| Citation: |
J.O. Akinlami, A.O. Ashamu. Optical properties of GaAs[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(3): 032002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/3/032002
****
J.O. Akinlami, A.O. Ashamu. Optical properties of GaAs[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(3): 032002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/3/032002.
|
-
Abstract
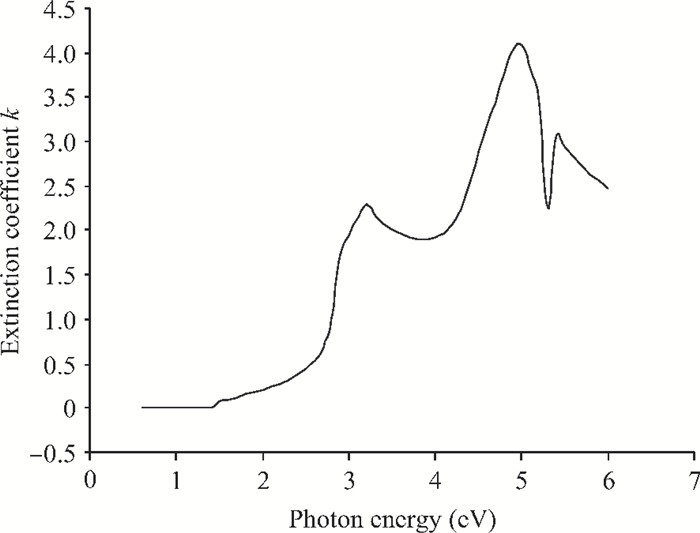
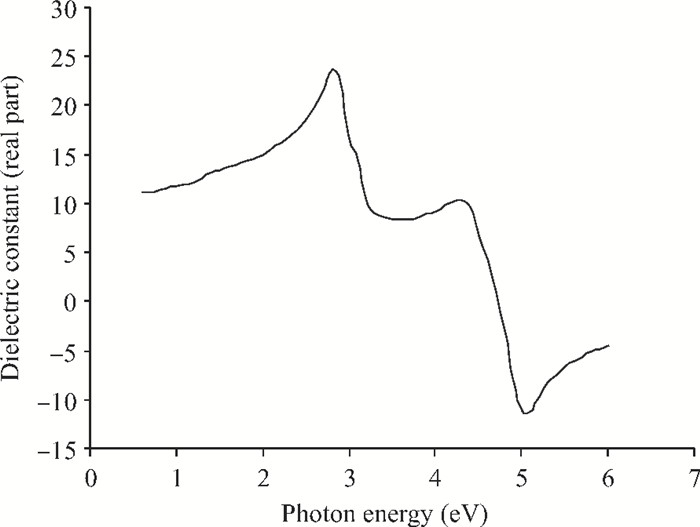
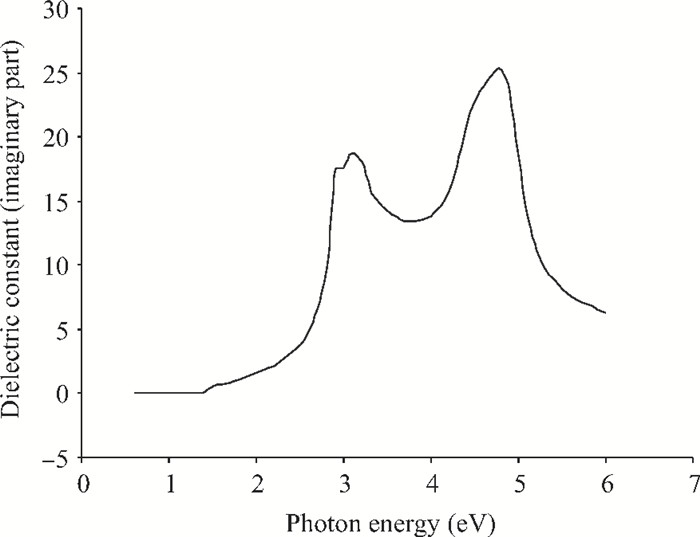
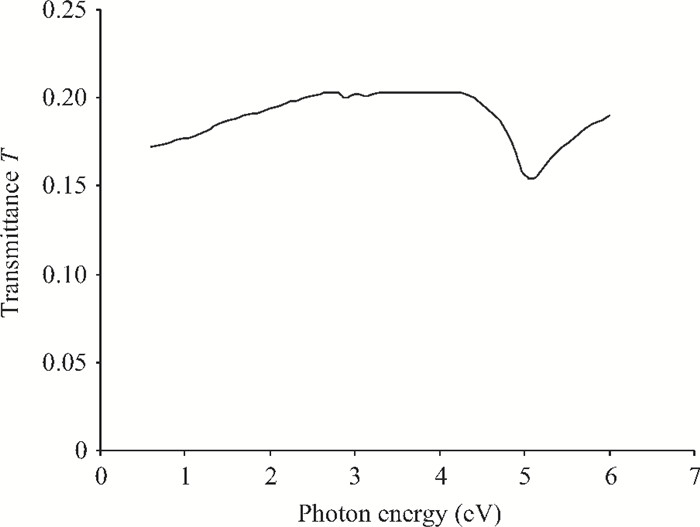
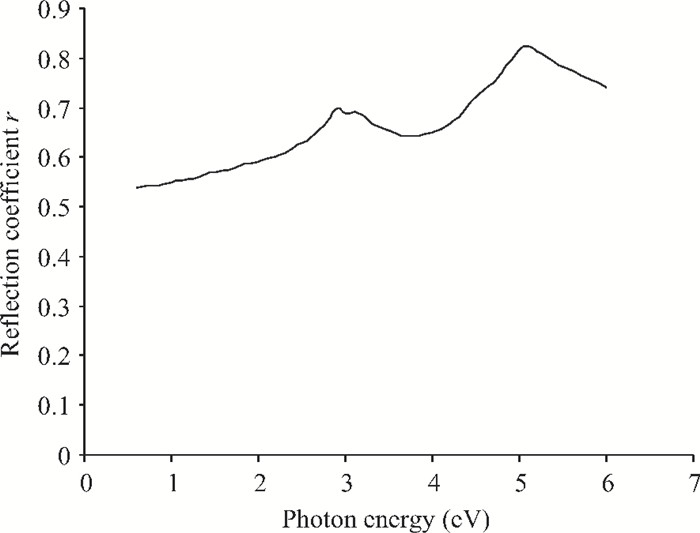
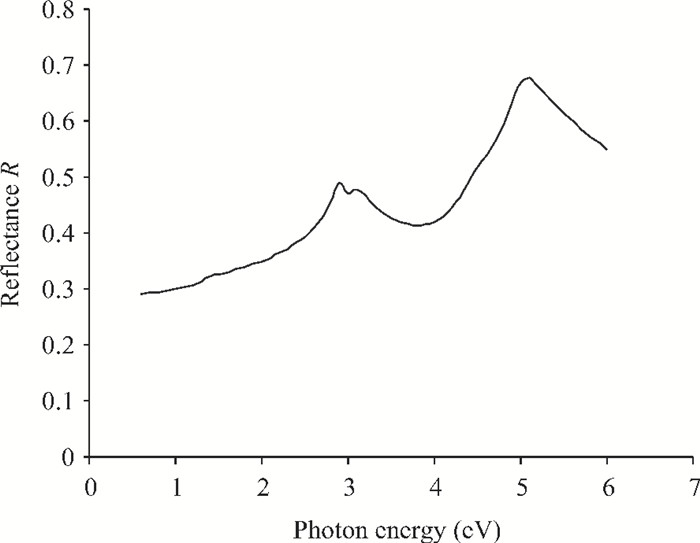
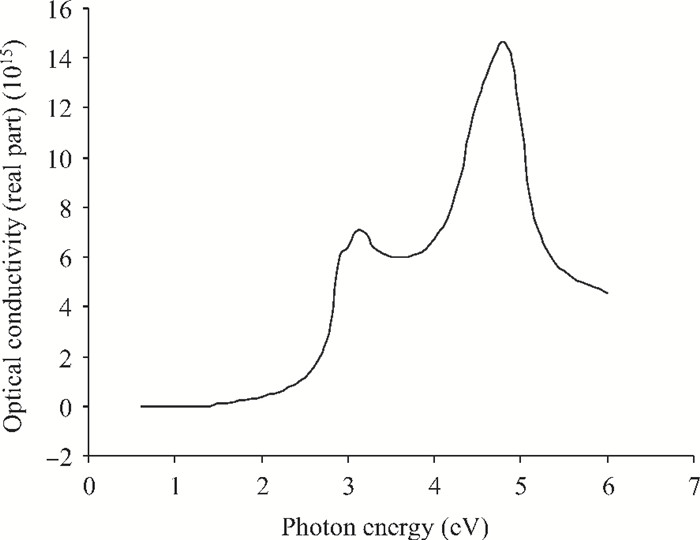
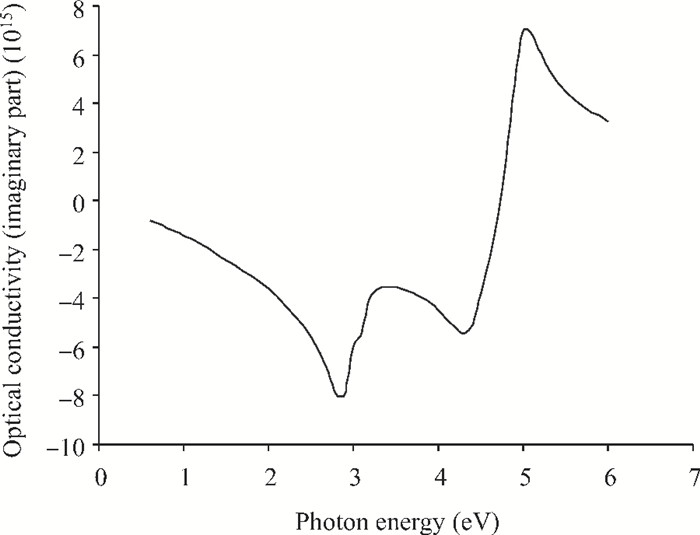
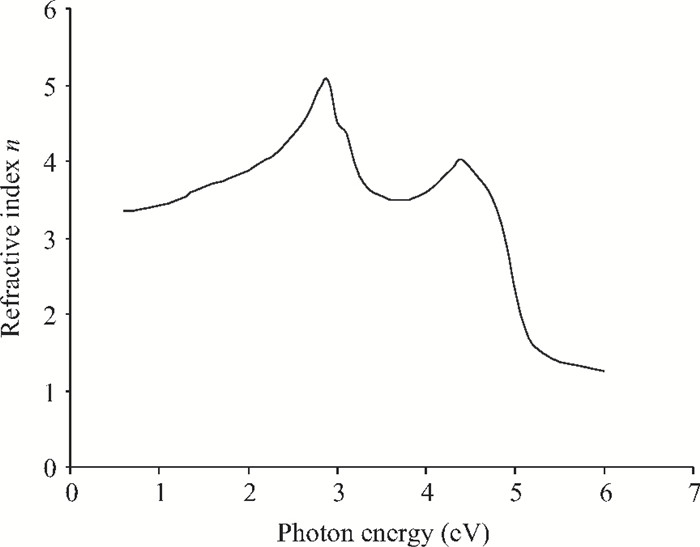
We have investigated the optical properties of gallium arsenide (GaAs) in the photon energy range 0.6-6.0 eV. We obtained a refractive index which has a maximum value of 5.0 at a photon energy of 3.1 eV; an extinction coefficient which has a maximum value of 4.2 at a photon energy of 5.0 eV; the dielectric constant, the real part of the complex dielectric constant has a maximum value of 24 at a photon energy of 2.8 eV and the imaginary part of the complex dielectric constant has a maximum value of 26.0 at a photon energy of 4.8 eV; the transmittance which has a maximum value of 0.22 at a photon energy of 4.0 eV; the absorption coefficient which has a maximum value of 0.22×108 m-1 at a photon energy of 4.8 eV, the reflectance which has a maximum value of 0.68 at 5.2eV; the reflection coefficient which has a maximum value of 0.82 at a photon energy of 5.2 eV; the real part of optical conductivity has a maximum value of 14.2×1015 at 4.8 eV and the imaginary part of the optical conductivity has a maximum value of 6.8×1015 at 5.0 eV. The values obtained for the optical properties of GaAs are in good agreement with other results. -
References
[1] Sze S M. Physics of semiconductor devices. New York:Wiley, 1969 http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1981psd..book.....S[2] Beliles R P. The metals. In:Clayton G D, Clayton F E, ed. Patty's industrial hygiene and toxicology. Vol. 26. 4th ed. New York:John Wiley and Sons, 1994:1879 http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94689X/201303/45044662.html[3] Sabot J L, Lauvray H. Gallium and gallium compounds. In:Kroschwitz J I, Howe-Grant M, ed. Kirk-Othmer encyclopedia of chemical technology. 4th ed. Vol. 12. New York:John Wiley and Sons, 1994:299[4] Goldschmidt V M. Crystal structure and chemical constitution. Trans Faraday Soc, 1929, 25:253 doi: 10.1039/tf9292500253[5] Tibermacine T, Mercizga A. Revue des energies renouvelables, 2009, 12(1):125[6] Sze S M, Ng K K. Physics of semiconductor devices. 3rd ed. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 2007[7] Jovanovic D, Gajic R, Hingerl K. Optical properties of GaAs 2D Archimedean photonic lattice tiling with the p4g symmetry. Science of Sintering, 2008, 40:167 doi: 10.2298/SOS0802167J[8] Ghosh C, Pal S, Goswami B, et al. Theoretical study of the electronic structure of GaAs nanotubes. J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111:12284 doi: 10.1021/jp0746695[9] Ng K K. Complete guide to semiconductor device. 2nd ed. New York:Wiley, 2002[10] Colombo C, Hei M, Gratzel M, et al. Gallium arsenide P-I-N radial structures for photovoltaic applications. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94:173108 doi: 10.1063/1.3125435[11] Kendall E J M. Transistors. New York:Pergamon Press, 1969[12] Wallmark J T. Field-effect transistors, physics, technology and applications. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliff, 1966[13] Liou J J, Schwierz F. RF MOSFET:recent advances, current status and future trends. Solid-State Electron, 2003, 47:1881 doi: 10.1016/S0038-1101(03)00225-9[14] Chakrabarti N B. GaAs integrated circuits. J Inst Electron Telecommun Eng, 1992, 38:163[15] Greber J F. Gallium and gallium compounds. In:Ullmann's encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. 6th Rev. ed. Vol. 15. Weinheim, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH and CO., 2003:235 http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94689X/201303/45044662.html[16] Fox M. Optical properties of solids. Oxford University Press, 2001:3 doi: 10.1119/1.1987434[17] Yu P Y, Cardona M. Fundamentals of semiconductors. Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 1996[18] Schubert E F. Refractive index and extinction coefficient of materials. 2004. http://www.rpi.edu/~schubert/Educational-resources/Materials-Refractive-index-and-extinction-coefficient.pdf[19] Goswami A. Thin film fundamentals. New Delhi:New Age International, 2005 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21928861[20] Sharma P, Katyal S C. Determination of optical parameters of a-(As2Se3)90Ge10 thin film. J Phys D:Appl Phys, 2007, 40:2115 doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/40/7/038[21] Blakemore J S. Semiconducting and other major properties of gallium arsenide. J Appl Phys, 1982, 53:10 doi: 10.1063/1.331665[22] Brian R B, Richard A S, Jesus A D. Carrier-induced change in refractive index of InP, GaAs and InGaAsP. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 1990, 26(1):113 doi: 10.1109/3.44924[23] De Boeij P L, Wijers C M J. Ab initio calculations of the reflectance anisotropy of GaAs (110):the role of nonlocal polarizability and local fields. Phys Lett A, 2000, 272:264 doi: 10.1016/S0375-9601(00)00427-8[24] Lautenschlager P, Garriga M, Logothetidis M. Interband critical points of GaAs and their temperature dependence. Cardona Phys Rev B, 1987, 35:9174 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.35.9174[25] Alouani M, Brey L, Christensen N E. Calculated optical properties of semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 1988, 37(3):1167 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.37.1167[26] Sturge M D. Optical absorption of gallium arsenide between 0.6 and 2.75 eV. Phys Rev, 1962, 127(3):768 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.127.768[27] Aloulou S, Fathallah M, Oueslati M, et al. Determination of absorption coefficients and thermal diffusivity of modulated doped GaAlAs/GaAs heterostructure by photothermal deflection spectroscopy. American Journal of Applied Sciences, 2005, 2(10):1412 doi: 10.3844/ajassp.2005.1412.1417[28] Holm R T, Gibson J W, Palik E D. Infrared reflectance studies of bulk and epitaxial-film n-type GaAs. J Appl Phys, 1977, 48:212 doi: 10.1063/1.323322[29] El-Nahass M M, Youssef S B, Ali H A M. Optical properties of Zn doped GaAs single crystals. J Optoelectron Adv Mater, 2011, 13(1):76[30] Phillip H R, Ehrenreich H. optical properties of semiconductors. Phys Rev, 1963, 129:1550 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.129.1550 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: