| Citation: |
Xuyang Wang, He Jia, Junhui Li, Yumei Guo, Yu Liu. Optical transmitter module with hybrid integration of DFB laser diode and proton-exchanged LiNbO3 modulator chip[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2022, 43(6): 062303. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/6/062303
****
X Y Wang, H Jia, J H Li, Y M Guo, Y Liu. Optical transmitter module with hybrid integration of DFB laser diode and proton-exchanged LiNbO3 modulator chip[J]. J. Semicond, 2022, 43(6): 062303. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/6/062303
|
Optical transmitter module with hybrid integration of DFB laser diode and proton-exchanged LiNbO3 modulator chip
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/6/062303
More Information
-
Abstract
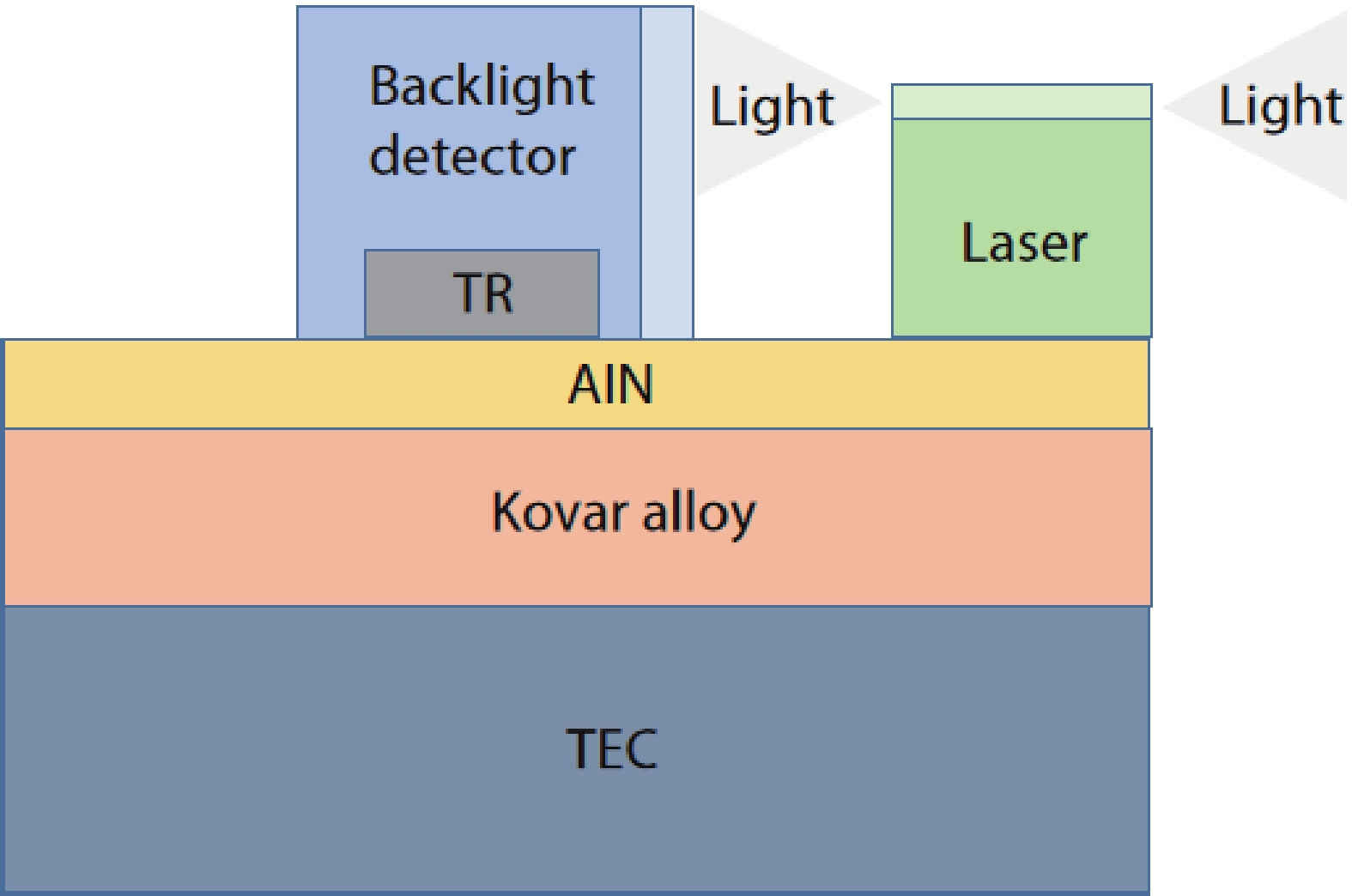
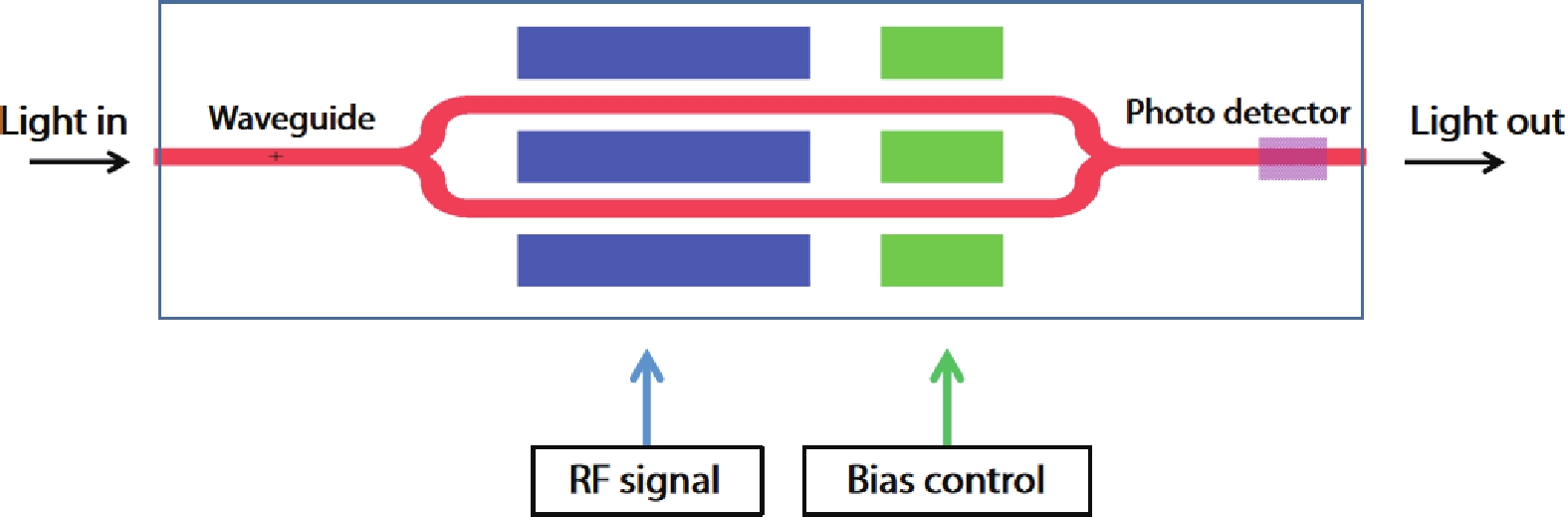
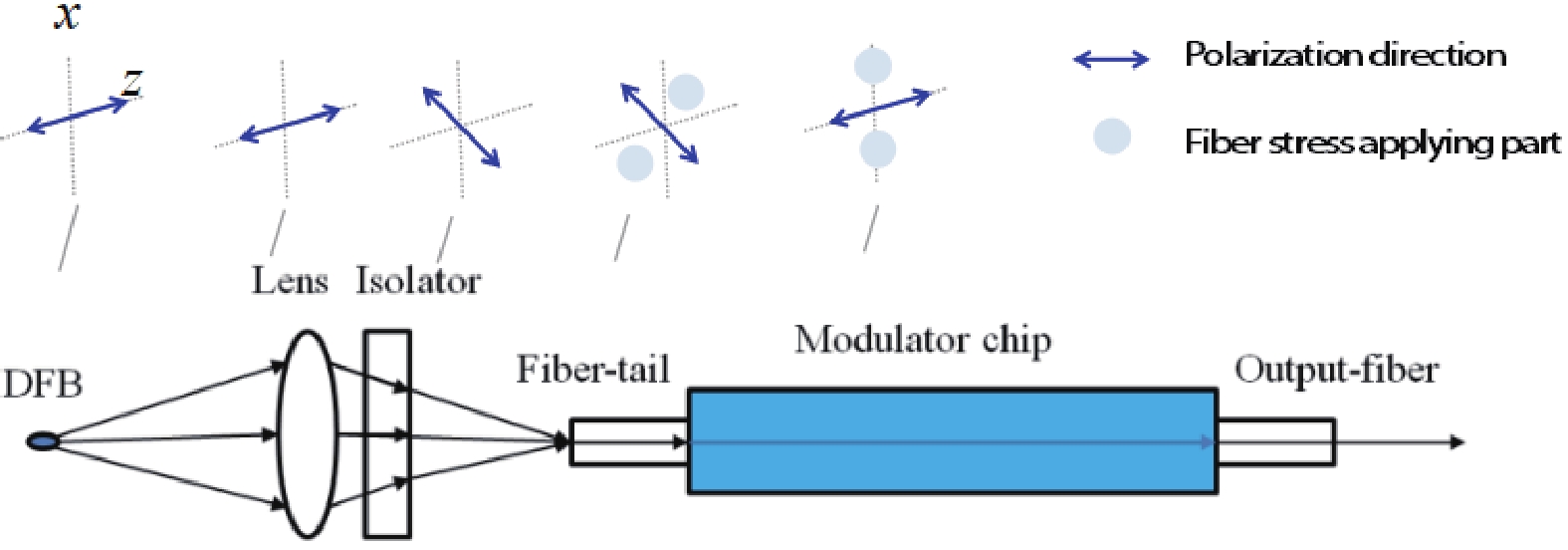
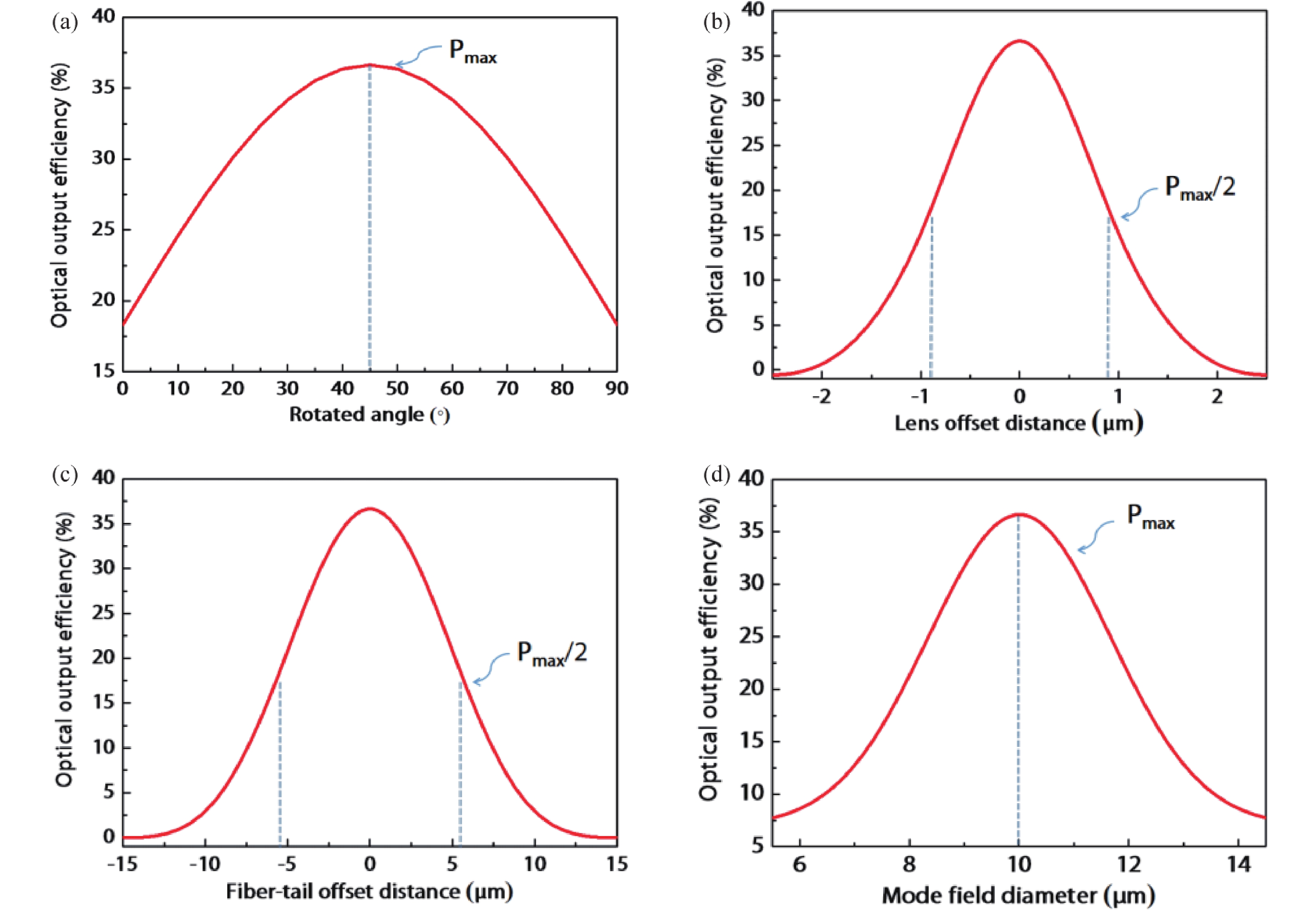
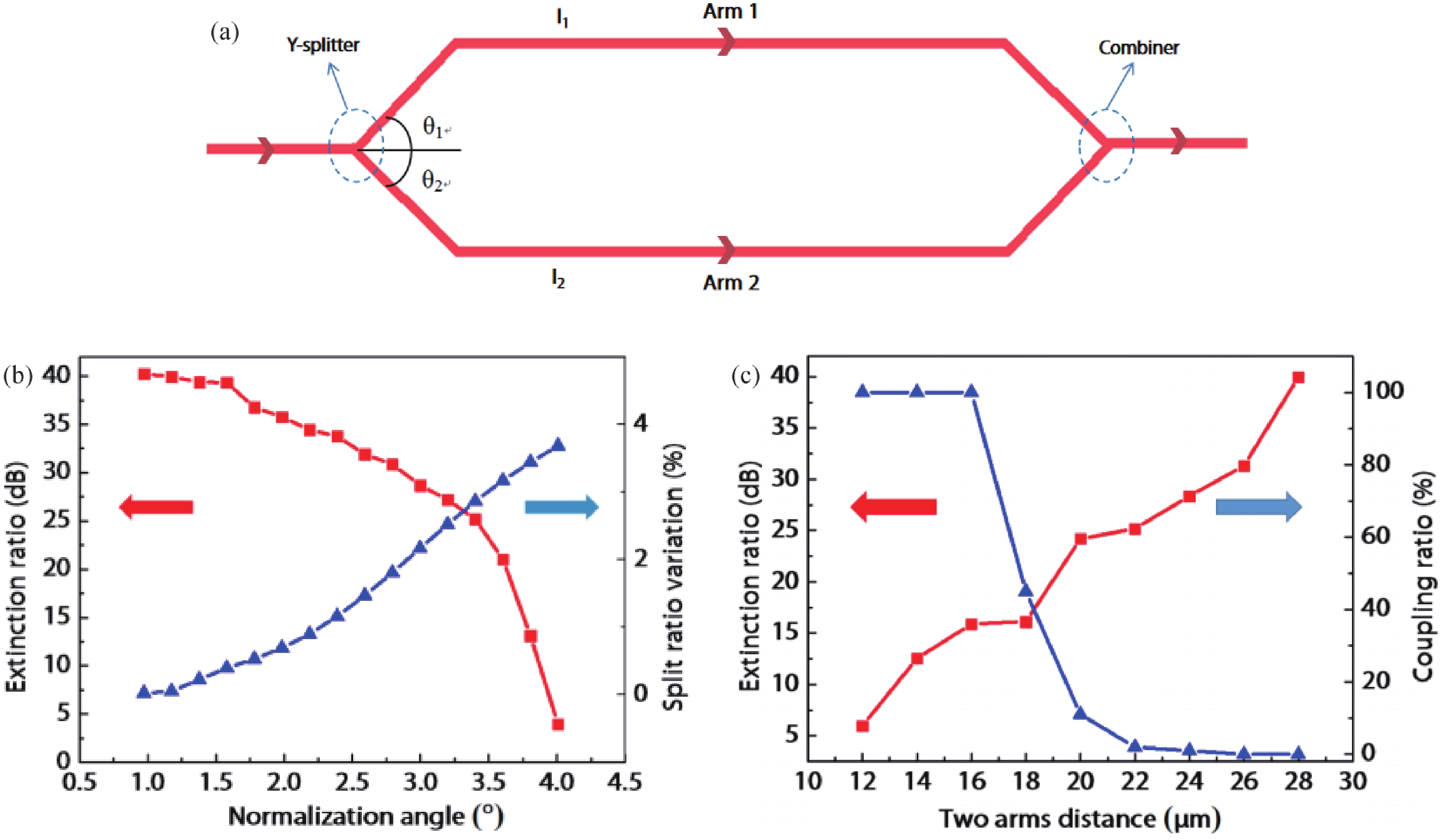
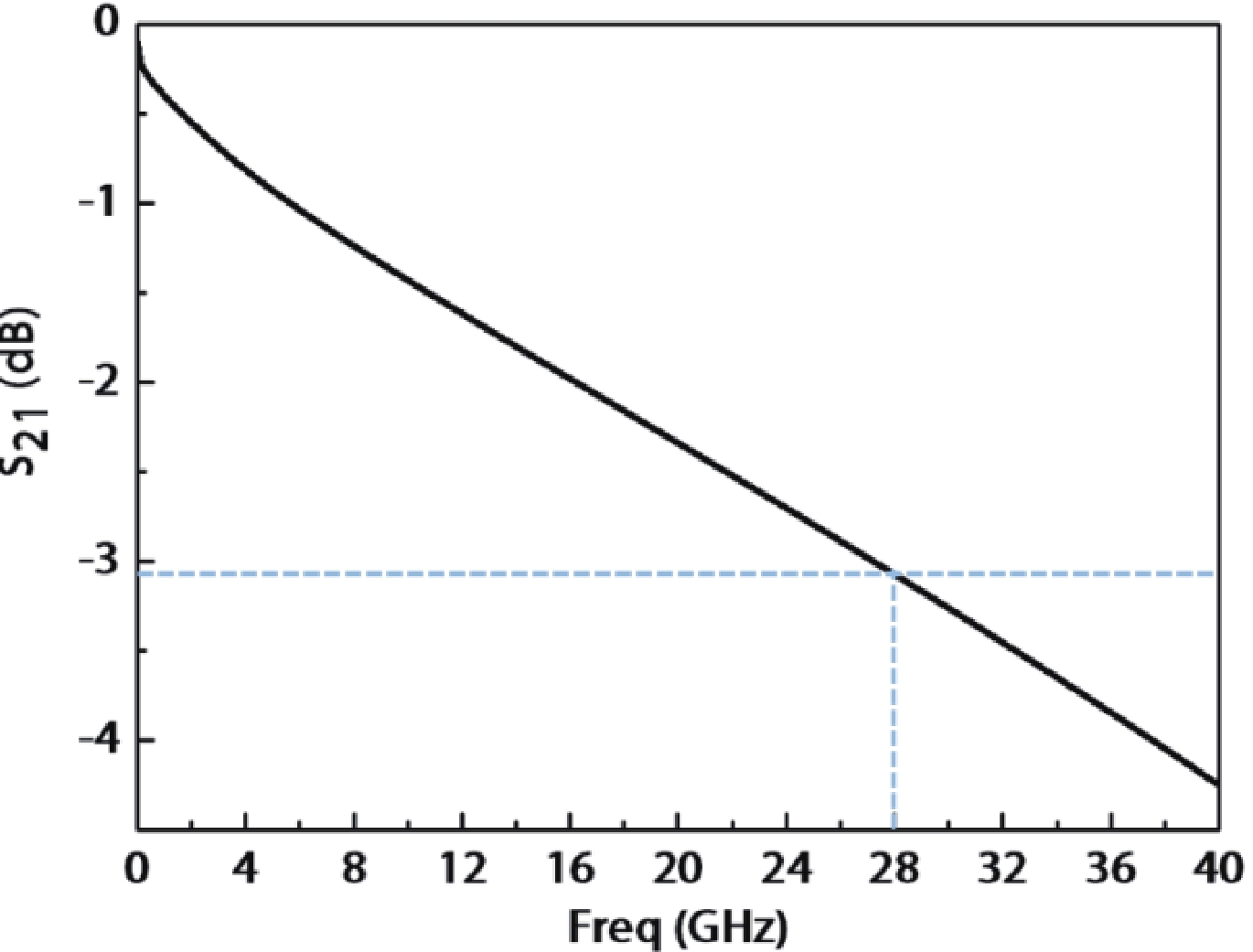
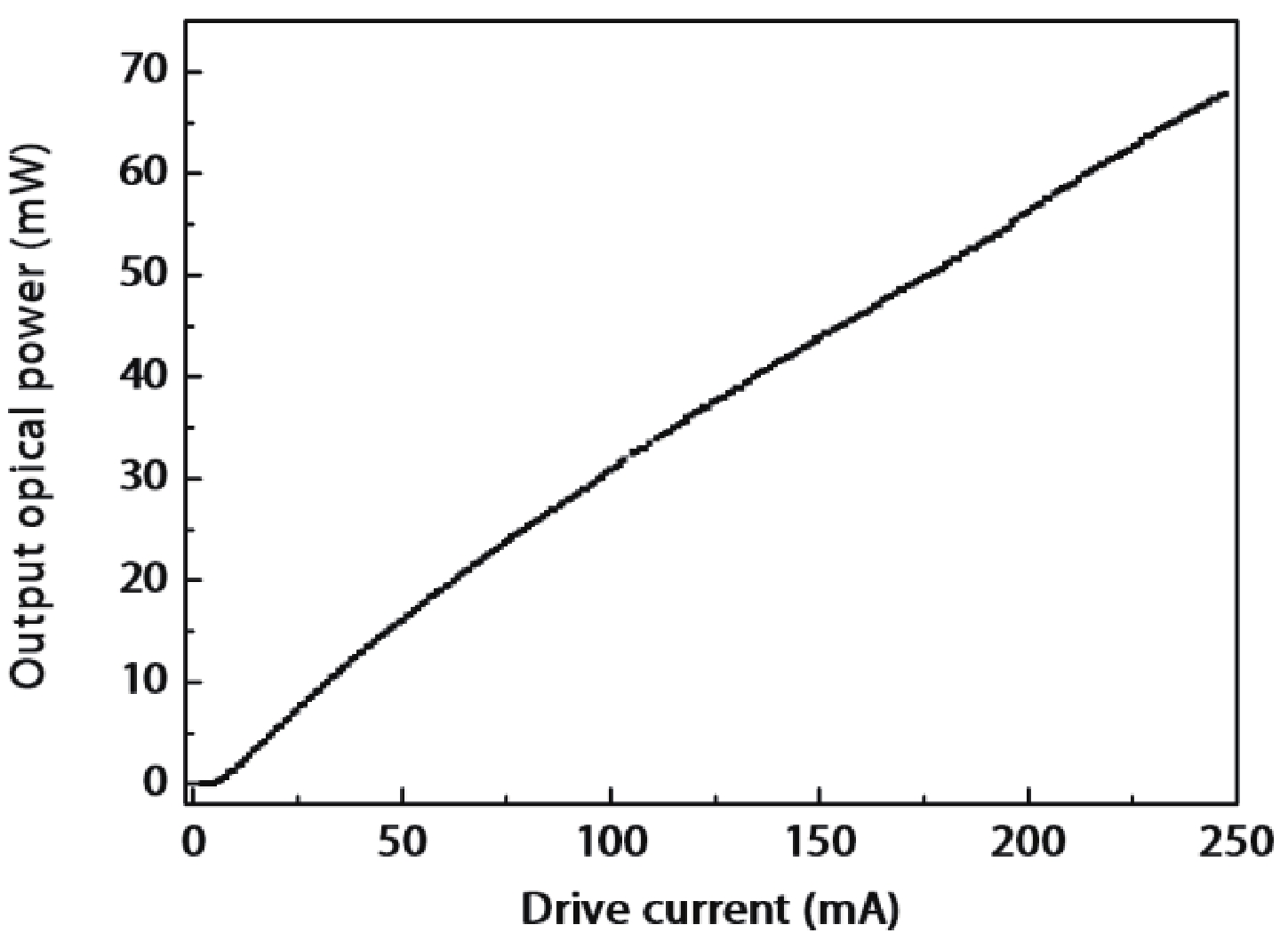
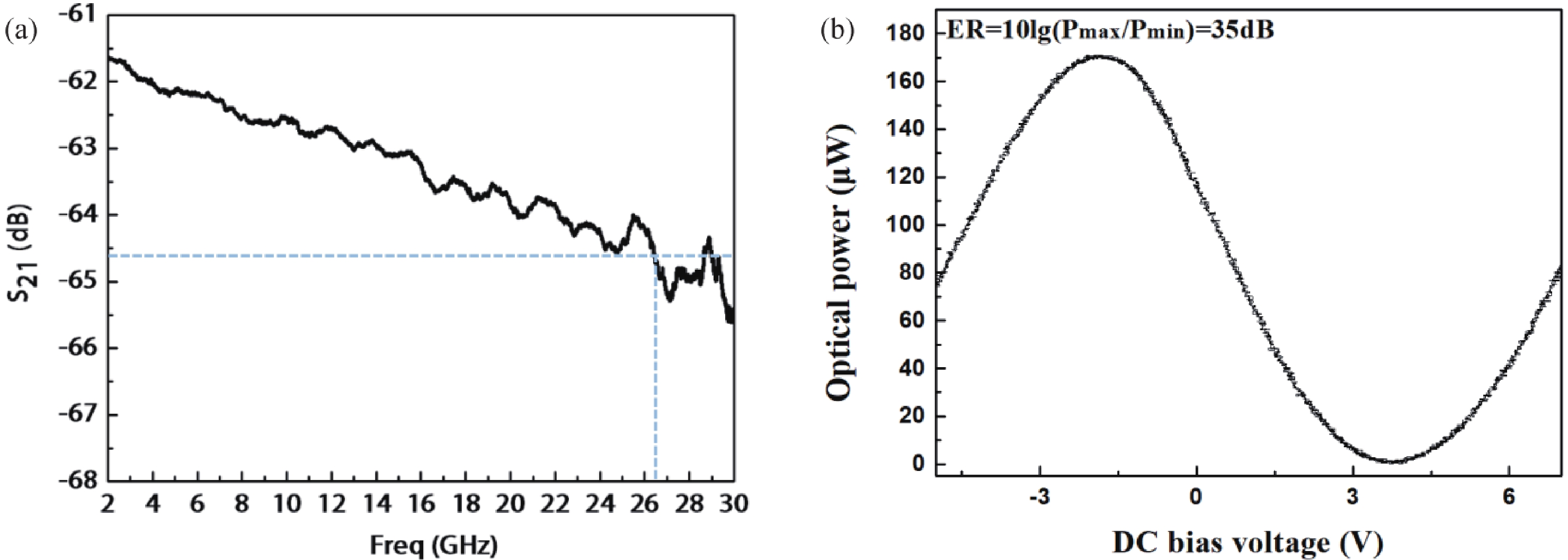
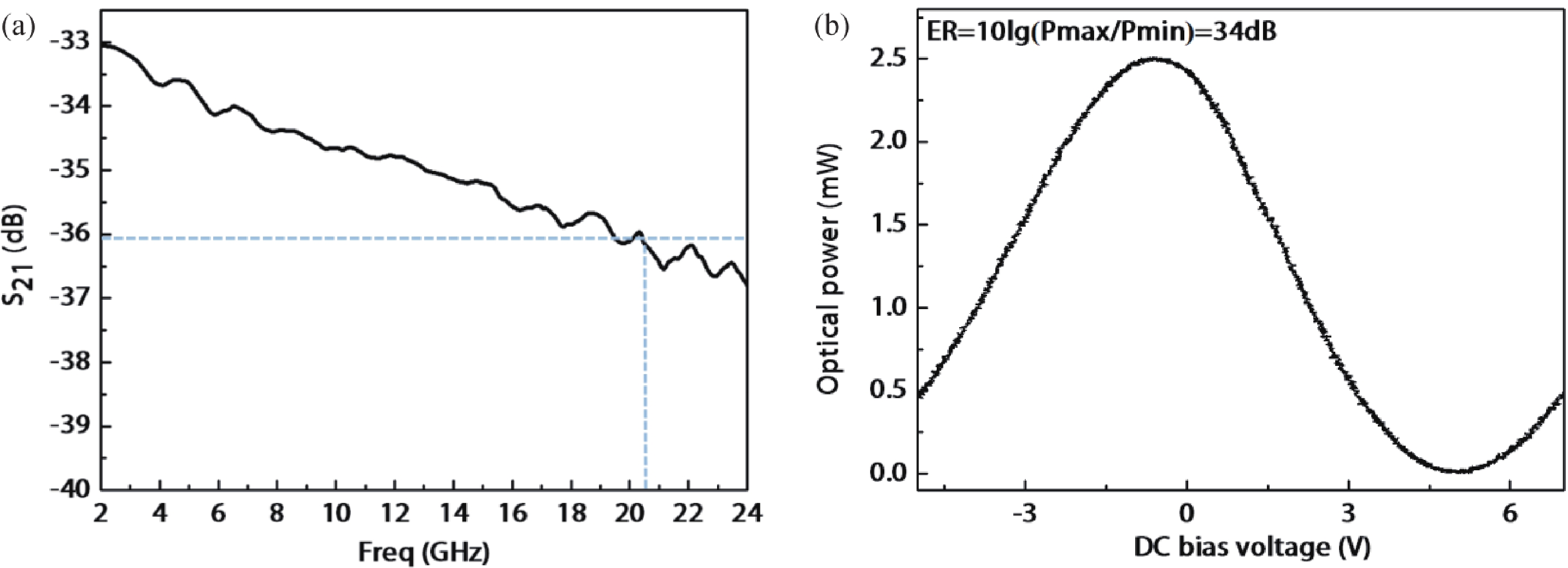
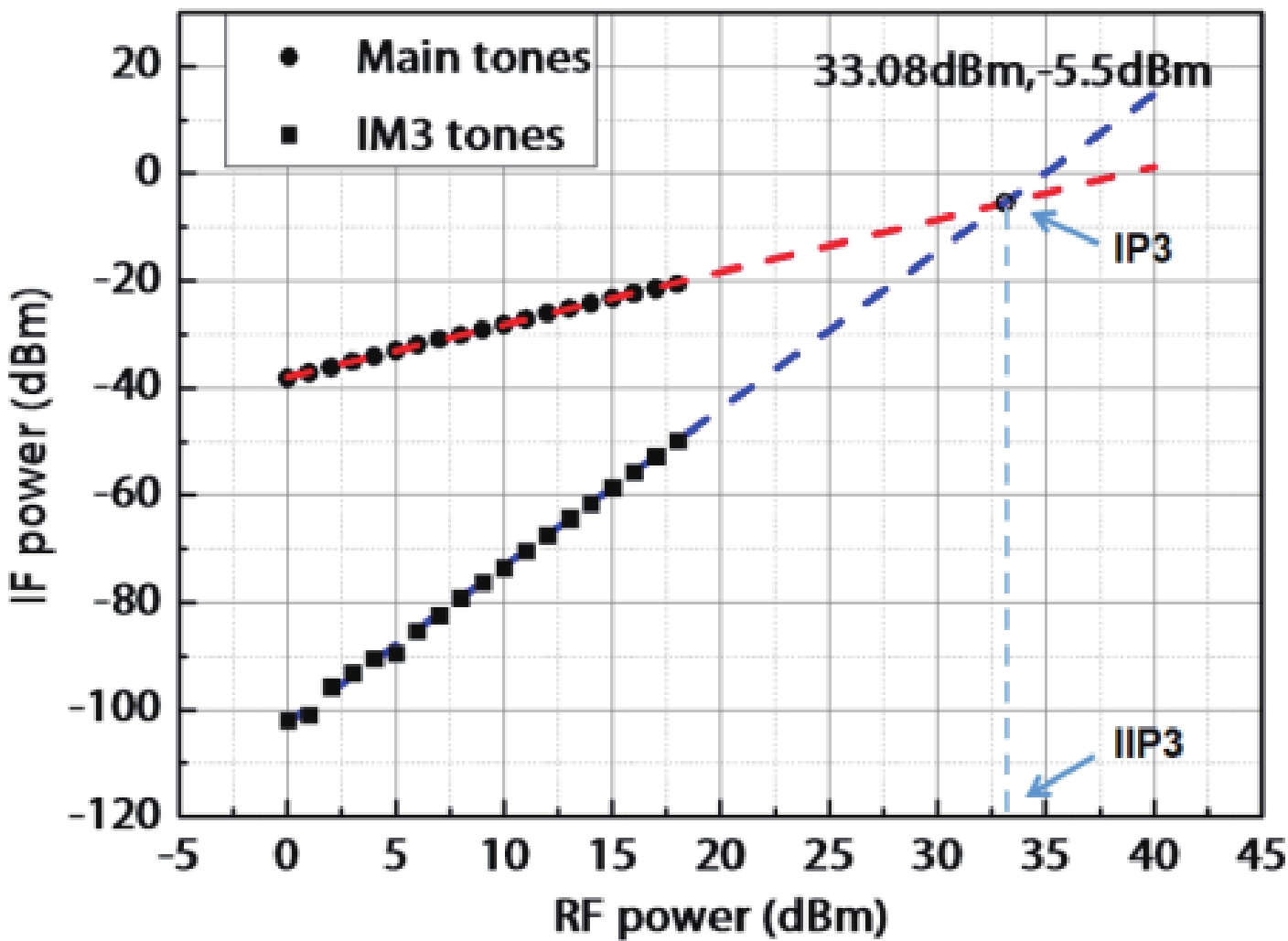
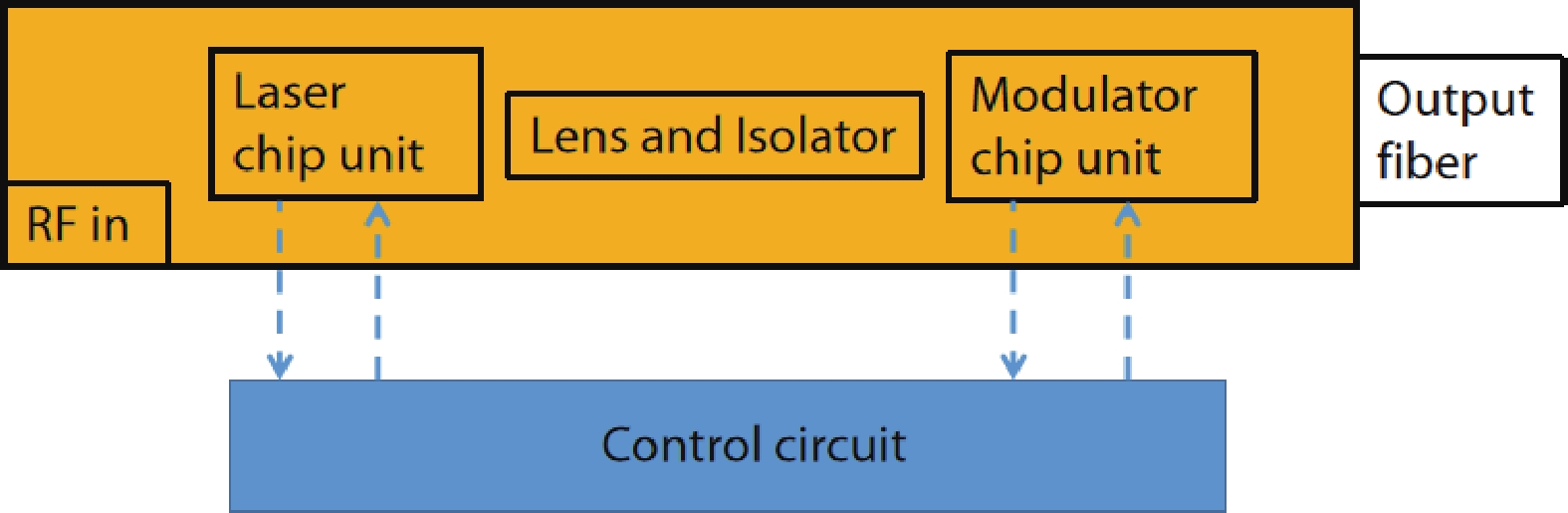
In this work, a hybrid integrated optical transmitter module was designed and fabricated. A proton-exchanged Mach–Zehnder lithium niobate (LiNbO3) modulator chip was chosen to enhance the output extinction ratio. A fiber was used to adjust the rotation of the polarization direction caused by the optical isolator. The whole optical path structure, including the laser chip, lens, fiber, and modulator chip, was simulated to achieve high optical output efficiency. After a series of process improvements, a module with an output extinction ratio of 34 dB and a bandwidth of 20.5 GHz (from 2 GHz) was obtained. The optical output efficiency of the whole module reached approximately 21%. The link performance of the module was also measured. -
References
[1] Li G L, Yu P K L. Optical intensity modulators for digital and analog applications. J Lightwave Technol, 2003, 21, 2010 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2003.815654[2] Dagli N. Wide-bandwidth lasers and modulators for RF photonics. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 1999, 47, 1151 doi: 10.1109/22.775453[3] Huang J N, Li C, Lu R G, et al. Beyond the 100 Gbaud directly modulated laser for short reach applications. J Semicond, 2021, 42, 041306 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/4/041306[4] Liu D P, Tang J, Meng Y, et al. Ultra-low Vpp and high-modulation-depth InP-based electro–optic microring modulator. J Semicond, 2021, 42, 082301 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/8/082301[5] Wang X X, Weigel P O, Zhao J, et al. Achieving beyond-100-GHz large-signal modulation bandwidth in hybrid silicon photonics Mach Zehnder modulators using thin film lithium niobate. APL Photonics, 2019, 4, 096101 doi: 10.1063/1.5115243[6] Wooten E L, Kissa K M, Yi-Yan A, et al. A review of lithium niobate modulators for fiber-optic communications systems. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron, 2000, 6, 69 doi: 10.1109/2944.826874[7] Marpaung D, Roeloffzen C, Heideman R, et al. Integrated microwave photonics. Laser Photonics Rev, 2013, 7, 506 doi: 10.1002/lpor.201200032[8] Lu Z Y, B Lu, Luo Y, et al. Design and research on small hybrid integrated teansmitter module of semiconductor and DFB laser. J Opto Laser, 2021, 32, 181[9] Li Y, Lan T, Li J, et al. High-efficiency edge-coupling based on lithium niobate on an insulator wire waveguide. Appl Opt, 2020, 59, 6694 doi: 10.1364/AO.395897[10] Li L Y, Ma Y X, Zhang Y S, et al. Multi-tip edge coupler for integration of a distributed feedback semiconductor laser with a thin-film lithium niobate modulator. Appl Opt, 2021, 60, 4814 doi: 10.1364/AO.425773[11] Qiu M. Vertically coupled photonic crystal optical filters. Opt Lett, 2005, 30, 1476 doi: 10.1364/OL.30.001476[12] Chakravarty S, Teng M, Safian R, et al. Hybrid material integration in silicon photonic integrated circuits. J Semicond, 2021, 42, 041303 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/4/041303[13] Matsumoto K, Kanaya Y, Kishikawa J, et al. Characteristics of film InP layer and Si substrate bonded interface bonded by wafer direct bonding. 2015 11th Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Pacific Rim, 2015, 7375926 doi: 10.1109/CLEOPR.2015.7375926[14] Olmstead M A, Ohuchi F S. Group III selenides: Controlling dimensionality, structure, and properties through defects and heteroepitaxial growth. J Vac Sci Technol A, 2021, 39, 020801 doi: 10.1116/6.0000598[15] Okamoto K. Fundamentals of optical waveguides. 2nd ed. Elsevier Inc. , 2006[16] Zhang J, Gao C X, Xue M Y, et al. Research on frequency modulation character of the current driven DFB semiconductor laser. Mod Phys Lett B, 2019, 33, 1850422 doi: 10.1142/S0217984918504225[17] Alferness R C. Waveguide electrooptic modulators. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 1982, 30, 1121 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.1982.1131213[18] Tan J, Chen X, Liu X, et al. Research on a bias control technique for quadrature-point locking in LiNbO3 MZ modulators. Semicond Optoe, 2018, 39(4), 575[19] Walton J R, Smee E J, Malladi D P. Pilot transmission schemes for wireless multi-carrier communication systems. USA Patent, US7280467, 2007[20] Wang L L, Kowalcyzk T. A versatile bias control technique for any-point locking in lithium niobate Mach–Zehnder modulators. J Lightwave Technol, 2010, 28, 1703 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2010.2048553[21] Yang G, Sergienko A V, Ndao A. Tunable polarization mode conversion using thin-film lithium niobate ridge waveguide. Opt Express, 2021, 29, 18565 doi: 10.1364/OE.426672[22] Fukuma M, Noda J. Optical properties of titanium-diffused LiNbO3 strip waveguides and their coupling-to-a-fiber characteristics. Appl Opt, 1980, 19, 591 doi: 10.1364/AO.19.000591[23] Paz-Pujalt G R, Tuschel D D, Braunstein G, et al. Characterization of proton exchange lithium niobate waveguides. J Appl Phys, 1994, 76, 3981 doi: 10.1063/1.358495[24] Méndez A, de la Paliza G, García-Cabañes A, et al. Comparison of the electro-optic coefficient r33 in well-defined phases of proton exchanged LiNbO3 waveguides. Appl Phys B, 2001, 73, 485 doi: 10.1007/s003400100711 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: