| Citation: |
Yuhua Li, Xiang Wang, Roy Davidson, Brent E. Little, Sai Tak Chu. Four-wave mixing in silicon-nanocrystal embedded high-index doped silica micro-ring resonator[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2021, 42(4): 042302. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/4/042302
****
Y H Li, X Wang, R Davidson, Brent E. Little, S T Chu, Four-wave mixing in silicon-nanocrystal embedded high-index doped silica micro-ring resonator[J]. J. Semicond., 2021, 42(4): 042302. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/4/042302.
|
Four-wave mixing in silicon-nanocrystal embedded high-index doped silica micro-ring resonator
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/4/042302
More Information
-
Abstract
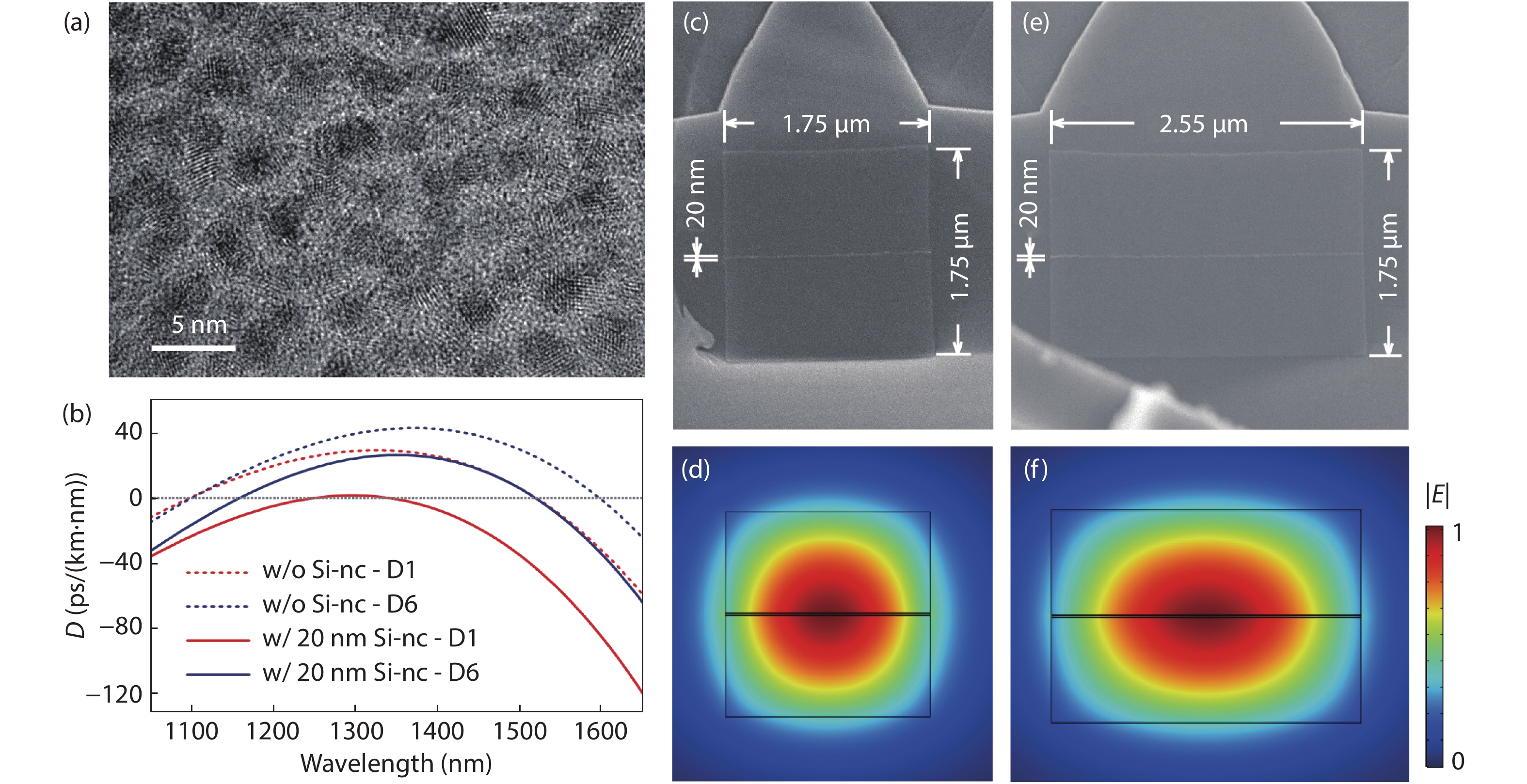
A nonlinear integrated optical platform that allows the fabrication of waveguide circuits with different material composition, and at small dimensions, offers advantages in terms of field enhancement and increased interaction length, thereby facilitating the observation of nonlinear optics effects at a much lower power level. To enhance the nonlinearity of the conventional waveguide structure, in this work, we propose and demonstrate a microstructured waveguide where silicon rich layer is embedded in the core of the conventional waveguide in order to increase its nonlinearity. By embedding a 20 nm thin film of silicon nanocrystal (Si-nc), we achieve a twofold increase of the nonlinear parameter, γ. The linear relationship between the four-wave mixing conversion efficiency and pump power reveals the negligible nonlinear absorption and small dispersion in the micro-ring resonators. This simple approach of embedding an ultra-thin Si-nc layer into conventional high-index doped silica dramatically increases its nonlinear performance, and could potentially find applications in all-optical processing functions. -
References
[1] Lin S Y, Schonbrun E, Crozier K. Optical manipulation with planar silicon microring resonators. Nano Lett, 2010, 10, 2408 doi: 10.1021/nl100501d[2] Lin Q, Zhang J, Piredda G, et al. Dispersion of silicon nonlinearities in the near infrared region. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 91, 021111 doi: 10.1063/1.2750523[3] Shoji Y, Ogasawara T, Kamei T, et al. Ultrafast nonlinear effects in hydrogenated amorphous silicon wire waveguide. Opt Express, 2010, 18, 5668 doi: 10.1364/OE.18.005668[4] Ikeda K, Saperstein R E, Alic N, et al. Thermal and Kerr nonlinear properties of plasma-deposited silicon nitride/silicon dioxide waveguides. Opt Express, 2008, 16, 12987 doi: 10.1364/OE.16.012987[5] Guo H R, Herkommer C, Billat A, et al. Mid-infrared frequency comb via coherent dispersive wave generation in silicon nitride nanophotonic waveguides. Nat Photonics, 2018, 12, 330 doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0144-1[6] Brasch V, Geiselmann M, Herr T, et al. Photonic chip–based optical frequency comb using soliton Cherenkov radiation. Science, 2016, 351, 357 doi: 10.1126/science.aad4811[7] Karpov M, Pfeiffer M H, Guo H R, et al. Dynamics of soliton crystals in optical microresonators. Nat Phys, 2019, 15, 1071 doi: 10.1038/s41567-019-0635-0[8] Bao H L, Cooper A, Rowley M, et al. Laser cavity-soliton microcombs. Nat Photonics, 2019, 13, 384 doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0379-5[9] Corcoran B, Tan M X, Xu X Y, et al. Ultra-dense optical data transmission over standard fibre with a single chip source. Nat Commun, 2020, 11, 2568 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16265-x[10] Singh N, Raval M, Ruocco A, et al. Broadband 200-nm second-harmonic generation in silicon in the telecom band. Light Sci Appl, 2020, 9, 17 doi: 10.1038/s41377-020-0254-7[11] Wang F X, Wang W Q, Niu R, et al. Quantum key distribution with on-chip dissipative kerr soliton. Laser Photonics Rev, 2020, 14, 1900190 doi: 10.1002/lpor.201900190[12] Lin H T, Song Y, Huang Y Z, et al. Chalcogenide glass-on-graphene photonics. Nat Photonics, 2017, 11(12), 798 doi: 10.1038/s41566-017-0033-z[13] Zhao Y, Lu J, Huo Y Y, et al. Enhanced third harmonic generation from graphene embedded in dielectric resonant waveguide gratings. Opt Commun, 2019, 447, 30 doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.04.087[14] Moss D J, Morandotti R, Gaeta A L, et al. New CMOS-compatible platforms based on silicon nitride and Hydex for nonlinear optics. Nat Photonics, 2013, 7, 597 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.183[15] Ferrera M, Razzari L, Duchesne D, et al. Low-power continuous-wave nonlinear optics in doped silica glass integrated waveguide structures. Nat Photonics, 2008, 2, 737 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2008.228[16] Ferrera M, Park Y, Razzari L, et al. On-chip CMOS-compatible all-optical integrator. Nat Commun, 2010, 1, 29 doi: 10.1038/ncomms1028[17] Razzari L, Duchesne D, Ferrera M, et al. CMOS-compatible integrated optical hyper-parametric oscillator. Nat Photonics, 2010, 4, 41 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2009.236[18] Pasquazi A, Peccianti M, Park Y, et al. Sub-picosecond phase-sensitive optical pulse characterization on a chip. Nat Photonics, 2011, 5, 618 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2011.199[19] Wei P, Wang S, Little B E, et al. Analysis of a Si-nanocrystal strip-loaded waveguide for nonlinear applications. International Conference on Photonics in Switching (PS), 2016[20] Martínez A, Hernández S, Lebour Y, et al. Two-photon absorption in Si-nanocrystals deposited by plasma-enhanced chemical-vapor deposition. Physica E, 2009, 41, 1002 doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2008.08.023[21] Little B. A VLSI photonics platform. Optical Fiber Communications Conference, 2003, 444[22] Wu J, Yang Y, Qu Y, et al. 2D layered graphene oxide films integrated with micro-ring resonators for enhanced nonlinear optics. Small, 2020, 16, 1906563 doi: 10.1002/smll.201906563[23] Sanchis P, Blasco J, Martinez A, et al. Design of silicon-based slot waveguide configurations for optimum nonlinear performance. J Lightwave Technol, 2007, 25, 1298 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2007.893909[24] Spano R, Daldosso N, Cazzanelli M, et al. Bound electronic and free carrier nonlinearities in Silicon nanocrystals at 1550 nm. Opt Express, 2009, 17, 3941 doi: 10.1364/OE.17.003941[25] Li Y H, Zhu K, Kang Z, et al. CMOS-compatible high-index doped silica waveguide with an embedded silicon-nanocrystal strip for all-optical analog-to-digital conversion. Photon Res, 2019, 7, 1200 doi: 10.1364/PRJ.7.001200[26] Rabus D G, Sada C. Sensors. Integrated Ring Resonators. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020, 293[27] Little B E, Chu S T, Haus H A, et al. Microring resonator channel dropping filters. J Lightwave Technol, 1997, 15, 998 doi: 10.1109/50.588673[28] Absil P P, Hryniewicz J V, Little B E, et al. Wavelength conversion in GaAs micro-ring resonators. Opt Lett, 2000, 25, 554 doi: 10.1364/OL.25.000554[29] Little B E, Chu S T, Absil P P, et al. Very high-order microring resonator filters for WDM applications. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2004, 16, 2263 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2004.834525[30] Ferrera M, Duchesne D, Razzari L, et al. Low power four wave mixing in an integrated, micro-ring resonator with Q = 1.2 million. Opt Express, 2009, 17, 14098 doi: 10.1364/OE.17.014098 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: