| Citation: |
D. Lalitha, A. John Peter. Effect of p-d exchange with an itinerant carrier in a GaMnAs quantum dot[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(7): 072001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/072001
****
D Lalitha, A J Peter. Effect of p-d exchange with an itinerant carrier in a GaMnAs quantum dot[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(7): 072001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/072001.
|
Effect of p-d exchange with an itinerant carrier in a GaMnAs quantum dot
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/072001
More Information
-
Abstract
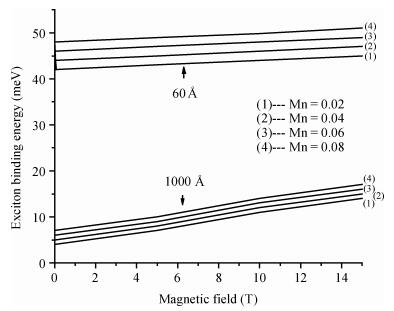
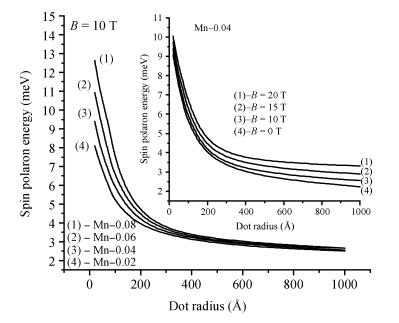
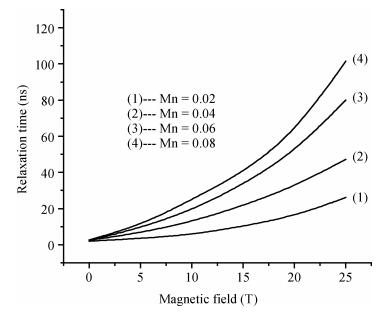
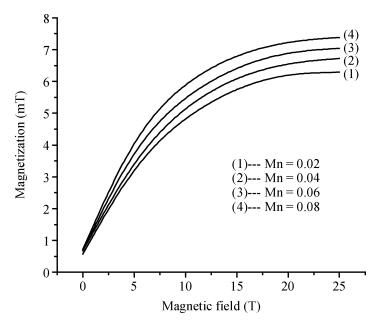
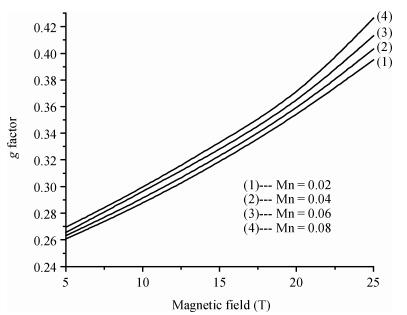
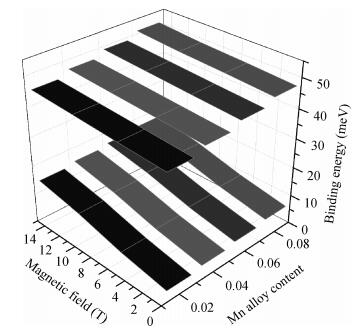
Hydrogenic acceptor binding energy as a function of dot radius in a GaMnAs/Ga0.6Al0.4As quantum dot is calculated including the exchange interaction of Mn alloy content with an itinerant carrier. Calculations are performed by varying its dot radius, for various Mn alloy contents in GaMnAs quantum dot within a single band effective mass approximation using variational method. The spin polaronic energy of the acceptor impurity for different Mn2+ is evaluated for different dot radii using a mean field theory in the presence of magnetic field strength. The magnetization is computed in the influence of magnetic field and the Mn ions. The effective g-factor of the valence band electron with the inclusion of effects of Mn ion impurities is found in the influence of the magnetic field. The exchange coupling constant is calculated for various magnetic field strengths. The results show that the p-d exchange interaction in the GaMnAs/Ga0.6Al0.4As quantum dot has a strong dependence on spatial confinement, effect of magnetic field strength and the Mn alloy content. Our results are in good agreement with the other investigators.-
Keywords:
- quantum dot,
- acceptor,
- diluted magnetic semiconductors
-
References
[1] Dietl T, Ohno H, Matsukura F. Ferromagnetic semiconductor heterostructures for spintronics. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2007, 54:945 doi: 10.1109/TED.2007.894622[2] Ku K C, Potashnik S J, Wang R F, et al. Highly enhanced Curie temperature in low-temperature annealed[Ga, Mn]As epilayers. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 82:2302 doi: 10.1063/1.1564285[3] Ohno H, Chiba D, Matsukura F, et al. Electric-field control of ferromagnetism. Nature, 2000, 408:944 doi: 10.1038/35050040[4] Wang J, Sun C, Hashimoto Y, et al. Ultrafast magneto-optics in ferromagnetic Ⅲ-Ⅴ semiconductors. J Phys:Condens Matter, 2006, 18:R501[5] Hashimoto Y, Kobayashi S, Munekata H. Photoinfduced precession of magnetization in ferromagnetic (Ga, Mn)As. Phys Rev Lett, 2008, 100:067202 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.067202[6] Nazmul A M, Sugahara S, Tanaka M. Temperature ferromagnetism in GaAs-based heterostructures with Mn d doping. Phys Rev B, 2003, 67:241308 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.67.241308[7] Jungwirth T, Wang K Y, Mašek J, et al. Prospects for high temperature ferromagnetism in {(Ga, Mn)As} semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 2005, 72:165204 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.72.165204[8] Ohno Y, Arata I, Matsukura F, et al. Valence band barrier at (Ga, Mn)As/GaAs interfaces. Physica E, 2002, 13:521 doi: 10.1016/S1386-9477(02)00185-6[9] Ohno Y, Young D K, Beschoten B, et al. Electrical spin injection in a ferromagnetic semiconductor heterostructure. Nature, 1999, 402:790 doi: 10.1038/45509[10] Breya L, Tejedor C, Fernández-Rossier J. Tunnel magnetoresistance in GaMnAs:going beyond Julliére formula. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85:1996 doi: 10.1063/1.1789241[11] Das Sarma S, Hwang E H, Kaminski A. Magnetotransport properties of a polarization-doped three-dimensional electron. Phys Rev B, 2003, 67:155201 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.67.155201[12] Jungwirth T, Sinova J, MacDonald A H, et al. Character of states near the Fermi level in (Ga, Mn)As:impurity to valence band crossover. Phys Rev B, 2007, 76:125206 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.76.125206[13] Dietl T. Origin of ferromagnetic response in diluted magnetic semiconductors and oxides. J Phys:Condens Matter, 2007, 19:165204 doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/19/16/165204[14] Schulthess T C, Temmerman W M, Szotek Z, et al. First-principles electronic structure of Mn-doped GaAs, GaP, and GaN semiconductors. J Phys:Condens Matter, 2007, 19:165207 doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/19/16/165207[15] Burch K S, Shrekenhamer D B, Singley E J, et al. High temperature ferromagnetic semiconductor. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 97:087208 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.087208[16] Simserides C. The density of states and the electron concentration of a double-heterojunction system subjected to an in-plane magnetic field. J Phys:Condens Matter, 1999, 11:5131 doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/11/26/314[17] Snelling M J, Flinn G P, Plaut A S, et al. Magnetic g factor of electrons in GaAs/AlxGa1-xAs quantum wells. Phys Rev B, 1991, 44:11345 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.44.11345[18] Das Sarma S, Hwang E H, Kaminski A. Temperature-dependent magnetization in diluted magnetic semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 2003, 67:155201 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.67.155201[19] Gaj J A, Planel R, Fishman G. Relation of magneto-optical properties of free excitons to spin alignment of Mn2+ ions in Cd1-xMnxTe. Solid-State Commun, 1979, 29:435[20] Béal-Monod M T, Weiner R A. Negative magnetoresistivity in dilute alloys. Phys Rev, 1968, 170:552 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.170.552[21] Dietl T, Ohno H, Matsukura F. Hole-mediated ferromagnetism in tetrahedrally coordinated semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 2001, 63:195205 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.63.195205[22] Gel'mont B L, D'yakonov M I. Impurity states in zero gap semiconductors. Zh Eksp Theor Fiz, 1972, 62:713[23] Sun B, Jiang D, Sun Z, et al. Photoinduced spin alignment of the magnetic ions in (Ga, Mn)As. J Appl Phys, 2006, 100:083104 doi: 10.1063/1.2358407[24] Zhou R, Sun B Q, Ruan X Z, et al. Temperature dependence of effective g factor in diluted magnetic semiconductor (Ga, Mn)As. J Appl Phys, 2008, 103:053901 doi: 10.1063/1.2842400[25] Camilleri C, Teppe F, Scalbert D, et al. Electron and hole spin relaxation in modulation-doped CdMnTe quantum wells. Phys Rev B, 2001, 64:085331 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.64.085331 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: