| Citation: |
V.K. Dwivedi, P. Srivastava, G. Vijaya Prakash. Photoconductivity and surface chemical analysis of ZnO thin films deposited by solution-processing techniques for nano and microstructure fabrication[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(3): 033001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/3/033001
****
V K Dwivedi, P Srivastava, G V Prakash. Photoconductivity and surface chemical analysis of ZnO thin films deposited by solution-processing techniques for nano and microstructure fabrication[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(3): 033001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/3/033001.
|
Photoconductivity and surface chemical analysis of ZnO thin films deposited by solution-processing techniques for nano and microstructure fabrication
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/3/033001
More Information
-
Abstract
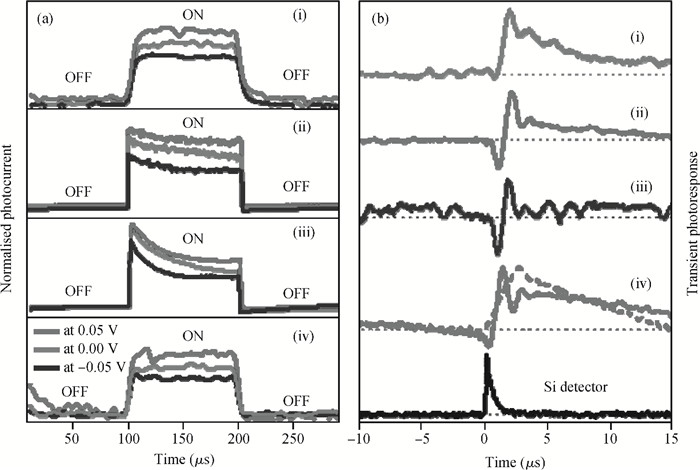
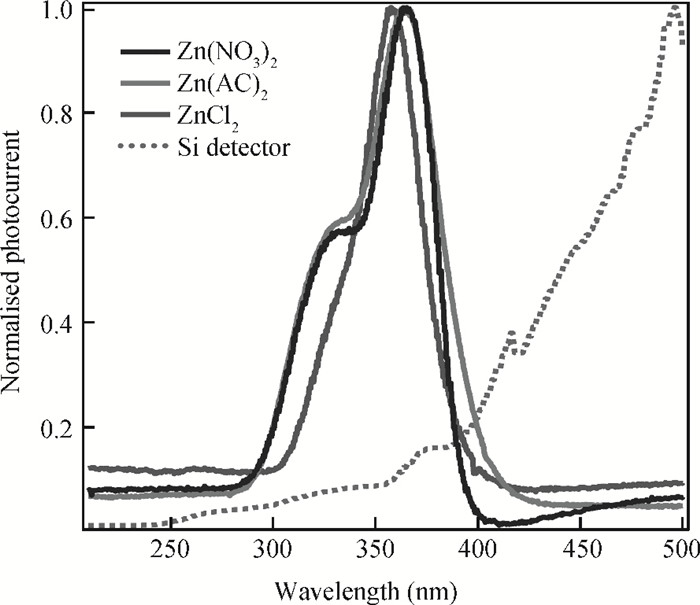
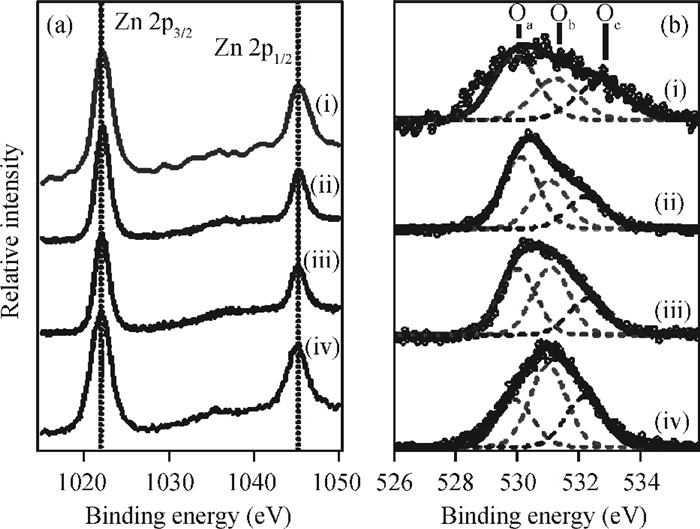
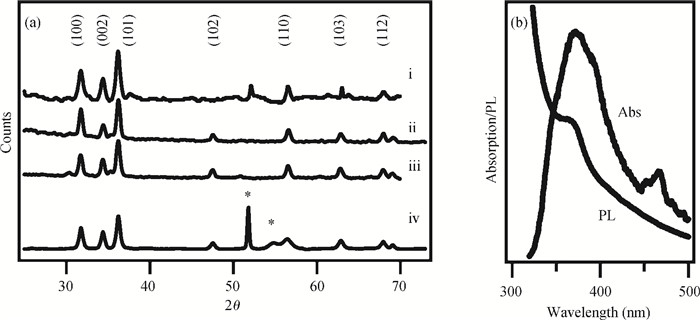
The fabrication of zinc oxide (ZnO) from inexpensive solution-processing techniques, namely, electrochemical deposition and electrospinning were explored on various conducting and mesoporous semiconducting surfaces. Optimised conditions were derived for template-and self-assisted nano/micro structures and composites. ZnO thin films were annealed at a fixed temperature under ambient conditions and characterised using physical and optical techniques. The photocurrent response in the UV region shows a fast rise and double decay behaviour with a fast component followed by a slow oscillatory decay. Photocurrent results were correlated with surface chemical analysis from X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Various characterisation details reveal the importance of fabrication parameter optimisation for useful low-cost optoelectronic applications. -
References
[1] Tan S T, Chen B J, Sun X W, et al. Blueshift of optical band gap in ZnO thin films grown by metal-organic chemical-vapor deposition. J Appl Phys, 2005, 98(1):013505 doi: 10.1063/1.1940137[2] Park J W, Kim J K, Suh K Y. Fabrication of zinc oxide nanostructures using solvent-assisted capillary lithography. Nanotechnology, 2006, 17(10):2631 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/17/10/031[3] Park J H, Jang S J, Kim S S, et al. Growth and characterization of single crystal ZnO thin films using inductively coupled plasma metal organic chemical vapor deposition. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89(12):121108 doi: 10.1063/1.2356075[4] Tian Z R, Voigt J A, Liu J, et al. Complex and oriented ZnO nanostructures. Nat Mater, 2003, 2(12):821 doi: 10.1038/nmat1014[5] Li Y, Meng G W, Zhang L D. Ordered semiconductor ZnO nanowire arrays and their photoluminescence properties. Appl Phys Lett, 2000, 76(15):2011 doi: 10.1063/1.126238[6] Prakash G V, Singh R, Kumar A, et al. Fabrication and characterisation of CdSe photonic structures from self-assembled templates. Mater Lett, 2006, 60(13/14):1744 http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=17628773[7] Prakash G V, Pradeesh K, Kumar A, et al. Fabrication and optoelectronic characterisation of ZnO photonic structures. Mater Lett, 2008, 62(8/9):1183 http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=20070298[8] Yang X, Shao C, Guan H, et al. Preparation and characterization of ZnO nano fibers by using electrospun PVA/zinc acetate composite fiber as precursor. Inorg Chem Commun, 2004, 7(2):176 doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2003.10.035[9] Teo W E, Ramakrishna S. A review on electrospinning design and nanofibre assemblies. Nanotechnology, 2006, 17(14):R89 http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=17975191[10] Mizuta T, Ishibashi T, Minemoto T, et al. Chemical deposition of zinc oxide thin films on silicon substrate. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 515(4):2458 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2006.06.035[11] Mu G, Gudavarthy R V, Kulp E A, et al. Tilted epitaxial ZnO nanospears on Si(001) by chemical bath deposition. Chem Mater, 2009, 21(17):3960 doi: 10.1021/cm9010019[12] Shaoqiang C, Jian Z, Xiao F, et al. Nanocrystalline ZnO thin films on porous silicon/silicon substrates obtained by sol-gel technique. Appl Surf Sci, 2005, 241(3/4):384 http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=16551843[13] Cai H, Shen H, Yin Y, et al. The effects of porous silicon on the crystal-line properties of ZnO thin film. J Phys Chem Solids, 2009, 70(6):967 doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2009.05.004[14] Kayahan E. White light luminescence from annealed thin ZnO deposited porous silicon. J Lumin, 2010, 130(7):1295 doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2010.02.042[15] Wong H. Recent developments in silicon optoelectronic devices. Microelectron Reliab, 2002, 42(3):317 doi: 10.1016/S0026-2714(02)00008-2[16] Mazzoleni C, Pavesi L. Application to optical components of dielectric porous silicon multilayers. Appl Phys Lett, 1995, 67(20):2983 doi: 10.1063/1.114833[17] Bettotti P, Cazzanelli M, Negro L D, et al. Silicon nanostructures for photonics. J Phys:Condens Matter, 2002, 14(35):8253 doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/14/35/305[18] Dwivedi V K, Pradeesh K, Prakash G V. Controlled emission from dye saturated single and coupled microcavities. Appl Surf Sci, 2011, 257(8):3468 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.11.048[19] Qiao H, Guan B, Bocking T, et al. Optical properties of Ⅱ-Ⅵ colloidal quantum dot doped porous silicon microcavities. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96(16):161106 doi: 10.1063/1.3404183[20] Yoshida T, Komatsu D, Shimokawa N, et al. Mechanism of cathodic electrodeposition of zinc oxide thin films from aqueous zinc nitrate baths. Thin Solid Films, 2004, 451:166 http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=15611202[21] Rappich J, Fahoume T M. Nonradiative recombination and band bending of p-Si(100) surfaces during electrochemical deposition of polycrystalline ZnO. Thin Solid Films, 2005, 487(1/2):157 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040609005000866[22] Markham M L. An investigation into the properties of nanoporous semiconductors. PhD Thesis, University of Southampton, 2006 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1387181114002753[23] Xu Q A, Zhang J W, Ju K R, et al. ZnO thin film photoconductive ultraviolet detector with fast photoresponse. J Cryst Growth, 2006, 289(1):44 doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2005.11.008[24] Liu K W, Ma J G, Zhang J Y, et al. Ultraviolet photoconductive detector with high visible rejection and fast photoresponse based on ZnO thin film. Solid State Electron, 2007, 51(5):757 doi: 10.1016/j.sse.2007.03.002[25] Yang W, Vispute R D, Choopun S, et al. Ultraviolet photoconductive detector based on epitaxial Mg0.34Zn0.66O thin films. Appl Phys Lett, 2001, 78(18):2781 doi: 10.1063/1.1368378[26] Liang S, Sheng H, Liu Y, et al. ZnO Schottky ultraviolet photodetectors. J Cryst Growth, 2001, 225(2-4):110 doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(01)00830-2[27] Liu C Y, Zhang B P, Lu Z W, et al. Fabrication and characterization of ZnO film based UV photodetector. J Mater Sci:Mater Electron, 2009, 20(3):197 doi: 10.1007/s10854-008-9698-x[28] Sharma P, Sreenivas K, Rao K V. Analysis of ultraviolet photoconductivity in ZnO films prepared by unbalanced magnetron sputtering. J Appl Phys, 2003, 93(7):3963 doi: 10.1063/1.1558994[29] Ra H W, Khan R, Kim J T, et al. Effects of surface modification of the individual ZnO nanowire with oxygen plasma treatment. Mater Lett, 2009, 63(28):2516 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2009.08.054[30] Lee J S, Islam M S, Kim S. Photoresponses of ZnO nanobridge devices fabricated using a single-step thermal evaporation method. Sensor Actuat B:Chem, 2007, 126(1):73 doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2006.10.042[31] Zhang L, Chen Z, Tang Y, et al. Low temperature cathodic electrodeposition of nanocrystalline zinc oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films, 2005, 492(1/2):24 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040609005006048[32] Pandey B, Ghosh S, Srivastava P, et al. Influence of microstructure on room temperature ferromagnetism in Ni implanted nanodimensional ZnO films. J Appl Phys, 2009, 105(3):033909 doi: 10.1063/1.3074517[33] Zhou H, Fang G, Yuan L, et al. Deep ultraviolet and near infrared photodiode based on n-ZnO/p-silicon nanowire heterojunction fabricated at low temperature. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94(1):013503 doi: 10.1063/1.3064161 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: