| Citation: |
Chenxu Wu, Yibai Xue, Han Bao, Ling Yang, Jiancong Li, Jing Tian, Shengguang Ren, Yi Li, Xiangshui Miao. Forward stagewise regression with multilevel memristor for sparse coding[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2023, 44(10): 104101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/10/104101
****
C X Wu, Y B Xue, H Bao, L Yang, J C Li, J Tian, S G Ren, Y Li, X S Miao. Forward stagewise regression with multilevel memristor for sparse coding[J]. J. Semicond, 2023, 44(10): 104101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/10/104101
|
Forward stagewise regression with multilevel memristor for sparse coding
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/10/104101
More Information
-
Abstract
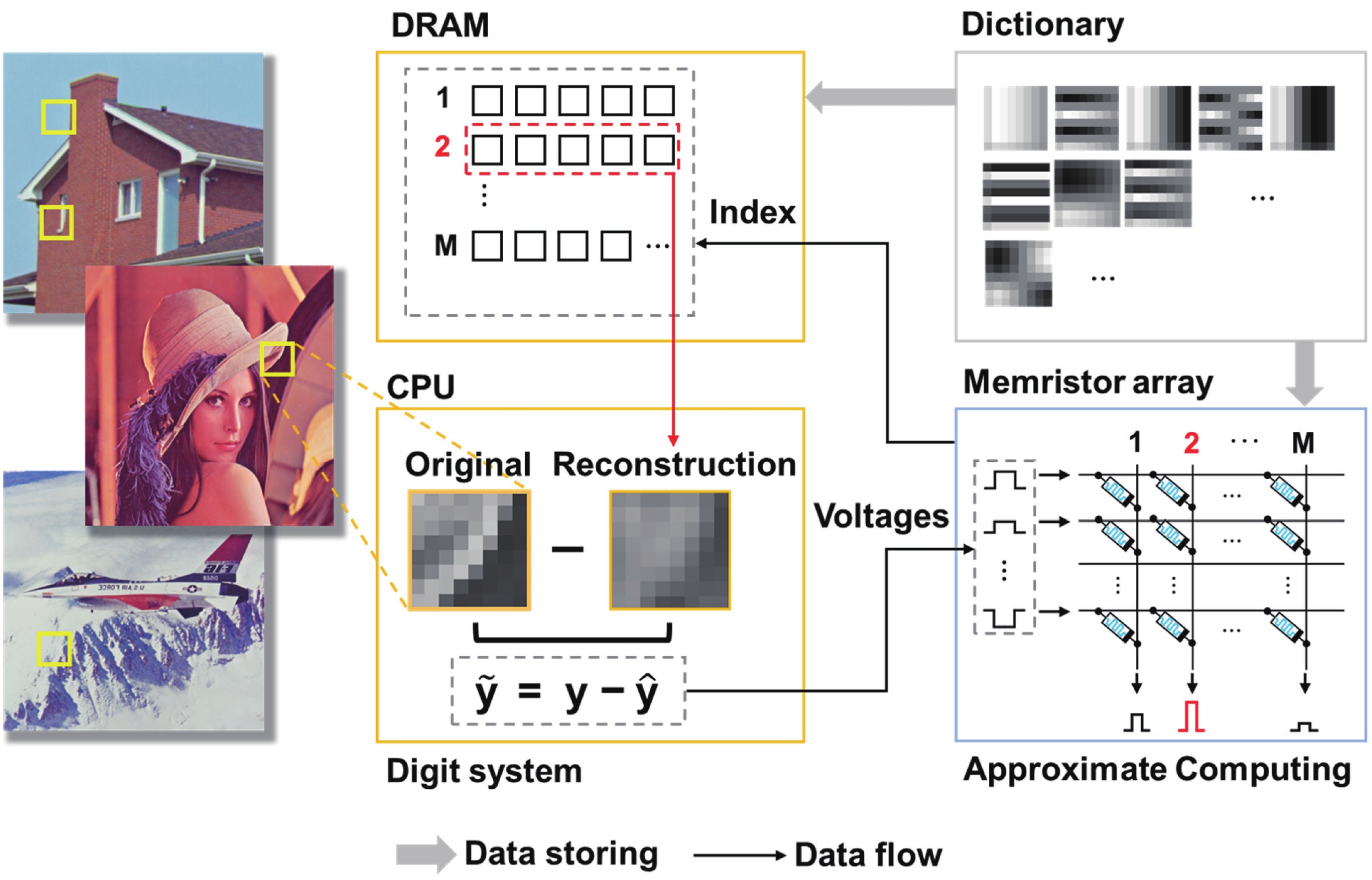
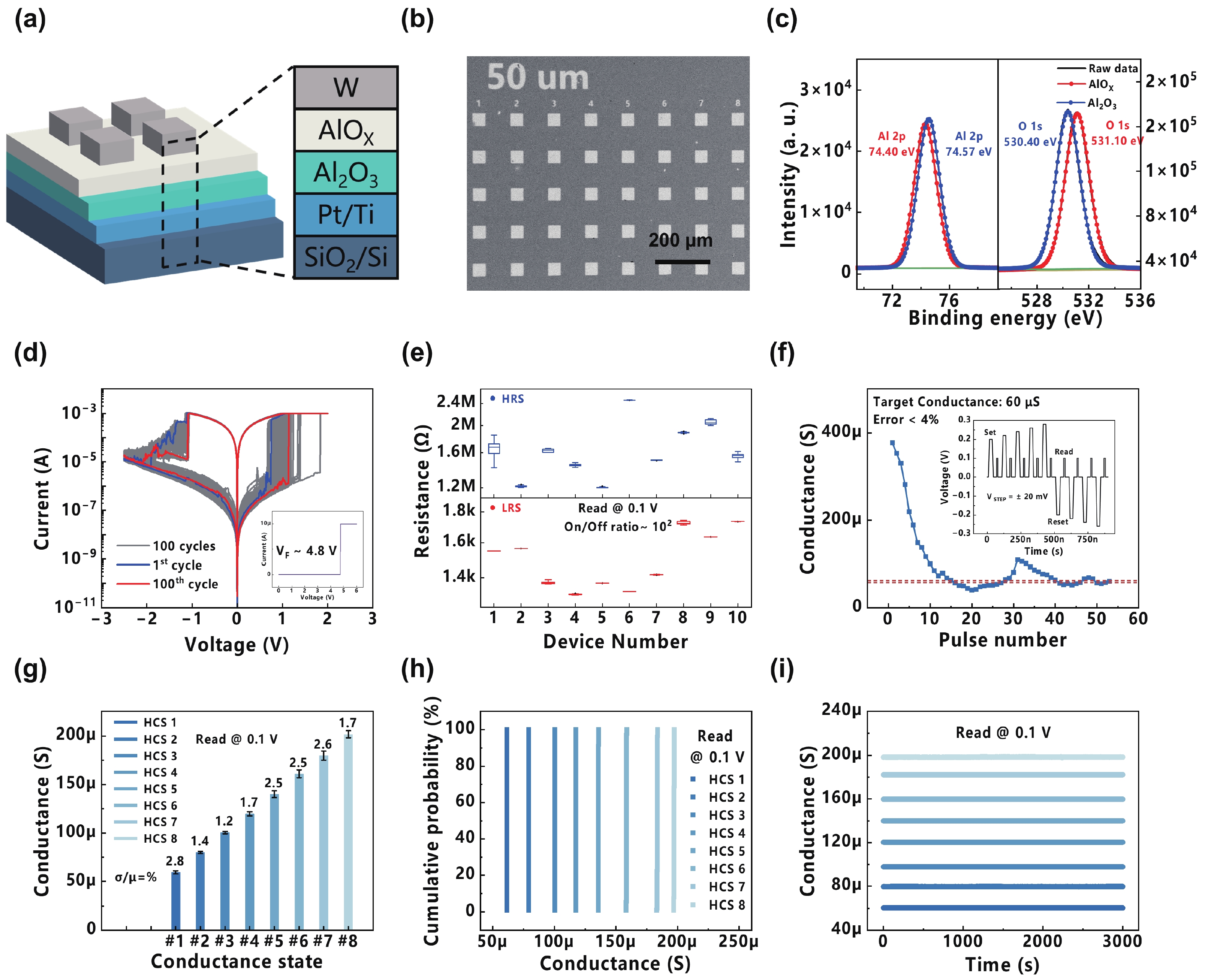
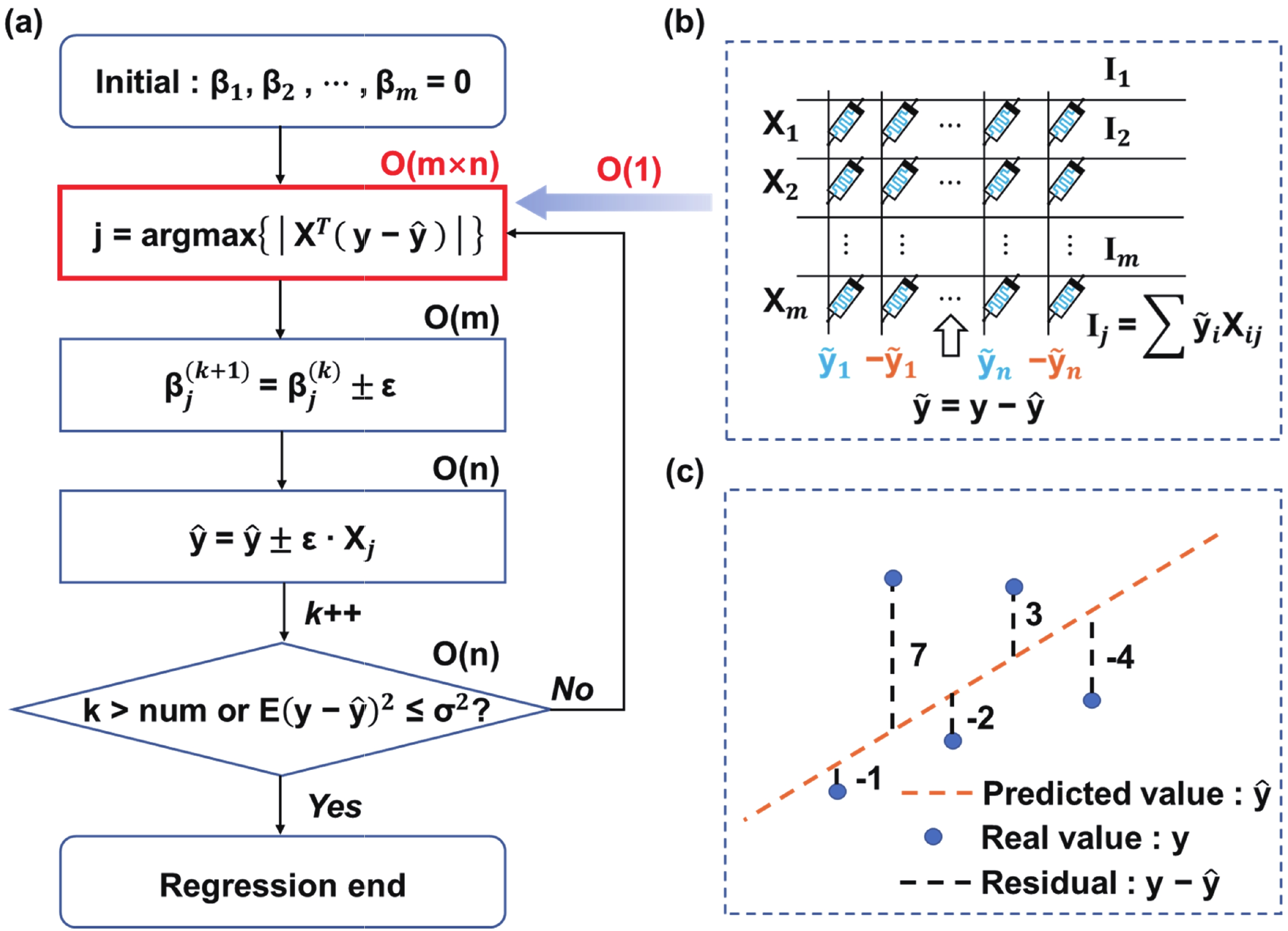
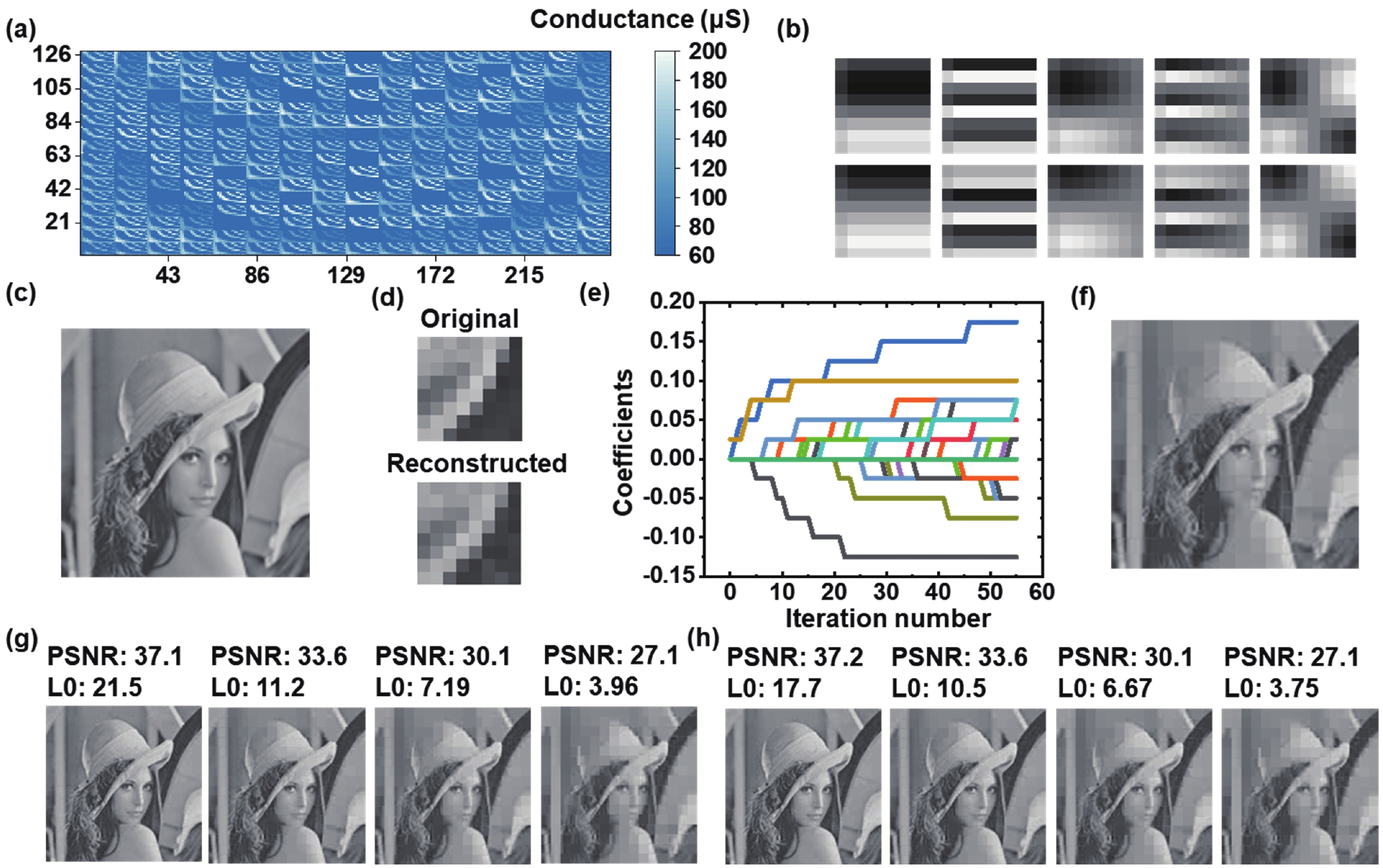
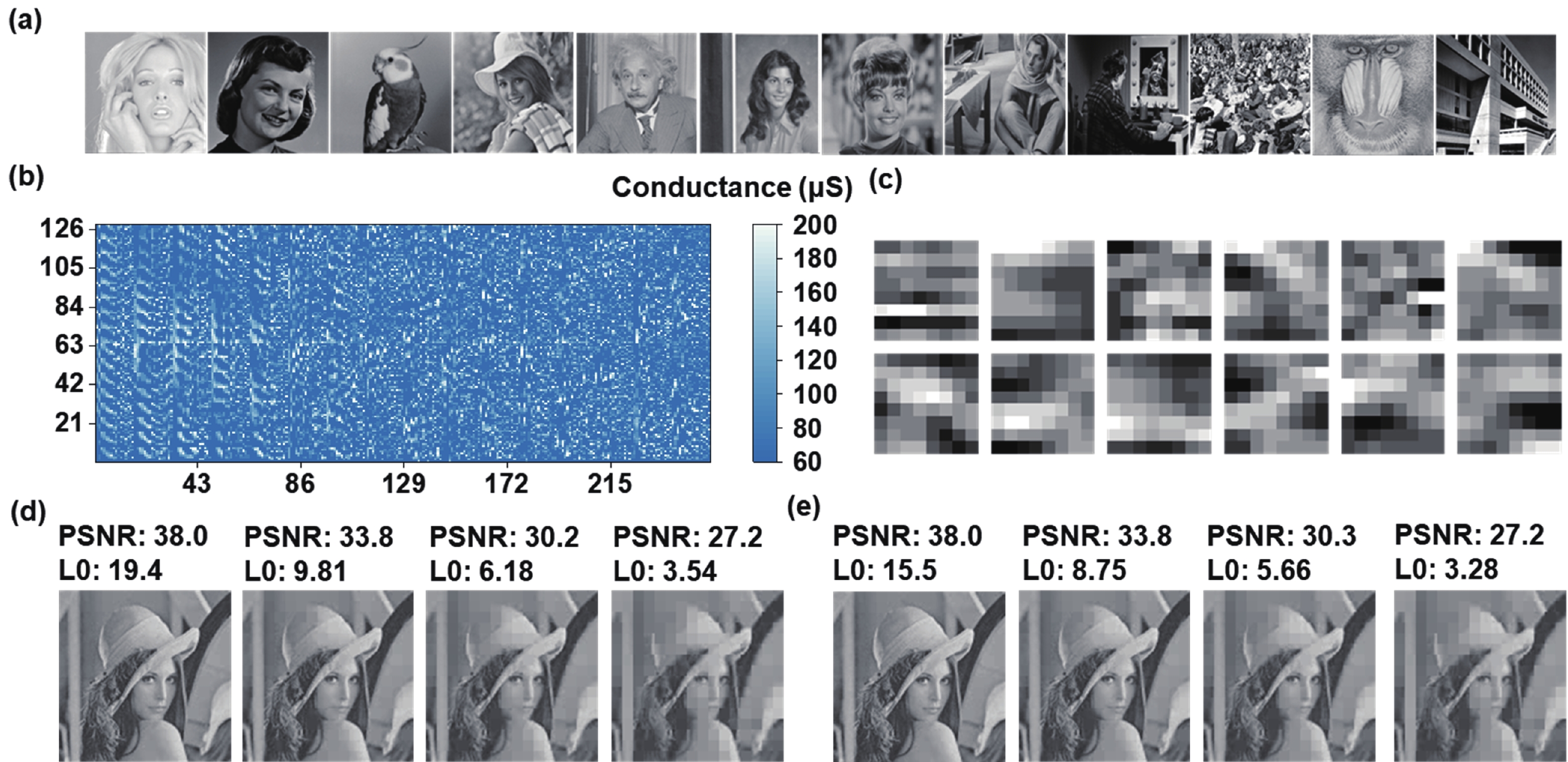
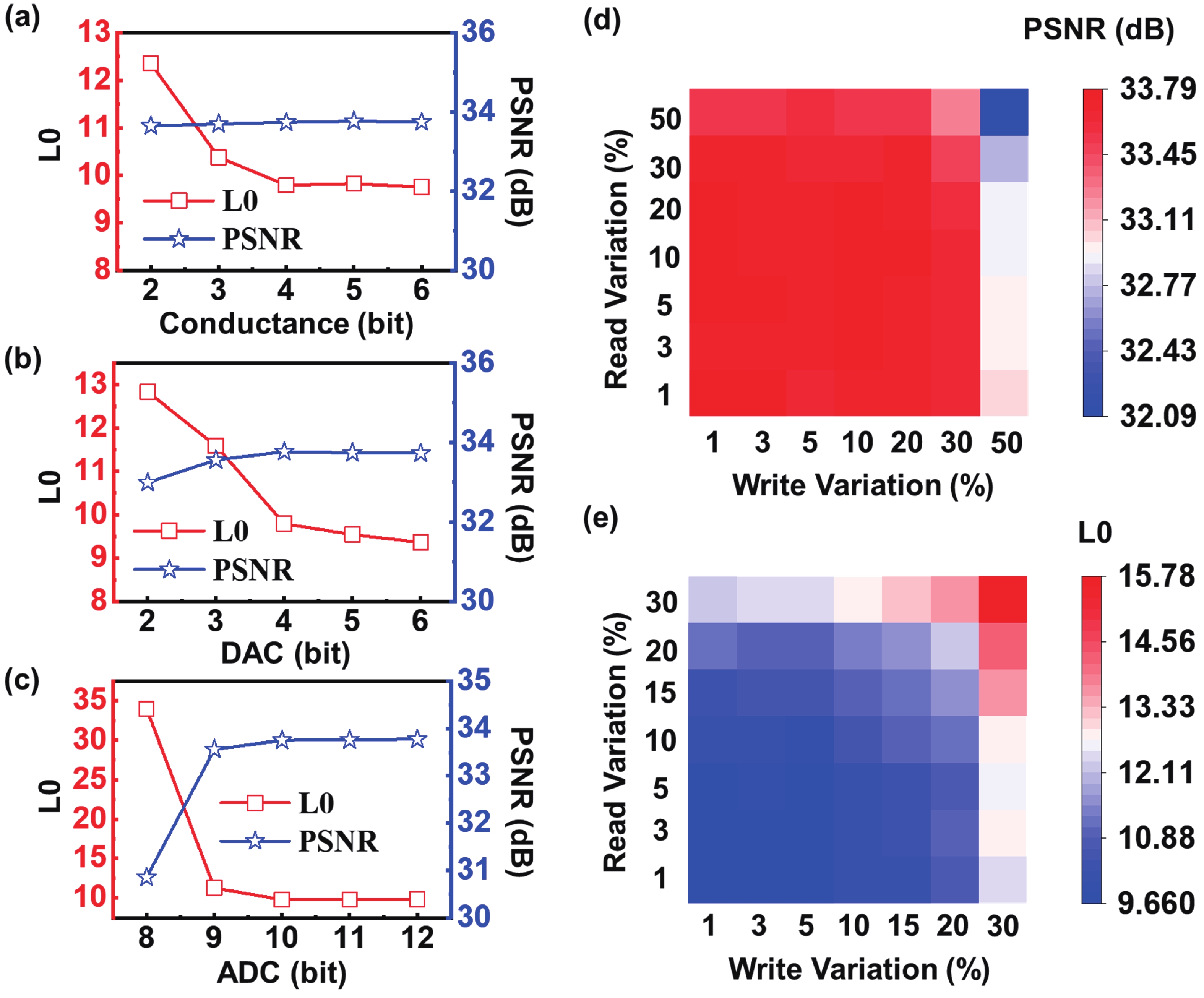
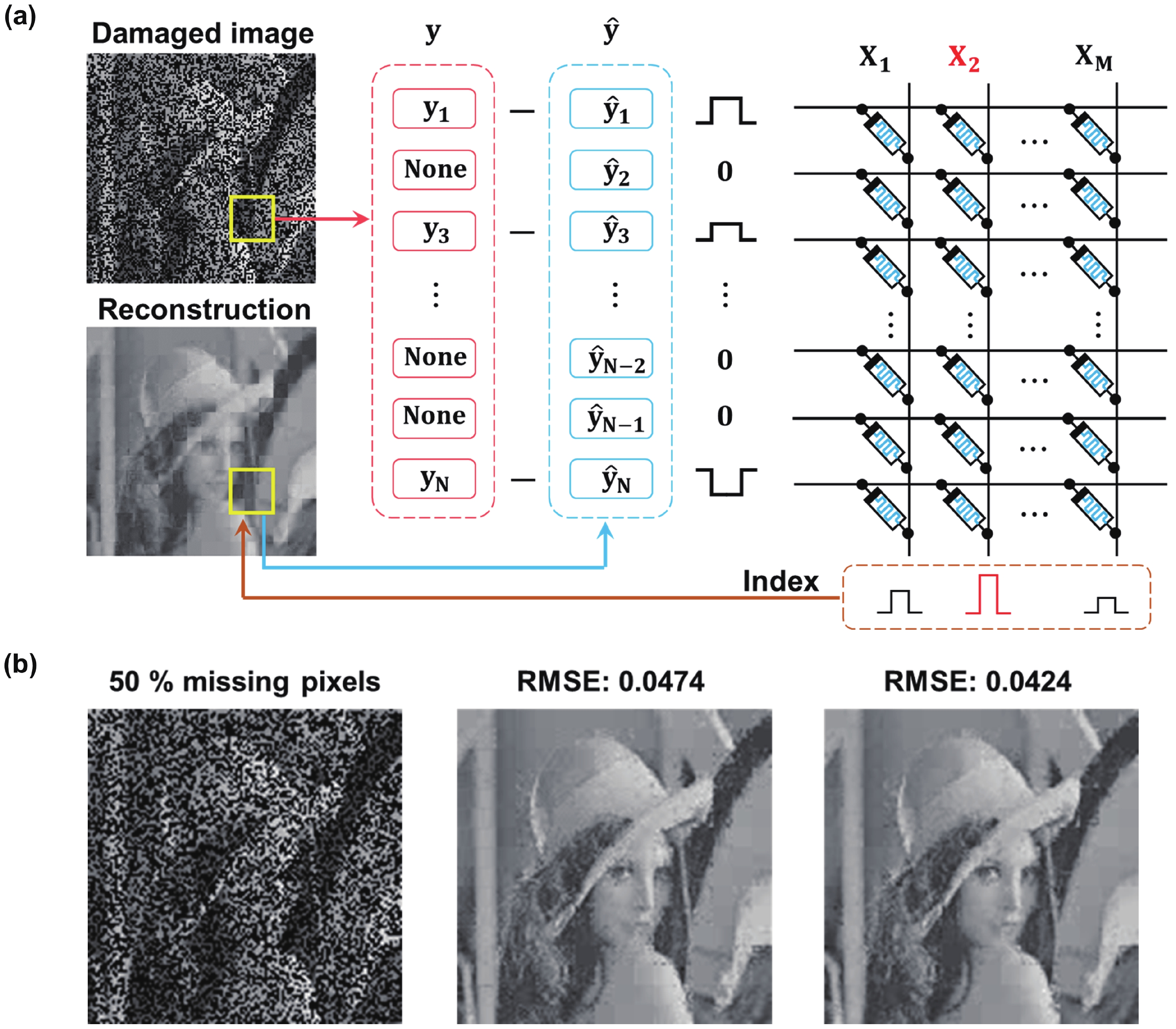
Sparse coding is a prevalent method for image inpainting and feature extraction, which can repair corrupted images or improve data processing efficiency, and has numerous applications in computer vision and signal processing. Recently, several memristor-based in-memory computing systems have been proposed to enhance the efficiency of sparse coding remarkably. However, the variations and low precision of the devices will deteriorate the dictionary, causing inevitable degradation in the accuracy and reliability of the application. In this work, a digital-analog hybrid memristive sparse coding system is proposed utilizing a multilevel Pt/Al2O3/AlOx/W memristor, which employs the forward stagewise regression algorithm: The approximate cosine distance calculation is conducted in the analog part to speed up the computation, followed by high-precision coefficient updates performed in the digital portion. We determine that four states of the aforementioned memristor are sufficient for the processing of natural images. Furthermore, through dynamic adjustment of the mapping ratio, the precision requirement for the digit-to-analog converters can be reduced to 4 bits. Compared to the previous system, our system achieves higher image reconstruction quality of the 38 dB peak-signal-to-noise ratio. Moreover, in the context of image inpainting, images containing 50% missing pixels can be restored with a reconstruction error of 0.0424 root-mean-squared error. -
References
[1] Wright J, Ma Y, Mairal J, et al. Sparse representation for computer vision and pattern recognition. Proc IEEE, 2010, 98, 1031 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2010.2044470[2] Aharon M, Elad M, Bruckstein A. K-SVD: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2006, 54, 4311 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.881199[3] Yang M, Zhang L, Yang J, et al. Robust sparse coding for face recognition. Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2011, 625 doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995393[4] Lee H, Battle A, Raina R, et al. Efficient sparse coding algorithms. Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2006, 801[5] Mairal J, Bach F, Ponce J, et al. Online dictionary learning for sparse coding. Proceedings of the 26th annual international conference on machine learning, 2009, 689 doi: 10.1145/1553374.1553463[6] Efron B, Hastie T, Johnstone I, et al. Least angle regression. Ann Statist, 2004, 32, 407 doi: 10.1214/009053604000000067[7] Tibshirani R J, Yu B. A general framework for fast stagewise algorithms. J Mach Learn Res, 2015, 16, 2543[8] Hastie T, Taylor J, Tibshirani R, et al. Forward stagewise regression and the monotone lasso. Electron J Statist, 2007, 1, 1 doi: 10.1214/07-EJS004[9] Wan W E, Kubendran R, Schaefer C, et al. A compute-in-memory chip based on resistive random-access memory. Nature, 2022, 608, 504 doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04992-8[10] Huo Q, Yang Y M, Wang Y M, et al. A computing-in-memory macro based on three-dimensional resistive random-access memory. Nat Electron, 2022, 5, 469 doi: 10.1038/s41928-022-00795-x[11] Liu Q, Gao B, Yao P, et al. A fully integrated analog ReRAM based 78.4TOPS/W compute-In-memory chip with fully parallel MAC computing. 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference - (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020, 500 doi: 10.1109/ISSCC19947.2020.9062953[12] Wang S C, Li Y, Wang D C, et al. Echo state graph neural networks with analogue random resistive memory arrays. Nat Mach Intell, 2023, 5, 104 doi: 10.1038/s42256-023-00609-5[13] Yao P, Wu H Q, Gao B, et al. Fully hardware-implemented memristor convolutional neural network. Nature, 2020, 577, 641 doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1942-4[14] Li C, Hu M, Li Y N, et al. Analogue signal and image processing with large memristor crossbars. Nat Electron, 2018, 1, 52 doi: 10.1038/s41928-017-0002-z[15] Sun Z, Pedretti G, Bricalli A, et al. One-step regression and classification with cross-point resistive memory arrays. Sci Adv, 2020, 6, eaay2378 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay2378[16] Sheridan P M, Cai F X, Du C, et al. Sparse coding with memristor networks. Nat Nanotechnol, 2017, 12, 784 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2017.83[17] Sheridan P M, Du C, Lu W D. Feature extraction using memristor networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2016, 27, 2327 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2482220[18] Woods W, Teuscher C. Fast and accurate sparse coding of visual stimuli with a simple, ultralow-energy spiking architecture. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2019, 30, 2173 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2878002[19] Ji X, Hu X F, Zhou Y, et al. Adaptive sparse coding based on memristive neural network with applications. Cogn Neurodyn, 2019, 13, 475 doi: 10.1007/s11571-019-09537-w[20] Huang X D, Li Y, Li H Y, et al. Enhancement of DC/AC resistive switching performance in AlOx memristor by two-technique bilayer approach. Appl Phys Lett, 2020, 116, 173504. doi: 10.1063/5.0006850[21] Huang X D, Li Y, Li H Y, et al. Forming-free, fast, uniform, and high endurance resistive switching from cryogenic to high temperatures in W/AlOx/Al2O3/Pt bilayer memristor. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2020, 41, 549 doi: 10.1109/LED.2020.2977397[22] Freund R M, Grigas P, Mazumder R. A new perspective on boosting in linear regression via subgradient optimization and relatives. Ann Statist, 2017, 45, 2328 doi: 10.1214/16-AOS1505[23] Cheadle C, Vawter M P, Freed W J, et al. Analysis of microarray data using Z score transformation. J Mol Diagn, 2003, 5, 73 doi: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60455-2[24] Rousseeuw P J, Leroy A M. Robust regression and outlier detection. John wiley & sons, 2005[25] Yang B, Li S T. Multifocus image fusion and restoration with sparse representation. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas, 2010, 59, 884 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2009.2026612[26] Schnass K, Vandergheynst P. Dictionary preconditioning for greedy algorithms. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2008, 56, 1994 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.911494[27] Wright J, Yang A Y, Ganesh A, et al. Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2009, 31, 210 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2008.79[28] Blanchet F G, Legendre P, Borcard D. Forward selection of explanatory variables. Ecology, 2008, 89, 2623 doi: 10.1890/07-0986.1[29] Guillemot C, Le Meur O. Image inpainting: Overview and recent advances. IEEE Signal Process Mag, 2014, 31, 127 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2013.2273004 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad:










 Chenxu Wu:is currently a postgraduate student in School of Integrated Circuits at Huazhong University of Science and Technology. He received his Bachelor degree in Harbin Engineering University in 2019. His research interests mainly focus on in-memory computing
Chenxu Wu:is currently a postgraduate student in School of Integrated Circuits at Huazhong University of Science and Technology. He received his Bachelor degree in Harbin Engineering University in 2019. His research interests mainly focus on in-memory computing Yibai Xue:is currently a postgraduate student in School of Integrated Circuits at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST). He received his Bachelor degree in HUST in 2021. His research interests mainly focus on metal oxide memristors, as well as nonvolatile memory technology
Yibai Xue:is currently a postgraduate student in School of Integrated Circuits at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST). He received his Bachelor degree in HUST in 2021. His research interests mainly focus on metal oxide memristors, as well as nonvolatile memory technology Yi Li:is currently an associate professor at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST). He received his PhD degree in microelectronics from HUST in 2014. His major research interests focus on memristors and their applications in neuromorphic computing and in-memory computing
Yi Li:is currently an associate professor at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST). He received his PhD degree in microelectronics from HUST in 2014. His major research interests focus on memristors and their applications in neuromorphic computing and in-memory computing



