| Citation: |
Yupeng Yuan, Yi Zhuo, Jianjun Tu, Qingjiang Xia, Yan Zhang, Wengao Lu, Xiangyang Li, Ding Ma. A cryogenic 3.3-V supply, 1.6% 3σ-accuracy all-CMOS voltage reference with 58-dB PSR@10 kHz in 0.18-μm CMOS[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2025, 46(8): 082201. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24120039
****
Y P Yuan, Y Zhuo, J J Tu, Q J Xia, Y Zhang, W G Lu, X Y Li, and D Ma, A cryogenic 3.3-V supply, 1.6% 3σ-accuracy all-CMOS voltage reference with 58-dB PSR@10 kHz in 0.18-μm CMOS[J]. J. Semicond., 2025, 46(8), 082201 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24120039
|
A cryogenic 3.3-V supply, 1.6% 3σ-accuracy all-CMOS voltage reference with 58-dB PSR@10 kHz in 0.18-μm CMOS
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/24120039
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.24120039
More Information-
Abstract
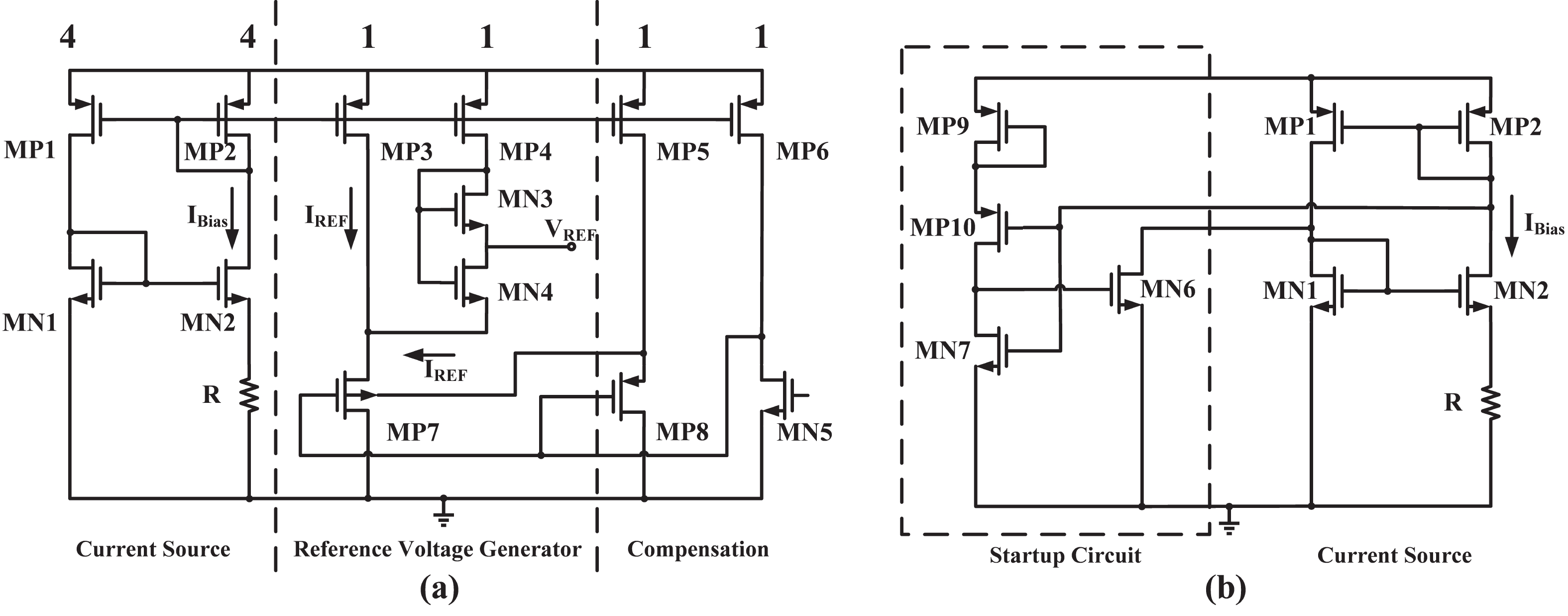
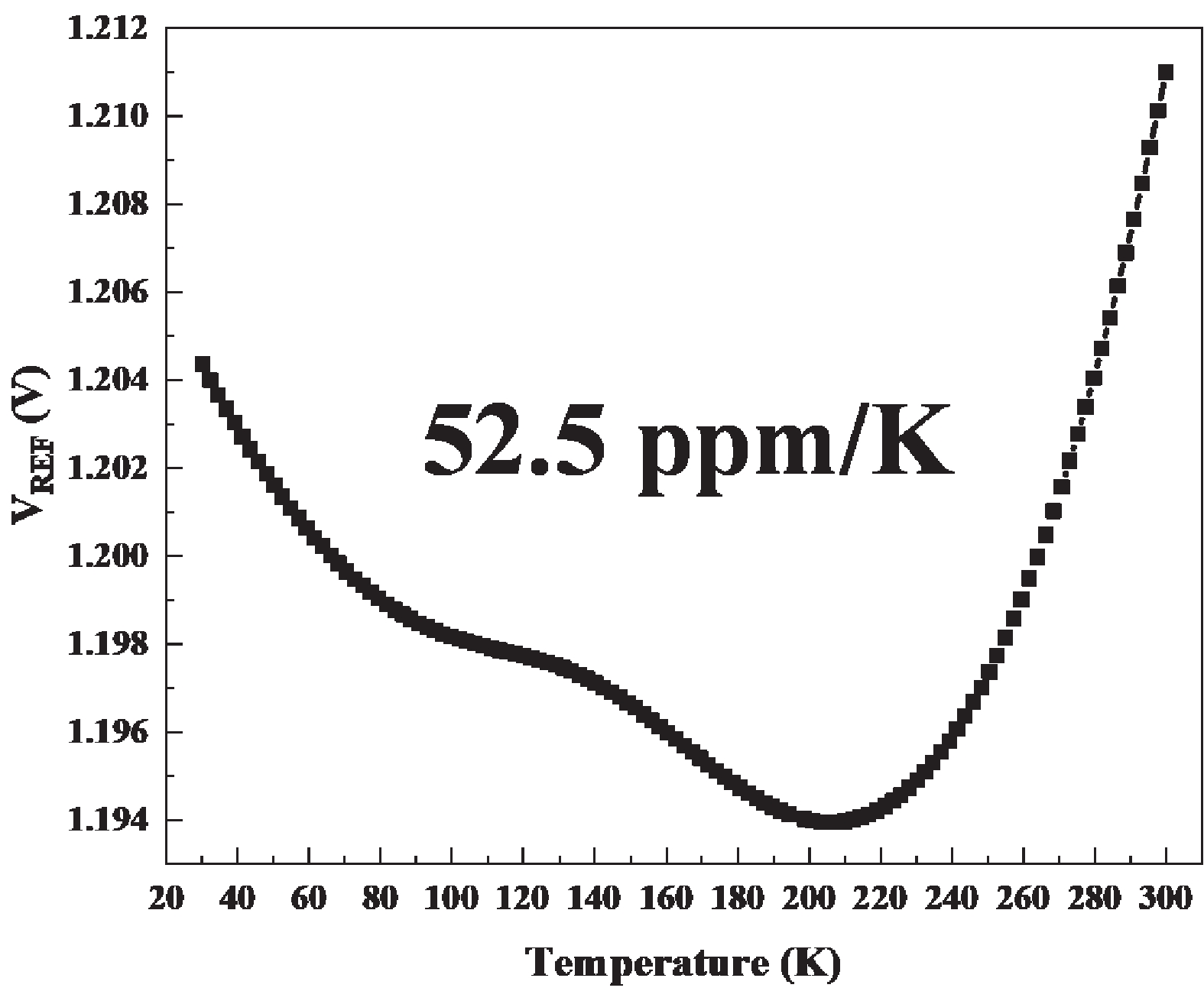
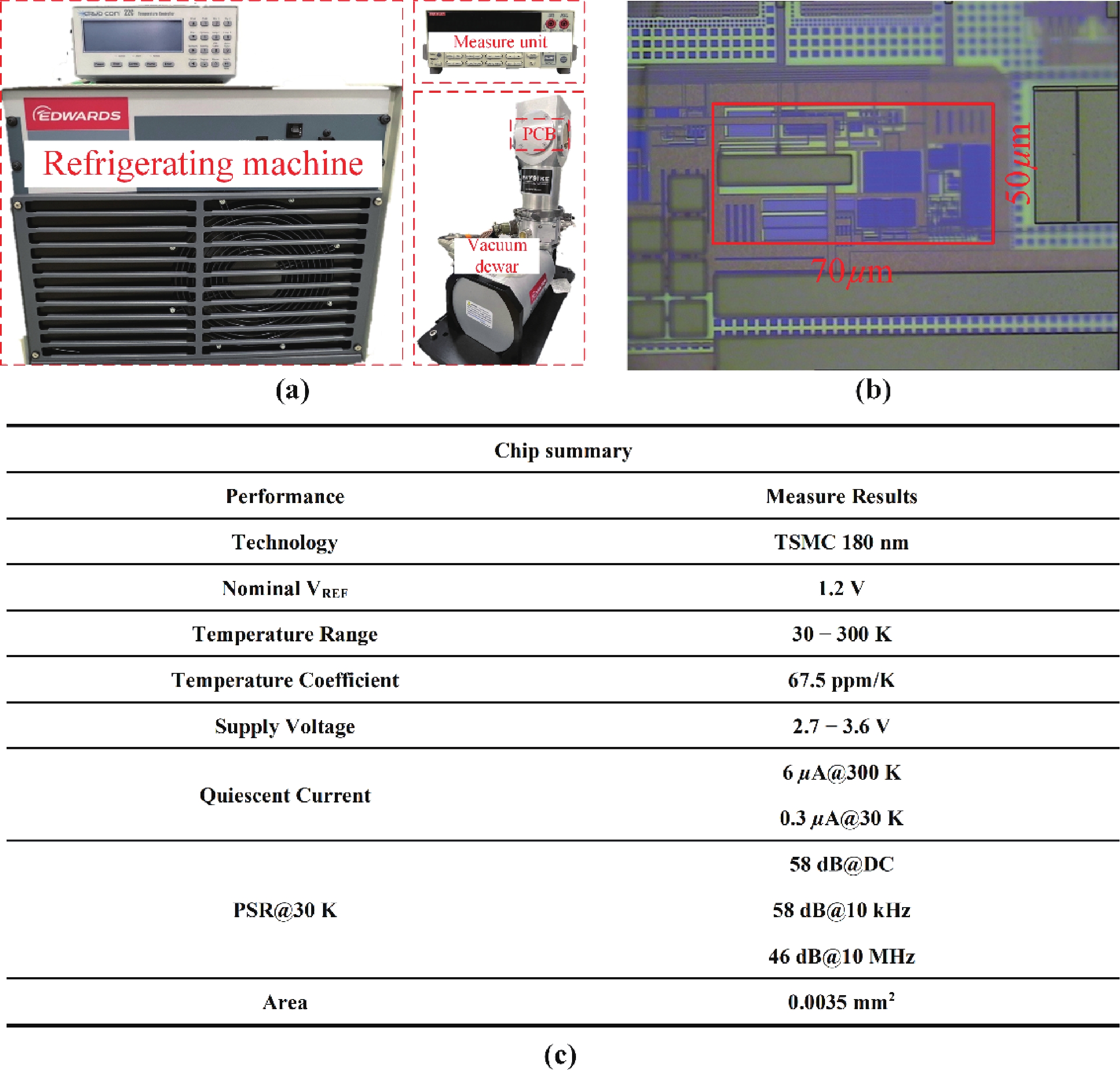
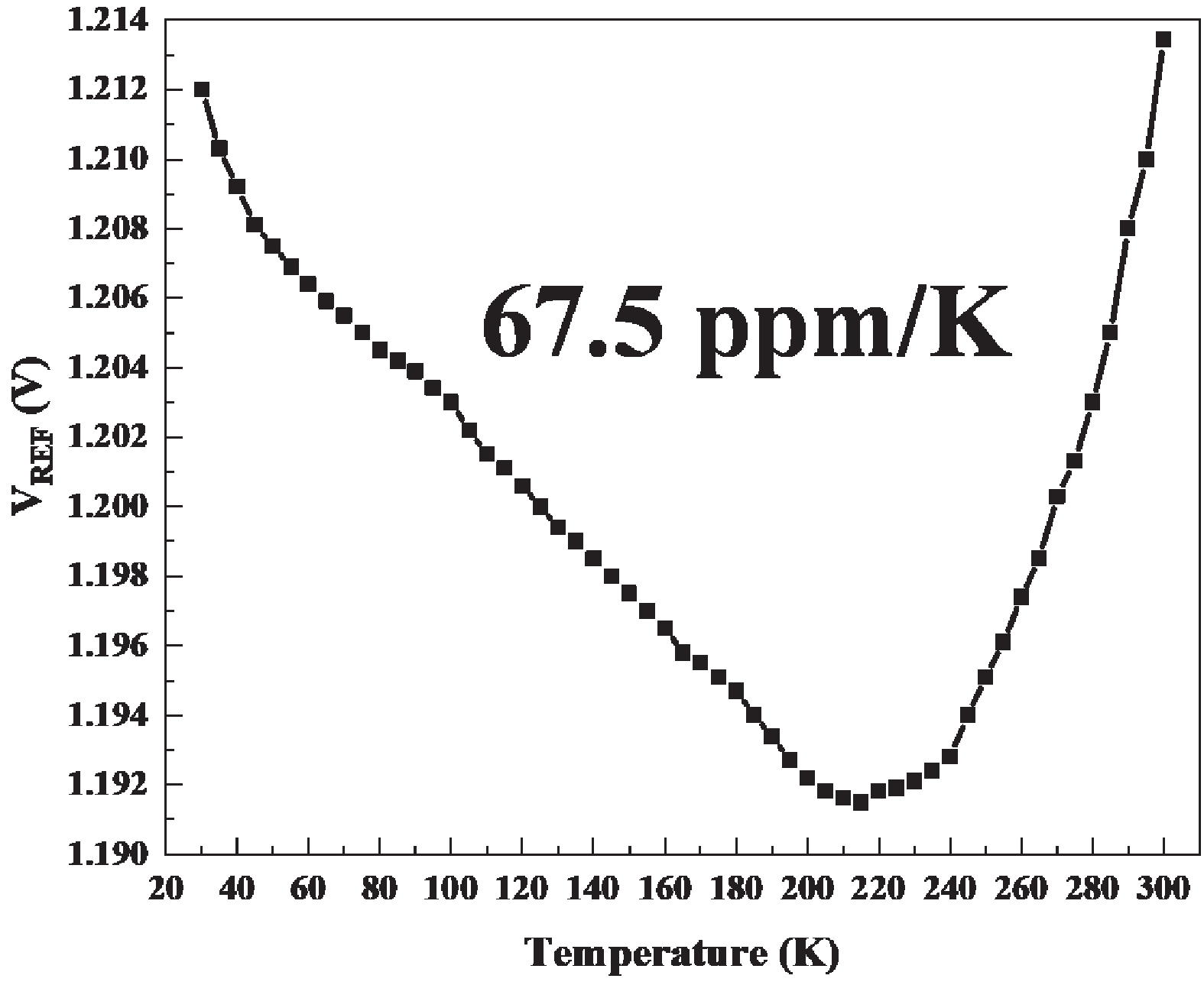
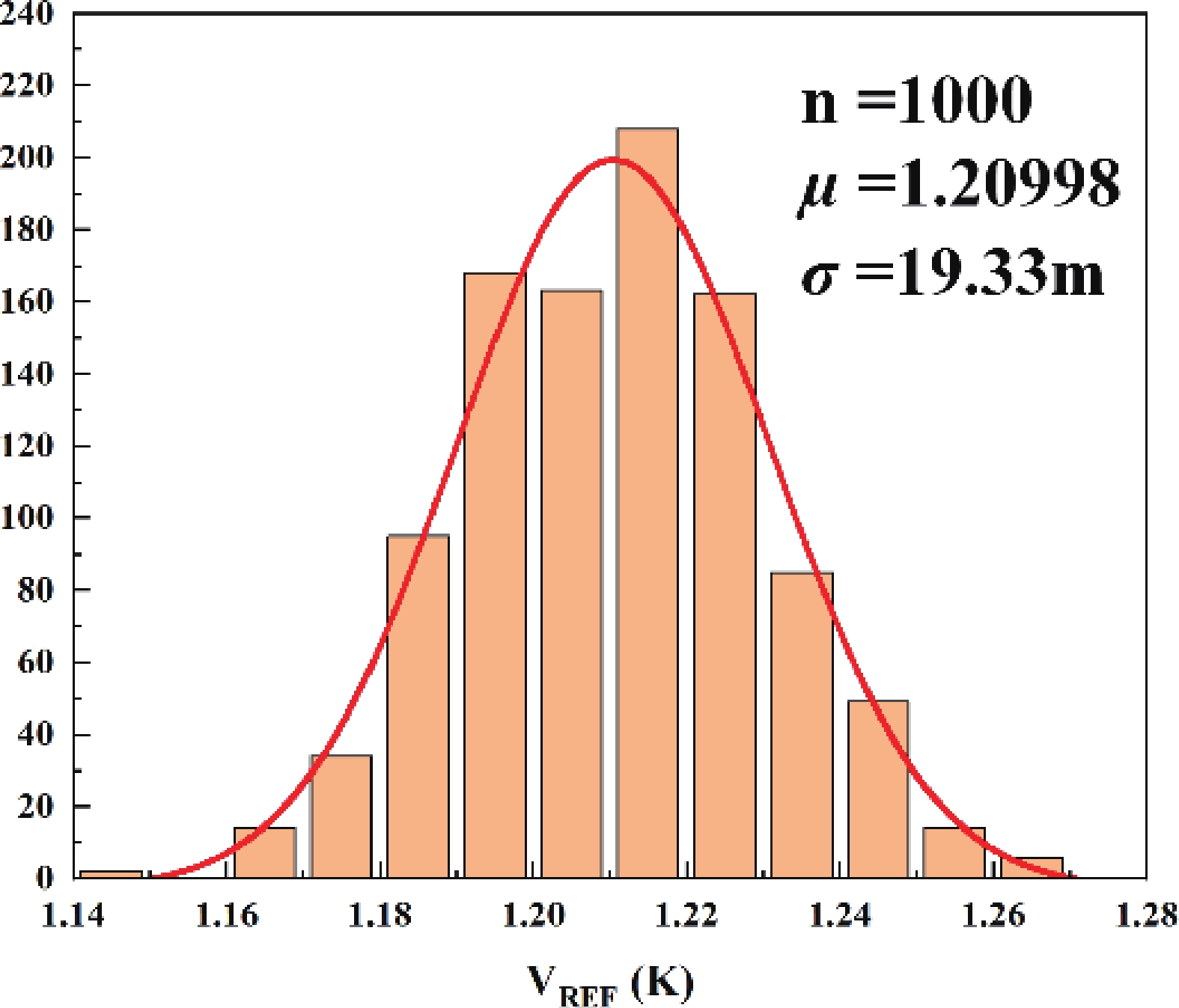
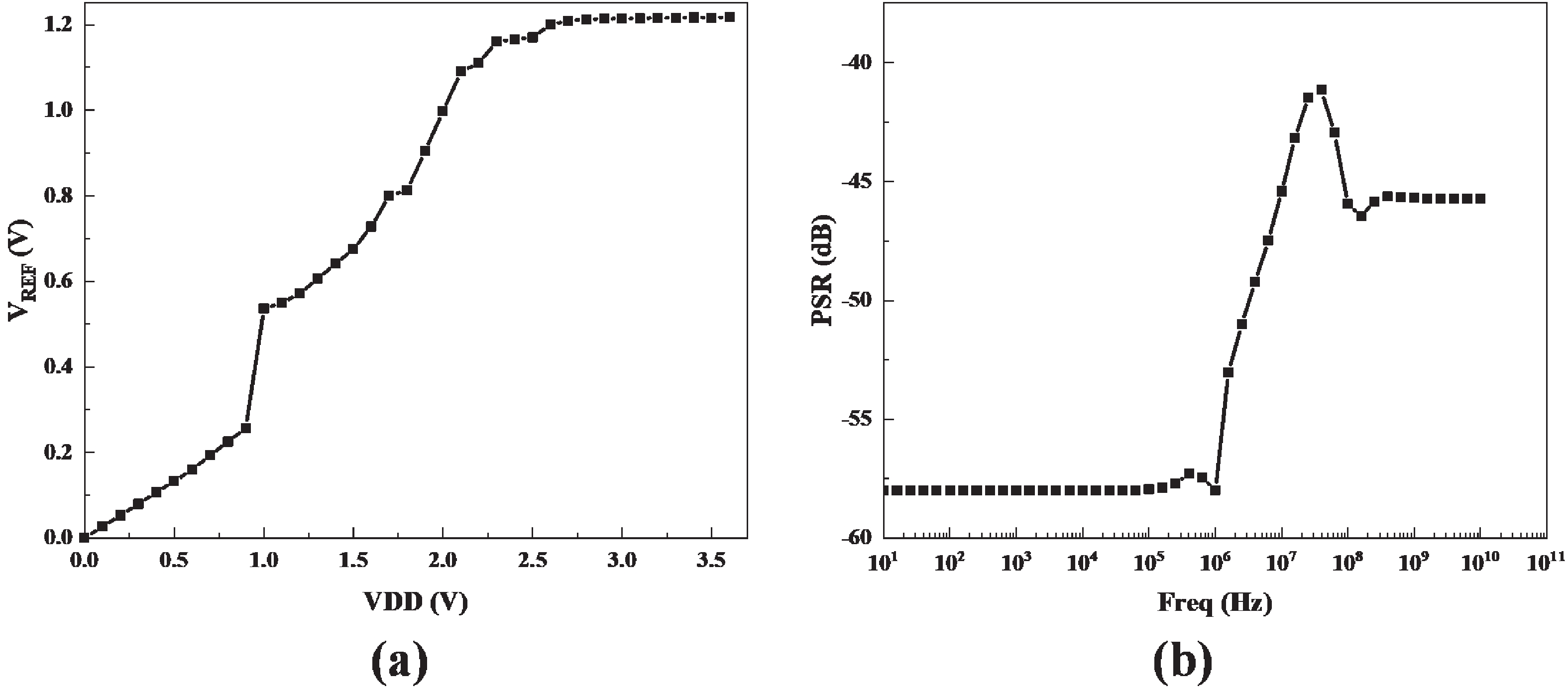
This brief presents a cryogenic voltage reference circuit designed to operate effectively across a wide temperature range from 30 to 300 K. A key feature of the proposed design is utilizing a current subtraction technique for temperature compensation of the reference current, avoiding the deployment of bipolar transistors to reduce area and power consumption. Implemented with a 0.18-µm CMOS process, the circuit achieves a temperature coefficient (TC) of 67.5 ppm/K, which was not achieved in previous works. The design can also attain a power supply rejection (PSR) of 58 dB at 10 kHz. Meanwhile, the average reference voltage is 1.2 V within a 1.6% 3σ-accuracy spread. Additionally, the design is characterized by a minimal power dissipation of 1 µW at 30 K and a compact chip area of 0.0035 mm². -
References
[1] Liao X F, Zhang Y X, Zhang S H, et al. A 3.0 μ vrms, 2.4 ppm/°C BGR with feedback coefficient enhancement and bowl-shaped curvature compensation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap, 2024, 71(5), 2424 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2024.3373788[2] Seok M, Kim G, Blaauw D, et al. A portable 2-transistor picowatt temperature-compensated voltage reference operating at 0.5 V. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2012, 47(10), 2534 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2012.2206683[3] Zhu Z M, Hu J, Wang Y T. A 0.45 V, nano-watt 0.033% line sensitivity MOSFET-only sub-threshold voltage reference with no amplifiers. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap, 2016, 63(9), 1370 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2016.2576643[4] Ji Y W, Lee J H, Kim B S, et al. A 192-pW voltage reference generating bandgap−Vth with process and temperature dependence compensation. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2019, 54(12), 3281 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2942356[5] Wang L D, Zhan C C. A 0.7-V 28-nW CMOS subthreshold voltage and current reference in one simple circuit. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap, 2019, 66(9), 3457 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2019.2927240[6] Song L, Homulle H, Charbon E, et al. Characterization of bipolar transistors for cryogenic temperature sensors in standard CMOS. 2016 IEEE SENSORS, 2016, 1 doi: 10.1109/ICSENS.2016.7808759[7] Deng C, Wu S, Liu C C, et al. A systematic review of voltage reference circuits: Spanning room temperature to cryogenic applications. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap, 2024, 72(4), 1533 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2024.3507783[8] Charbon E. Cryo-CMOS electronics for quantum computing: Bringing classical electronics closer to qubits in space and temperature. IEEE Solid State Circuits Mag, 2021, 13(2), 54 doi: 10.1109/MSSC.2021.3072808[9] Wang Z W, Tang Z D, Guo A, et al. Temperature-driven gate geometry effects in nanoscale cryogenic MOSFETs. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2020, 41(5), 661 doi: 10.1109/LED.2020.2984280[10] van Staveren J, Padalia P M, Charbon E, et al. Cryo-CMOS voltage references for the ultrawide temperature range from 300 K down to 4.2 K. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2024, 59(9), 2884 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2024.3378768[11] Yang Y Y, Das K, Moini A, et al. A cryo-CMOS voltage reference in 28-nm FDSOI. IEEE Solid State Circuits Lett, 2020, 3, 186 doi: 10.1109/LSSC.2020.3010234[12] Loose M, Beletic J, Garnett J, et al. High-performance focal plane arrays based on the HAWAII-2RG/4G and the SIDECAR ASIC. Proc SPIE, 2010, 6690, 124 doi: 10.1117/12.735625[13] Marqués-García J, Pérez-Bailón J, Celma S, et al. Characterization of 65-nm CMOS integrated resistors in the cryogenic regime. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas, 2024, 73, 2003303 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2024.3381286[14] Vittoz E A, Neyroud O. A low-voltage CMOS bandgap reference. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 1979, 14(3), 573 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.1979.1051218[15] Jiang J Z, Shu W, Chang J S. A 5.6 ppm/°C temperature coefficient, 87-dB PSRR, sub-1-V voltage reference in 65-nm CMOS exploiting the zero-temperature-coefficient point. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2017, 52(3), 623 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2016.2627544[16] Ueno K, Hirose T, Asai T, et al. A 300 nW, 15 ppm/℃, 20 ppm/V CMOS voltage reference circuit consisting of subthreshold MOSFETs. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2009, 44(7), 2047 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2009.2021922[17] Cao Y R, Zhuang H Y, Li Q. A 0.8-V supply, 1.58% 3σ-accuracy, 1.9-μW bandgap reference in 0.13-μm CMOS. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs, 2024, 71(4), 1884 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2023.3339236 -
Proportional views




 Yupeng Yuan got his B.S. degree from Hefei University of Technology, he is a master student at ShanghaiTech University and under the supervision of Prof. Xiangyang Li in the National Key Laboratory of Infrared Detection Technologies, Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. His research focuses on low-power circuit design.
Yupeng Yuan got his B.S. degree from Hefei University of Technology, he is a master student at ShanghaiTech University and under the supervision of Prof. Xiangyang Li in the National Key Laboratory of Infrared Detection Technologies, Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. His research focuses on low-power circuit design. Xiangyang Li is a Professor in the National Key Laboratory of Infrared Detection Technologies, Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. He received his Ph.D. degree from Shandong University in 1998. His research interests focus on the semiconductor photodetector of HgCdTe, QWIP, and AlGaN.
Xiangyang Li is a Professor in the National Key Laboratory of Infrared Detection Technologies, Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. He received his Ph.D. degree from Shandong University in 1998. His research interests focus on the semiconductor photodetector of HgCdTe, QWIP, and AlGaN. Ding Ma is an Associate Professor in the National Key Laboratory of Infrared Detection Technologies, Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. He received his Ph.D. degree from Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2018. His research interests focus on readout circuit for high dynamic range.
Ding Ma is an Associate Professor in the National Key Laboratory of Infrared Detection Technologies, Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. He received his Ph.D. degree from Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2018. His research interests focus on readout circuit for high dynamic range.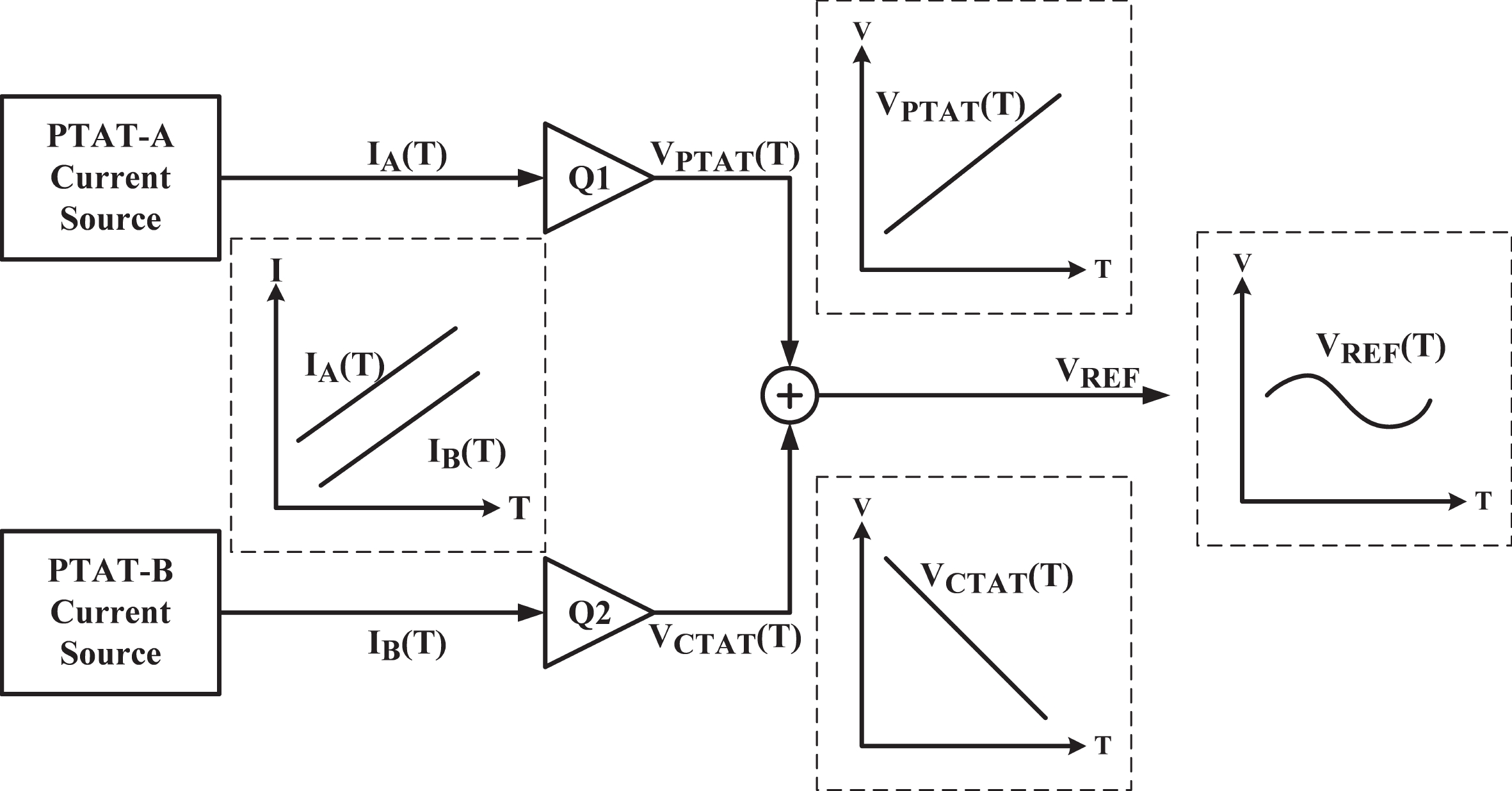
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: