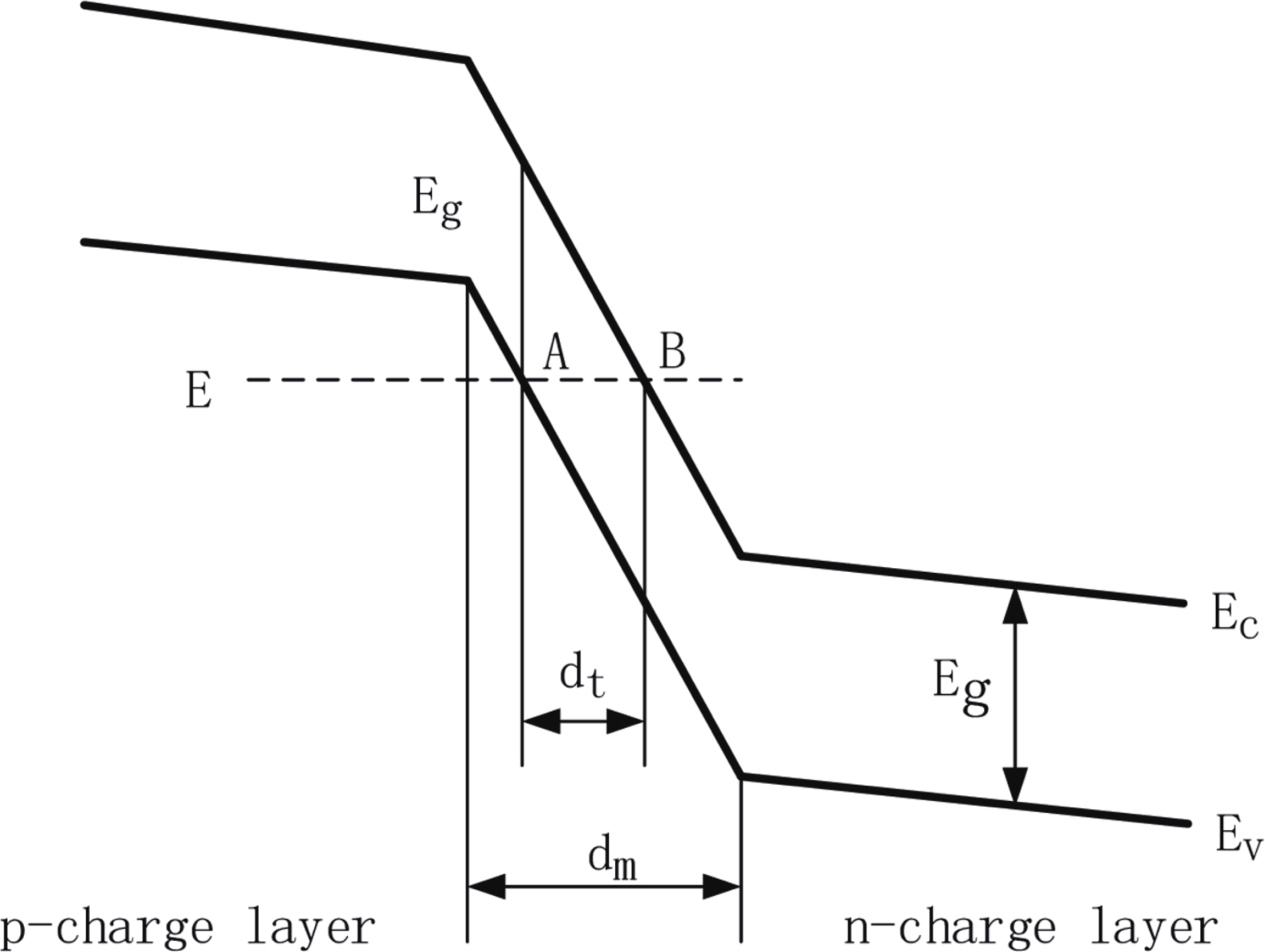
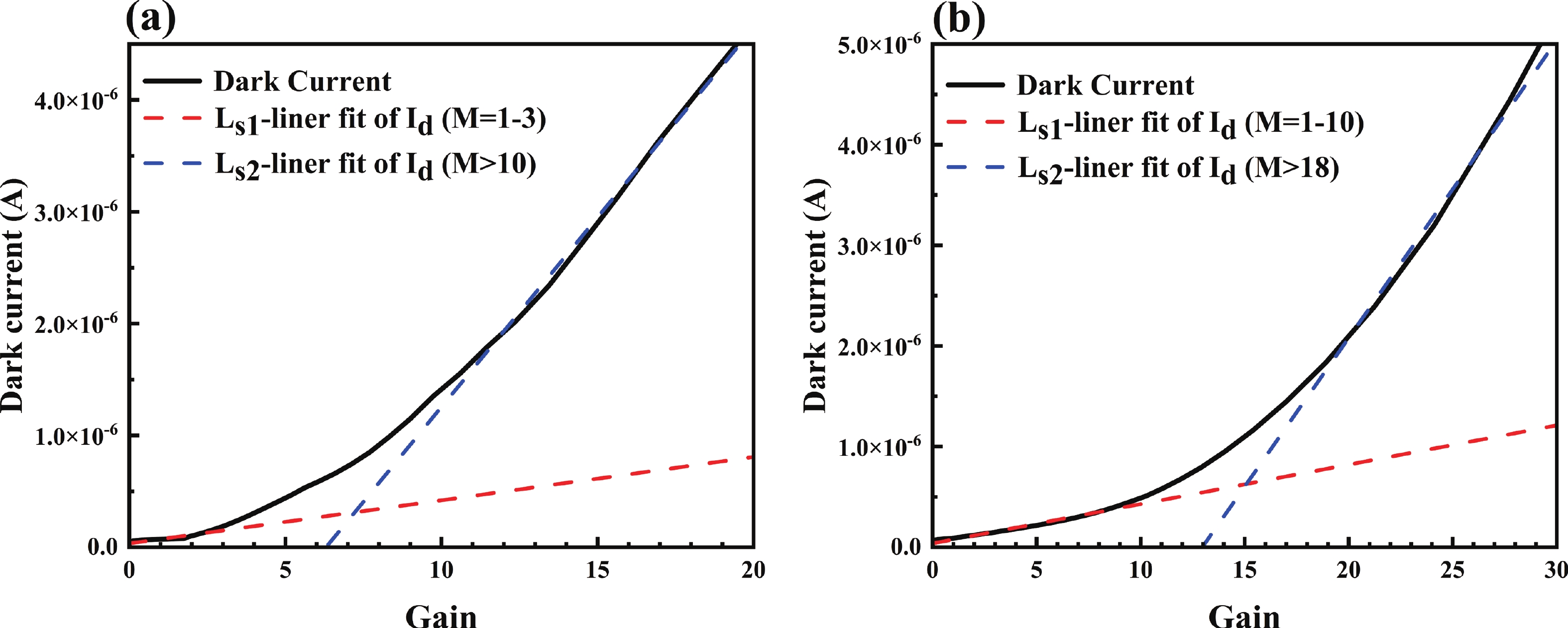
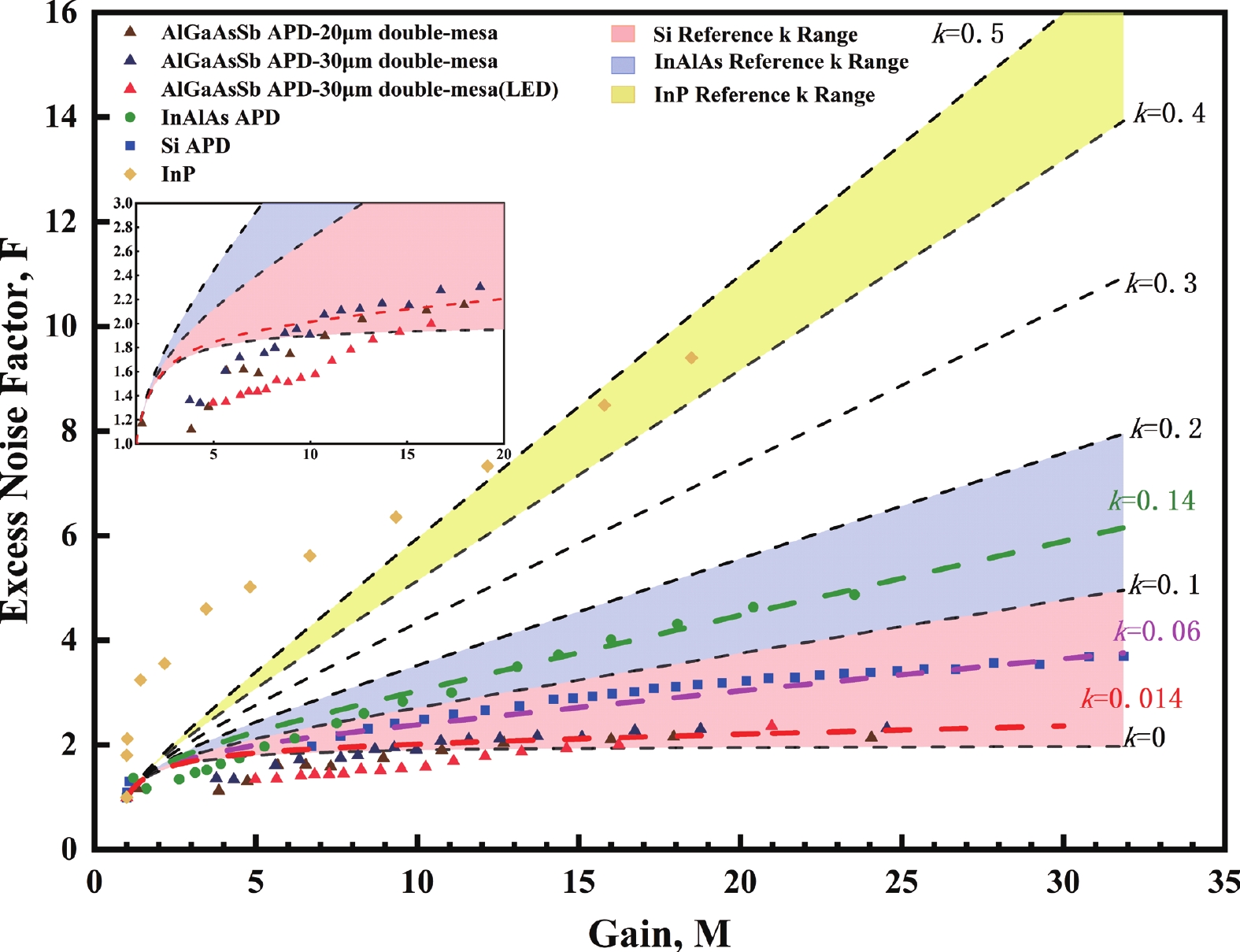
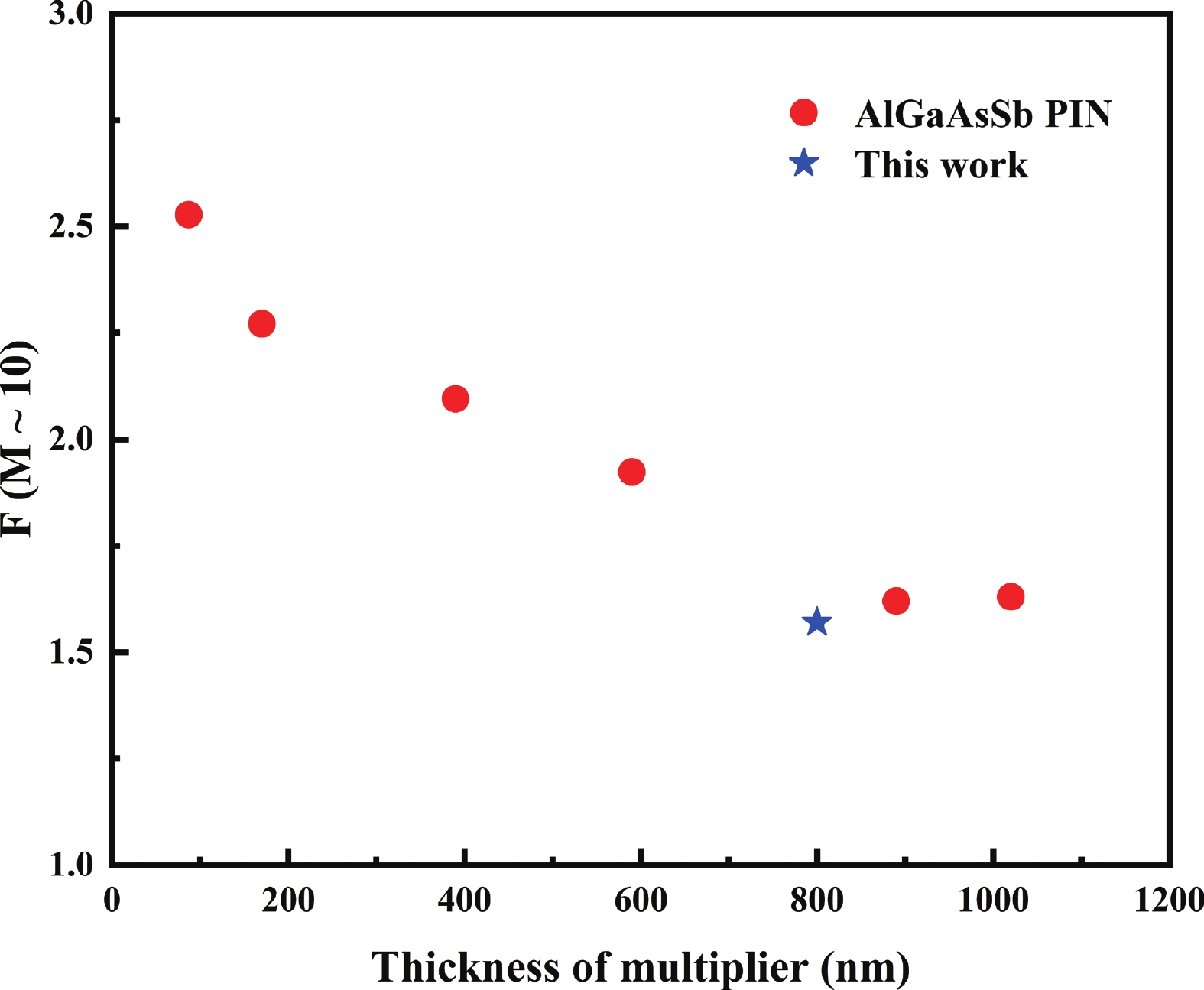
| Citation: |
Yuhang He, Rui Wang, Yan Liang, Yingqiang Xu, Guowei Wang, Haiqiao Ni, Shuo Wang, Zhichuan Niu, Xiaohong Yang. Mesa-structured AlGaAsSb APD: dark current and noise analysis[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2025, In Press. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25020025
****
Y H He, R Wang, Y Liang, Y Q Xu, G W Wang, H Q Ni, S Wang, Z C Niu, and X H Yang, Mesa-structured AlGaAsSb APD: dark current and noise analysis[J]. J. Semicond., 2025, 46(11), 112401 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25020025
|
Mesa-structured AlGaAsSb APD: dark current and noise analysis
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/25020025
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.25020025
More Information-
Abstract
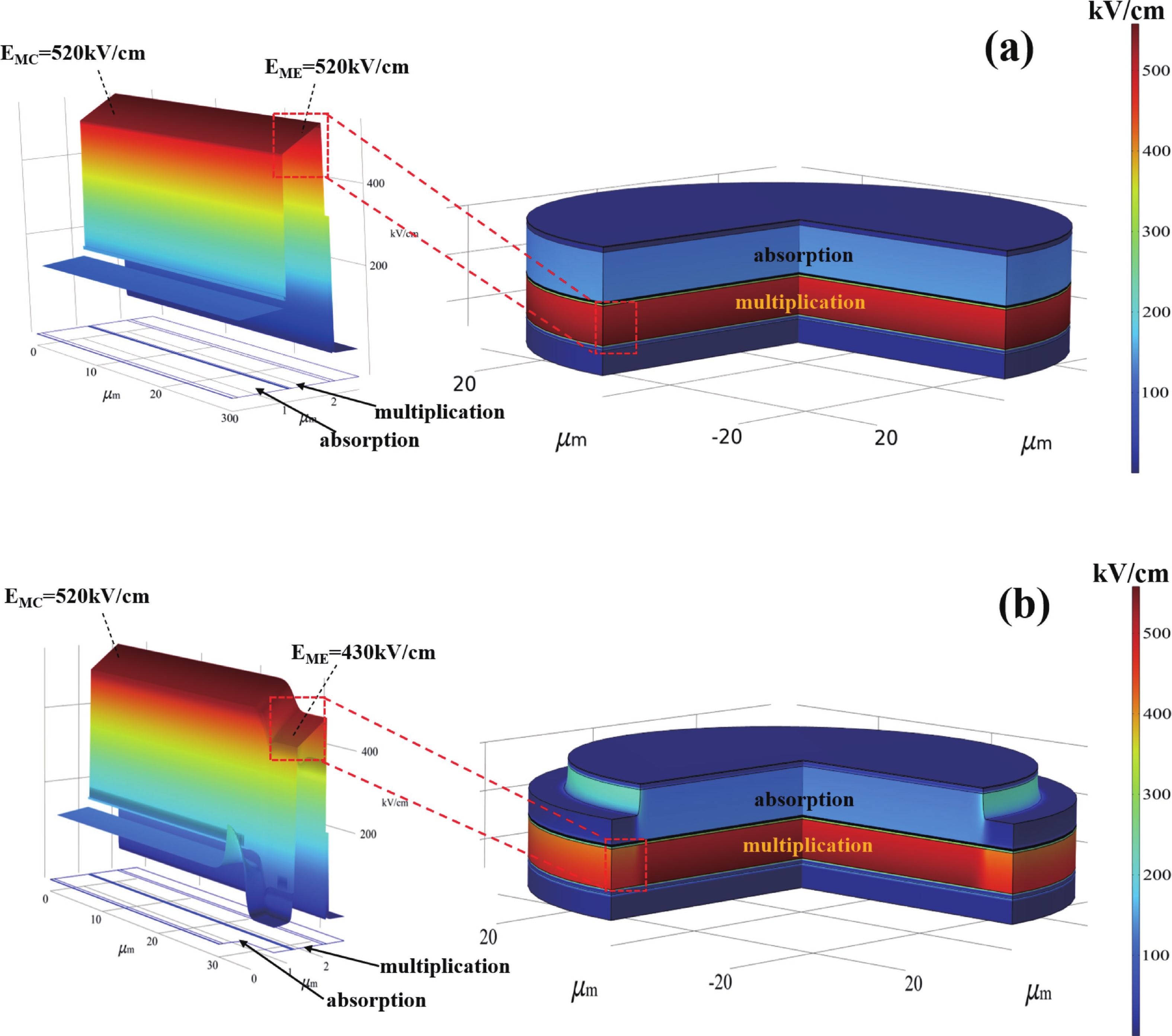
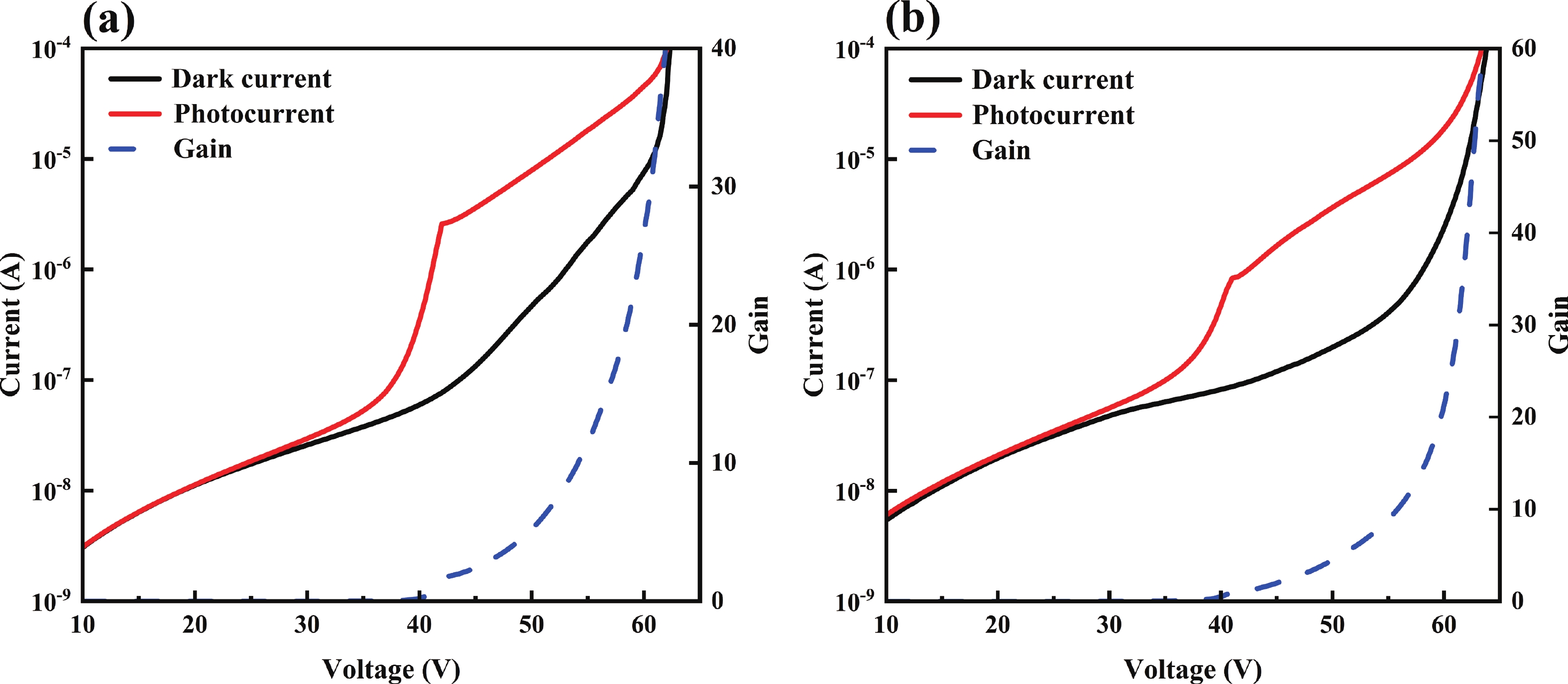
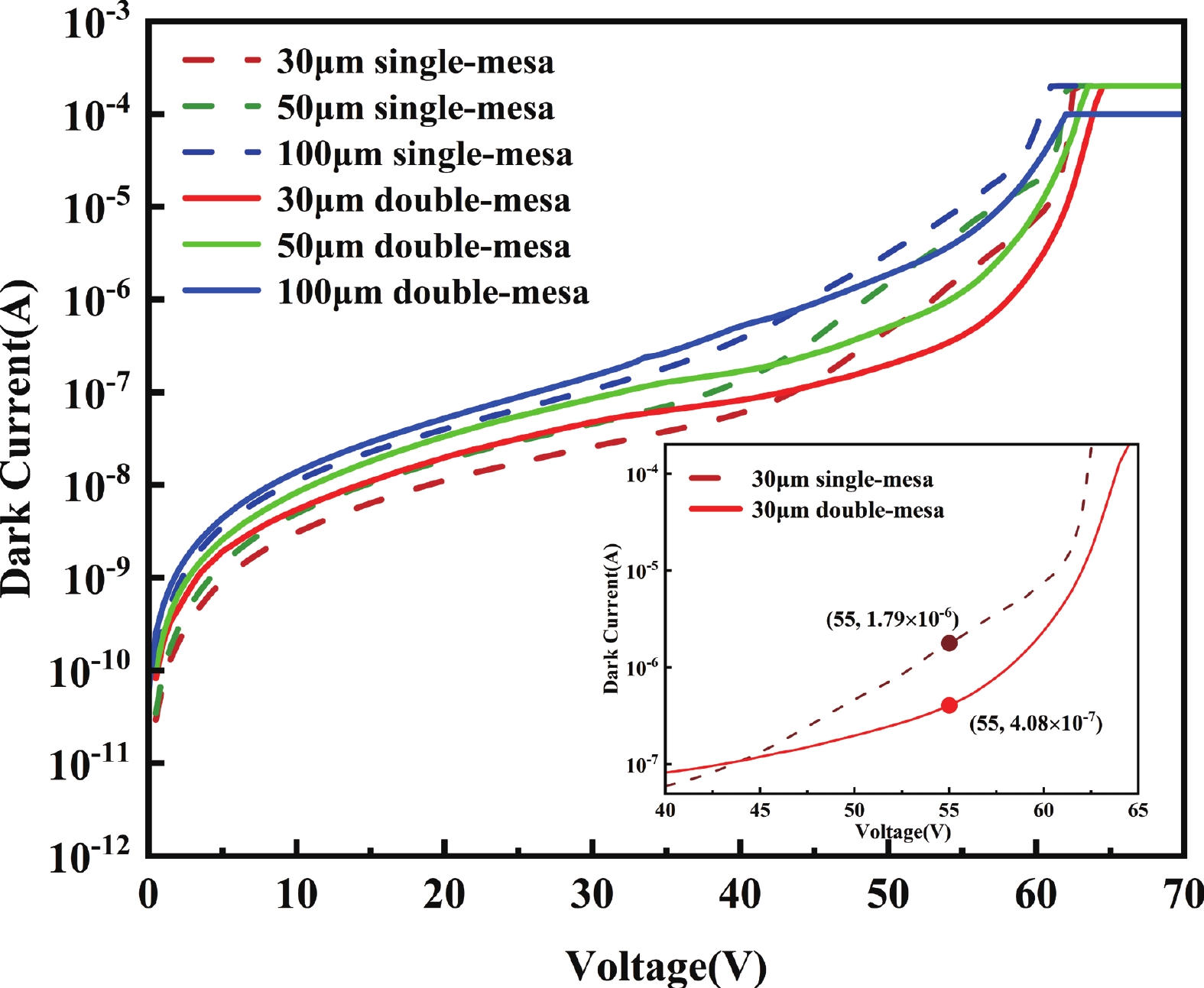
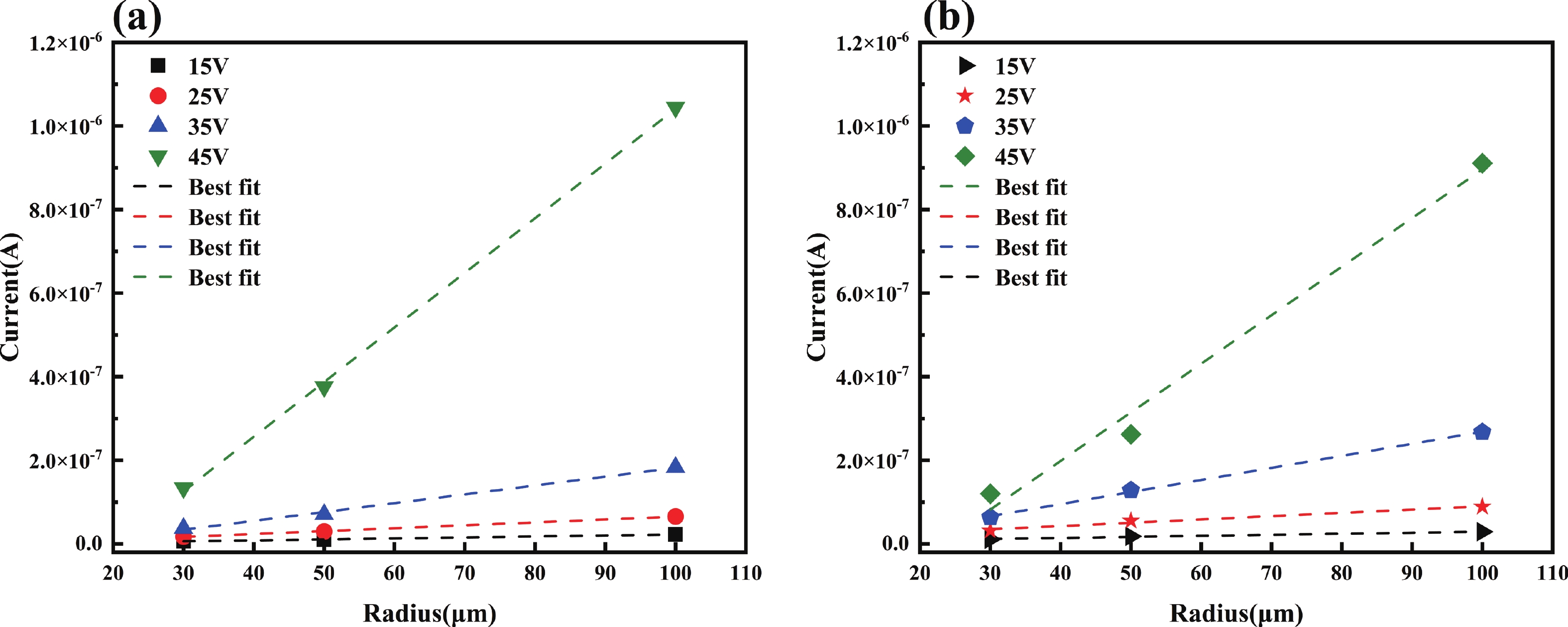
Avalanche photodiode (APD) is a kind of photodetector with important applications in optical communication, LIDAR and other fields. APDs fabricated using the recently developed AlGaAsSb as the multiplication material exhibit excellent noise performance. In this work, we report a low-noise separate absorption, grading, charge, and multiplication (SAGCM) InGaAs/AlGaAsSb APD operating at 1550 nm. A double-mesa structure was fabricated to reduce the dark current. Numerical simulations were conducted to compare two different mesa-structured APDs. By analyzing the electric field distribution, it was found that the electric field at the edge of the multiplication region in the double-mesa APD is nearly 100 kV/cm lower than that of the single-mesa structure. Experimental results demonstrate that after device punch-through, the double-mesa APD’s dark current can be reduced by up to four times compared to the single-mesa APD. Quantitative analysis of the dark current components in the AlGaAsSb APD further confirms that the low sidewall electric field in the double-mesa structure effectively suppresses the trap-assisted tunneling. Additionally, noise measurements indicate a k-value of approximately 0.014, which is significantly lower than that of traditional multiplication materials. This work provides preliminary validation for further performance improvements in low noise and low dark current AlGaAsSb APDs.-
Keywords:
- avalanche photodiode,
- dark current,
- excess noise
-
References
[1] Aina L. True 3D, angle resolved, ultrasensitive IR laser sensor for autonomous vehicles. Infrared Technology and Applications XLV, 2019, 110021G[2] Ara I, Fairooz S, Islam A K M N. Effect of scintillation on an optical M-ary PPM over FSO turbulent channel with pointing error using APD receiver. 2018 4th International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information & Communication Technology (iCEEiCT), 2018, 210[3] Refaat T F, Petros M, Remus R, et al. MCT APD detection system for atmospheric profiling applications using two-micron lidar. EPJ Web Conf, 2020, 237, 01013 doi: 10.1051/epjconf/202023701013[4] Yi X, Xie S Y, Liang B L, et al. Extremely low excess noise and high sensitivity AlAs0.56Sb0.44 avalanche photodiodes. Nat Photonics, 2019, 13(10), 683 doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0477-4[5] Ren M, Maddox S J, Woodson M E, et al. Characteristics of AlxIn1−xAsySb1−y (x: 0.3–0.7) avalanche photodiodes. J Lightwave Technol, 2017, 35(12), 2380 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2017.2681041[6] Jones A H, March S D, Bank S R, et al. Low-noise high-temperature AlInAsSb/GaSb avalanche photodiodes for 2-μm applications. Nat Photonics, 2020, 14(9), 559 doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-0637-6[7] Guo B T, Schwartz M, Kodati S H, et al. InGaAs/AlInAsSb avalanche photodiodes with low noise and strong temperature stability. APL Photonics, 2023, 8(11), 116112 doi: 10.1063/5.0168134[8] Jung H, Lee S, Jin X, et al. Low excess noise and high quantum efficiency avalanche photodiodes for beyond 2 µm wavelength detection. Commun Mater, 2024, 5(1), 219 doi: 10.1038/s43246-024-00627-9[9] Collins X, White B, Cao Y, et al. Low-noise AlGaAsSb avalanche photodiodes for 1550nm light detection. Optical Components and Materials XIX, 2022, 1199709[10] Collins X, Sheridan B, Price D, et al. Low-noise AlGaAsSb avalanche photodiodes for 1550 nm light detection. Optical Components and Materials XX, 2023, 124170K[11] Sheridan B, Collins X, Taylor-Mew J, et al. An extremely low noise-equivalent power photoreceiver using high-gain InGaAs/AlGaAsSb APDs. J Light Technol, 2025, 43(2), 741 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2024.3447284[12] Lee S, Jin X, Jung H, et al. High gain, low noise 1550 nm GaAsSb/AlGaAsSb avalanche photodiodes. Optica, 2023, 10(2), 147 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.476963[13] Cao Y, Blain T, Taylor-Mew J D, et al. Extremely low excess noise avalanche photodiode with GaAsSb absorption region and AlGaAsSb avalanche region. Appl Phys Lett, 2023, 122(5), 051103 doi: 10.1063/5.0139495[14] Cao Y, Blain T, Li L, et al. GaAsSb/AlGaAsSb avalanche photodiode with high gain-linearity. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2024, 71(10), 6161 doi: 10.1109/TED.2024.3440279[15] Xie S Y, Zhou X X, Zhang S Y, et al. InGaAs/AlGaAsSb avalanche photodiode with high gain-bandwidth product. Opt Express, 2016, 24(21), 24242 doi: 10.1364/OE.24.024242[16] Zhou X, Zhang S, David J P R, et al. Avalanche breakdown characteristics of Al1–xGaxAs0.56Sb0.44 quaternary alloys. IEEE Photon Technol Lett, 2016, 28(22), 2495 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2016.2601651[17] Pinel L L G, Dimler S J, Zhou X X, et al. Effects of carrier injection profile on low noise thin Al0.85Ga0.15As0.56Sb0.44 avalanche photodiodes. Opt Express, 2018, 26(3), 3568 doi: 10.1364/OE.26.003568[18] Zhou X X, Pinel L L G, Dimler S J, et al. Thin Al1−xGaxAs0.56Sb0.44 diodes with low excess noise. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron, 2017, 24(2), 1[19] Lee S, Kodati S H, Guo B, et al. Low noise Al0.85Ga0.15As0.56Sb0.44 avalanche photodiodes on InP substrates. Appl Phys Lett, 2021, 118(8), 081106 doi: 10.1063/5.0035571[20] Taylor-Mew J, Shulyak V, White B, et al. Low excess noise of Al0.85Ga0.15As0.56Sb0.44 avalanche photodiode from pure electron injection. IEEE Photon Technol Lett, 2021, 33(20), 1155 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2021.3110123[21] Lee S, Guo B, Kodati S H, et al. Random alloy thick AlGaAsSb avalanche photodiodes on InP substrates. Appl Phys Lett, 2022, 120(7), 071101 doi: 10.1063/5.0067408[22] Guo B T, Jin X, Lee S, et al. Impact ionization coefficients of digital alloy and random alloy Al0.85Ga0.15As0.56Sb0.44 in a wide electric field range. J Lightwave Technol, 2022, 40(14), 4758 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2022.3169008[23] Krishna S, Lee S, Kodati S H, et al. Linear mode avalanche photodiodes with antimonide multipliers on InP substrates. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 2022, 58(4), 1[24] Wang H, Yang X H, Wang R, et al. Low dark current and high gain-bandwidth product of avalanche photodiodes: Optimization and realization. Opt Express, 2020, 28(11), 16211 doi: 10.1364/OE.393063[25] McIntyre R J. Multiplication noise in uniform avalanche diodes. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 1966, ED-13(1), 164 doi: 10.1109/T-ED.1966.15651[26] Liu Y J, Yang X H, Wang R, et al. Excess noise factor measurement for low-noise high-speed avalanche photodiodes. Phys Scr, 2023, 98(10), 105517 doi: 10.1088/1402-4896/acf629[27] Karimi H, Herrera D J, Dadey A A, et al. Analysis of the effect of different scattering mechanisms on the excess noise behavior of Sb-based avalanche photodiodes. Opt Express, 2025, 33(4), 7337 doi: 10.1364/OE.549807[28] Lewis H I J, Jin X, Guo B T, et al. Anomalous excess noise behavior in thick Al0.85Ga0.15As0.56Sb0.44 avalanche photodiodes. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1), 9936 doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36744-7 -
Proportional views




 Yuhang He got his bachelor’s degree in 2022 from Shijiazhuang Tiedao University. Now he is a master student at Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences under the supervision of Prof. YANG Xiaohong. His research focuses on low-noise near-infrared avalanche photodiodes.
Yuhang He got his bachelor’s degree in 2022 from Shijiazhuang Tiedao University. Now he is a master student at Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences under the supervision of Prof. YANG Xiaohong. His research focuses on low-noise near-infrared avalanche photodiodes. Xiaohong Yang received her doctoral degree from the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, in 2001. She is currently a Senior Researcher at the institute. Her research focuses on semiconductor photodetection devices.
Xiaohong Yang received her doctoral degree from the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, in 2001. She is currently a Senior Researcher at the institute. Her research focuses on semiconductor photodetection devices.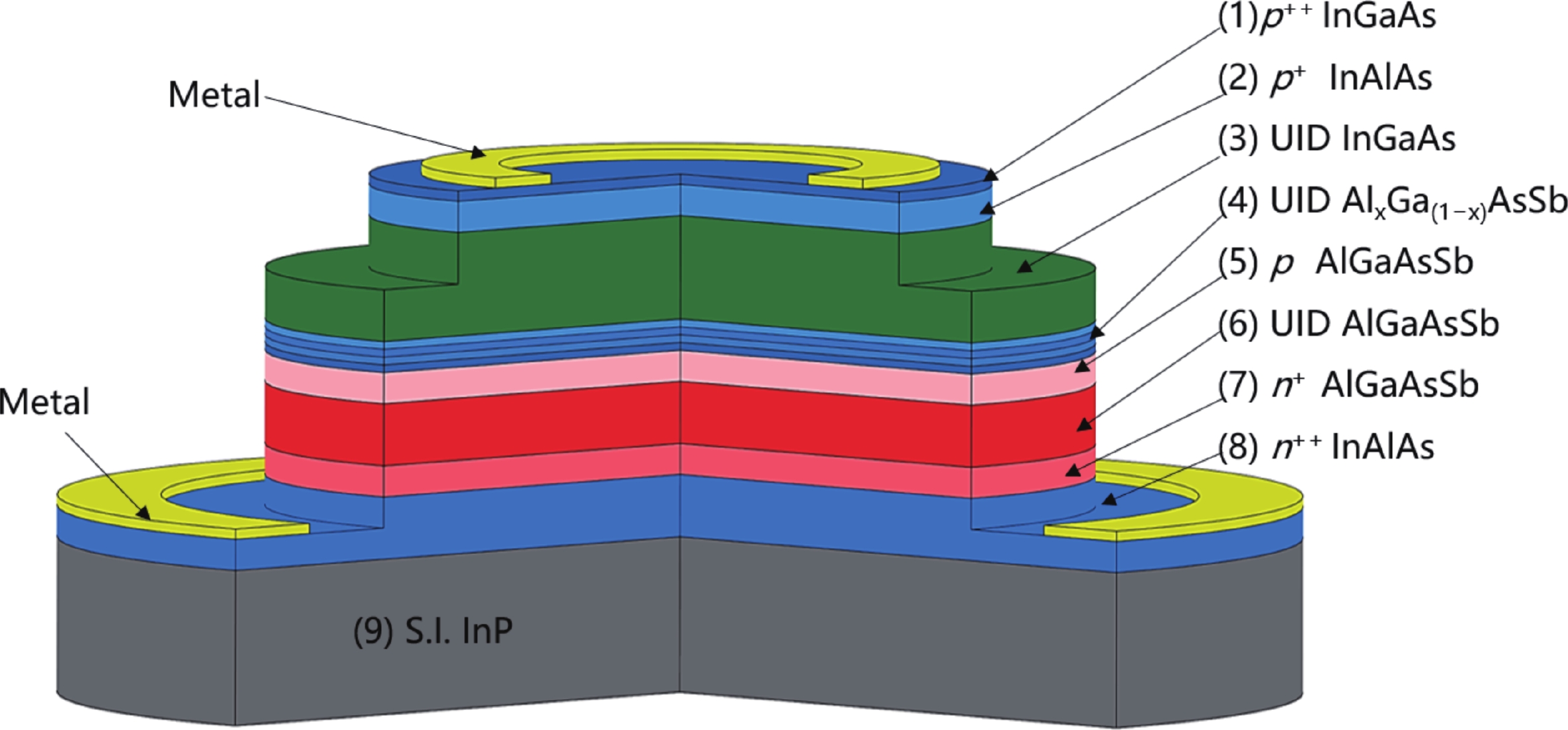
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: