| Citation: |
Yuchen Gao, Yu Ye. Interaction of moiré excitons with cavity photons in two-dimensional semiconductor hetero-bilayers[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2023, 44(1): 011903. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/1/011903
****
Y C Gao, Y Ye. Interaction of moiré excitons with cavity photons in two-dimensional semiconductor hetero-bilayers[J]. J. Semicond, 2023, 44(1): 011903. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/1/011903
|
Interaction of moiré excitons with cavity photons in two-dimensional semiconductor hetero-bilayers
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/1/011903
More Information
-
Abstract
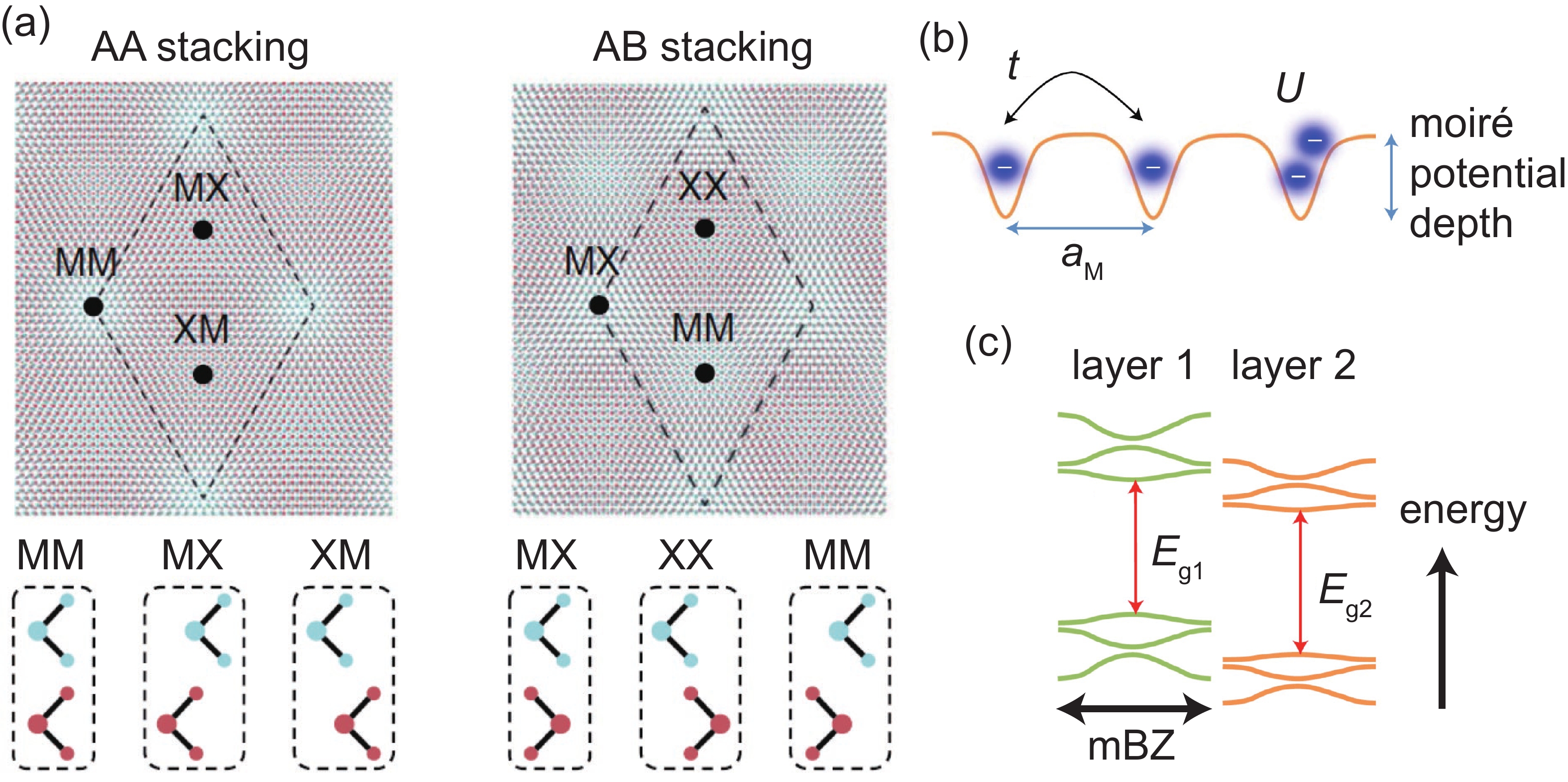
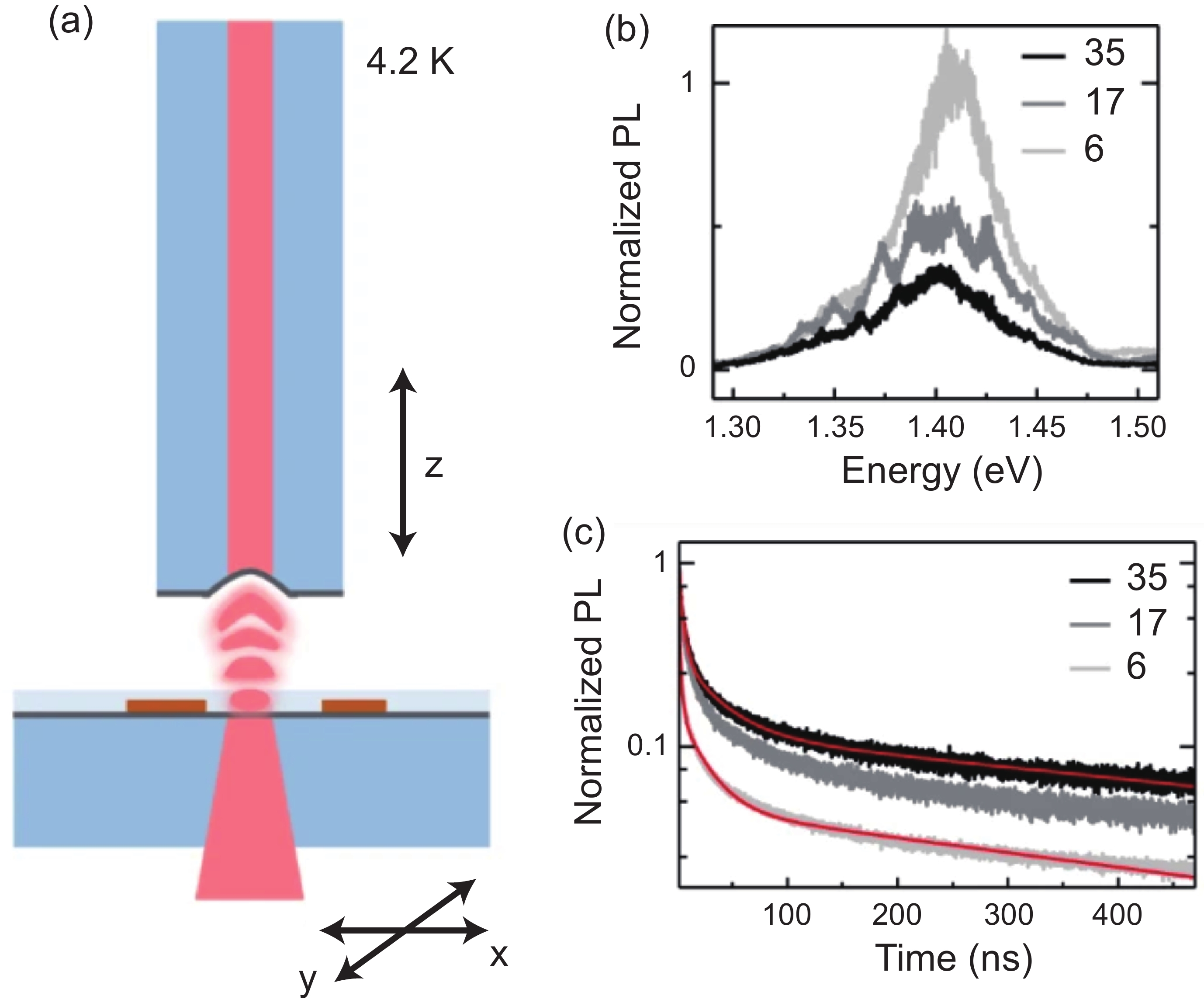
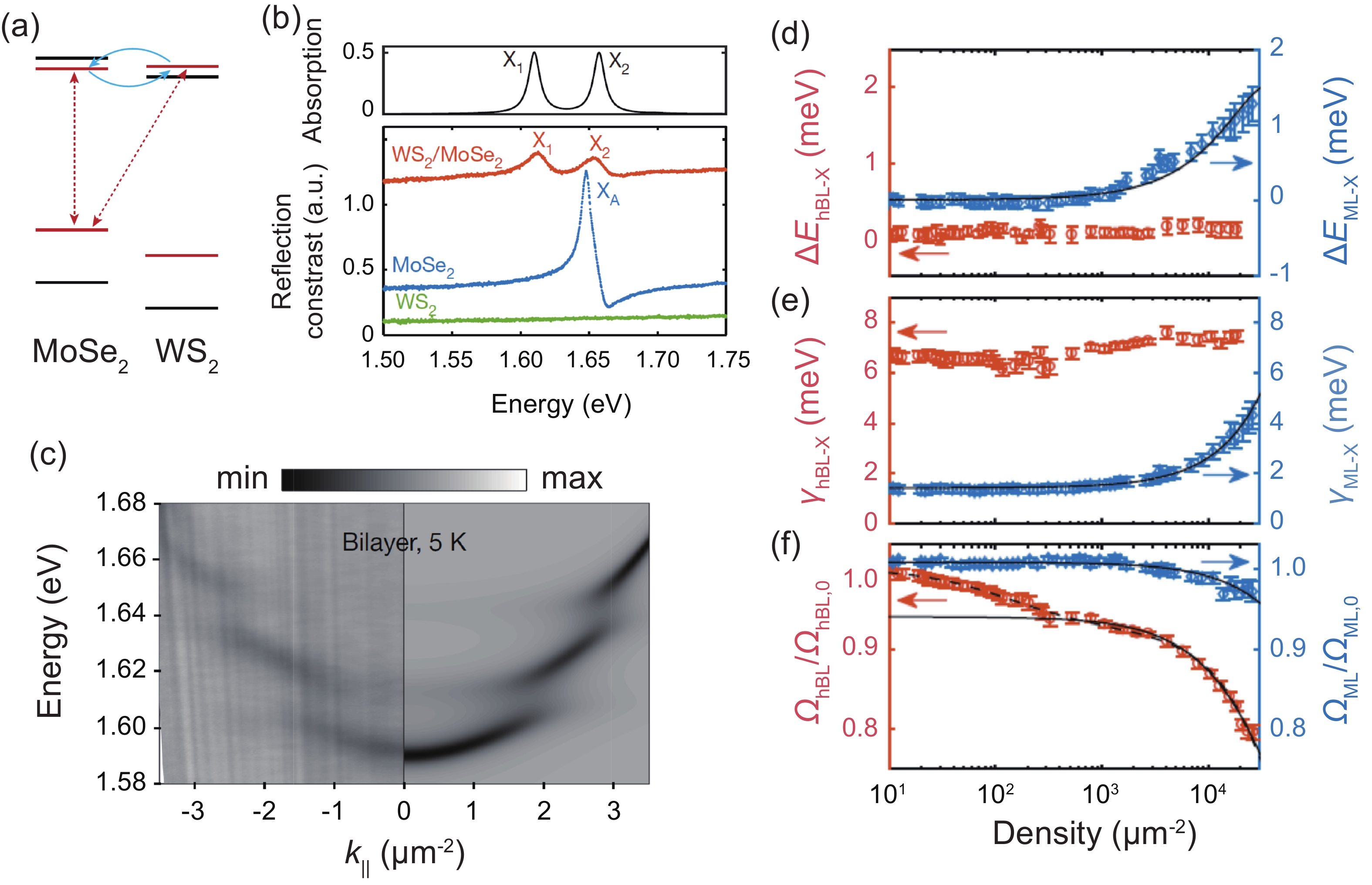
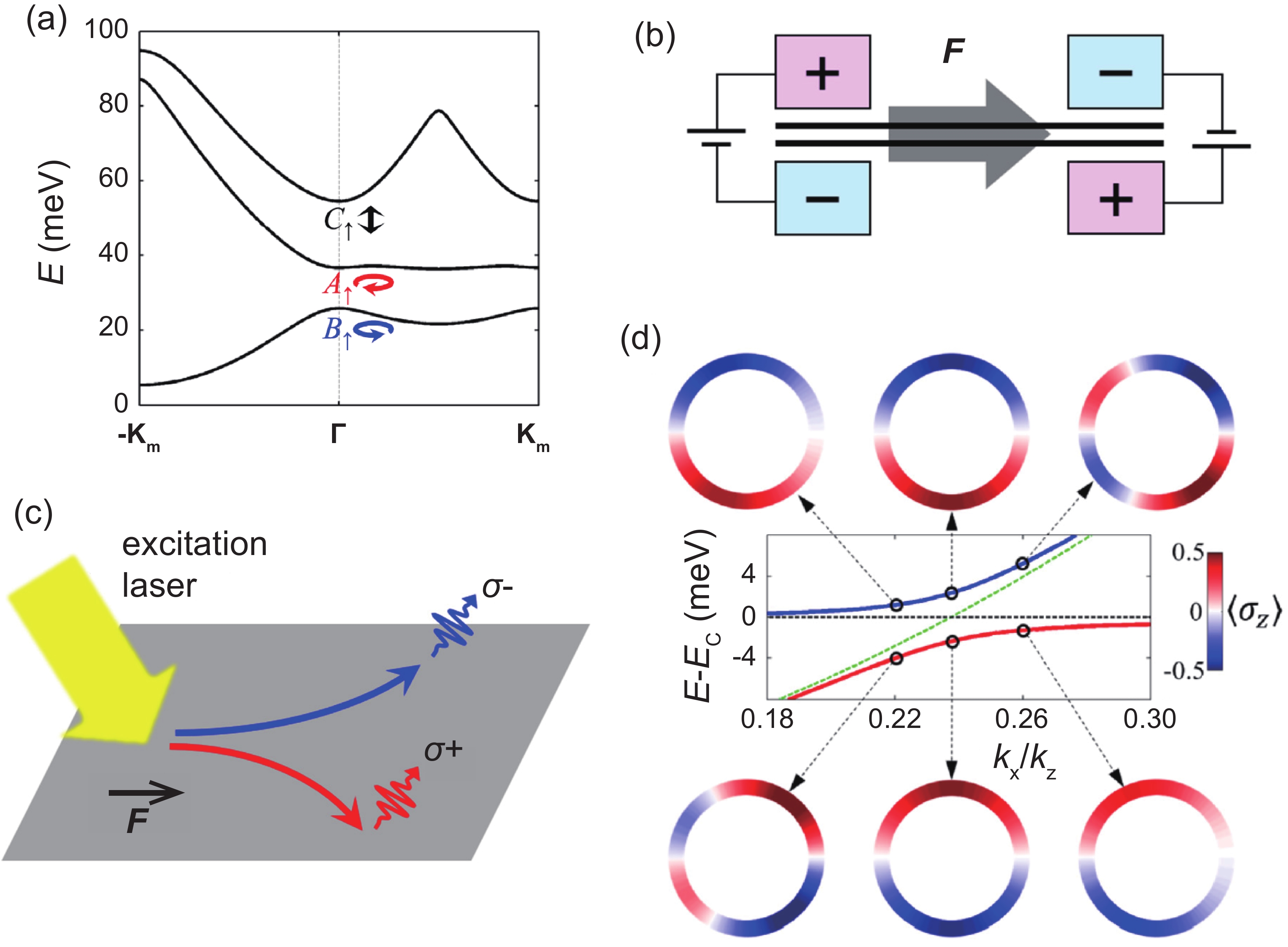
Moiré materials, composed of two single-layer two-dimensional semiconductors, are important because they are good platforms for studying strongly correlated physics. Among them, moiré materials based on transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) have been intensively studied. The hetero-bilayer can support moiré interlayer excitons if there is a small twist angle or small lattice constant difference between the TMDs in the hetero-bilayer and form a type-II band alignment. The coupling of moiré interlayer excitons to cavity modes can induce exotic phenomena. Here, we review recent advances in the coupling of moiré interlayer excitons to cavities, and comment on the current difficulties and possible future research directions in this field. -
References
[1] Tang Y, Li L, Li T, et al. Simulation of Hubbard model physicals in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattices. Nature, 2020, 579, 353 doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2085-3[2] Jinn C, Tao Z, Li T, et al. Stripe phases in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattices. Nat Mater, 2021, 20, 940 doi: 10.1038/s41563-021-00959-8[3] Kennes D M, Classen M, Xian L, et al. Moiré heterostructures as a condensed-matter quantum simulator. Nat Phys, 2021, 17, 155 doi: 10.1038/s41567-020-01154-3[4] Li T, Jiang S, Shen B, et al. Quantum anomalous Hall effect from intertwined moiré bands. Nature, 2021, 600, 641 doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04171-1[5] Iwasaki T, Endo K, Watanabe E, et al. Bubble-free transfer technique for high-quality graphene/hexagonal boron nitride van der Waals heterostructures. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2020, 12, 8533 doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b19191[6] Mak K F, Shan J. Semiconductor moiré materials. Nat Nanotechnol, 2022, 17, 686 doi: 10.1038/s41565-022-01165-6[7] Choi J, Hsu W T, Lu L S, et al. Moiré potential impedes interlayer exciton diffusion in van der Waals heterostructures. Sci Adv, 2020, 6, eaba8866 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba8866[8] Seyler K L, Rivera P, Yu H, et al. Signatures of moiré-trapped valley excitons in MoSe2/WSe2 heterobilayers. Nature, 2019, 567, 66 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0957-1[9] Padhi B, Chitra R, Phillips P W. Generalized Wigner crystallization in moiré materials. Phys Rev B, 2021, 103, 125146 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.103.125146[10] Regan E C, Wang D, Jin C, et al. Mott and generalized Wigner crystal states in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattices. Nature, 2020, 579, 359 doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2092-4[11] Yan T, Qiao X, Liu X, et al. Photoluminescence properties and exciton dynamics in monolayer WSe2. Appl Phys Lett, 2014, 105, 101901 doi: 10.1063/1.4895471[12] Rivera P, Schaibley J R, Jones A M, et al. Observation of long-lived interlayer excitons in monolayer MoSe2-WSe2 heterostructures. Nat Commun, 2015, 6, 6242 doi: 10.1038/ncomms7242[13] Gao S, Yang L, Spataru C D. Interlayer coupling and gate-tunable excitons in transition metal dichalcogenide heterostructures. Nano Lett, 2017, 17, 7809 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b04021[14] Li W, Lu X, Dubey S, et al. Dipolar interactions between localized interlayer excitons in van der Waals heterostructures. Nat Mater, 2020, 19, 624 doi: 10.1038/s41563-020-0661-4[15] Deng H, Haug H, Yamamoto Y. Exciton–polariton Bose-Einstein condensation. Rev Mod Phys, 2010, 82, 1489 doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.82.1489[16] Amo A, Lefrère J, Pigeon S, et al. Superfluidity of polaritons in semiconductor microcavities. Nat Phys, 2009, 5, 805 doi: 10.1038/nphys1364[17] Fraser M D, Höfling S, Yamamoto Y. Physics and applications of exciton–polariton lasers. Nat Mater, 2016, 15, 1049 doi: 10.1038/nmat4762[18] Latini S, Ronca E, Giovannini U D, et al. Cavity control of excitons in two-dimensional materials. Nano Lett, 2019, 19, 3473 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b00183[19] Förg M, Colombier L, Patel R K, et al. Cavity-control of interlayer excitons in van der Waals heterostructures. Nat Commun, 2019, 10, 3697 doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11620-z[20] Zhang L, Wu F, Hou S, et al. Van der Waals heterostructure polaritons with moiré-induced nonlinearity. Nature, 2021, 591, 61 doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03228-5[21] Wilson N P, Yao W, Shan J, et al. Exciton and emergent quantum phenomena in stacked 2D semiconductors. Nature, 2021, 599, 383 doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03979-1[22] Yu H, Yao W. Electrically tunable topological transport of moiré polaritons. Sci Bull, 2020, 65, 1555 doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2020.05.030[23] Camacho-Guardian A, Cooper N R. Moiré-induced optical nonlinearities: single- and multiphoton resonances. Phys Rev Lett, 2022, 128, 207401 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.207401[24] Fizgerald J M, Thompson J J P, Malic E. Twist angle tuning of moiré exciton polaritons in van der Waals heterostructures. Nano Lett, 2022, 22, 4468 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c01175[25] Rivera P, Fryett T K, Chen Y, et al. Coupling of photonic crystal cavity and interlayer exciton in heterobilayer of transition metal dichalcogenides. 2D Mater, 2020, 7, 015027 doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/ab597d[26] Paik E Y, Zhang L, Burg G W, et al. Interlayer exciton laser of extended spatial coherence in atomically thin heterostructures. Nature, 2019, 576, 80 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1779-x[27] Ubrig N, Ponomarev E, Zultak J, et al. Design of van der Waals interfaces for broad-spectrum optoelectronics. Nat Mater, 2020, 19, 299 doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0601-3[28] Shanks D N, Mahdikhanysarvejahany F, Stanfill T G, et al. Interlayer exciton diode and transistor. Nano Lett, 2022, 16, 6599 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c01905[29] Dusel M, Betzold S, Egorov O A, et al. Room temperature organic exciton–polariton condensate in a lattice. Nat Commun, 2020, 11, 2863 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16656-0[30] Sala V G, Solnyshkov D D, Carusotto I, et al. Spin-orbit coupling for photons and polaritons in microstructures. Phys Rev X, 2015, 5, 011034 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.5.011034[31] Whittaker C E, Cancellieri E, Walker P M, et al. Exciton polaritons in a two-dimensional Lieb lattice with spin-orbit coupling. Phys Rev Lett, 2018, 120, 097401 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.097401[32] Alyatkin S, Sigurdsson H, Askitopoulos A, et al. Quantum fluids of light in all-optical scatter lattices. Nat Commun, 2021, 12, 5571 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25845-4 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad:










 Yuchen Gao:received his bachelor's degree in physics at Peking University in 2022. After that, he became a Ph.D. student at Peking University with Yu Ye as his advisor. His scientific interests are focused on the physics of optical spectroscopy and electrical transport in 2D materials and their van der Waals heterostructures
Yuchen Gao:received his bachelor's degree in physics at Peking University in 2022. After that, he became a Ph.D. student at Peking University with Yu Ye as his advisor. His scientific interests are focused on the physics of optical spectroscopy and electrical transport in 2D materials and their van der Waals heterostructures Yu Ye:is a tenured associated professor in School of Physics at Peking University. He received his Ph.D. degree in condensed matter physics from Peking University in 2012. Prior to joining PKU in July 2016, Yu was working as a postdoctoral researcher at University of California, Berkeley. His group currently is interested in light-matter interactions and electrical transport properties in condensed matter physics, with an emphasis on novel physical phenomena emerging in atomically thin materials, van der Waals heterostructures and surfaces/interfaces by nanoscale device designs, optical spectroscopy, electrical transport, and scanning photocurrent measurements
Yu Ye:is a tenured associated professor in School of Physics at Peking University. He received his Ph.D. degree in condensed matter physics from Peking University in 2012. Prior to joining PKU in July 2016, Yu was working as a postdoctoral researcher at University of California, Berkeley. His group currently is interested in light-matter interactions and electrical transport properties in condensed matter physics, with an emphasis on novel physical phenomena emerging in atomically thin materials, van der Waals heterostructures and surfaces/interfaces by nanoscale device designs, optical spectroscopy, electrical transport, and scanning photocurrent measurements



