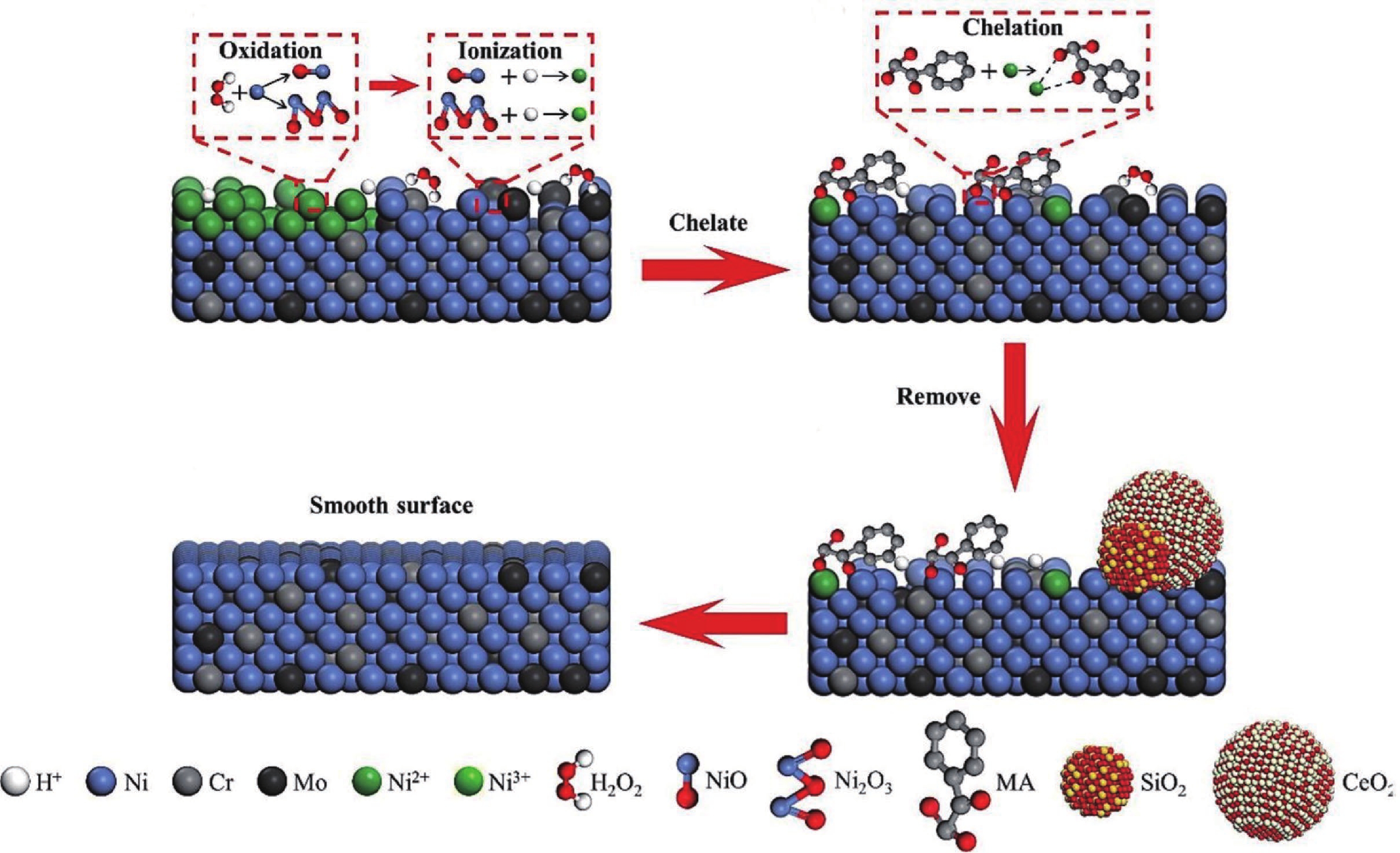
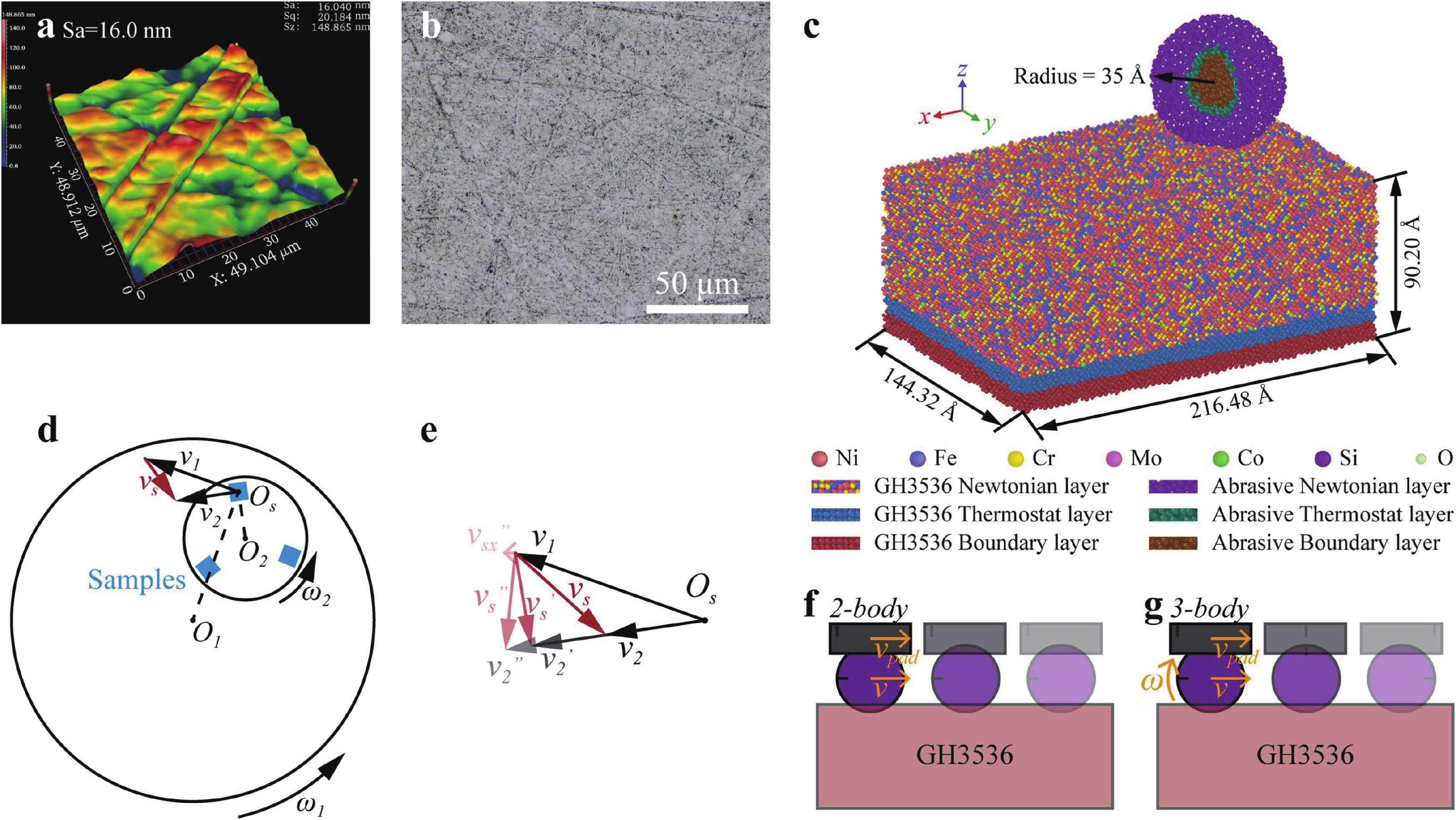
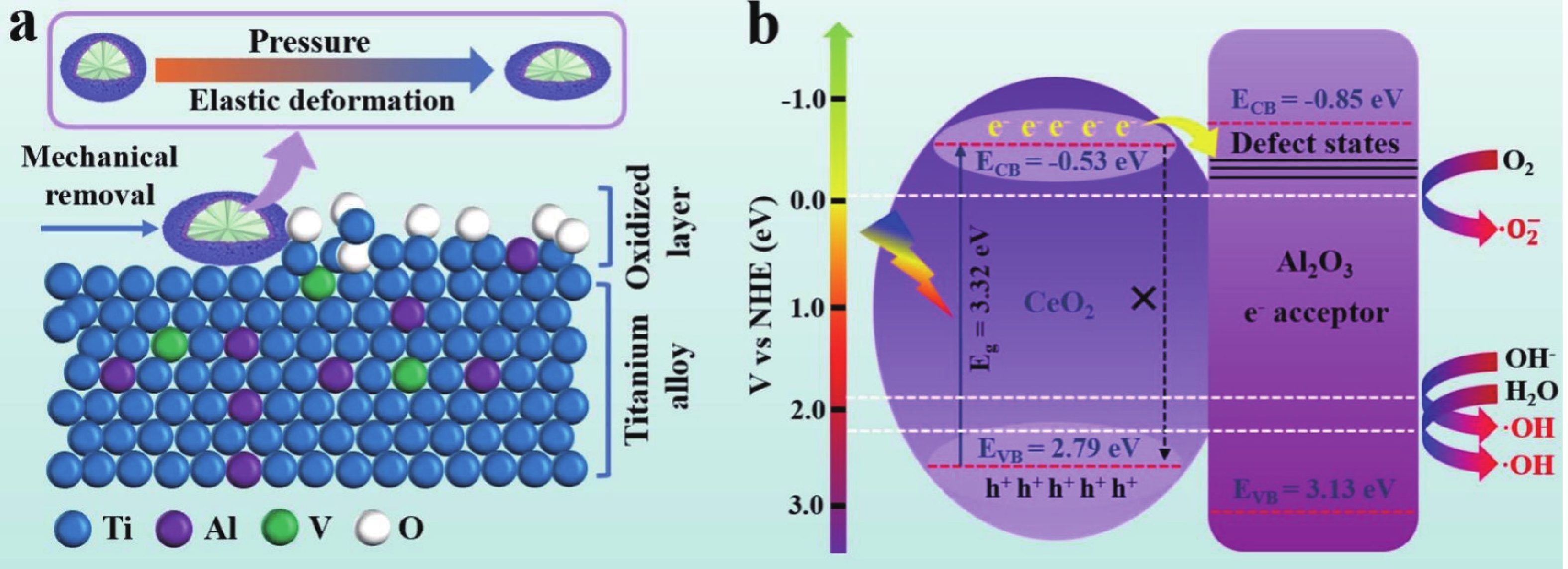
| Citation: |
Zuozuo Wu, Jinglin Cheng, Zhiguo Yu, Wei Zhou, Yangjian Li, Jianwei Cao, Wei Sun, Shuai Yuan, Deren Yang. Challenges, development and future of silica abrasives in chemical mechanical polishing derived from past six decades[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2026, In Press. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25060003
****
Z Z Wu, J L Cheng, Z G Yu, W Zhou, Y J Li, J W Cao, W Sun, S Yuan, and D R Yang, Challenges, development and future of silica abrasives in chemical mechanical polishing derived from past six decades[J]. J. Semicond., 2026, 47(4), 041301 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25060003
|
Challenges, development and future of silica abrasives in chemical mechanical polishing derived from past six decades
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/25060003
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.25060003
More Information-
Abstract
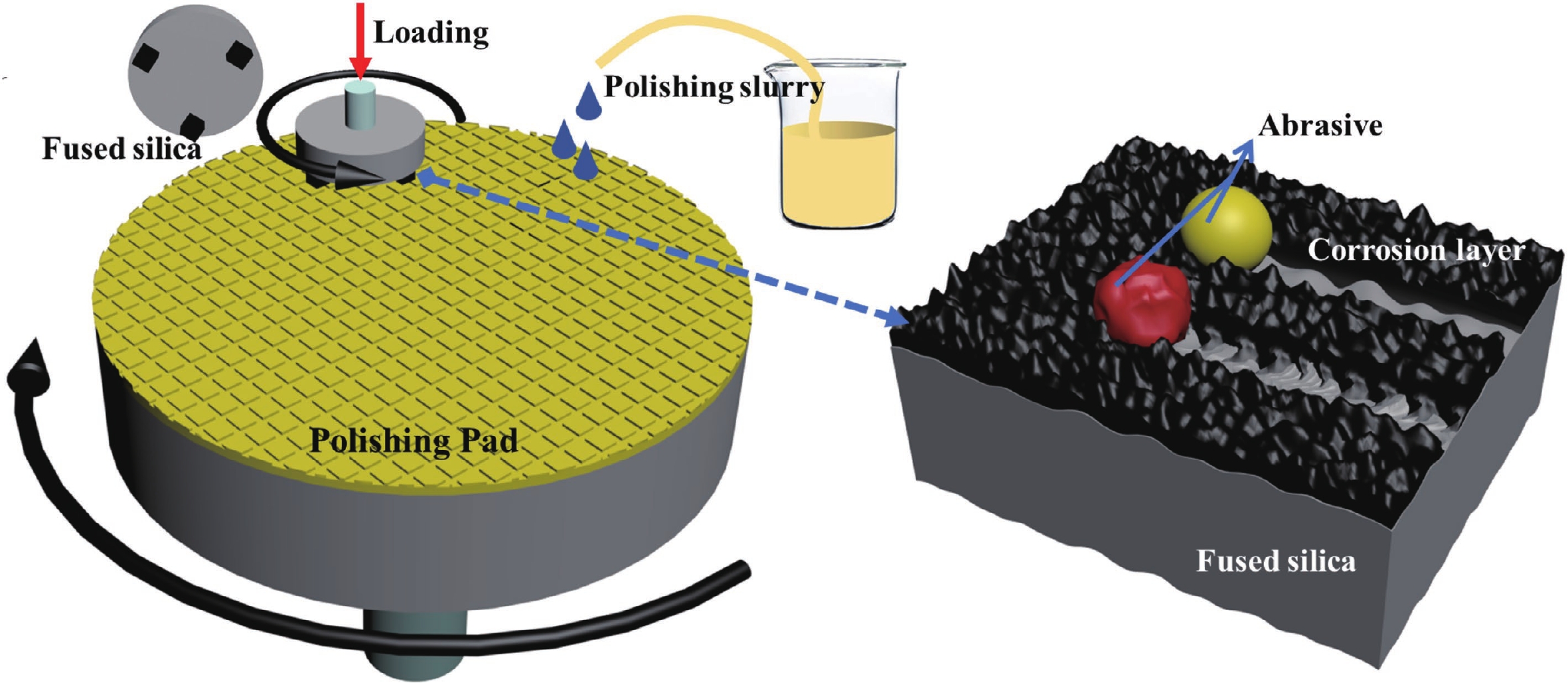
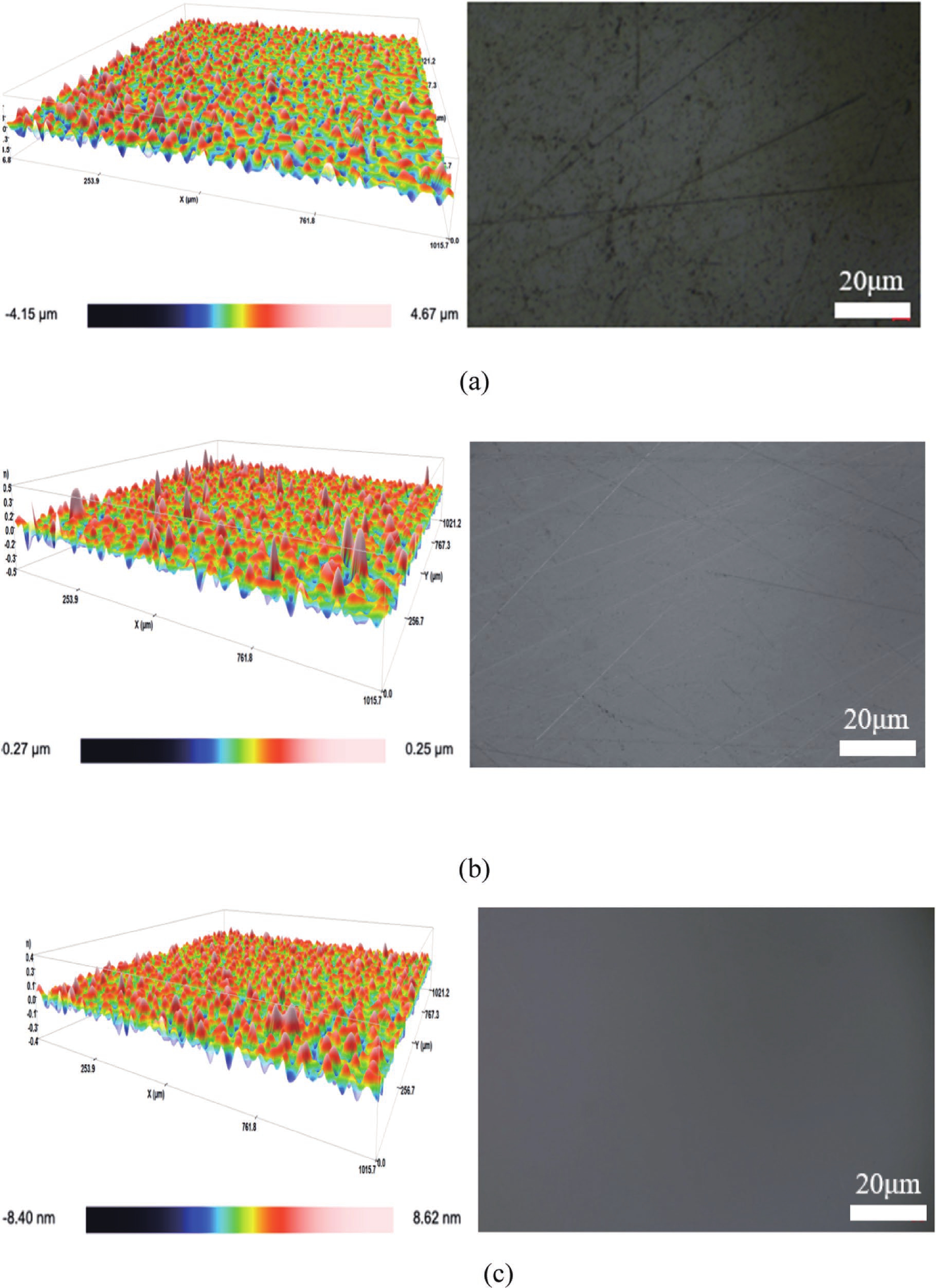
Chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) serves as an indispensable process for achieving global planarization in semiconductor manufacturing, especially as integrated circuit (IC) technology advances to sub-7 nm nodes, where atomic-level surface flatness becomes crucial. Silica abrasives, which account for over 90% of the abrasive market in advanced CMP processes, operate not through simple mechanical grinding but through a key "chemical-mechanical synergistic" mechanism: chemically softening the wafer surface, then mechanically removing the softened layer to expose a new surface, which is further softened and removed, repeating this cycle to produce a smooth wafer. Despite their prevalence, conventional silica abrasives still face challenges, including relatively low material removal rate (MRR), a tendency to agglomerate, leading to poor dispersion and surface defects, and limitations in achieving ultimate surface uniformity. Significant progress has been made to address these issues. Development has progressed from simple spherical particles to complex structural designs (such as mesoporous, hollow, and raspberry-shaped structures) to enhance slurry transport and mechanical action. Surface chemical modifications (e.g., using amino or polymer groups) can improve dispersion stability and reduce scratching. Furthermore, composites with other materials (e.g., ceria, polymers) and precise control of particle size distribution are key to enhancing performance. These innovative approaches have yielded significant performance gains. State-of-the-art slurries have demonstrated the ability to achieve surface roughness below 0.1 nm rms. The development of silica abrasives is increasingly focused on sustainability and smart manufacturing. A prominent direction is the design of biodegradable abrasives that disintegrate after use, thereby simplifying post-chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) cleanup and minimizing environmental impact—an approach fully aligned with green manufacturing principles. This review systematically summarizes the progress of silica abrasives for CMP over the past 60 years. This summary provides theoretical insights and forward-looking strategies to overcome the current limitations of abrasive technology. We believe this review will be helpful in advancing the field of CMP abrasives towards next-generation semiconductor manufacturing. -
References
[1] Hong J, Niu X H, Wang J, et al. Research on Si (100) crystal substrate CMP based on FA/O alkaline slurry. Appl Surf Sci, 2017, 420, 483 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.05.128[2] Lin Z C, Wang R Y, Ma S H. Theoretical model and experimental analysis of chemical mechanical polishing with the effect of slurry for abrasive removal depth and surface morphology of silicon wafer. Tribol Int, 2018, 117, 119 doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2017.08.021[3] Fisher G, Seacrist M R, Standley R W. Silicon crystal growth and wafer technologies. Proc IEEE, 2012, 100 (Special Centennial Issue), 1454[4] Bu Z Z, Niu F L, Chen J P, et al. Single crystal silicon wafer polishing by pretreating pad adsorbing SiO2 grains and abrasive-free slurries. Mater Sci Semicond Process, 2022, 141, 106418 doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2021.106418[5] Xu J, Luo J B, Lu X C, et al. Progress in material removal mechanisms of surface polishing with ultra precision. Chin Sci Bull, 2004, 49(16), 1687[6] Zhao F, Zhang Z Y, Deng X Q, et al. Atomic surface achieved through a novel cross-scale model from macroscale to nanoscale. Nanoscale, 2024, 16(5), 2318 doi: 10.1039/D3NR05278H[7] Zhong Z W. Recent developments and applications of chemical mechanical polishing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol, 2020, 109(5), 1419[8] Meng F N, Zhang Z Y, Gao P L, et al. Design of composite abrasives and substrate materials for chemical mechanical polishing applications. Appl Nanosci, 2020, 10(5), 1379 doi: 10.1007/s13204-019-01211-1[9] Hu X K, Song Z T, Wang H B, et al. Investigation on the controllable growth of monodisperse silica colloid abrasives for the chemical mechanical polishing application. Microelectron Eng, 2010, 87(9), 1751 doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2009.10.005[10] Li G Z, Xiao C, Zhang S B, et al. An experimental investigation of silicon wafer thinning by sequentially using constant-pressure diamond grinding and fixed-abrasive chemical mechanical polishing. J Mater Process Technol, 2022, 301, 117453 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117453[11] Pei Z J, Fisher G R, Liu J. Grinding of silicon wafers: A review from historical perspectives. Int J Mach Tools Manuf, 2008, 48(12/13), 1297[12] Lee D, Lee H, Jeong H. Slurry components in metal chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) process: A review. Int J Precis Eng Manuf, 2016, 17(12), 1751 doi: 10.1007/s12541-016-0201-y[13] Banerjee G, Rhoades R L. Chemical mechanical planarization historical review and future direction. ECS Trans, 2008, 13(4), 1 doi: 10.1149/1.2912973[14] Zhang X Y, Wang C W, Zhou J W, et al. Effect and mechanism of dual-official group of ethanolamines on the chemical mechanical polishing of monocrystalline silicon. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol, 2022, 11(9), 093005 doi: 10.1149/2162-8777/ac911c[15] Seidel H, Csepregi L, Heuberger A, et al. Anisotropic etching of crystalline silicon in alkaline solutions: I. orientation dependence and behavior of passivation layers. J Electrochem Soc, 137(11), 3612[16] Sinha D. Evaluation of etch behavior of doped silicon wafer in wet cleaning process. J Electrochem Soc, 2008, 155(4), H228 doi: 10.1149/1.2835209[17] Zhang X L, Meng N, Li X H, et al. The role of ammonium citrate and dodecyl pyridinium chloride on chemical mechanical polishing relevant to SiO2 dielectric layer. J Manuf Process, 2023, 107, 333 doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.10.054[18] Chen J Y, Lin Z H, Jin T Y, et al. Study on incompatible mechanism in chemical mechanical polishing of the novel graphite/diamond composite. Appl Surf Sci, 2023, 641, 158500 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.158500[19] Datta D, Rai H, Singh S, et al. Nanoscale tribological aspects of chemical mechanical polishing: A review. Appl Surf Sci Adv, 2022, 11, 100286 doi: 10.1016/j.apsadv.2022.100286[20] Seo J, Paik U. Preparation and characterization of slurry for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP). Advances in chemical mechanical planarization (CMP), 2016, 273, 98[21] Kim N Y, Hwang U, Sung J, et al. Particle size dependence of nanoclustered ceria abrasives on surface activity and chemical mechanical planarization performance. Appl Surf Sci, 2024, 663, 160123 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.160123[22] Chen Y, Xia Y F, Wang C, et al. Nanocasting synthesis of mesoporous CeO2 particle abrasives from mesoporous SiO2 hard templates for enhanced chemical mechanical polishing performance. Ceram Int, 2024, 50(24), 53818 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.10.236[23] Zhang J W, Ren G Y, Wang L, et al. Effect of nanosilica abrasive properties on tungsten chemical mechanical planarization. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2024, 35(5), 338 doi: 10.1007/s10854-023-11914-5[24] Gong J T, Wang W L, Liu W L, et al. Polishing mechanism of CMP 4H-SiC crystal substrate (0001) Si surface based on an alumina (Al2O3) abrasive. Materials, 2024, 17(3), 679 doi: 10.3390/ma17030679[25] Kim N H, Choi G W, Seo Y J, et al. Effects of various oxidizers on chemical mechanical polishing performance of nickel for microelectromechanical system applications. J Vac Sci Technol A Vac Surf Films, 2006, 24(4), 1297 doi: 10.1116/1.2194926[26] Zhang P J, Lei H, Zhang Z F, et al. Synthesis of Al2O3@MnO2 composite abrasives and their chemical mechanical polishing performance on silicon carbide (SiC). Ceram Int, 2024, 50(11), 19935 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.03.120[27] Park S W, Seo Y J, Lee W S. A study on the chemical mechanical polishing of oxide film using a zirconia (ZrO2)-mixed abrasive slurry (MAS). Microelectron Eng, 2008, 85(4), 682 doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2007.12.049[28] Wu P F, Liu N, Li X, et al. Material removal rate model for chemical–mechanical polishing of single-crystal SiC substrates using agglomerated diamond abrasive. Precis Eng, 2024, 88, 572 doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2024.04.002[29] Ahn Y, Yoon J Y, Baek C W, et al. Chemical mechanical polishing by colloidal silica-based slurry for micro-scratch reduction. Wear, 2004, 257(7/8), 785[30] Seo Y J, Park S W, Kim N H, et al. Chemical mechanical polishing performances by filtering and retreatment of used silica abrasives slurry. Microelectron Eng, 2005, 77(3/4), 358[31] Pan G S, Gu Z H, Zhou Y, et al. Preparation of silane modified SiO2 abrasive particles and their chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) performances. Wear, 2011, 273(1), 100 doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2011.05.044[32] Liu Y L, Zhang K L, Wang F, et al. Investigation on the final polishing slurry and technique of silicon substrate in ULSI. Microelectron Eng, 2003, 66(1/2/3/4), 438[33] Liu T T, Lei H. Nd3+-doped colloidal SiO2 composite abrasives: Synthesis and the effects on chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) performances of sapphire wafers. Appl Surf Sci, 2017, 413, 16 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.270[34] Chen A L, Duan Y H, Mu Z Y, et al. Meso-silica/erbium-doped ceria binary particles as functionalized abrasives for photochemical mechanical polishing (PCMP). Appl Surf Sci, 2021, 550, 149353 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149353[35] Cahn R. Silicon: child and progenitor of revolution. Into the Nano Era: Moore’s Law Beyond Planar Silicon CMOS. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009, 3[36] Huff H. Into the nano era: Moore's law beyond planar silicon CMOS. Springer Science & Business Media, 2008[37] Thomas J. Silicon. Marshall Cavendish, 2002[38] Kerker M. Classics and classicists of colloid and interface science III. The(Theodor) Svedberg. J Colloid Interface Sci, 1986, 114(1), 295 doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(86)90269-9[39] Sánchez M G. Development of silica gels and impact of silica research on studies of other colloidal systems. ACS Publications, 1994, 470[40] Faust Jr J W. Factors that influence the damaged layer caused by abrasion on Si and Ge. Electrochem Tech, 1964, 2, 11[41] Lee H, Kim M, Jeong H. Effect of non-spherical colloidal silica particles on removal rate in oxide CMP. Int J Precis Eng Manuf, 2015, 16(13), 2611 doi: 10.1007/s12541-015-0334-4[42] Morinaga H. Origin and innovations of CMP slurry. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol, 2024, 13(7), 074006 doi: 10.1149/2162-8777/ad5fb6[43] Morinaga H, Tamai K. Challenges and mechanisms of CMP slurries for 32nm and beyond. ECS Trans, 2011, 34(1), 591 doi: 10.1149/1.3567643[44] Rashid A B, Shishir S I, Mahfuz M A, et al. Silica aerogel: Synthesis, characterization, applications, and recent advancements. Part & Part Syst Charact, 2023, 40(6), 2200186[45] Yu S R. FUSO develops ultra-high purity colloidal silica. Fine and Specialty Chemicals, 2004, 12(009), 31 (in Chinese)[46] Singh B N, Bajaj R, Meuris M, et al. A symposium. Approaches to controlling cardiac arrhythmias, 1993, 1999[47] Liu B, Wei W, Qu X Z, et al. Janus colloids formed by biphasic grafting at a Pickering emulsion interface. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2008, 47(21), 3973 doi: 10.1002/anie.200705103[48] White L, Duffy G. Staff-industry collaborative report Vapor-Phase production of colloidal silica. Ind Eng Chem, 1959, 51(3), 232 doi: 10.1021/ie51394a019[49] Hyde E D E R, Seyfaee A, Neville F, et al. Colloidal silica particle synthesis and future industrial manufacturing pathways: A review. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2016, 55(33), 8891 doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.6b01839[50] Barthel H, Heinemann M, Stintz M, et al. Particle sizes of fumed silica. Chem Eng Technol, 1998, 21(9), 745 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4125(199809)21:9<745::AID-CEAT745>3.0.CO;2-Q[51] Jin Y F, Song K D, Gellermann N, et al. Printing of hydrophobic materials in fumed silica nanoparticle suspension. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2019, 11(32), 29207 doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b07433[52] Wagner E, Brünner H. Aerosil, herstellung, eigenschaften und verhalten in organischen Flüssigkeiten. Angew Chem, 1960, 72(19/20), 744[53] Kim E, Lee J, Park Y, et al. Shape classification of fumed silica abrasive and its effects on chemical mechanical polishing. Powder Technol, 2021, 381, 451 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.11.058[54] Li S T, Gaudet G, Sun F, et al. ILD CMP with silica abrasive particles: Interfacial removal kinetics and effect of pad surface textures. J Electrochem Soc, 2010, 157(11), H1061 doi: 10.1149/1.3486806[55] Croissant J G, Butler K S, Zink J I, et al. Synthetic amorphous silica nanoparticles: Toxicity, biomedical and environmental implications. Nat Rev Mater, 2020, 5, 886 doi: 10.1038/s41578-020-0230-0[56] Chaudhuri T K, Tiwari D. Earth-abundant non-toxic Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films by direct liquid coating from metal–thiourea precursor solution. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2012, 101, 46 doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2012.02.012[57] Gustafsson H, Holmberg K. Emulsion-based synthesis of porous silica. Adv Colloid Interface Sci, 2017, 247, 426 doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2017.03.002[58] Xu L, Lei H, Wang T X, et al. Preparation of flower-shaped silica abrasives by double system template method and its effect on polishing performance of sapphire wafers. Ceram Int, 2019, 45(7), 8471 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.01.158[59] Murphy R P, Hong K L, Wagner N J. Synthetic control of the size, shape, and polydispersity of anisotropic silica colloids. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2017, 501, 45 doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.04.026[60] Chang C L, Fogler H S. Kinetics of silica particle formation in nonionic W/O microemulsions from TEOS. AlChE J, 1996, 42(11), 3153 doi: 10.1002/aic.690421115[61] Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci, 1968, 26(1), 62 doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(68)90272-5[62] Peedikakkandy L, Kalita L, Kavle P, et al. Preparation of spherical ceria coated silica nanoparticle abrasives for CMP application. Appl Surf Sci, 2015, 357, 1306 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.09.149[63] Yang R X, Lei H, Zhang J H. Preparation of SiO2@MnO2 composite abrasives and their performance in chemical-mechanical polishing of SiC substrates. Ceram Int, 2024, 50(19), 34796 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.06.288[64] Zhao X B, Long R W, Chen Y, et al. Synthesis, characterization of CeO2@SiO2 nanoparticles and their oxide CMP behavior. Microelectron Eng, 2010, 87(9), 1716 doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2009.09.012[65] Feng X D, Sayle D C, Wang Z L, et al. Converting ceria polyhedral nanoparticles into single-crystal nanospheres. Science, 2006, 312(5779), 1504 doi: 10.1126/science.1125767[66] Luo J Z, Lannutti J J, Seghi R R. Effect of filler porosity on the abrasion resistance of nanoporous silica gel/polymer composites. Dent Mater, 1998, 14(1), 29 doi: 10.1016/S0109-5641(98)00006-2[67] Baltes M, Cassiers K, Van Der Voort P, et al. MCM-48-supported vanadium oxide catalysts, prepared by the molecular designed dispersion of VO(acac)2: A detailed study of the highly reactive MCM-48 surface and the structure and activity of the deposited VOx. J Catal, 2001, 197(1), 160 doi: 10.1006/jcat.2000.3066[68] Chen R L, Jiang R R, Lei H, et al. Material removal mechanism during porous silica cluster impact on crystal silicon substrate studied by molecular dynamics simulation. Appl Surf Sci, 2013, 264, 148 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.09.147[69] Liu P, Lei H, Chen R L. Polishing properties of porous silica abrasive on hard disk substrate CMP. Int J Abras Technol, 2010, 3(3), 228 doi: 10.1504/IJAT.2010.034053[70] Shih Z W, Chang K Y, Tseng C L, et al. Method for preparing shape-changed nanosize colloidal silica. US Patent, US2003113251A1, 2003[71] Liang C L, Wang L Y, Liu W L, et al. Non-spherical colloidal silica particles: Preparation, application and model. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects, 2014, 457, 67 doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.05.053[72] Dong Y, Lei H, Liu W Q, et al. Preparation of non-spherical silica composite abrasives by lanthanum ion-induced effect and its chemical–mechanical polishing properties on sapphire substrates. J Mater Sci, 2018, 53(15), 10732 doi: 10.1007/s10853-018-2357-6[73] Wang J, Lu Y. Facile synthesis of asymmetrical flower-like silica. Mater Des, 2016, 111, 206 doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.08.093[74] Kuijk A, van Blaaderen A, Imhof A. Synthesis of monodisperse, rodlike silica colloids with tunable aspect ratio. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133(8), 2346 doi: 10.1021/ja109524h[75] Dai S W, Lei H, Fu J F. Self-assembly preparation of popcorn-like colloidal silica and its application on chemical mechanical polishing of zirconia ceramic. Ceram Int, 2020, 46(15), 24225 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.06.202[76] Zhang Y, Yang P, Zhong W Q, et al. Numerical simulation of the effects of different particle properties on the separation characteristics of mixed non-spherical particles of different sizes. J Power Eng, 2015, 8, 652 (in Chinese)[77] Zhu X H, Chung C, Korach C S, et al. Experimental study and modeling of the effect of mixed size abrasive grits on surface topology and removal rate in wafer lapping. Wear, 2013, 305(1/2), 14[78] Chen Y, Li Z N, Miao N M. Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)/CeO2 hybrid particles for enhanced chemical mechanical polishing performance. Tribol Int, 2015, 82, 211 doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2014.10.013[79] He Q. Experimental study on polishing performance of CeO2 and nano-SiO2 mixed abrasive. Appl Nanosci, 2018, 8(1), 163[80] Liu D D, Zhang Z Y, Zhou H X, et al. Angstrom surface on copper induced by novel green chemical mechanical polishing using ceria and silica composite abrasives. Appl Surf Sci, 2023, 640, 158382 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.158382[81] Lee Y, Seo Y J, Lee H, et al. Effect of diluted colloidal silica slurry mixed with ceria abrasives on CMP characteristic. Int J Precis Eng Manuf Green Technol, 2016, 3(1), 13 doi: 10.1007/s40684-016-0002-x[82] Lin F, Nolan L, Xu Z, et al. A study of the colloidal stability of mixed abrasive slurries and their role in CMP. J Electrochem Soc, 2012, 159(5), H482 doi: 10.1149/2.jes113470[83] Dai S W, Fu J F, Lei H, et al. Study on the interaction between SiO2 and ZrO2 in the chemical mechanical polishing of zirconia ceramic with colloidal silica. Ceram Int, 2021, 47(15), 21642 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.177[84] Jindal A, Hegde S, Babu S V. Chemical mechanical polishing using mixed abrasive slurries. Electrochem Solid-State Lett, 2002, 5(7), G48 doi: 10.1149/1.1479297[85] Seo Y J, Lee W S, Yeh P. Improvements of oxide-chemical mechanical polishing performances and aging effect of alumina and silica mixed abrasive slurries. Microelectron Eng, 2004, 75(4), 361 doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2004.07.062[86] Lee H S, Kim D I, An J H, et al. Hybrid polishing mechanism of single crystal SiC using mixed abrasive slurry (MAS). CIRP Ann, 2010, 59(1), 333 doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2010.03.114[87] Zhu X X, Ding J X, Mo Z C, et al. Evaluation of chemical mechanical polishing characteristics using mixed abrasive slurry: A study on polishing behavior and material removal mechanism. Appl Surf Sci, 2025, 679, 161157 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.161157[88] Xu Y C, Lu J, Xu X P. Study on planarization machining of sapphire wafer with soft-hard mixed abrasive through mechanical chemical polishing. Appl Surf Sci, 2016, 389, 713 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.07.155[89] Bhagavat S, Liberato J C, Chung C, et al. Effects of mixed abrasive grits in slurries on free abrasive machining (FAM) processes. Int J Mach Tools Manuf, 2010, 50(9), 843 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2010.04.006[90] Lee H, Jeong H. Analysis of removal mechanism on oxide CMP using mixed abrasive slurry. Int J Precis Eng Manuf, 2015, 16(3), 603 doi: 10.1007/s12541-015-0081-6[91] Bun-Athuek N, Takazaki H, Yoshimoto Y, et al. Effects of mixed ultrafine colloidal silica particles on chemical mechanical polishing of sapphire. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2018, 57(7S2), 07MD03 doi: 10.7567/JJAP.57.07MD03[92] Tai Y L, Qian J S, Zhang Y C, et al. Study of surface modification of nano-SiO2 with macromolecular coupling agent (LMPB-g-MAH). Chem Eng J, 2008, 141(1/2/3), 354[93] Lee C H, Park S H, Chung W, et al. Preparation and characterization of surface modified silica nanoparticles with organo-silane compounds. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects, 2011, 384(1/2/3), 318[94] Wang Z W, Wang T J, Wang Z W, et al. Organic modification of nano-SiO2 particles in supercritical CO2. J Supercrit Fluids, 2006, 37(1), 125 doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2005.06.011[95] Lei H, Gu Q. Preparation of Cu-doped colloidal SiO2 abrasives and their chemical mechanical polishing behavior on sapphire substrates. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2015, 26(12), 10194 doi: 10.1007/s10854-015-3708-6[96] Lei H, Tong K Y. Preparation of La-doped colloidal SiO2 composite abrasives and their chemical mechanical polishing behavior on sapphire substrates. Precis Eng, 2016, 44, 124 doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2015.10.009[97] Lei H, Tong K Y, Zhang B C, et al. Preparation of monodisperse Ti-doped colloidal SiO2 composite abrasives and their chemical mechanical polishing performances on sapphire substrates. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol, 2016, 5(12), 674 doi: 10.1149/2.0231612jss[98] Lei H, Liu T T, Xu L. Synthesis of Sm-doped colloidal SiO2 composite abrasives and their chemical mechanical polishing performances on sapphire substrates. Mater Chem Phys, 2019, 237, 121819 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.121819[99] Yin D, Niu X H, Zhang K, et al. Preparation of MgO doped colloidal SiO2 abrasive and their chemical mechanical polishing performance on c-, r- and a-plane sapphire substrate. Ceram Int, 2018, 44(12), 14631 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.05.087[100] Lei H, Huang L Q, Gu Q. Synthesis of Zn-doped colloidal SiO2 abrasives and their applications in sapphire chemical mechanical polishing slurry. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2017, 28(2), 1229 doi: 10.1007/s10854-016-5650-7[101] Ma P, Lei H, Chen R L. Preparation of cobalt-doped colloidal silica abrasives and their chemical mechanical polishing performances on sapphire. Micro Nano Lett, 2015, 10(11), 657 doi: 10.1049/mnl.2015.0292[102] Lei H, Gu Q, Chen R L, et al. Preparation of Fe-doped colloidal SiO2 abrasives and their chemical mechanical polishing behavior on sapphire substrates. Appl Opt, 2015, 54(24), 7188 doi: 10.1364/AO.54.007188[103] Ma P, Lei H, Chen Y, et al. Preparation of Ni-doped colloidal silica abrasives and their chemical mechanical polishing performances on sapphire. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol, 2016, 5(5), Q132 doi: 10.1149/2.0221605jss[104] Fang F F, Kim J H, Choi H J. Synthesis of core–shell structured PS/Fe3O4 microbeads and their magnetorheology. Polymer, 2009, 50(10), 2290 doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2009.03.023[105] Gao B, Zhai W J, Zhai Q, et al. Polystyrene/CeO2Core/shell abrasives for high-quality 4H-SiC surface in ECMP: The effects of shell thickness. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol, 2020, 9(4), 044005 doi: 10.1149/2162-8777/ab8b71[106] Murata J, Ueno Y, Yodogawa K, et al. Polymer/CeO2–Fe3O4 multicomponent core–shell particles for high-efficiency magnetic-field-assisted polishing processes. Int J Mach Tools Manuf, 2016, 101, 28 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2015.11.004[107] Chen Y, Mu Z Y, Wang W Y, et al. Development of mesoporous SiO2/CeO2 core/shell nanoparticles with tunable structures for non-damage and efficient polishing. Ceram Int, 2020, 46(4), 4670 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.10.198[108] Gawande M B, Goswami A, Asefa T, et al. Core-shell nanoparticles: Synthesis and applications in catalysis and electrocatalysis. Chem Soc Rev, 2015, 44(21), 7540 doi: 10.1039/C5CS00343A[109] Wang H, Chen L Y, Feng Y H, et al. Exploiting core-shell synergy for nanosynthesis and mechanistic investigation. Acc Chem Res, 2013, 46(7), 1636 doi: 10.1021/ar400020j[110] Lauhon L J, Gudiksen M S, Wang D L, et al. Epitaxial core-shell and core-multishell nanowire heterostructures. Nature, 2002, 420(6911), 57 doi: 10.1038/nature01141[111] Park H H, Woo K, Ahn J P. Core-shell bimetallic nanoparticles robustly fixed on the outermost surface of magnetic silica microspheres. Sci Rep, 2013, 3, 1497 doi: 10.1038/srep01497[112] Chiozzi V, Rossi F. Inorganic–organic core/shell nanoparticles: Progress and applications. Nanoscale Adv, 2020, 2(11), 5090 doi: 10.1039/D0NA00411A[113] Pathak S, Greci M T, Kwong R C, et al. Synthesis and applications of palladium-coated poly(vinylpyridine) nanospheres. Chem Mater, 2000, 12(7), 1985 doi: 10.1021/cm0001556[114] Shi S, Yu Y, Wang T, et al. Poly(methyl methacrylate)/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) core-shell particles prepared by seeded precipitation polymerization: Unusual morphology and thermo-sensitivity of zeta potential. Chin J Polym Sci, 2014, 32(5), 524 doi: 10.1007/s10118-014-1435-8[115] Ghosh Chaudhuri R, Paria S. Core/shell nanoparticles: Classes, properties, synthesis mechanisms, characterization, and applications. Chem Rev, 2012, 112(4), 2373 doi: 10.1021/cr100449n[116] Shi N, Chen Y L, Yin L, et al. Monodispersion of SiO2/CeO2 binary nano-abrasives with adjustable size in chemical mechanical polishing performance of copper. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol, 2023, 12(7), 074001 doi: 10.1149/2162-8777/acdffc[117] Chen Y, Zuo C Z, Ma X Y, et al. Solid-silica core/mesoporous-silica shell composite abrasives: Synthesis, characterization, and the effect of mesoporous shell structures on CMP. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2018, 29(5), 3817 doi: 10.1007/s10854-017-8317-0[118] Chen Y, Wang Y Y, Qin J W, et al. Core/shell structured solid-silica/mesoporous-silica microspheres as novel abrasives for chemical mechanical polishing. Tribol Lett, 2015, 58(3), 37 doi: 10.1007/s11249-015-0513-6[119] Chen A L, Chen Y, Wang Y Y, et al. Silica abrasives containing solid cores and mesoporous shells: Synthesis, characterization and polishing behavior for SiO2 film. J Alloys Compd, 2016, 663, 60 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.12.109[120] Chen Y, Zuo C Z, Li Z F, et al. Design of ceria grafted mesoporous silica composite particles for high-efficiency and damage-free oxide chemical mechanical polishing. J Alloys Compd, 2018, 736, 276 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.11.112[121] Chen A L, Long J L, Li Z F, et al. Dependency of structural change and polishing efficiency of meso-silica/ceria core/shell composite abrasives on calcination temperatures. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2018, 29(13), 11466 doi: 10.1007/s10854-018-9239-1[122] Zhang L, Wang H B, Zhang Z F, et al. Preparation of monodisperse polystyrene/silica core–shell nano-composite abrasive with controllable size and its chemical mechanical polishing performance on copper. Appl Surf Sci, 2011, 258(3), 1217 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.09.074[123] Zhang Z F, Liu W L, Zhu J K, et al. Synthesis, characterization of ceria-coated silica particles and their chemical mechanical polishing performance on glass substrate. Appl Surf Sci, 2010, 257(5), 1750 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.09.009[124] Zhang X, Pan G S, Wang W Q, et al. Polishing behavior of PS/SiO2 Core-Shell nanoparticles with different shell thickness on fused silica Chemical Mechanical Polishing. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng, 2019, 563(2), 022048 doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/563/2/022048[125] Chen A L, Chen Y, Zhao X B, et al. Core/shell structured PS/mSiO2 hybrid particles: Controlled preparation, mechanical property, and their size-dependent CMP performance. J Alloys Compd, 2019, 779, 511 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.11.314[126] Armini S, Vakarelski I U, Whelan C M, et al. Nanoscale indentation of polymer and composite polymer-silica core-shell submicrometer particles by atomic force microscopy. Langmuir, 2007, 23(4), 2007 doi: 10.1021/la062271e[127] Armini S, Whelan C M, Maex K. Engineering polymer core–silica shell size in the composite abrasives for CMP applications. Electrochem Solid-State Lett, 2008, 11(10), H280 doi: 10.1149/1.2953227[128] Armini S, Whelan C M, Moinpour M, et al. Composite polymer core–silica shell abrasives: The effect of the shape of the silica particles on oxide CMP. J Electrochem Soc, 2008, 155(6), H401 doi: 10.1149/1.2901864[129] Armini S, De Messemaeker J, Whelan C M, et al. Composite polymer core–ceria shell abrasive particles during oxide CMP: A defectivity study. J Electrochem Soc, 2008, 155(9), H653 doi: 10.1149/1.2949085[130] Armini S, De Messemaeker J, Burtovyy R, et al. Composite polymer core–ceria shell abrasive particles during silicon oxide CMP. MRS Online Proc Libr, 2007, 991(1), 804[131] Armini S, Caroline M W, Moinpour M, et al. Copper CMP with composite polymer core-silica shell abrasives: A defectivity study. MRS Online Proc Libr, 2008, 1079(1), 1104[132] Chen A L, Ma X Y, Cai W J, et al. Polystyrene-supported dendritic mesoporous silica hybrid core/shell particles: Controlled synthesis and their pore size-dependent polishing behavior. J Mater Sci, 2020, 55(2), 577 doi: 10.1007/s10853-019-03960-4[133] Chen Y, Chen A L, Qin J W. Polystyrene core–silica shell composite particles: Effect of mesoporous shell structures on oxide CMP and mechanical stability. RSC Adv, 2017, 7(11), 6548 doi: 10.1039/C6RA26437A[134] Chen Y, Qian C, Miao N M. Atomic force microscopy indentation to determine mechanical property for polystyrene–silica core–shell hybrid particles with controlled shell thickness. Thin Solid Films, 2015, 579, 57 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2015.02.049[135] Chen Y, Li Z F, Qin J W, et al. Monodispersed mesoporous silica (mSiO2) spheres as abrasives for improved chemical mechanical planarization performance. J Mater Sci, 2016, 51(12), 5811 doi: 10.1007/s10853-016-9882-y[136] Wang L, Ren G Y, Xie W X, et al. Controllable synthesis of core-shell SiO2@CeO2 abrasives for chemical mechanical polishing on SiO2 film. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects, 2024, 682, 132901 doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.132901[137] Shi C J, Fan Y H, Zhang Z Y, et al. Development of core–shell SiO2@A-TiO2 abrasives and novel photocatalytic chemical machinal polishing for atomic surface of fused silica. Appl Surf Sci, 2024, 652, 159293 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.159293[138] Chen Y, Cai W J, Wang W Y, et al. Preparation, characterization, and application of dendritic silica-supported samarium-doped ceria nanoparticles in ultra-precision polishing for silica films. J Nanopart Res, 2019, 21(11), 226 doi: 10.1007/s11051-019-4684-1[139] Kou Z H, Wang C, Zhou W J, et al. Trivalent lanthanum and ytterbium doped meso-silica/ceria abrasive systems toward chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) and ultraviolet irradiation-assisted photochemical mechanical polishing (PCMP). Appl Surf Sci, 2024, 657, 159733 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.159733[140] Wang M H, Mu Z Y, Wang T Y, et al. Double-layered core–shell heterostructures of mSiO2@CdS@CeO2 abrasive systems toward photochemical mechanical polishing (PCMP) applications. Appl Surf Sci, 2023, 614, 156274 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.156274[141] Chen C D, Yue S J, Liu Y, et al. Unveiling superior chemical mechanical polishing properties of a novel shell-core structure: Insights from an atomic-scale perspective. Appl Surf Sci, 2024, 672, 160845 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.160845[142] Liu Z S, Zhang Z Y, Feng J Y, et al. A novel atomic removal model for chemical mechanical polishing using developed mesoporous shell/core abrasives based on molecular dynamics. Nanoscale, 2023, 16(1), 85[143] Seo J, Hur J U, Kim S, et al. Recovery and reuse of magnetic silica-coated iron oxide particles for eco-friendly chemical mechanical planarization. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects, 2024, 694, 134064 doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2024.134064[144] Jiao J, Fan Y Y, Chen C D, et al. Preparation, characterization, and application of Nd-doped ceria-coated silica nanoparticles for chemical mechanical polishing. J Mater Sci, 2023, 58(48), 18014 doi: 10.1007/s10853-023-09103-0[145] Wang T X, Lei H. Novel polyelectrolyte–Al2O3/SiO2 composite nanoabrasives for improved chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) of sapphire. J Mater Res, 2019, 34(6), 1073 doi: 10.1557/jmr.2018.443[146] Ma J H, Xu N, Cheng J, et al. A review on the development of ceria for chemical mechanical polishing. Powder Technol, 2024, 444, 119989 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2024.119989[147] Lee H, Lee S. Investigation of pad wear in CMP with swing-arm conditioning and uniformity of material removal. Precis Eng, 2017, 49, 85 doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2017.01.015[148] Preston F W. The theory and design of plate glass polishing machines. J Society of glass Tech, 1927, 11, 214[149] Cook L M. Chemical processes in glass polishing. J Non Cryst Solids, 1990, 120(1/2/3), 152[150] Luo Q, Ramarajan S, Babu S V. Modification of the Preston equation for the chemical–mechanical polishing of copper. Thin Solid Films, 1998, 335(1/2), 160[151] Ryan J G, Geffken R M, Poulin N R, et al. The evolution of interconnection technology at IBM. IBM J Res Dev, 1995, 39(4), 371 doi: 10.1147/rd.394.0371[152] Verwey E W. Theory of the stability of lyophobic colloids. J Phys Colloid Chem, 1947, 51(3), 631 doi: 10.1021/j150453a001[153] Masliyah J H, Bhatta Charjee S. Electrokinetic and colloid transport phenomena. John Wiley & Sons, 2006[154] Gun’ko V M, Zarko V I, Leboda R, et al. Influence of modification of fine silica by organosilicon compounds on particle-particle interaction in aqueous suspensions. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects, 1998, 132(2/3), 241[155] Choi W, Mahajan U, Lee S M, et al. Effect of slurry ionic salts at dielectric silica CMP. J Electrochem Soc, 2004, 151(3), G185 doi: 10.1149/1.1644609[156] Seo J, Kim J H, Lee M, et al. Size-dependent interactions of silica nanoparticles with a flat silica surface. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2016, 483, 177 doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.08.041[157] Kosmulski M. Compilation of PZC and IEP of sparingly soluble metal oxides and hydroxides from literature. Adv Colloid Interface Sci, 2009, 152(1/2), 14[158] Luo J F, Dornfeld D A. Effects of abrasive size distribution in chemical mechanical planarization: Modeling and verification. IEEE Trans Semicond Manuf, 2003, 16(3), 469 doi: 10.1109/TSM.2003.815199[159] Si L N, Guo D, Luo J B, et al. Monoatomic layer removal mechanism in chemical mechanical polishing process: A molecular dynamics study. J Appl Phys, 2010, 107(6), 064310 doi: 10.1063/1.3327448[160] Wen J L, Ma T B, Zhang W W, et al. Atomistic mechanisms of Si chemical mechanical polishing in aqueous H2O2: ReaxFF reactive molecular dynamics simulations. Comput Mater Sci, 2017, 131, 230 doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2017.02.005[161] Czichos H. Tribology: a systems approach to the science and technology of friction, lubrication, and wear. Elsevier, 2009[162] Misra A, Finnie I. On the size effect in abrasive and erosive wear. Wear, 1981, 65(3), 359 doi: 10.1016/0043-1648(81)90062-4[163] Zhao G Y, Wei Z, Wang W L, et al. Review on modeling and application of chemical mechanical polishing. Nanotechnol Rev, 2020, 9(1), 182 doi: 10.1515/ntrev-2020-0016[164] Zhou Y, Pan G S, Gong H, et al. Characterization of sapphire chemical mechanical polishing performances using silica with different sizes and their removal mechanisms. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects, 2017, 513, 153 doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.09.049[165] Shi X L, Pan G S, Zhou Y, et al. Characterization of colloidal silica abrasives with different sizes and their chemical–mechanical polishing performance on 4H-SiC (0001). Appl Surf Sci, 2014, 307, 414 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.04.048[166] Xia G, Wang Z R, Yao Q Y, et al. Modeling of material removal rate considering the chemical mechanical effects of lubricant, oxidant, and abrasive particles for aluminum chemical mechanical polishing at low pressure. Wear, 2023, 530, 205023[167] Xu G H, Zhang Z Y, Meng F N, et al. Atomic-scale surface of fused silica induced by chemical mechanical polishing with controlled size spherical ceria abrasives. J Manuf Process, 2023, 85, 783 doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.12.008[168] Malik F, Hasan M. Manufacturability of the CMP process. Thin Solid Films, 1995, 270(1/2), 612[169] Xu F, Wang W L, Xu A X, et al. Effect of particle size and pH value of slurry on chemical mechanical polishing of SiO2 film. J Solid State Sci Technol, 2022, 11(1), 013004 doi: 10.1149/2162-8777/ac495f[170] Wang S L, Li Z X, Yang L B, et al. Polishing mechanism and technology of hard disk substrates by colloidal silica alkaline slurry. Appl Mech Mater, 2010, 44/45/46/47, 3072[171] Jiang L, Wu Y, Zhang Y S, et al. Research progress and challenges in chip atomic layer polishing. 2025, 65(2), 215 (in Chinese)[172] Park C, Kim H, Lee S, et al. The influence of abrasive size on high-pressure chemical mechanical polishing of sapphire wafer. Int J Precis Eng Manuf Green Technol, 2015, 2(2), 157 doi: 10.1007/s40684-015-0020-0[173] Zhou C H, Shan L, Hight J R, et al. Influence of colloidal abrasive size on material removal rate and surface finish in SiO2 chemical mechanical polishing. Tribol Trans, 2002, 45(2), 232 doi: 10.1080/10402000208982545[174] Chen Y, Li Z N, Qian C. Core–shell structured polystyrene coated silica composite abrasives with homogeneous shells: The effects of polishing pressure and particle size on oxide-CMP. Precis Eng, 2016, 43, 71 doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2015.06.011[175] Oshima Y, Onda T. Study of abrasive-particle size dependence of polishing rate based on a simple mechanical model. Proceedings of International Conference on Planarization/CMP Technology 2014, 2014, 35[176] Zhang J H, Tsai S, Surisetty C, et al. CMP challenges for advanced technology nodes beyond Si. MRS Adv, 2017, 2(51), 2891 doi: 10.1557/adv.2017.339[177] Lu Z Y, Lee S H, Gorantla V R K, et al. Effects of mixed abrasives in chemical mechanical polishing of oxide films. J Mater Res, 2003, 18(10), 2323 doi: 10.1557/JMR.2003.0326[178] Fu G H, Chandra A, Guha S, et al. A plasticity-based model of material removal in chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP). IEEE Trans Semicond Manuf, 2001, 14(4), 406 doi: 10.1109/66.964328[179] Lu Z Y, Lee S H, Babu S V, et al. The use of monodispersed colloids in the polishing of copper and tantalum. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2003, 261(1), 55 doi: 10.1016/S0021-9797(02)00166-2[180] Yang J C, Oh D W, Lee G W, et al. Step height removal mechanism of chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) for sub-nano-surface finish. Wear, 2010, 268(3/4), 505[181] Wang Y G, Chen Y, Qi F, et al. A molecular-scale analytic model to evaluate material removal rate in chemical mechanical planarization considering the abrasive shape. Microelectron Eng, 2015, 134, 54 doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2015.02.012[182] Wang Y G, Zhao Y W, An W, et al. Modeling effects of abrasive particle size and concentration on material removal at molecular scale in chemical mechanical polishing. Appl Surf Sci, 2010, 257(1), 249 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.06.077[183] Li H R. Study on the galvanic corrosion of cobalt barrier layer of copper interconnect and the stability of alkaline polishing solution. Master Dissertation, Hebei University of Technology, 2022 (in Chinese)[184] Lee H. Material removal characteristics of abrasive-free Cu chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP) using electrolytic ionization via Ni electrodes. Micromachines, 2023, 14(2), 272 doi: 10.3390/mi14020272[185] Zhang Z Y, Liu J, Hu W, et al. Chemical mechanical polishing for sapphire wafers using a developed slurry. J Manuf Process, 2021, 62, 762 doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.01.004[186] Kwon T Y, Ramachandran M, Park J G. Scratch formation and its mechanism in chemical mechanical planarization (CMP). Friction, 2013, 1(4), 279 doi: 10.1007/s40544-013-0026-y[187] Li X A, Xi M F, Guo W, et al. Two-step chemical mechanical polishing of stainless steel. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol, 2022, 11(4), 044001 doi: 10.1149/2162-8777/ac5eae[188] Gao S, Huang H, Zhu X L, et al. Surface integrity and removal mechanism of silicon wafers in chemo-mechanical grinding using a newly developed soft abrasive grinding wheel. Mater Sci Semicond Process, 2017, 63, 97 doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2017.02.001[189] Luo J, Dornfeld D A. Integrated modeling of chemical mechanical planarization for sub-micron IC fabrication: from particle scale to feature, die and wafer scales. Springer Science & Business Media, 2013[190] Wang Z Y, Zhang Z Y, Zhou H X, et al. Close atomic surface on aluminum alloy using green chemical mechanical polishing with synergistic effect between yttria and silica abrasives. Appl Surf Sci, 2025, 681, 161586 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.161586[191] Song Z Z, Wang D, Zhang Z Y, et al. Close atomic surface of stainless steel produced by developed novel green chemical mechanical polishing using silica and Samaria composite abrasives. Surf Interfaces, 2025, 64, 106474 doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2025.106474[192] Xie W X, Zhang Z Y, Liao L X, et al. Green chemical mechanical polishing of sapphire wafers using a novel slurry. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(44), 22518 doi: 10.1039/D0NR04705H[193] Wang D, Liu L, Zhang Z Y, et al. Atomic-scale planarization surface of quartz glass induced by novel green chemical mechanical polishing using three ingredients. Mater Today Sustain, 2024, 25, 100669[194] Lee H, Kim H, Jeong H. Approaches to sustainability in chemical mechanical polishing (CMP): A review. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 2021, 9(1), 349[195] Irimia-Vladu M. "Green" electronics: Biodegradable and biocompatible materials and devices for sustainable future. Chem Soc Rev, 2014, 43(2), 588 doi: 10.1039/C3CS60235D[196] Krolczyk G M, Maruda R W, Krolczyk J B, et al. Ecological trends in machining as a key factor in sustainable production–A review. J Clean Prod, 2019, 218, 601 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.017[197] Zhang Z Y, Shi Z F, Du Y F, et al. A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing for a titanium alloy using an environment-friendly slurry. Appl Surf Sci, 2018, 427, 409 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.064[198] Peethala B C, Amanapu H P, Lagudu U R K, et al. Cobalt polishing with reduced galvanic corrosion at copper/cobalt interface using hydrogen peroxide as an oxidizer in colloidal silica-based slurries. J Electrochem Soc, 2012, 159(6), H582 doi: 10.1149/2.073206jes[199] Liu L, Zhang Z Y, Wu B, et al. A review: Green chemical mechanical polishing for metals and brittle wafers. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2021, 54(37), 373001 doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/ac0c4a[200] Li H D, Zhang Z Y, Shi C J, et al. Novel green chemical mechanical polishing by controlling pH values and redox reaction for achieving atomic surface of a nickel alloy. Appl Surf Sci, 2024, 657, 159787 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.159787[201] Dong L G, Zhang Z Y, Zhao F, et al. Atomic surface on a Ni alloy produced by novel green chemical mechanical polishing. Tribol Int, 2025, 211, 110902 doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2025.110902[202] Cui X X, Zhang Z Y, Yu S Q, et al. Unprecedented atomic surface of silicon induced by environmentally friendly chemical mechanical polishing. Nanoscale, 2023, 15(21), 9304 doi: 10.1039/D3NR01149F[203] Yu Z B, Jia Z H, Liu W, et al. Facet-dependent oxidative fabrication of diamond determined by operando scanning electron microscopy. Nano Lett, 2025, 25(13), 5391 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5c00236[204] Zhang S, Wang D, Zhao F, et al. Close atomic surface of titanium alloy produced by novel photocatalytic chemical mechanical polishing using developed SiO2@Al2O3@CeO2 composite abrasives with high material removal rate. Appl Surf Sci, 2025, 703, 163436 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2025.163436[205] Zhao F, Zhang Z Y, Zhou H X, et al. Novel full-scale model verified by atomic surface and developed composite microfiber and slurry polishing system. Compos Part B Eng, 2024, 283, 111598 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2024.111598[206] Yu Z B, Zhang Z Y, Zeng Z N, et al. Atomic surface of diamond induced by novel green photocatalytic chemical mechanical polishing with high material removal rate. Int J Extrem Manuf, 2025, 7(2), 025102 doi: 10.1088/2631-7990/ad97f7[207] Zhao F, Zhang Z Y, Zhou H X, et al. Unprecedented developed composite polishing system to achieve atomic surface integrating rough and fine polishing using a novel hyper-conjugated pad through controlling the temperature of a proposed green slurry. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater, 2025, 8(3), 234 doi: 10.1007/s42114-025-01306-0 -
Proportional views




 Zuozuo Wu received the Ph.D. degree from Heidelberg University. She is a researcher at Zhejiang University. Her research focuses on precision semiconductor technology, encompassing semiconductor silicon materials, and advanced processing techniques.
Zuozuo Wu received the Ph.D. degree from Heidelberg University. She is a researcher at Zhejiang University. Her research focuses on precision semiconductor technology, encompassing semiconductor silicon materials, and advanced processing techniques. Jinglin Cheng received the M.S. degree from Shanghai Institute of Technology. She is an assistant engineer at Shangyu Institute of Semiconductor Materials, primarily engaged in research on chemical mechanical polishing of large-size silicon wafers.
Jinglin Cheng received the M.S. degree from Shanghai Institute of Technology. She is an assistant engineer at Shangyu Institute of Semiconductor Materials, primarily engaged in research on chemical mechanical polishing of large-size silicon wafers. Zhiguo Yu received the Ph.D. degree from University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. He is a researcher at ZJU-Hangzhou Global Scientific and Technological Innovation Center. His research focuses on preparation and purification technologies of high-purity silica.
Zhiguo Yu received the Ph.D. degree from University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. He is a researcher at ZJU-Hangzhou Global Scientific and Technological Innovation Center. His research focuses on preparation and purification technologies of high-purity silica. Wei Zhou received the M.S. degree in Materials Science and Engineering from Xiangtan University. He works at Zhejiang Jingsheng Electromechanical Co., Ltd., where he conducts research on chemical mechanical polishing processes.
Wei Zhou received the M.S. degree in Materials Science and Engineering from Xiangtan University. He works at Zhejiang Jingsheng Electromechanical Co., Ltd., where he conducts research on chemical mechanical polishing processes. Yangjian Li received the Ph.D. degree from Zhejiang University. He currently works at Zhejiang Jingsheng Electromechanical Co., Ltd. He is dedicated to the research of chemical mechanical polishing equipment and processes.
Yangjian Li received the Ph.D. degree from Zhejiang University. He currently works at Zhejiang Jingsheng Electromechanical Co., Ltd. He is dedicated to the research of chemical mechanical polishing equipment and processes. Jianwei Cao received the Ph.D. degree from Zhejiang University. He is the Chairman of Zhejiang Jingsheng Electromechanical Co., Ltd., and also serves as the Director of its R & D Center. His expertise lies in electromechanical control and hydraulic transmission and control.
Jianwei Cao received the Ph.D. degree from Zhejiang University. He is the Chairman of Zhejiang Jingsheng Electromechanical Co., Ltd., and also serves as the Director of its R & D Center. His expertise lies in electromechanical control and hydraulic transmission and control. Wei Sun received the Ph.D. degree from University of Toronto. He is working as a Tenured Associate Professor at Zhejiang University. His research centers on silicon nanostructures for catalysis and devices.
Wei Sun received the Ph.D. degree from University of Toronto. He is working as a Tenured Associate Professor at Zhejiang University. His research centers on silicon nanostructures for catalysis and devices. Shuai Yuan received the Ph.D. degree in Materials Science and Engineering from Zhejiang University. He is working as a tenure-track Professor at Zhejiang university. His research specializes in silicon materials for integrated circuits (IC) and photovoltaics (PV).
Shuai Yuan received the Ph.D. degree in Materials Science and Engineering from Zhejiang University. He is working as a tenure-track Professor at Zhejiang university. His research specializes in silicon materials for integrated circuits (IC) and photovoltaics (PV). Deren Yang is an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the professor and director of the state key laboratory of silicon and advanced semiconductor materials at Zhejiang University. His research centers on semiconductor materials, covering silicon, silicon carbide, gallium oxide, perovskite and other advanced semiconductor materials.
Deren Yang is an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the professor and director of the state key laboratory of silicon and advanced semiconductor materials at Zhejiang University. His research centers on semiconductor materials, covering silicon, silicon carbide, gallium oxide, perovskite and other advanced semiconductor materials.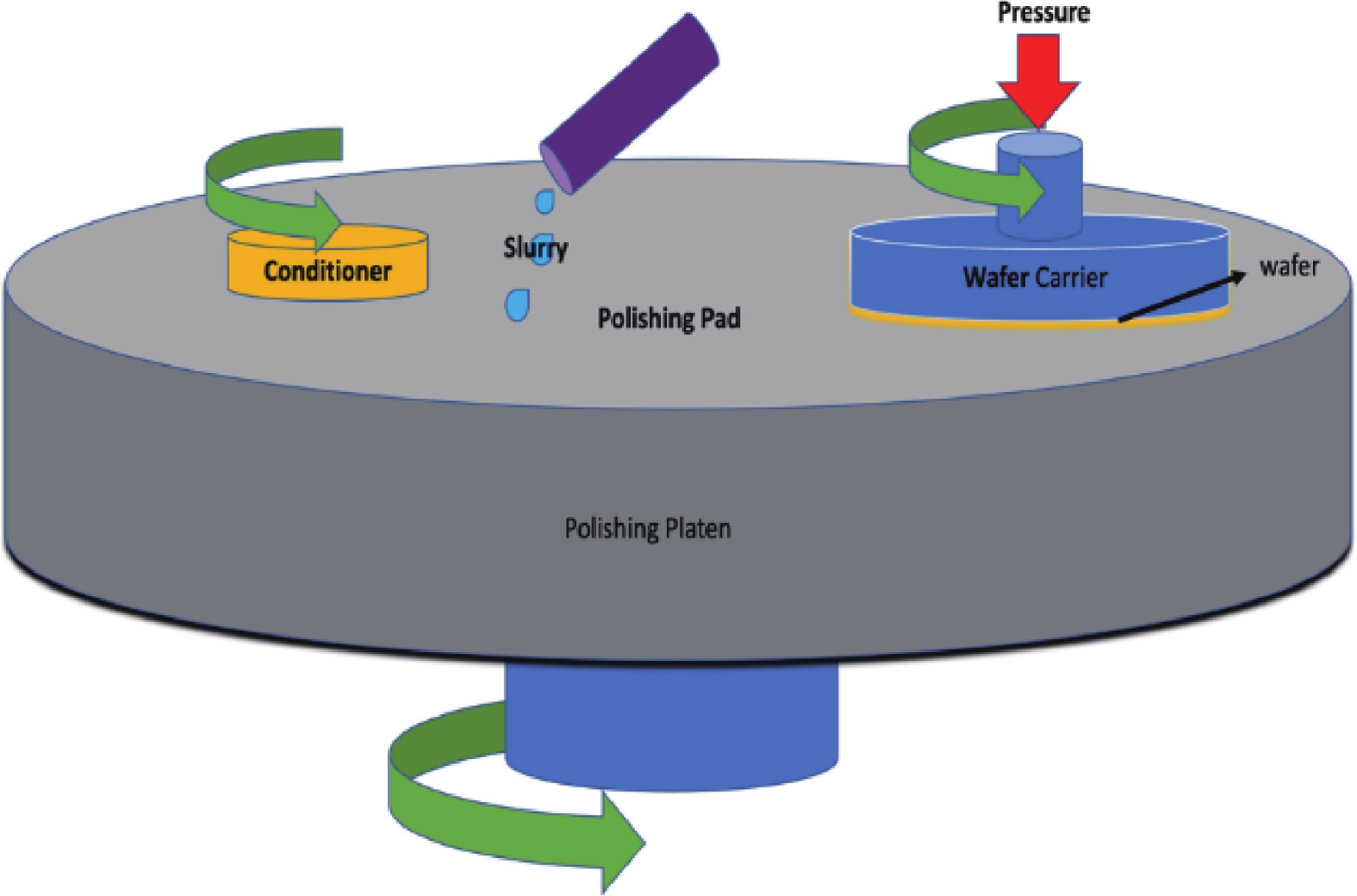
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: