| Citation: |
Yunfei Xu, Weijiang Li, Yu Ma, Quanyong Lu, Jinchuan Zhang, Shenqiang Zhai, Ning Zhuo, Junqi Liu, Shuman Liu, Fengmin Cheng, Lijun Wang, Fengqi Liu. Phase-locked single-mode terahertz quantum cascade lasers array[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2024, 45(6): 062401. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/23120010
****
Y F Xu, W J Li, Y Ma, Q Y Lu, J C Zhang, S Q Zhai, N Zhuo, J Q Liu, S M Liu, F M Cheng, L J Wang, and F Q Liu, Phase-locked single-mode terahertz quantum cascade lasers array[J]. J. Semicond., 2024, 45(6), 062401 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/23120010
|
Phase-locked single-mode terahertz quantum cascade lasers array
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/23120010
More Information
-
Abstract
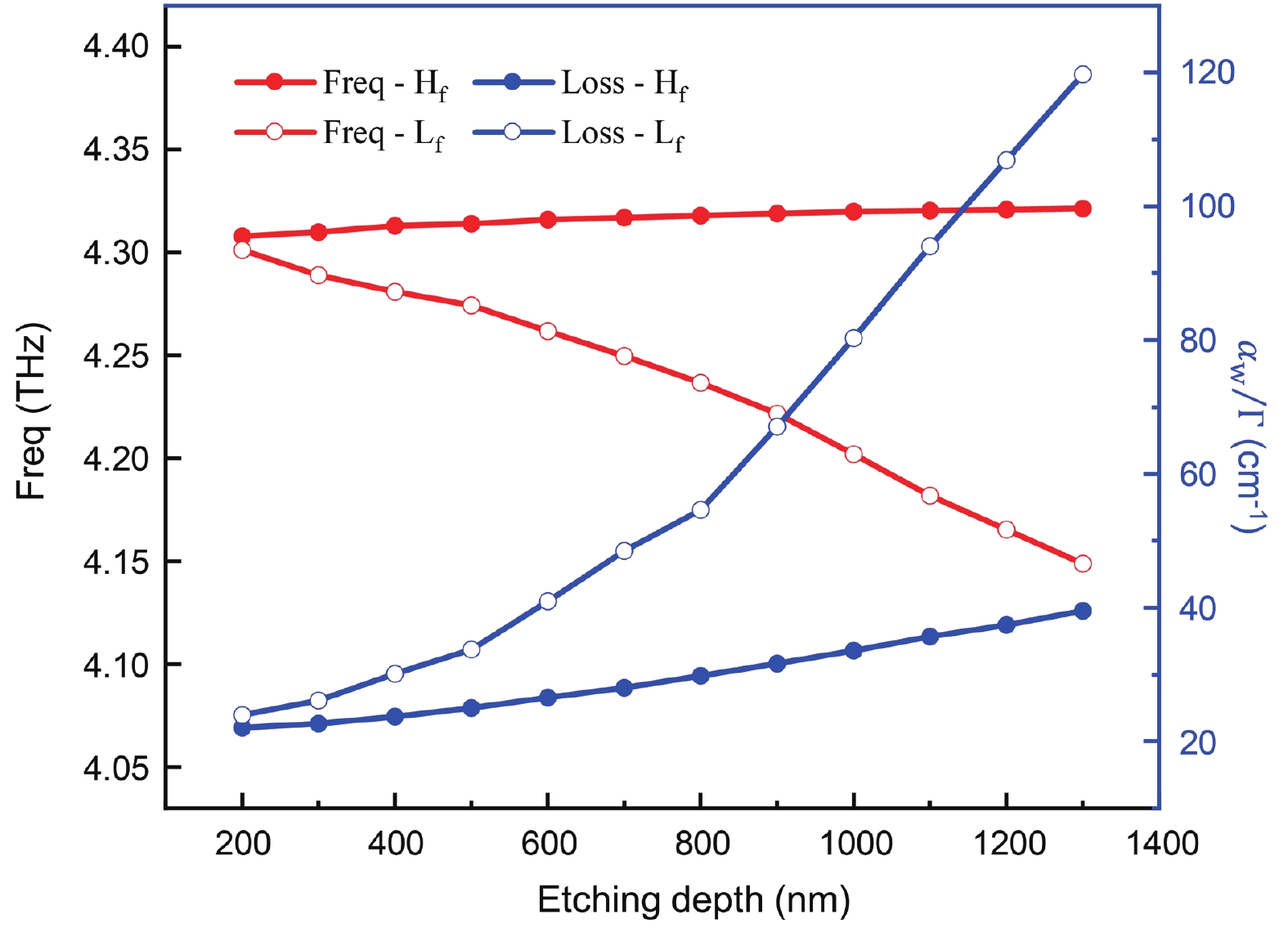
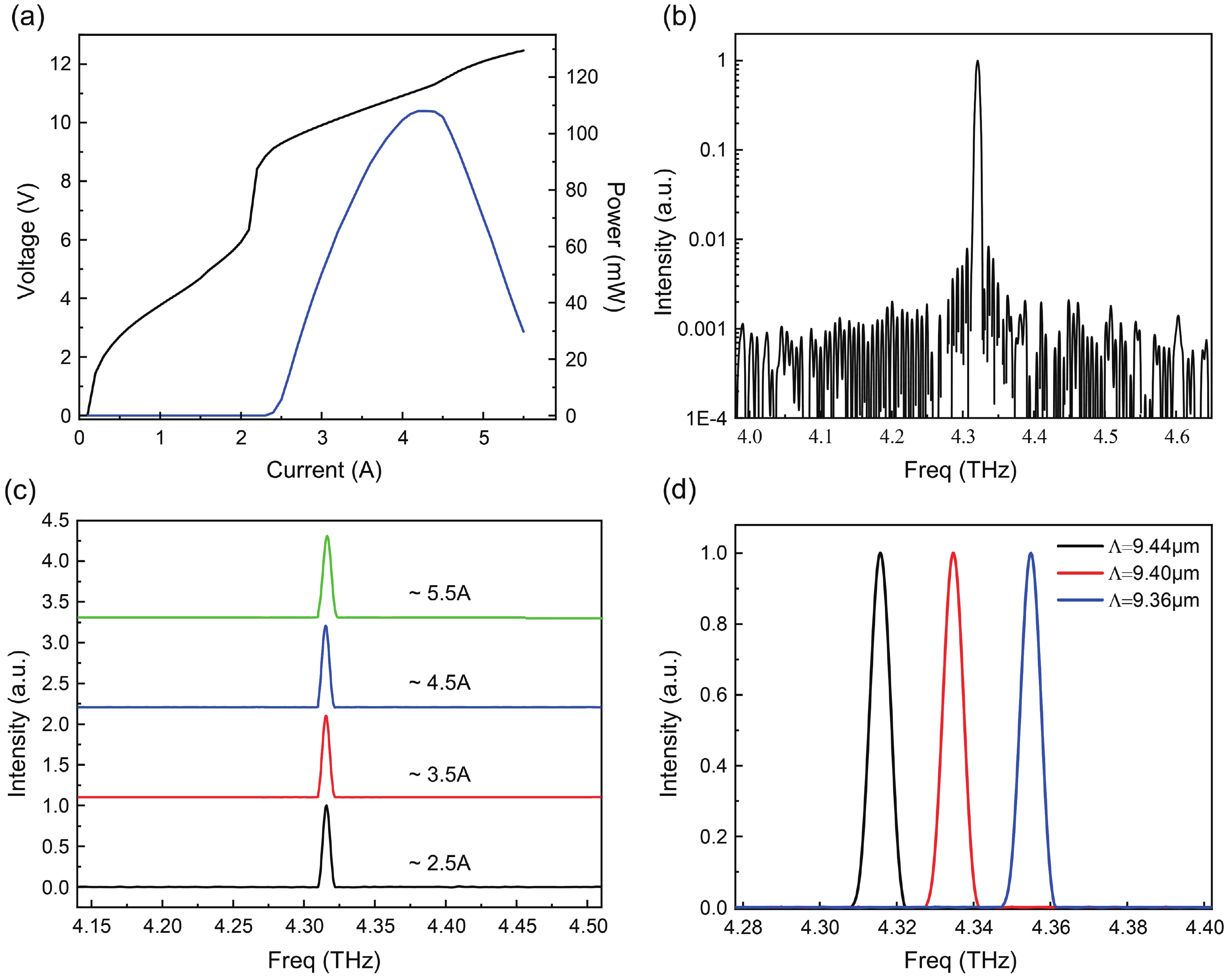
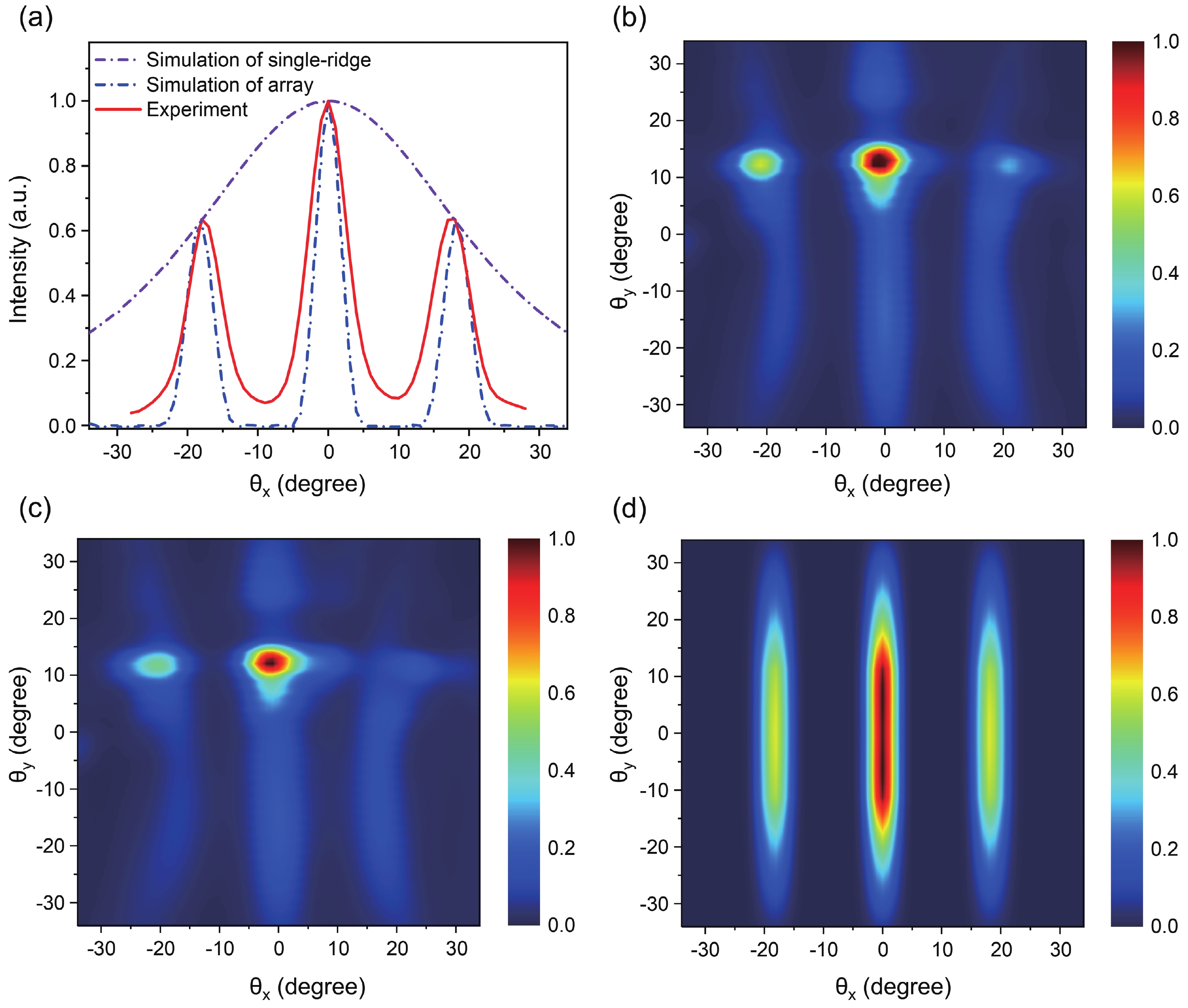
We demonstrated a scheme of phase-locked terahertz quantum cascade lasers (THz QCLs) array, with a single-mode pulse power of 108 mW at 13 K. The device utilizes a Talbot cavity to achieve phase locking among five ridge lasers with first-order buried distributed feedback (DFB) grating, resulting in nearly five times amplification of the single-mode power. Due to the optimum length of Talbot cavity depends on wavelength, the combination of Talbot cavity with the DFB grating leads to better power amplification than the combination with multimode Fabry−Perot (F−P) cavities. The Talbot cavity facet reflects light back to the ridge array direction and achieves self-imaging in the array, enabling phase-locked operation of ridges. We set the spacing between adjacent elements to be 220 μm, much larger than the free-space wavelength, ensuring the operation of the fundamental supermode throughout the laser's dynamic range and obtaining a high-brightness far-field distribution. This scheme provides a new approach for enhancing the single-mode power of THz QCLs.-
Keywords:
- quantum cascade lasers,
- phase locking,
- terahertz,
- single mode
-
References
[1] Faist J, Capasso F, Sivco D L, et al. Quantum cascade laser. Science, 1994, 264, 553 doi: 10.1126/science.264.5158.553[2] Köhler R, Tredicucci A, Beltram F, et al. Terahertz semiconductor-heterostructure laser. Nature, 2002, 417, 156 doi: 10.1038/417156a[3] Vitiello M S, Scalari G, Williams B, et al. Quantum cascade lasers: 20 years of challenges. Opt Express, 2015, 23, 5167 doi: 10.1364/OE.23.005167[4] Williams B S. Terahertz quantum-cascade lasers. Nat Photonics, 2007, 1, 517 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.166[5] Bai Y, Slivken S, Darvish S R, et al. High power broad area quantum cascade lasers. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 95, 221104 doi: 10.1063/1.3270043[6] Zhao Y, Yan F L, Zhang J C, et al. Broad area quantum cascade lasers operating in pulsed mode above 100 °C λ ~4.7 μm. J Semicond, 2017, 38, 074005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/7/074005[7] Kapon E, Katz J, Yariv A. Supermode analysis of phase-locked arrays of semiconductor lasers: Erratum. Opt Lett, 1984, 9, 318 doi: 10.1364/OL.9.000318[8] Yaeli J, Streifer W, Scifres D R, et al. Array mode selection utilizing an external cavity configuration. Appl Phys Lett, 1985, 47, 89 doi: 10.1063/1.96261[9] Apollonov V V, Kislov V I, Prokhorov A M. Phase locking of a semiconductor diode array in an external cavity. Quantum Electron, 1996, 26, 1051 doi: 10.1070/QE1996v026n12ABEH000872[10] Leger J R. Lateral mode control of an AlGaAs laser array in a Talbot cavity. Appl Phys Lett, 1989, 55, 334 doi: 10.1063/1.101900[11] Khalatpour A, Reno J L, Hu Q. Phase-locked photonic wire lasers by π coupling. Nat Photonics, 2019, 13, 47 doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0307-0[12] Halioua Y, Xu G Y, Moumdji S, et al. Phase-locked arrays of surface-emitting graded-photonic-heterostructure terahertz semiconductor lasers. Opt Express, 2015, 23, 6915 doi: 10.1364/OE.23.006915[13] Chang G L, Zhu H, Yu C R, et al. Phase-locked pair of terahertz quantum cascade lasers through evanescent-wave coupling. Infrared Phys Technol, 2020, 109, 103427 doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2020.103427[14] Kao T Y, Hu Q, Reno J L. Phase-locked arrays of surface-emitting terahertz quantum-cascade lasers. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, 2010, 1[15] Katz J, Margalit S, Yariv A. Diffraction-coupled phase-locked semiconductor laser array. Appl Phys Lett, 1983, 42, 554 doi: 10.1063/1.94025[16] Brunner D, Fischer I. Reconfigurable semiconductor laser networks based on diffractive coupling. Opt Lett, 2015, 40, 3854 doi: 10.1364/OL.40.003854[17] Xu Y F, Sun Y Q, Li W J, et al. Phase-locked terahertz quantum cascade laser array integrated with a Talbot cavity. Opt Express, 2022, 30, 36783 doi: 10.1364/OE.470993[18] Chuang S L. Physics of Photonic Devices. John Wiley & Sons, 2012 -
Proportional views




 Yunfei Xu earned his bachelor’s degree in Microelectronics from the School of Physics of Shandong University in 2019. He is now a PhD Student in Key Laboratory of Semiconductor Materials Science at the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences. He is mainly interested in the research of design and fabrication of mid-infrared and terahertz quantum cascade lasers.
Yunfei Xu earned his bachelor’s degree in Microelectronics from the School of Physics of Shandong University in 2019. He is now a PhD Student in Key Laboratory of Semiconductor Materials Science at the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences. He is mainly interested in the research of design and fabrication of mid-infrared and terahertz quantum cascade lasers. Quanyong Lu received his doctoral degree from Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2010. He was a postdoctoral researcher and then a Research Assistant Professor in Northwestern University from 2010 to 2020. He is currently a Professor of Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences (BAQIS) since 2021. His research is focused on quantum devices and systems, including quantum cascade lasers, frequency combs, terahertz lasers, and other quantum devices.
Quanyong Lu received his doctoral degree from Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2010. He was a postdoctoral researcher and then a Research Assistant Professor in Northwestern University from 2010 to 2020. He is currently a Professor of Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences (BAQIS) since 2021. His research is focused on quantum devices and systems, including quantum cascade lasers, frequency combs, terahertz lasers, and other quantum devices. Lijun Wang is a researcher and doctoral supervisor at the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences. He received the Ph.D. degree in physics from West Virginia University, USA in 2004. His current research interests include the design and fabrication of mid-infrared and terahertz quantum cascade lasers.
Lijun Wang is a researcher and doctoral supervisor at the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences. He received the Ph.D. degree in physics from West Virginia University, USA in 2004. His current research interests include the design and fabrication of mid-infrared and terahertz quantum cascade lasers.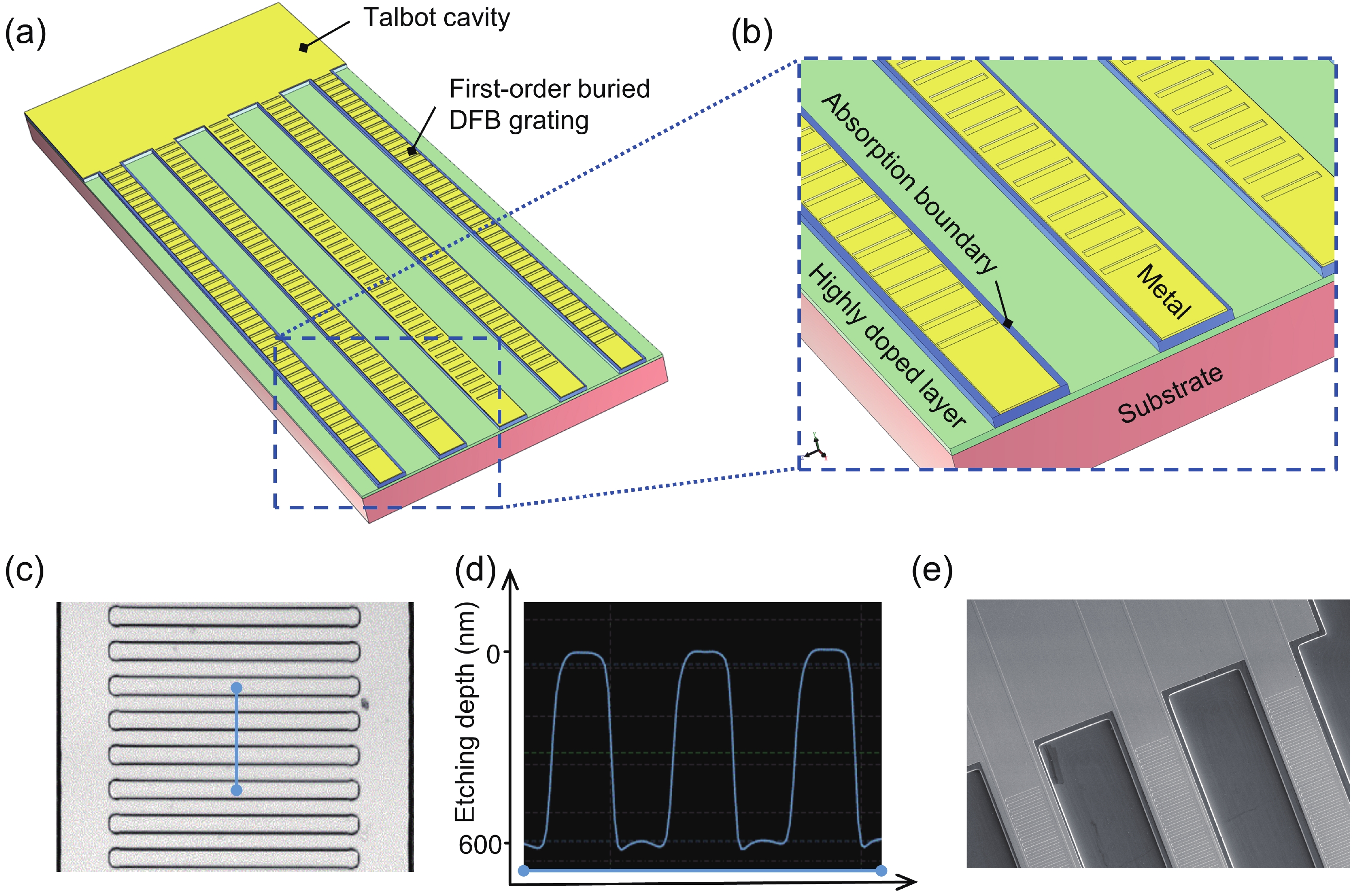
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: