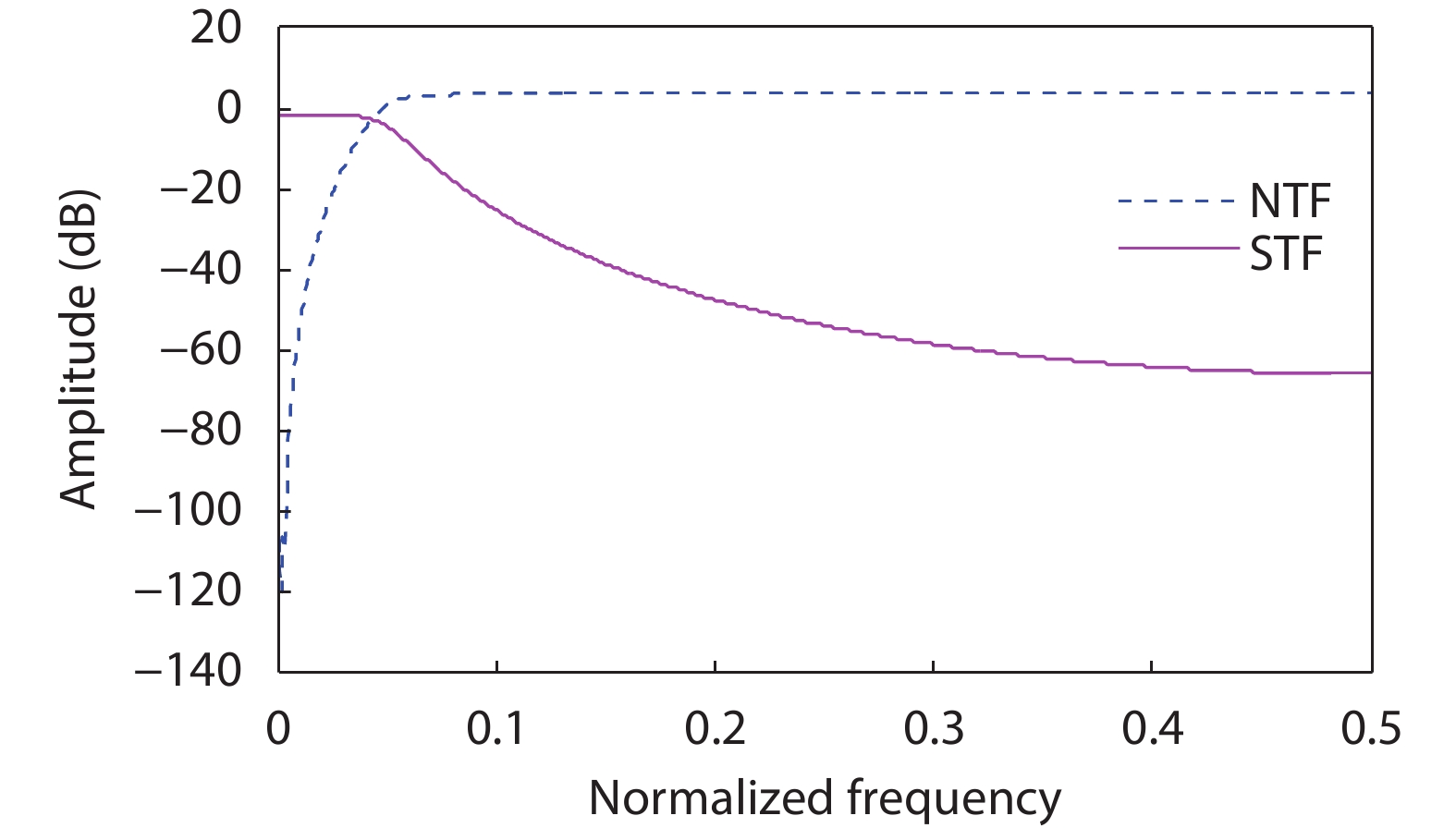
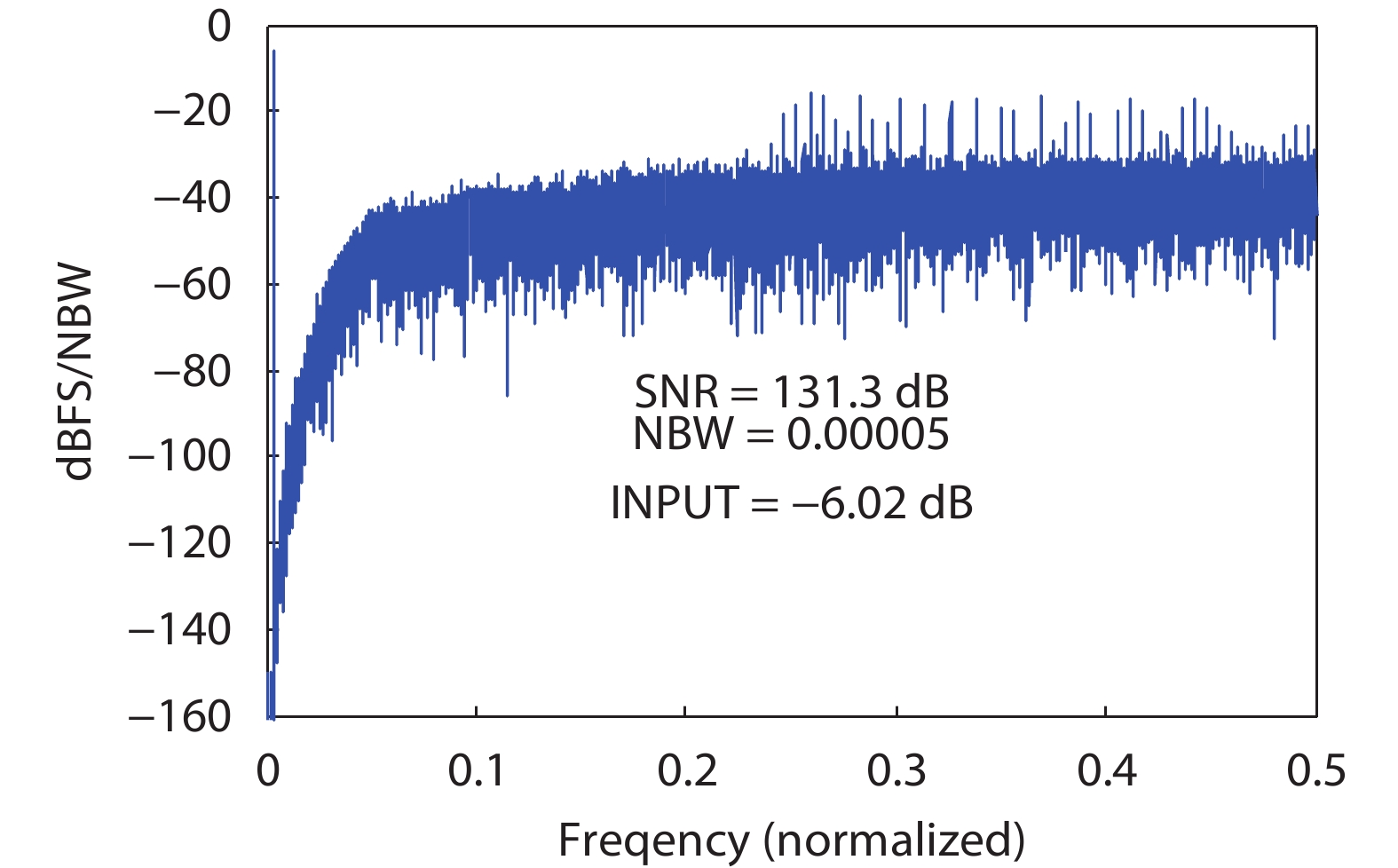
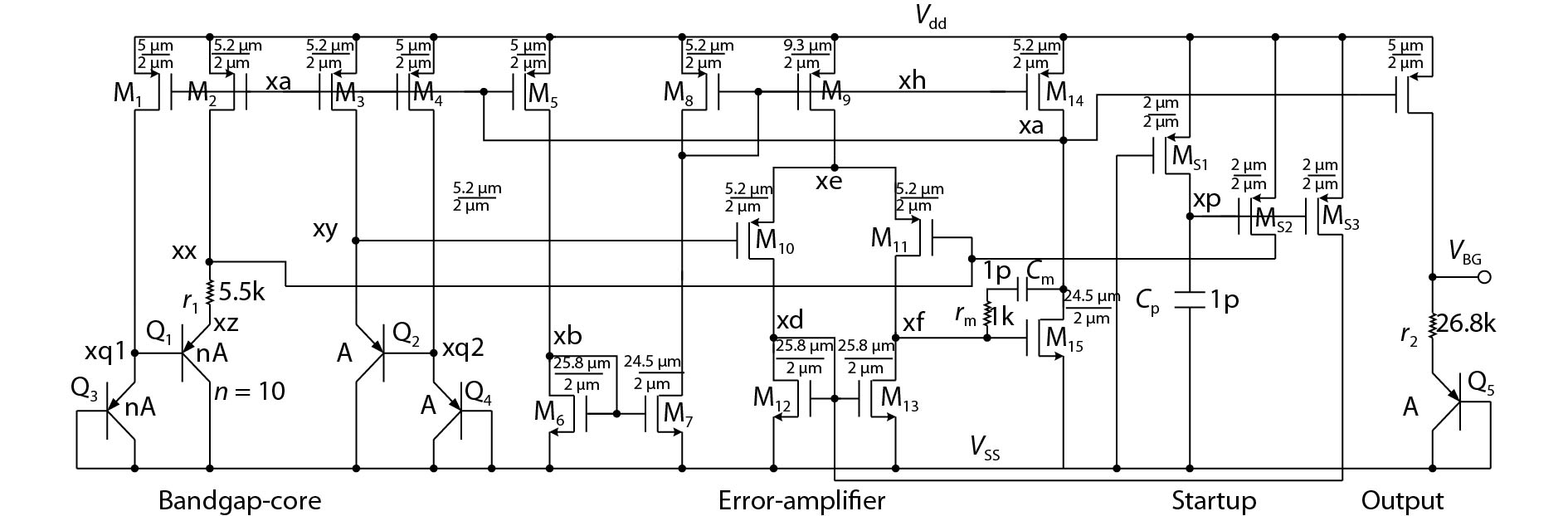
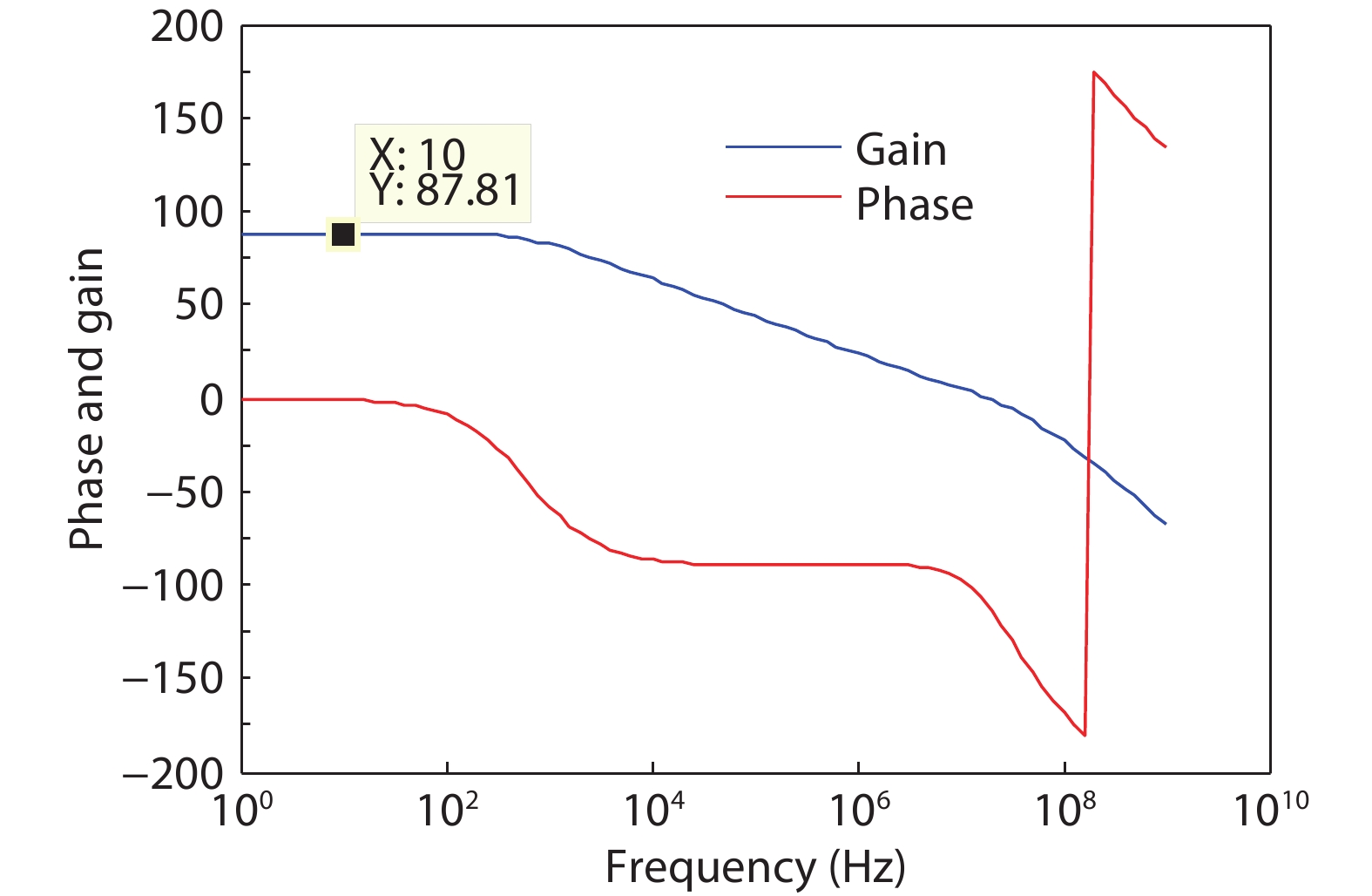
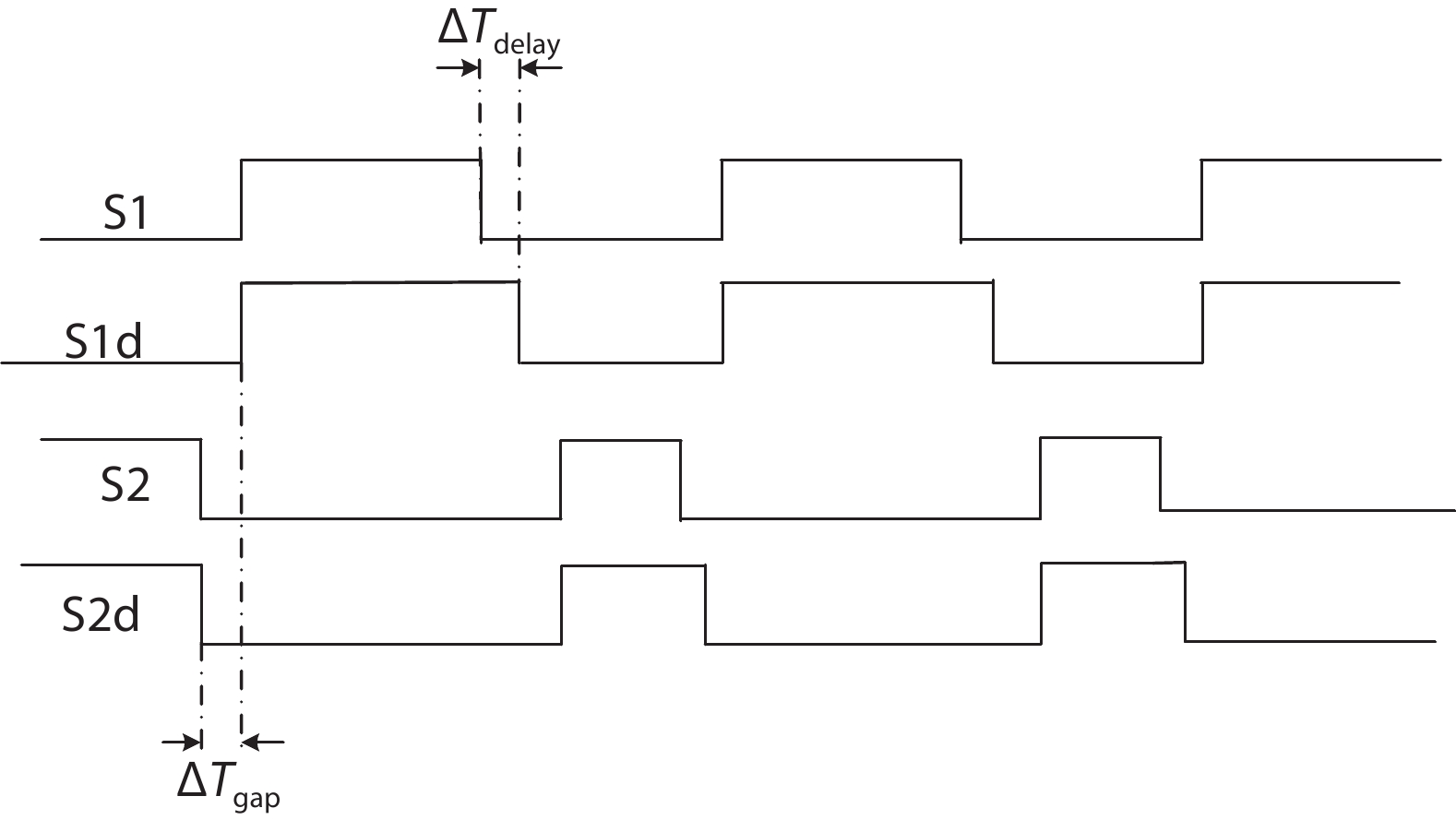
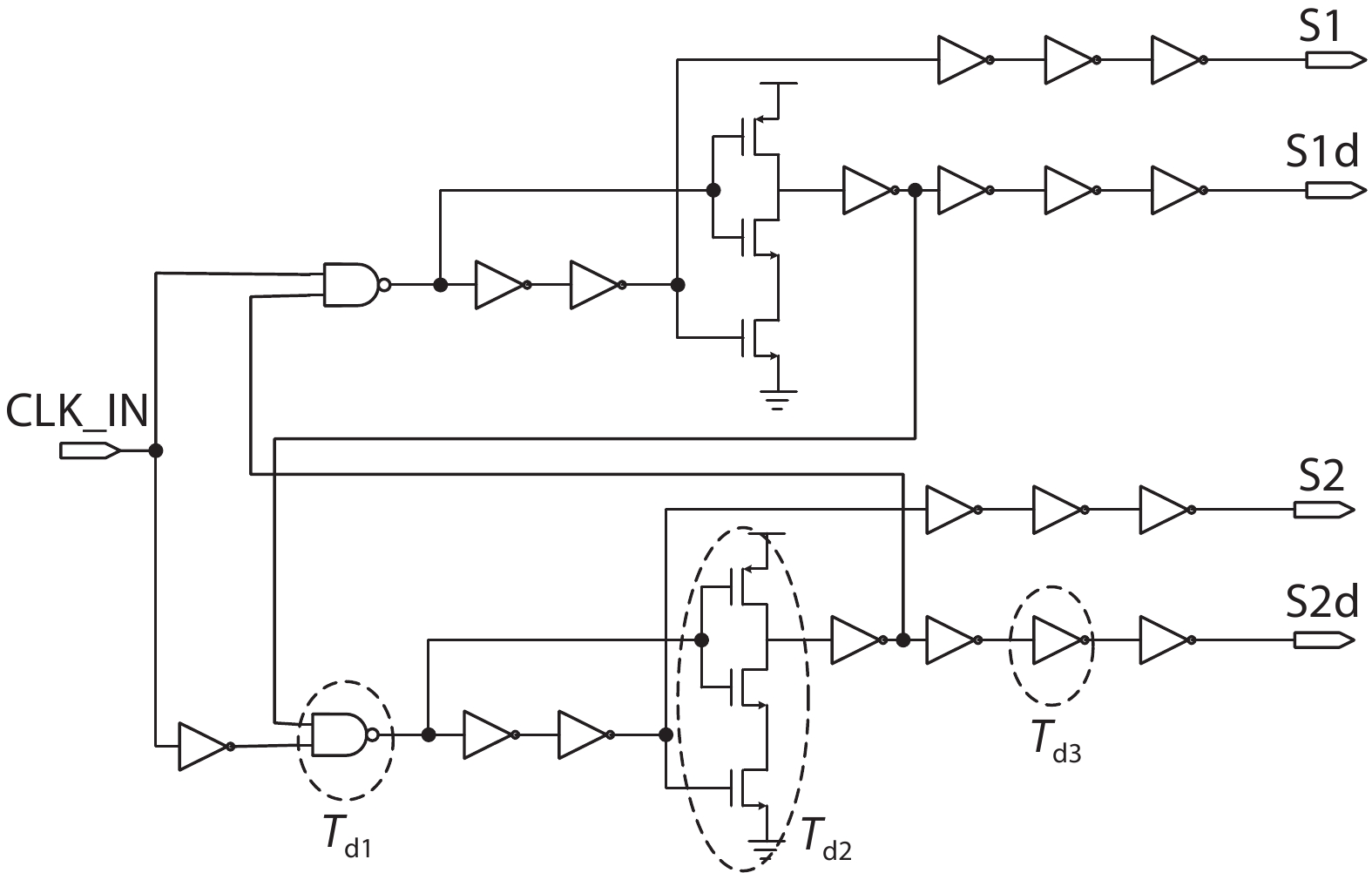
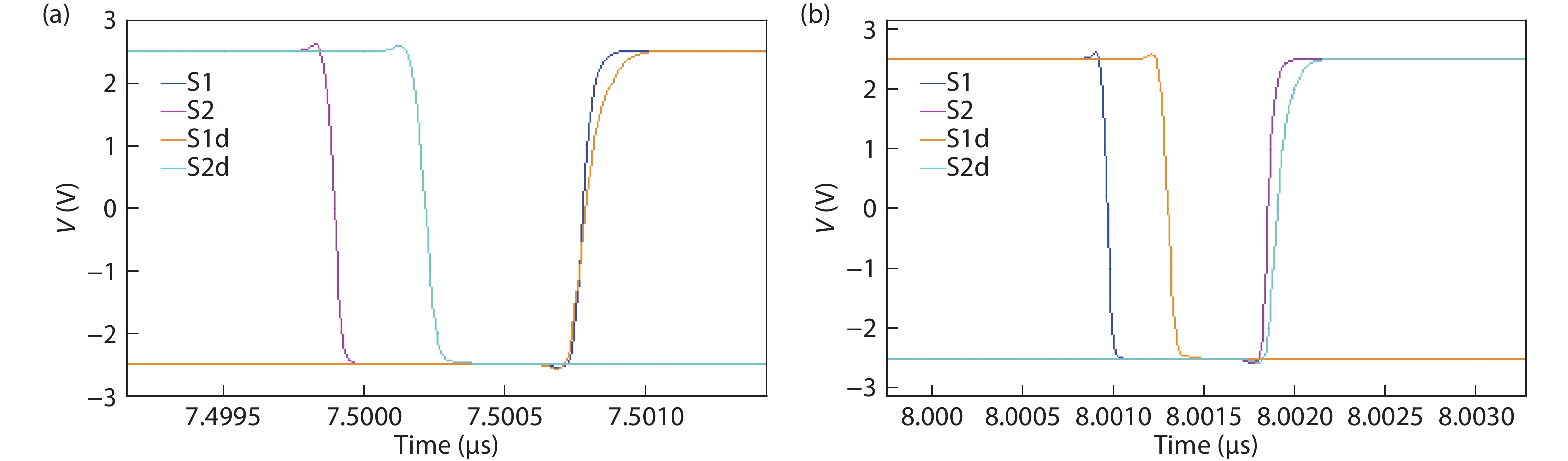
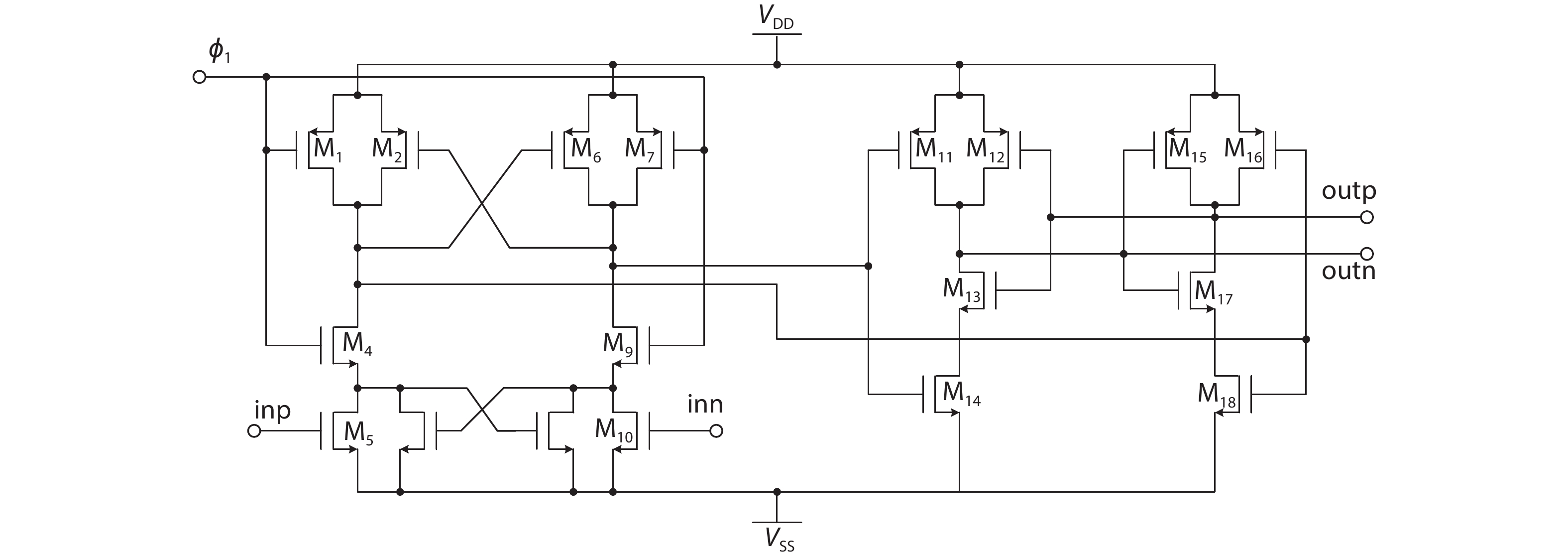
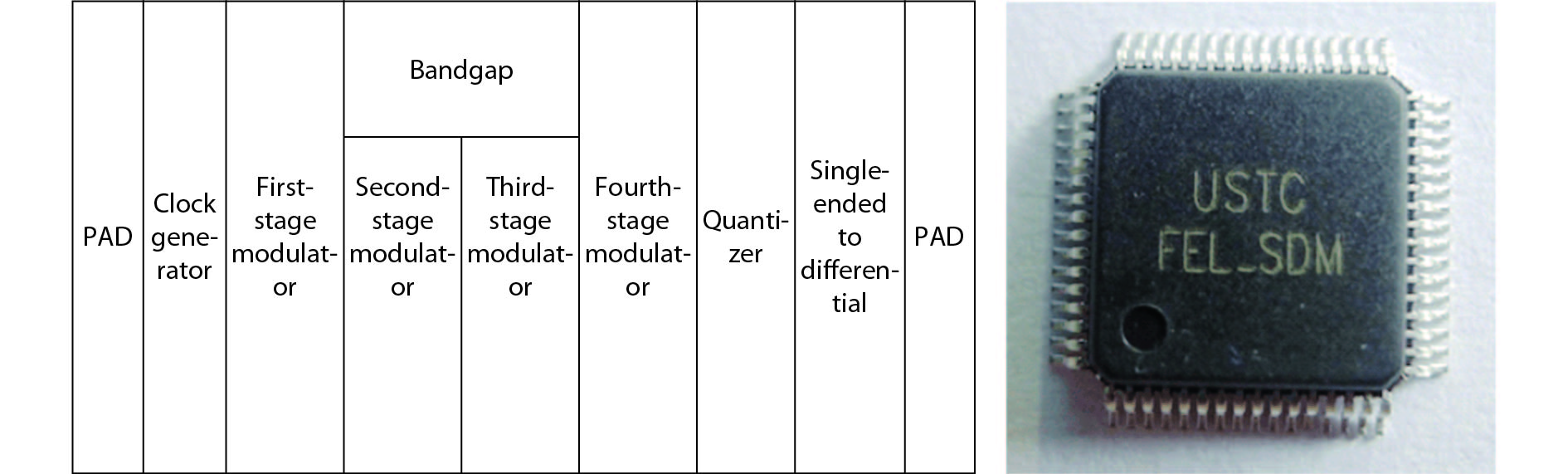
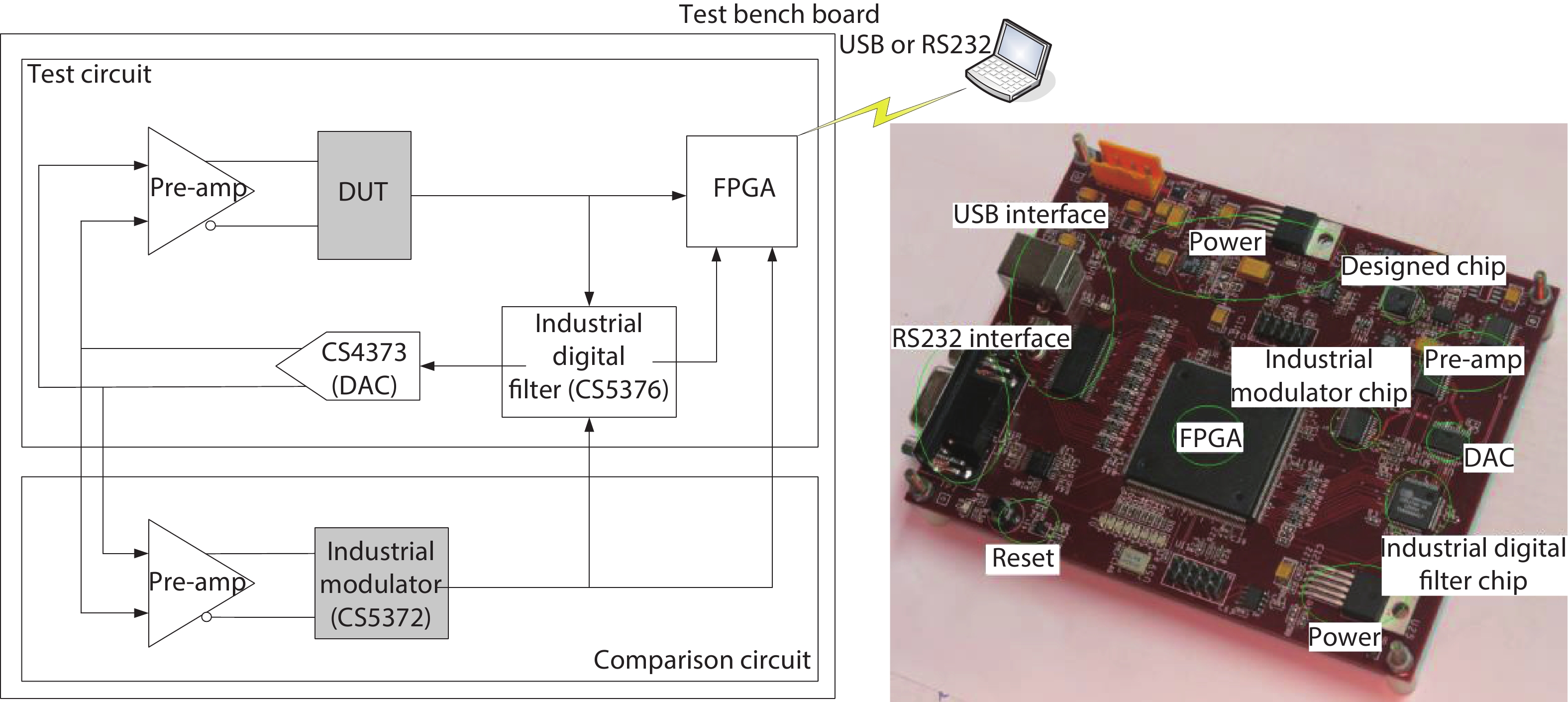
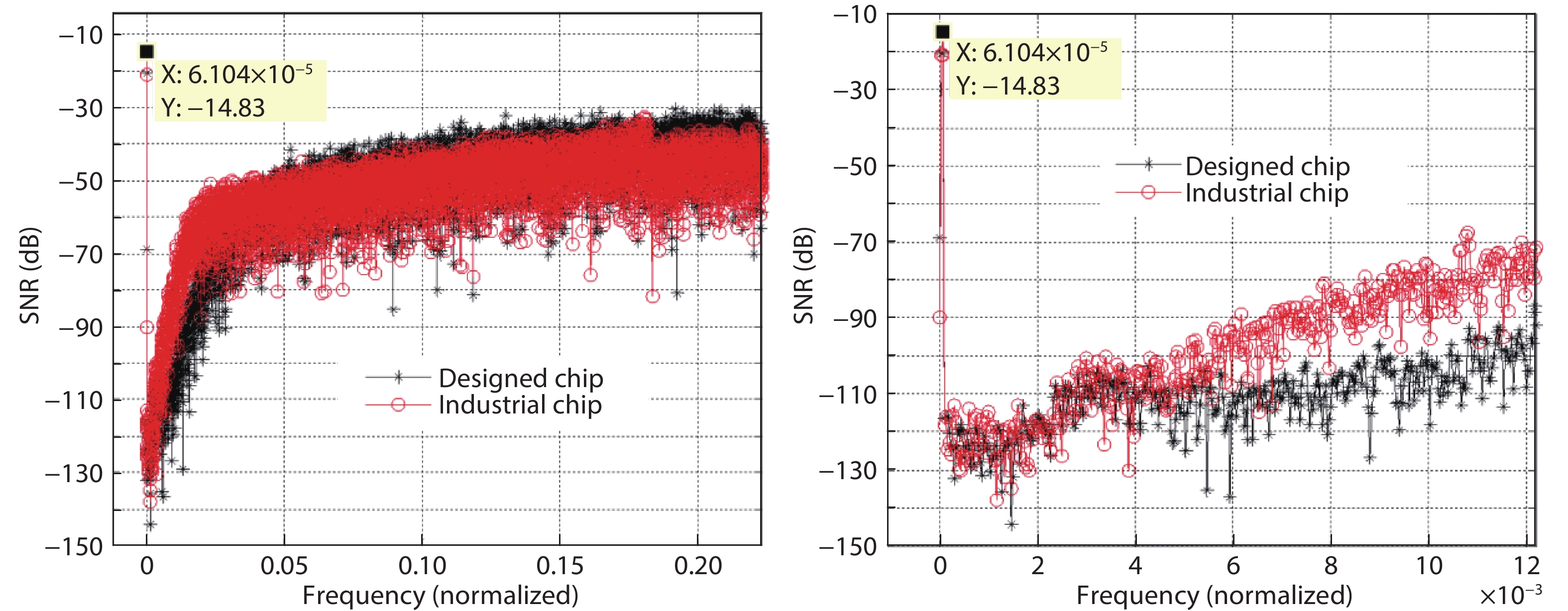
Oversampling sigma–delta (Σ–Δ) analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) are currently one of the most widely used architectures for high-resolution ADCs. The rapid development of integrated circuit manufacturing processes has allowed the realization of a high resolution in exchange for speed. Structurally, the Σ–Δ ADC is divided into two parts: a front-end analog modulator and a back-end digital filter. The performance of the front-end analog modulator has a marked influence on the entire Σ–Δ ADC system. In this paper, a 4-order single-loop switched-capacitor modulator with a CIFB (cascade-of-integrators feed-back) structure is proposed. Based on the chosen modulator architecture, the ASIC circuit is implemented using a chartered 0.35 μm CMOS process with a chip area of 1.72 × 0.75 mm2. The chip operates with a 3.3-V power supply and a power dissipation of 22 mW. According to the results, the performance of the designed modulator has been improved compared with a mature industrial chip and the effective number of bits (ENOB) was almost 18-bit. -
References
[1] Inose H, Inose H, Yasuda Y, et al. A telemetering system by code modulation — Δ–Σ modulation. IRE Trans Space Electron Telemetry, 1962, 8, 204 doi: 10.1109/IRET-SET.1962.5008839[2] Ritchie G R, Candy J, Ninke W. Interpolative digital to analog converters. IEEE Trans Commun, 1974, 22, 1797 doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1974.1092117[3] Candy J C. A use of limit cycle oscillations to obtain robust analog-to-digital converters. IEEE Trans Commun, 1974, 22(3), 298 doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1974.1092194[4] Candy J C, Wooley B, Benjamin O. A voiceband codec with digital filtering. IEEE Trans Commun, 1981, 29(6), 815 doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1981.1095061[5] Candy J C, Benjamin O J. The structure of quantization noise from sigma-delta modulation. IEEE Trans Commun, 1981, 29(9), 1316 doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1981.1095151[6] Candy J C. A use of double integration in sigma-delta modulations. IEEE Trans Commun, 1985, 33(3), 249 doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1985.1096276[7] Candy J C, Huynh A. Double Interpolation for digital-to-analog conversion. IEEE Trans Commun, 1986, 34(1), 77 doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1986.1096428[8] Hayashi T, Inabe Y, Uchimura K, et al. A multistage delta-sigma modulator without double integration loop. ISSCC Digest of Technical Papers, 1986, 182[9] Chen J Q, Ren J Y, Xun J, et al. An 80 dB dynamic range modulator for a GSM system. Chin J Semicond, 2007, 28(2), 294[10] Cao Y, Ren T L, Hong Z L, et al. A 16 bit 96 kHz chopper-stabilized sigma-delta ADC. Chin J Semicond, 2007, 28(8), 1204[11] Yuan J, Zhang Z F, Wu J, et al. Continuous time sigma delta ADC design and non-idealities analysis. J Semicond, 2011, 32(12), 125007 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/12/125007[12] Li R, Li J, Yi T, et al. A 18-mW, 20-MHz bandwidth, 12-bit continuous-time modulator using a power-efficient multi-stage amplifier. J Semicond, 2012, 33(1), 015007 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/33/1/015007[13] Caldwell T C, Johns D A. An 8-th order MASH delta-sigma with an OSR of 3. ESSCIRC, 2009, 476[14] Chiang J S, Chen H L, Chou P C. A 2.5-V 14-bit MASH sigma-delta modulator for ADSL. IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Advanced System Integrated Circuits, 2004, 24[15] Yao L, Steyaert M, Sansen W M. Low-power low-voltage sigma-delta modulators in nanometer CMOS. Springer Science & Business Media, 2006[16] Chao K C, Nadeem S, Lee W L, et al. A higher order topology for interpolative modulators for oversampling A/D converters. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst, 1990, 37(3), 309 doi: 10.1109/31.52724[17] Cao G. Study and ASIC implementation of high-resolution sigma-delta modulator. PhD Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, 2012[18] Wang F, Harjani R. Power analysis and optimal design of opamps for oversampled converters. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II, 1999, 46, 359 doi: 10.1109/82.755407[19] Medeiro F, Pérez-Verdú B, de la Rosa J M, et al. Fourth-order cascade SC sigma delta modulator: a comparative study. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 1998, 45(10), 1041 doi: 10.1109/81.728858[20] Ericson M N. High-temperature, high-resolution A/D conversion using 2nd and 4th-order sigma delta modulation in 3.3 V 0.5 µm SOS-CMOS. PhD Thesis, University of Tennessee, 2002[21] Geets Y, Steyaert M, Sansen W. A 2.5 M sample/s multi-bit sigma delta CMOS ADC with 95 dB SN. Digest of Technical Papers, Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2000, 336[22] Balmelli P, Huang Q. A 25 MS/s 14 b 200 mW Σ∆ modulator in 0.18 µm cmos. ISSCC Dig Tech Papers, 2005, 74[23] Brigati S, Francesconi F, Malcovati P, et al. A Fourth-order singla-bit switched capacitor sigma delta modulator for distributed sensor applications. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas, 2004, 53(2), 266 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2003.822480[24] Gerosa A, Neviani A. A 1.8 µW sigma delta modulator for 8-bit digitization of cardiac signals in implantable pacemakers operating down to 1.8 V. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II, 2005, 52(2), 71 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2004.840480[25] Yao L, Steyaert M, Sansen W. A 1-V, 1 MS/s, 88-dB sigma delta modulator in 0.13-µm digital CMOS technology. Symposium on VLSI Circuits Digest of Technical, 2005, 180[26] Chen L. High precision Σ∆ ADC. PhD Thesis, Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2006 -
Proportional views






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: