| Citation: |
Zhouhao Zhao, Qian Chen, Yixing Lu, Haigang Feng. A 0.1−5.1 GHz high-gain LNA with inductorless composite resistor−capacitor feedback structure based on a 0.25 μm SiGe BiCMOS process[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2025, 46(8): 082202. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24110028
****
Z H Zhao, Q Chen, Y X Lu, and H G Feng, A 0.1−5.1 GHz high-gain LNA with inductorless composite resistor−capacitor feedback structure based on a 0.25 μm SiGe BiCMOS process[J]. J. Semicond., 2025, 46(8), 082202 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24110028
|
A 0.1−5.1 GHz high-gain LNA with inductorless composite resistor−capacitor feedback structure based on a 0.25 μm SiGe BiCMOS process
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/24110028
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.24110028
More Information-
Abstract
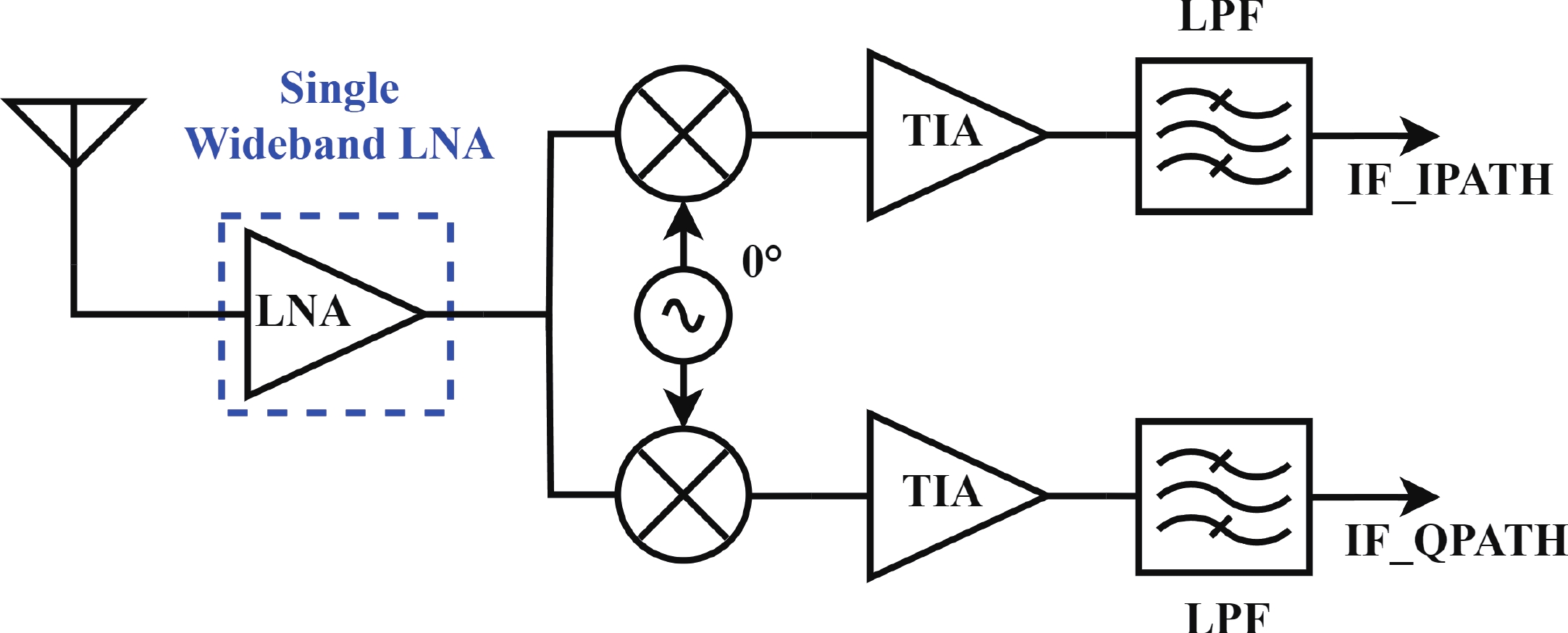
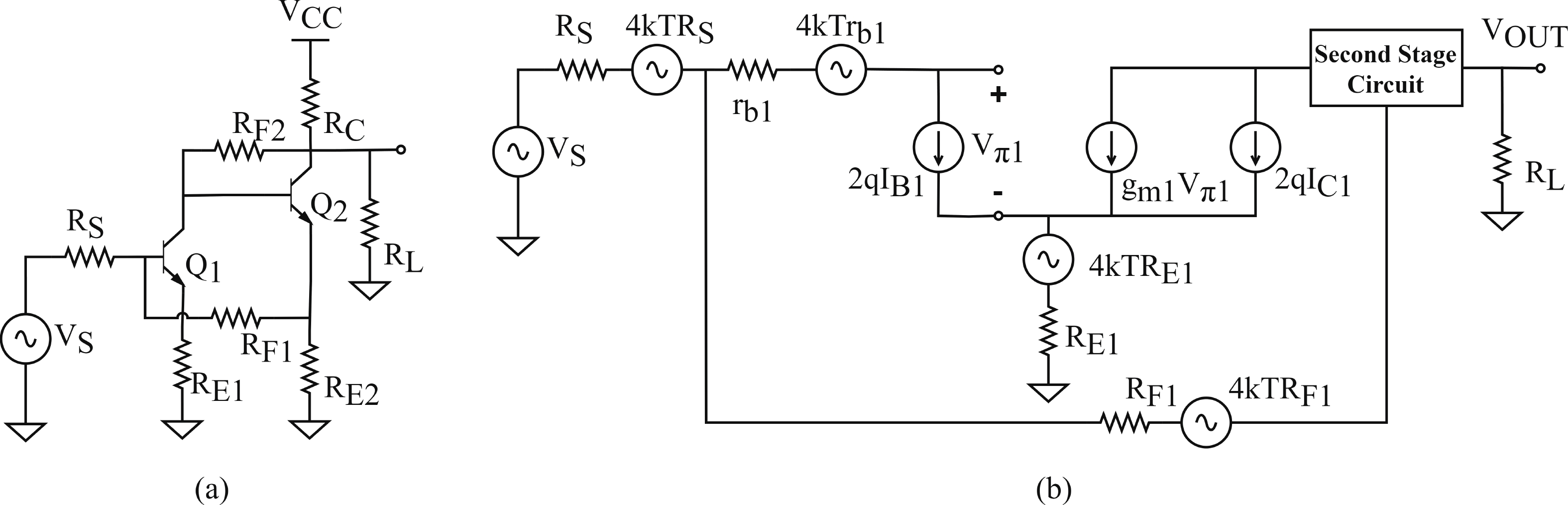
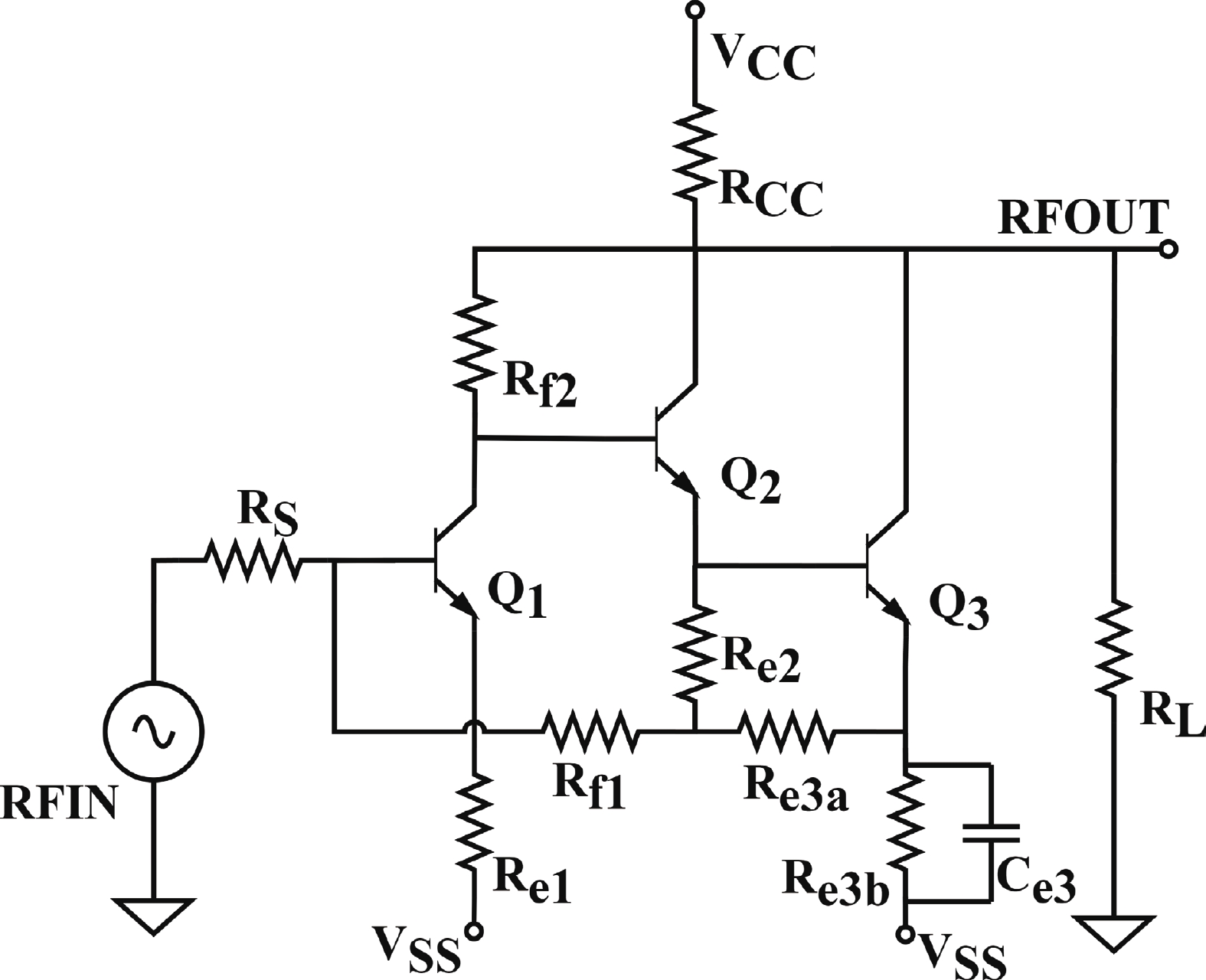
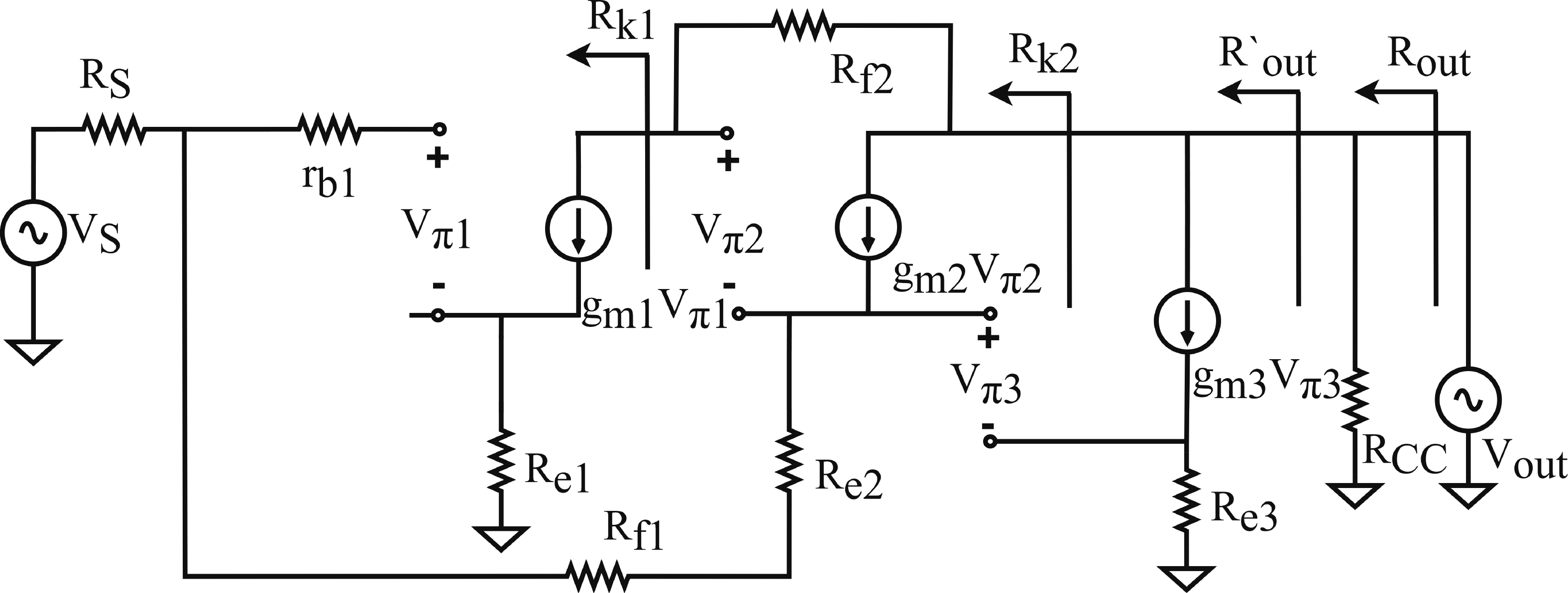
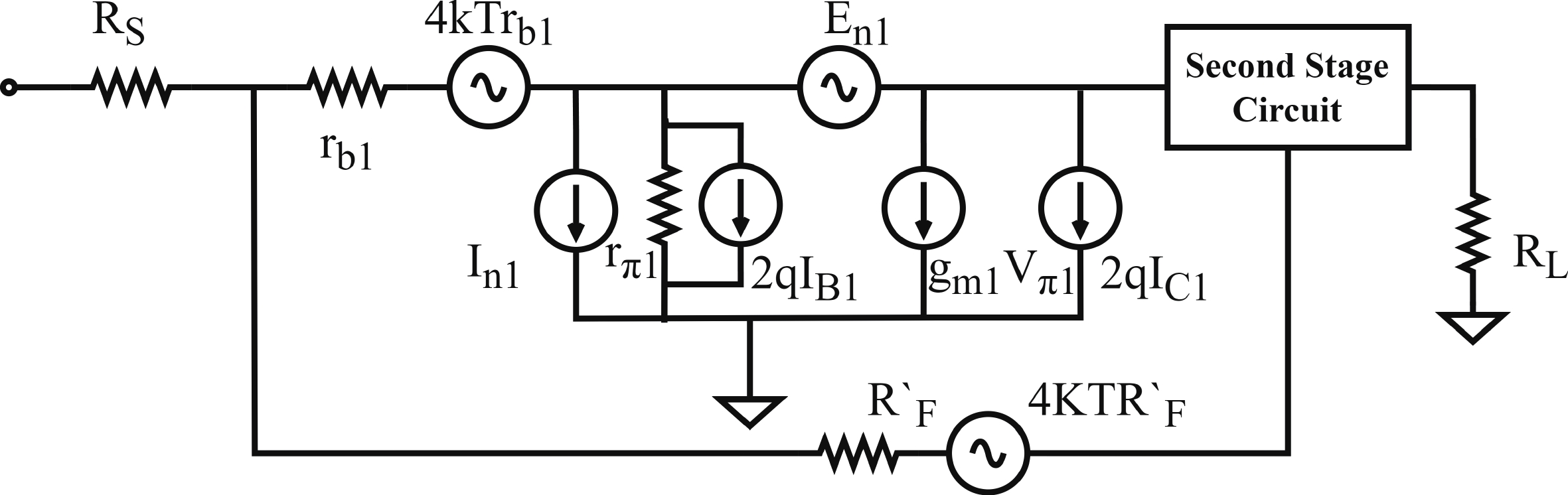
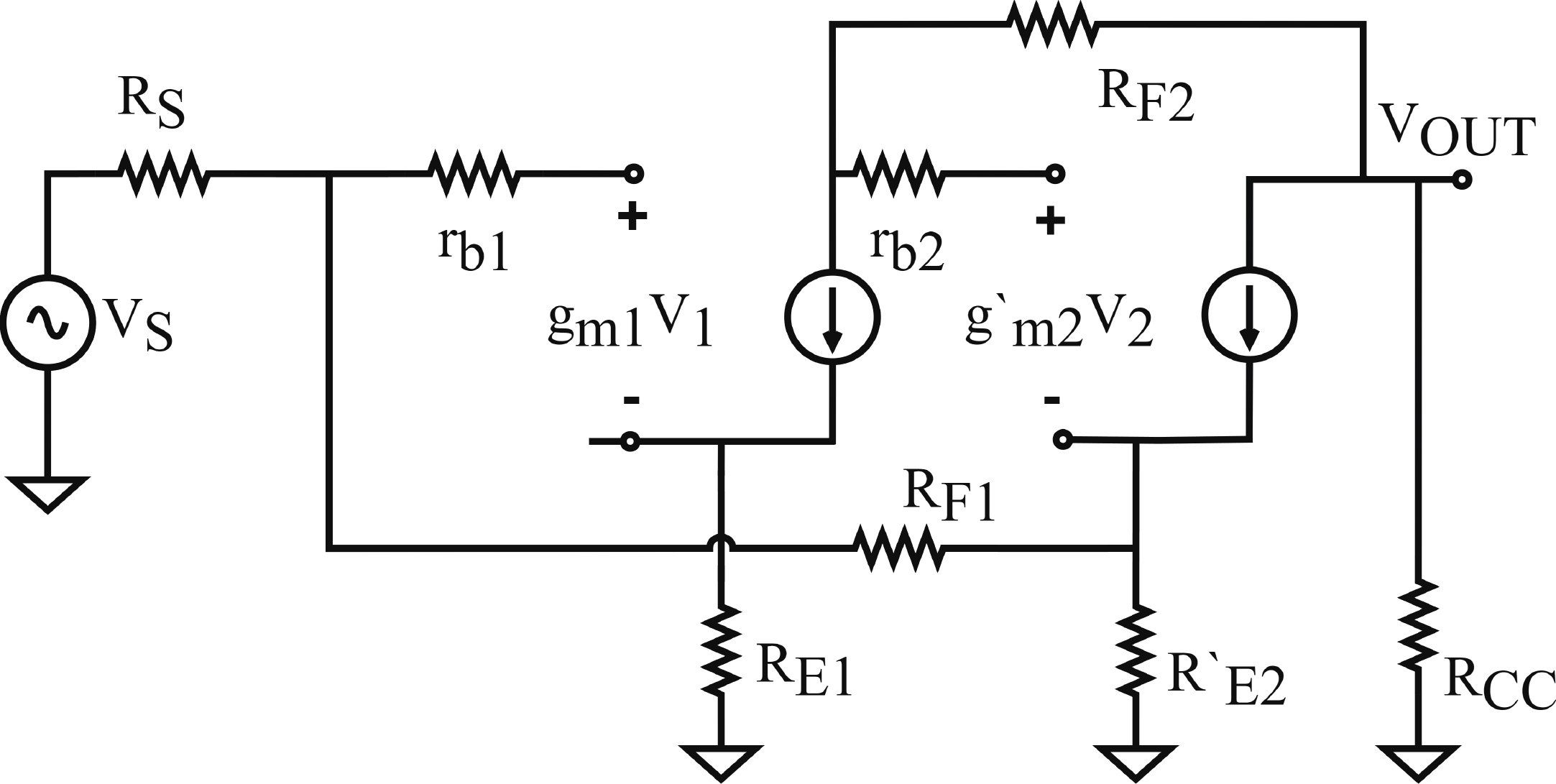
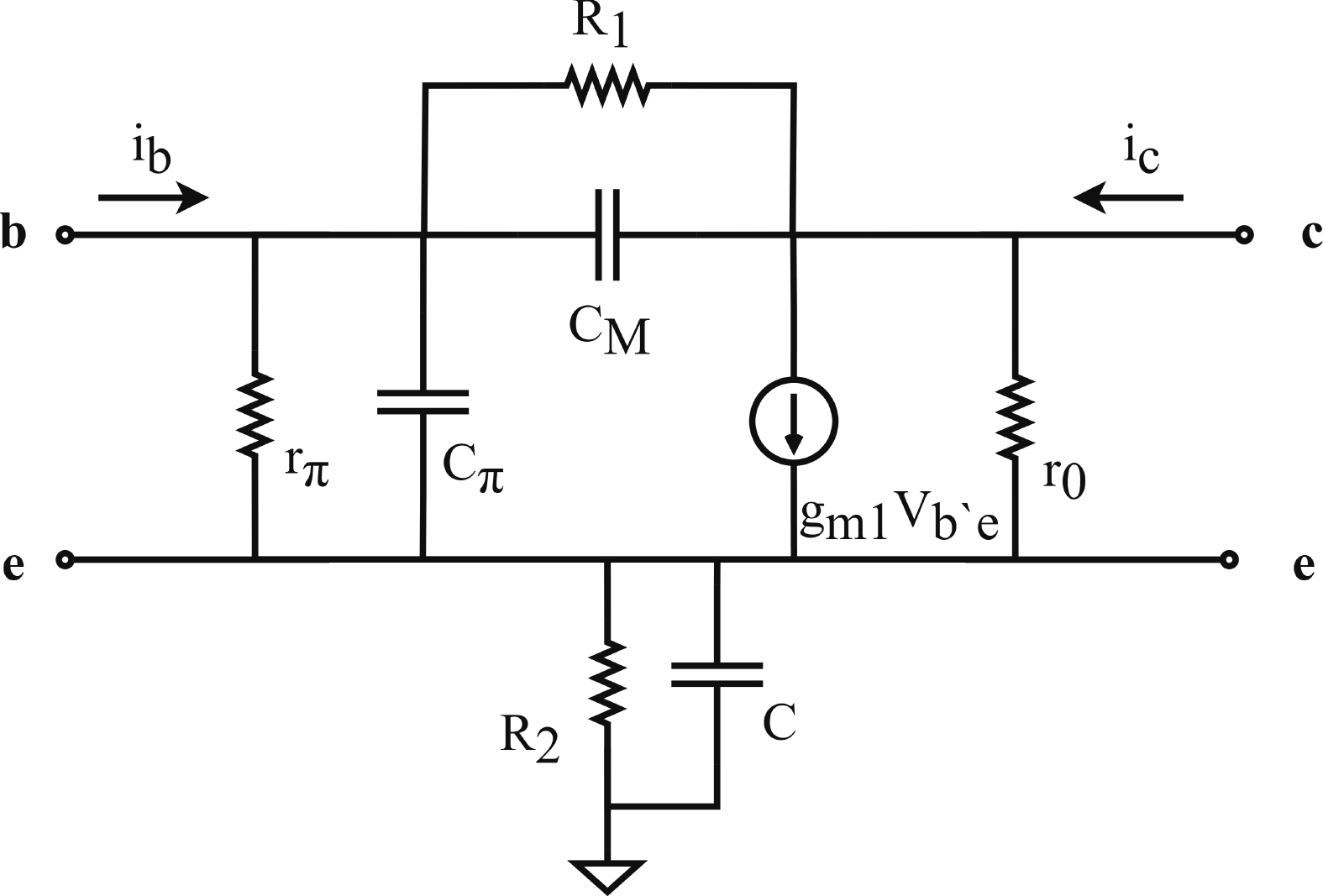
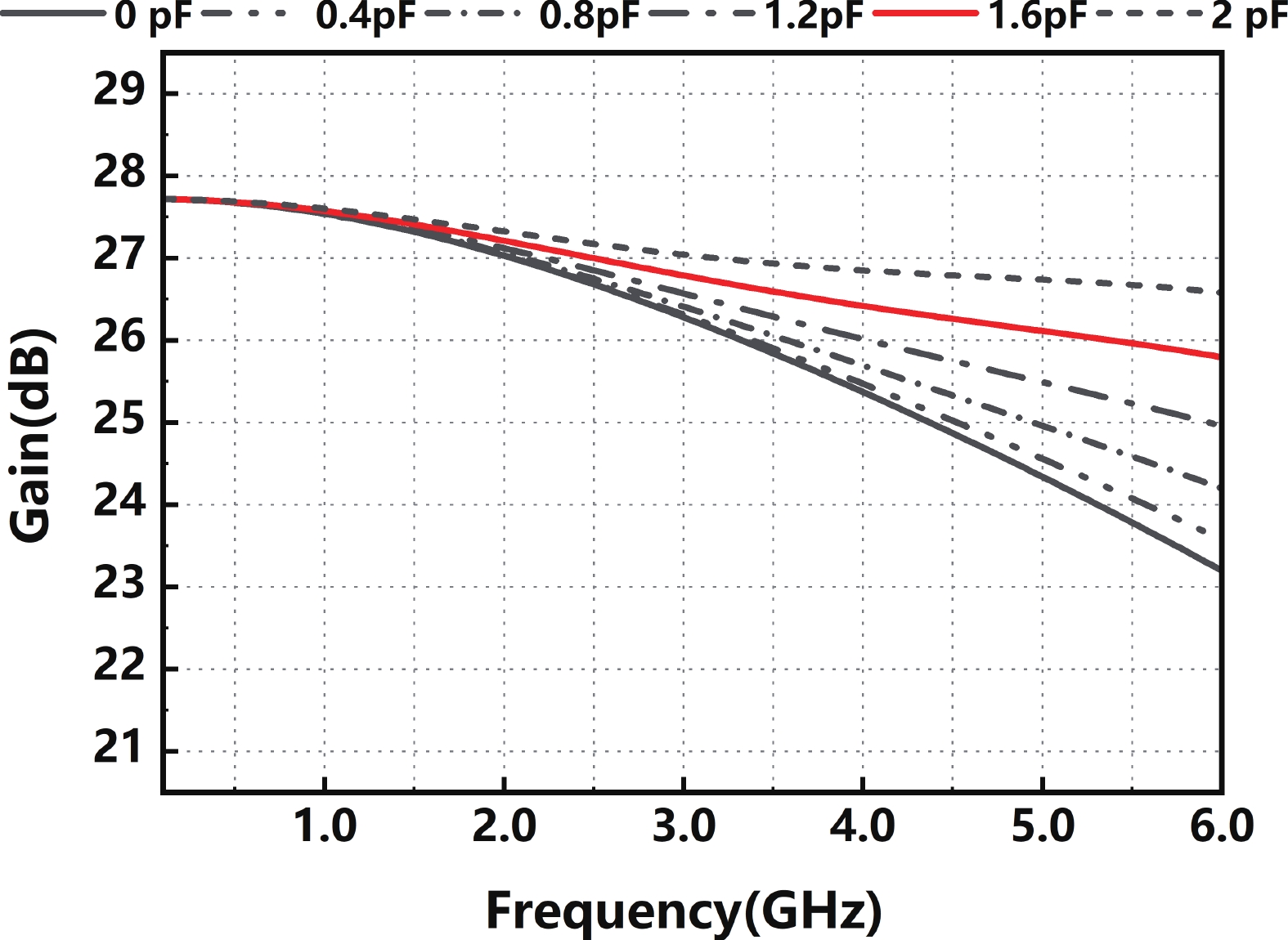
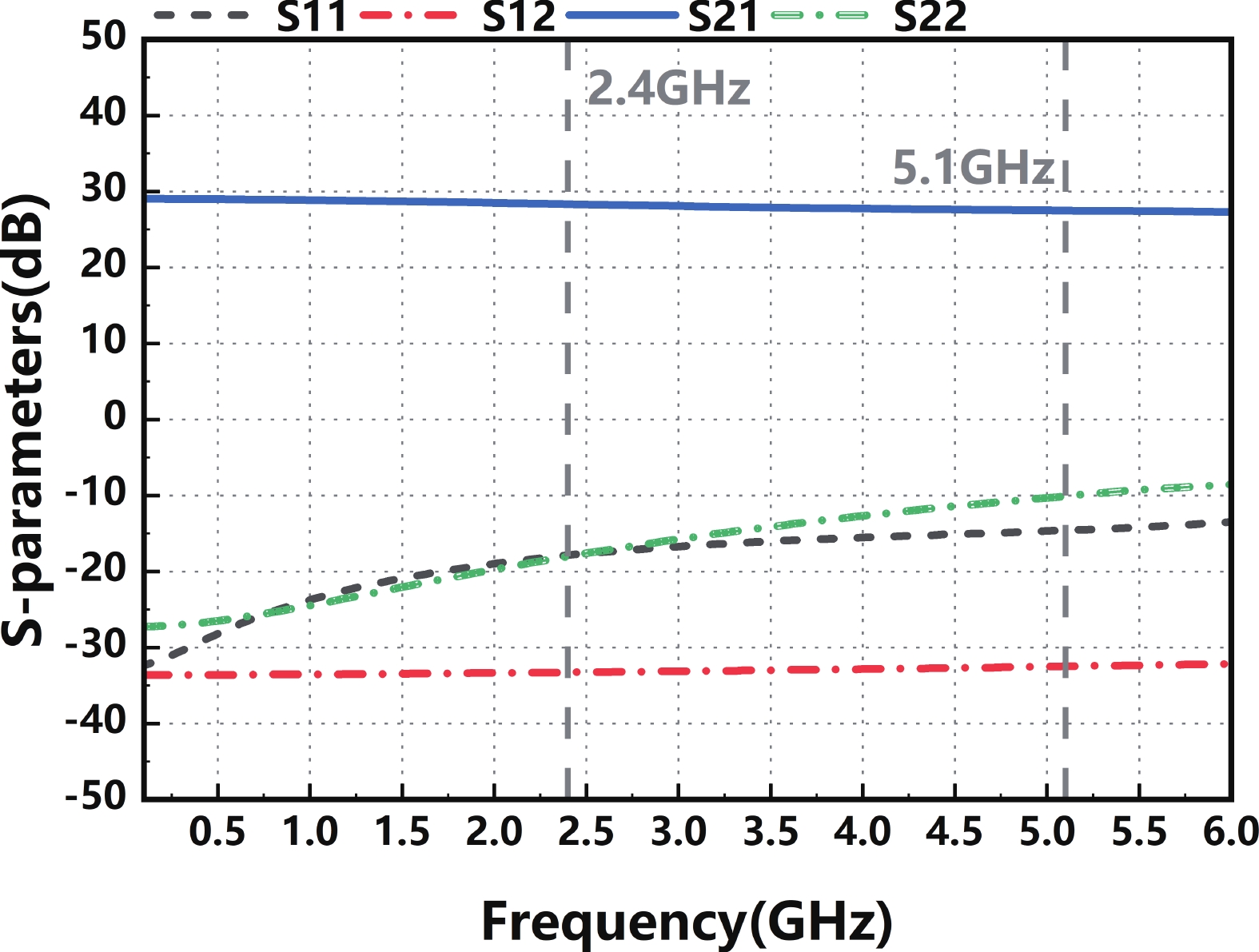
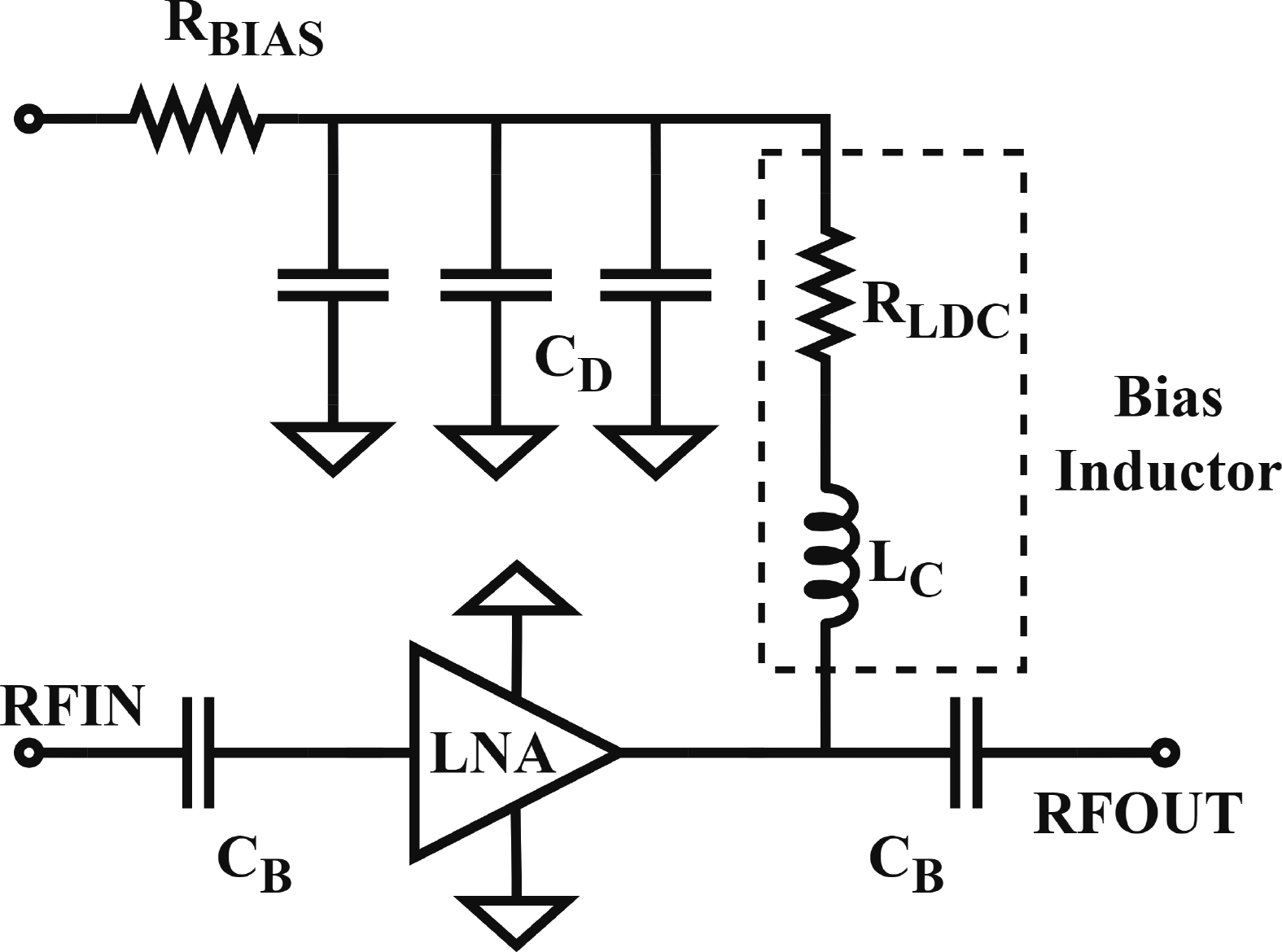
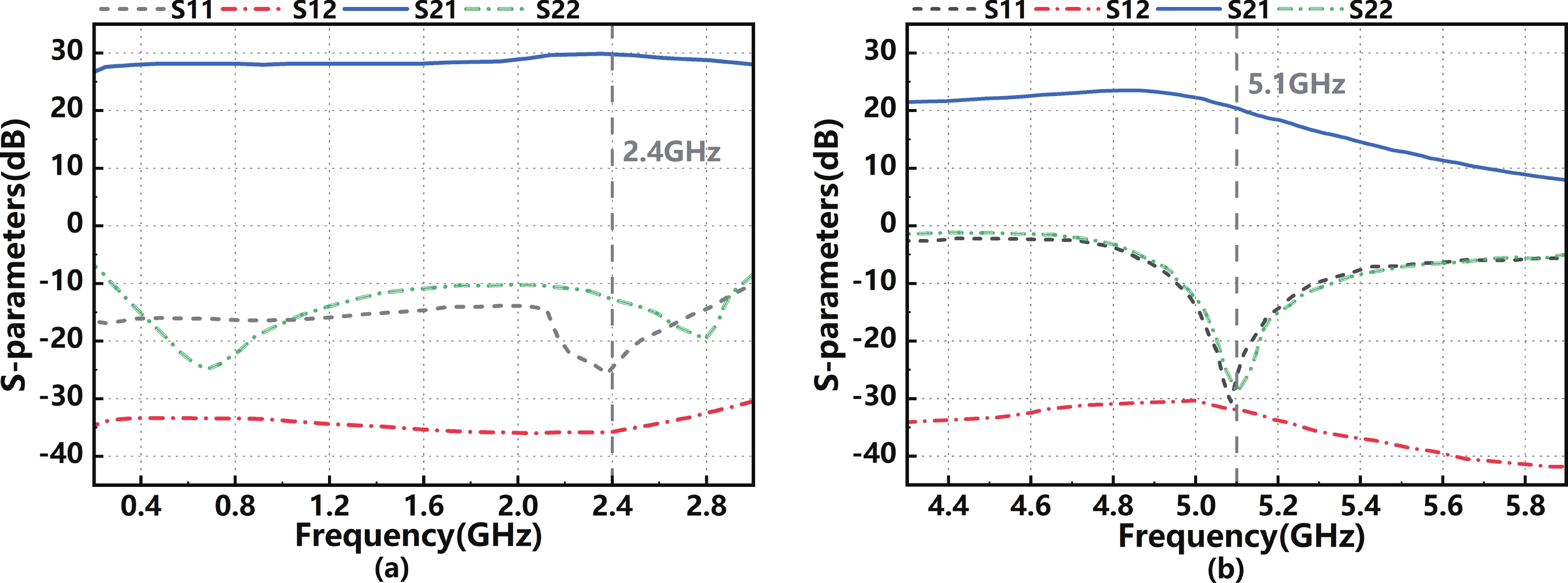
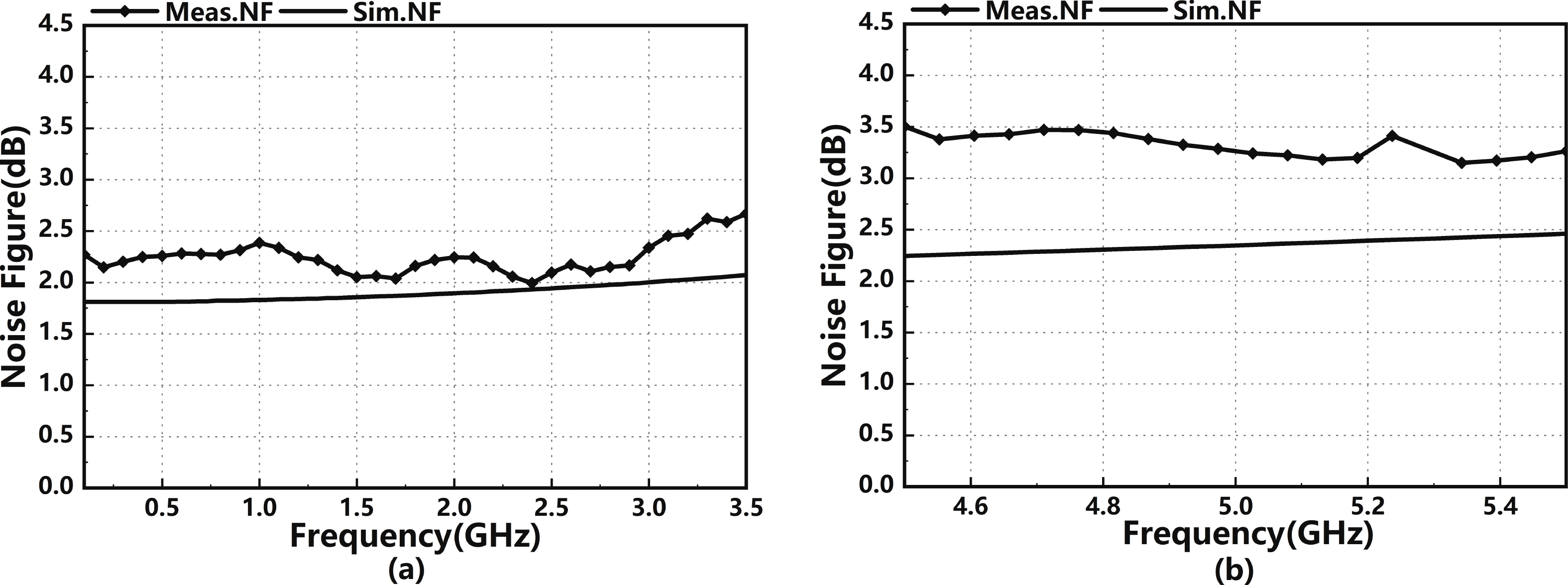
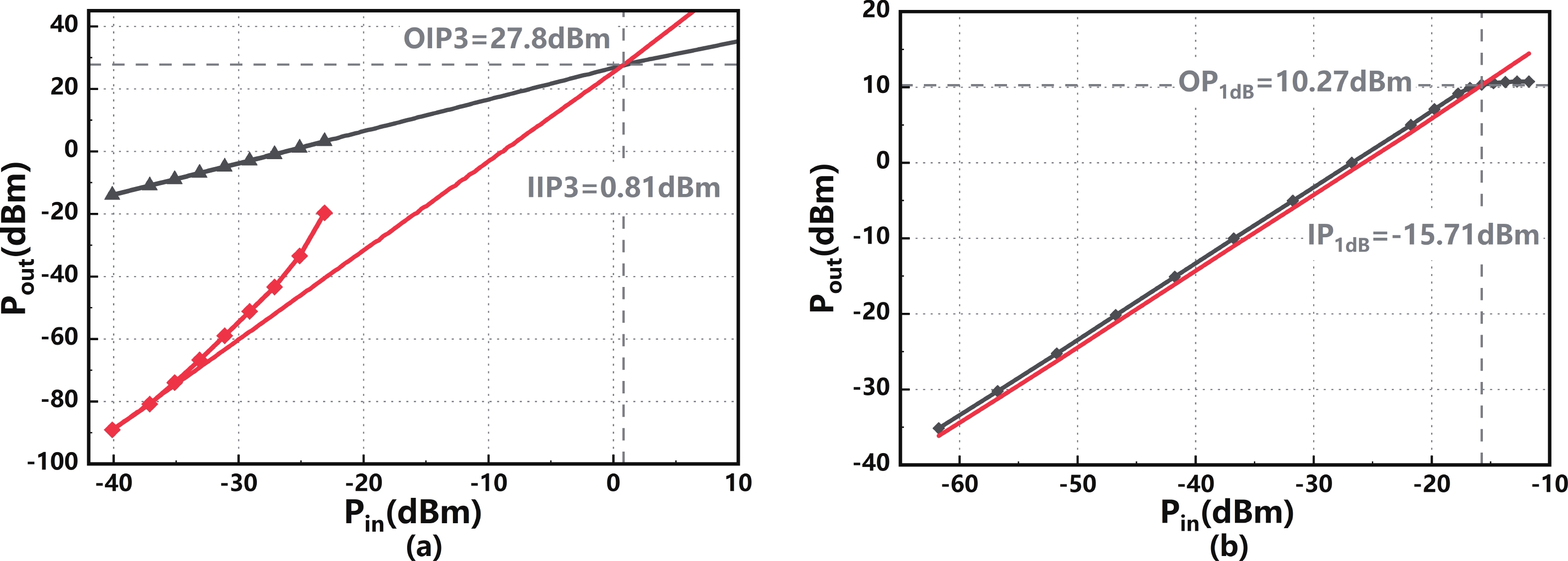
In this paper, a high-gain inductorless LNA (low-noise amplifier) compatible with multiple communication protocols from 0.1 to 5.1 GHz is proposed. A composite resistor−capacitor feedback structure is employed to achieve a wide bandwidth matching range and good gain flatness. A second stage with a Darlington pair is used to increase the overall gain of the amplifier, while the gain of the first stage is reduced to reduce the overall noise. The amplifier is based on a 0.25 μm SiGe BiCMOS process, and thanks to the inductorless circuit structure, the core circuit area is only 0.03 mm2. Test results show that the lowest noise figure (NF) in the operating band is 1.99 dB, the power gain reaches 29.7 dB, the S11 and S22 are less than −10 dB, the S12 is less than −30 dB, the IIP3 is 0.81dBm, and the OP1dB is 10.27 dBm. The operating current is 31.18 mA at 3.8 V supply.-
Keywords:
- SiGe BiCMOS,
- low noise amplifier,
- wideband,
- inductorless,
- integrated circuits
-
References
[1] Kaczman D, Shah M, Alam M, et al. A single–chip 10-band WCDMA/HSDPA 4-band GSM/EDGE SAW-less CMOS receiver with DigRF 3G interface and +90 dBm IIP2. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2009, 44(3), 718 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2009.2013762[2] Chen R, Hashemi H. Dual-carrier aggregation receiver with reconfigurable front-end RF signal conditioning. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2015, 50(8), 1874 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2414430[3] Shaheen R A, Rahkonen T, Pärssinen A. Millimeter-wave frequency reconfigurable low noise amplifiers for 5G. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs, 2021, 68(2), 642 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2020.3014571[4] Aravinth Kumar A R, Dutta A, Sahoo B D. A low-power reconfigurable narrowband/wideband LNA for cognitive radio-wireless sensor network. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr VLSI Syst, 2020, 28(1), 212 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2019.2939708[5] Li J J, Zhang Y M, Wei Z N, et al. A high-gain wideband balun-LNA with multiple noise-optimized technique. AEU Int J Electron Commun, 2024, 175, 155117 doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2024.155117[6] Deng H, Feng H G, Zhang N. A 0.03-3GHz wideband inductorless receiver in 65nm CMOS. 2021 4th International Conference on Circuits, Systems and Simulation (ICCSS), 2021, 11 doi: 10.1109/ICCSS51193.2021.9464186[7] Deng H, Feng H G, Zhang N. A 0.03-3GHz inductorless wideband low noise amplifier in 65nm CMOS. 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET), 2020, 79 doi: 10.1109/ICET49382.2020.9119683[8] Welch R, Jenkins T, Neidhard B, et al. Low noise hybrid amplifier using AlGaN/GaN power HEMT devices. GaAs IC Symposium. IEEE Gallium Arsenide Integrated Circuit Symposium. 23rd Annual Technical Digest 2001, 2001, 153 doi: 10.1109/GAAS.2001.964367[9] Panda S R, Fregonese S, Chakravorty A, et al. SiGe-based nanowire HBT for THz applications. 2023 7th IEEE Electron Devices Technology & Manufacturing Conference (EDTM), 2023, 1 doi: 10.1109/EDTM55494.2023.10103008[10] Razavi B, Microelectronics R F. Prentice Hall. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 1998, 7458[11] Li G J, Xu Y X. Design of high-gain and wide-band SiGe HBT low noise amplifier. Semicond Technol, 2013, 38(4), 259 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-353x.2013.04.004[12] Shen P, Zhang W R, Xie H Y, et al. An ultra-wideband Darlington low noise amplifier design based on SiGe HBT. 2008 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, 2008, 1372 doi: 10.1109/ICMMT.2008.4540696[13] Shen P, Zhang W R, Jin D Y, et al. Design and fabrication of SiGe HBT low noise amplifier. J Electron Inf Technol, 2010, 32(8), 2028 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01016[14] Huang Y W, Zhang W R, Xie H Y, et al. Design of an inductorless ultra-wideband low noise amplifier. Microelectronics, 2009, 39(6), 807 (in Chinese)[15] El-Gharniti O, Kerherve E, Begueret J B, et al. 3~5-GHz SiGe UWB LNA using on-chip transformer for broadband matching. 2006 Proceedings of the 32nd European Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2006, 255 doi: 10.1109/ESSCIR.2006.307579[16] Li Z R, Duan Y M, Li Z, et al. A 0.3–6 GHz noise and distortion cancelling LNA achieving an NF of 2.8±0.3 dB in 0.18-μm SiGe BiCMOS process. Microelectron J, 2020, 105, 104904 doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2020.104904[17] Luo Y B, Shi J, Ma C Y, et al. A high linearity SiGe HBT LNA for GPS receiver. J Semicond, 2014, 35(4), 96 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/045001[18] Tarighat A P. Ultra-low power inductorless differential LNA for WSN application. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process, 2021, 108(2), 409 doi: 10.1007/s10470-021-01892-1[19] Huynh P B T, Kim J H, Yun T Y. Dual-resistive feedback wideband LNA for noise cancellation and robust linearization. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2022, 70(4), 2224 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3139331[20] Zhou R, Liu S B, Liu J Y, et al. A 0.1–3.5-GHz inductorless noise-canceling CMOS LNA with IIP3 optimization technique. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2022, 70(6), 3234 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2022.3161279[21] Yu H H, Chen Y, Boon C C, et al. A 0.044-mm2 0.5-to-7-GHz resistor-plus-source-follower-feedback noise-cancelling LNA achieving a flat NF of 3.3±0.45 dB. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs, 2019, 66(1), 71 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2018.2833553 -
Proportional views




 Zhouhao Zhao received his B.S. degree from Northeastern University in 2023 and is currently a M.S. student at Tsinghua University under the supervision of Associate Prof. Haigang Feng. His research interests include transceiver signal link and timing circuit integrated circuit design.
Zhouhao Zhao received his B.S. degree from Northeastern University in 2023 and is currently a M.S. student at Tsinghua University under the supervision of Associate Prof. Haigang Feng. His research interests include transceiver signal link and timing circuit integrated circuit design. Haigang Feng (S’99-M’05) received the B.S. degree from Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, in 1998, and the Ph.D. degree in Electrical and Computer Engineering from Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, IL, USA, in 2005. He is currently an associate Professor with the Division of data and Information Science, Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University, since 2014. Dr. Feng has numerous contribution in journals and conference papers, as well as patents. His research interests include IOT system, low power, RFA/MM design, EM compatibility and ESD protection.
Haigang Feng (S’99-M’05) received the B.S. degree from Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, in 1998, and the Ph.D. degree in Electrical and Computer Engineering from Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, IL, USA, in 2005. He is currently an associate Professor with the Division of data and Information Science, Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University, since 2014. Dr. Feng has numerous contribution in journals and conference papers, as well as patents. His research interests include IOT system, low power, RFA/MM design, EM compatibility and ESD protection.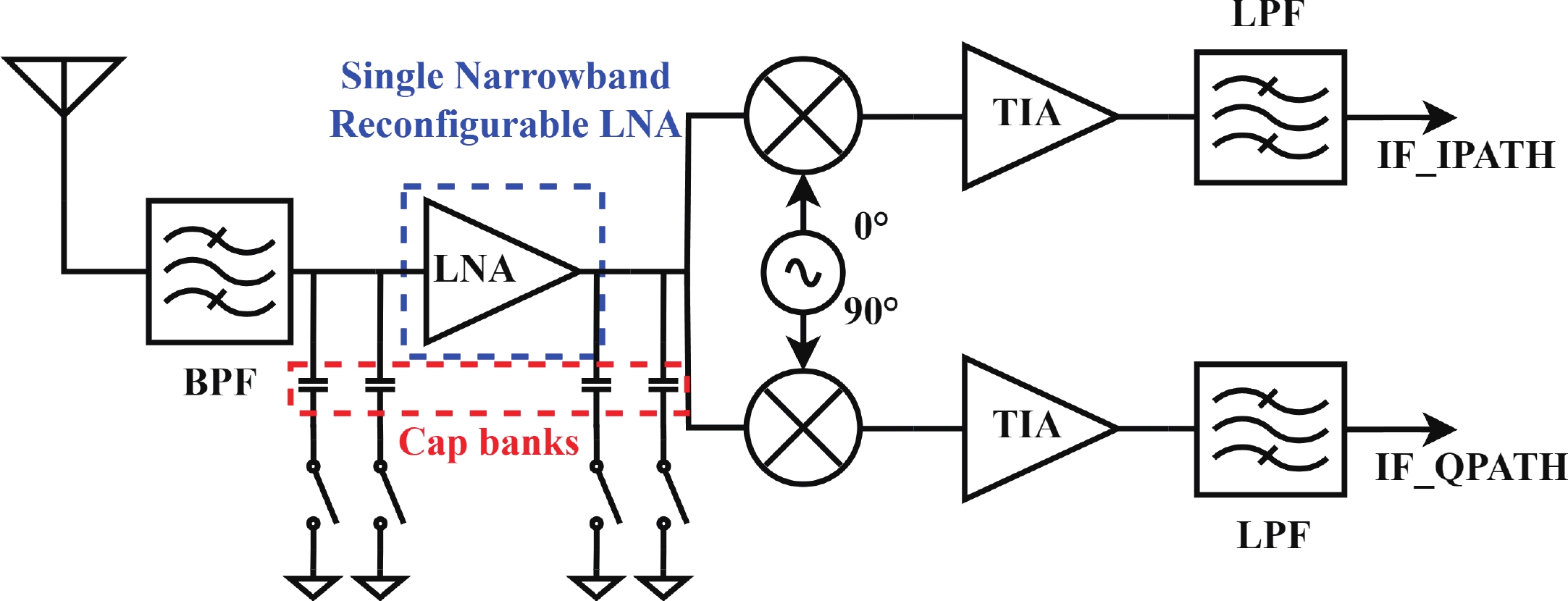
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: