| Citation: |
Wei Zhu, Baoyong Chi, Lixue Kuang, Wen Jia, Zhihua Wang. An inductorless CMOS programmable-gain amplifier with a > 3 GHz bandwidth for 60 GHz wireless transceivers[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(10): 105001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/105001
****
W Zhu, B Y Chi, L X Kuang, W Jia, Z H Wang. An inductorless CMOS programmable-gain amplifier with a > 3 GHz bandwidth for 60 GHz wireless transceivers[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(10): 105001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/105001.
|
An inductorless CMOS programmable-gain amplifier with a > 3 GHz bandwidth for 60 GHz wireless transceivers
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/105001
More Information
-
Abstract
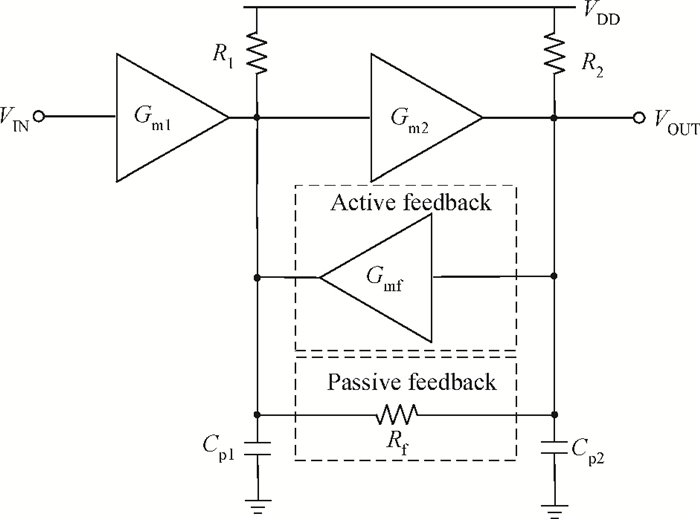
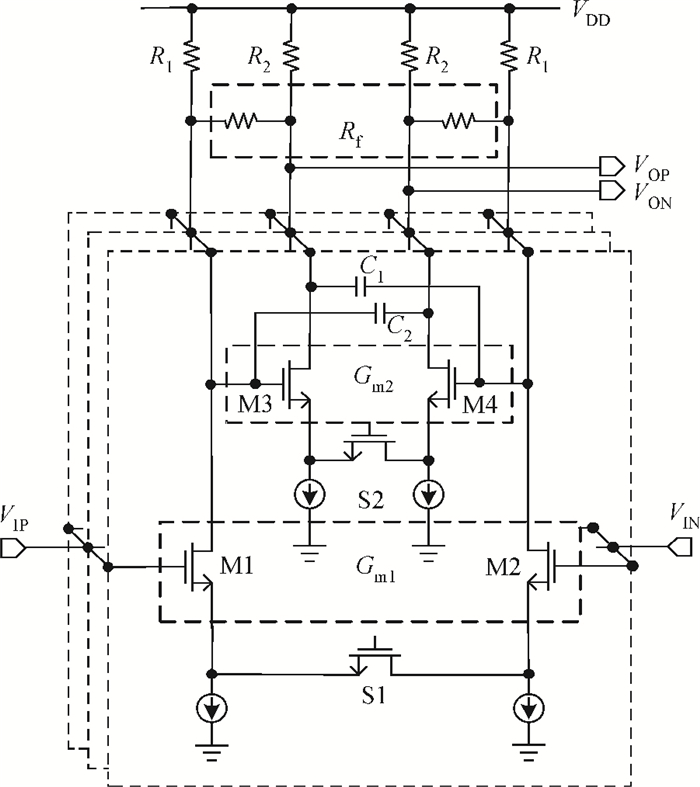
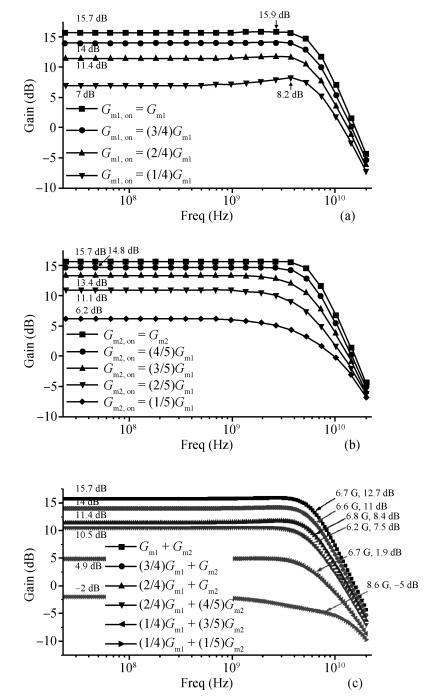
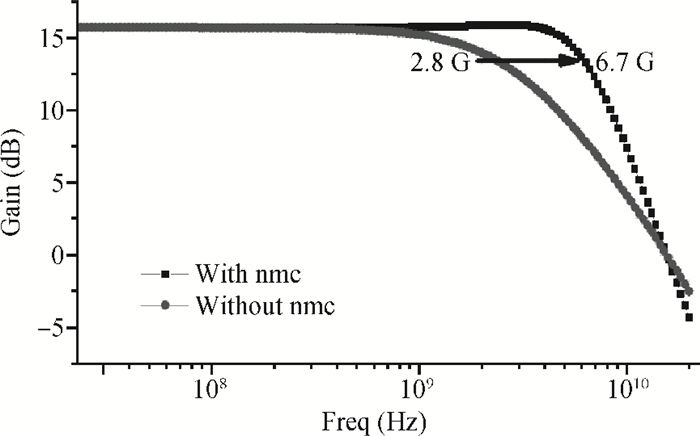
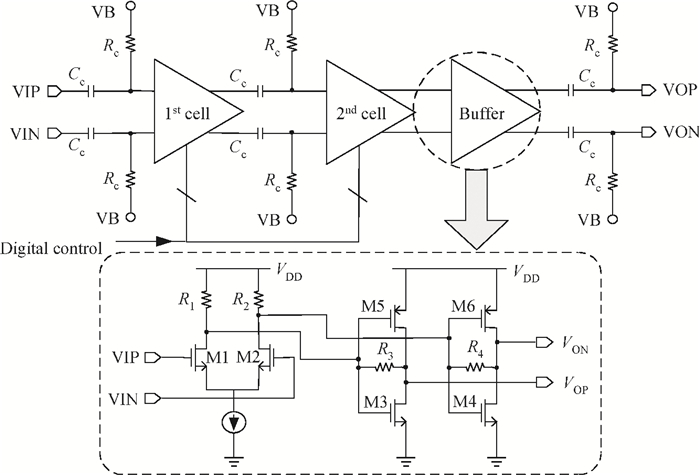
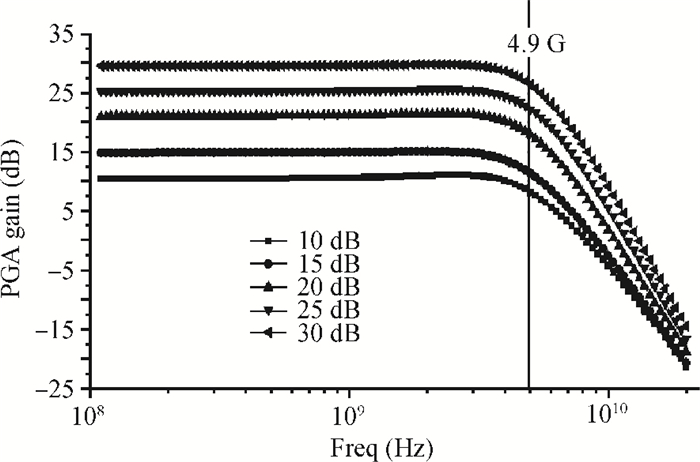
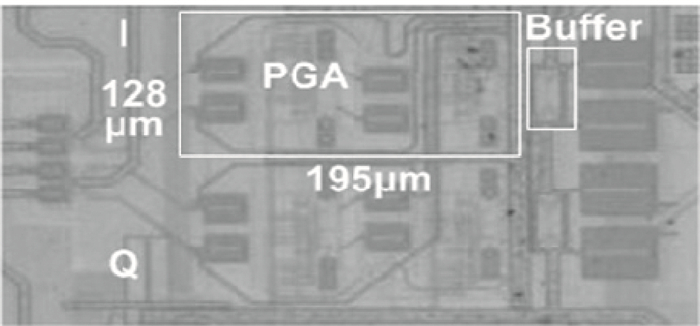
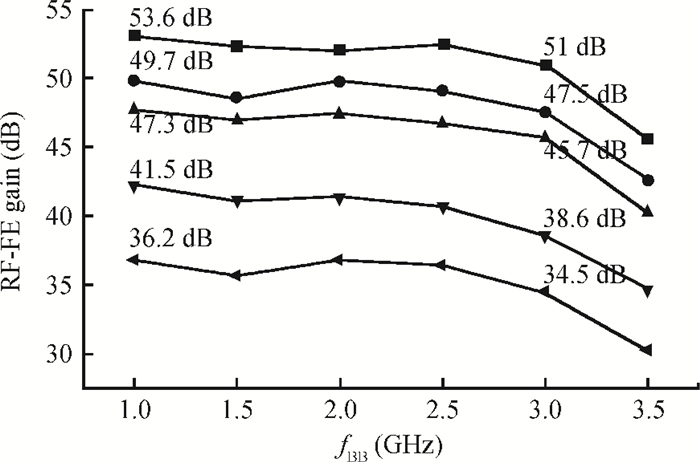
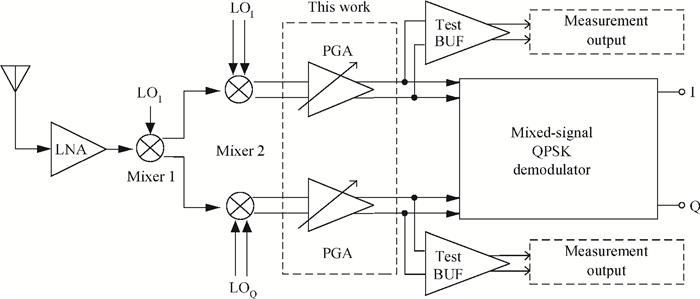
An inductorless wideband programmable-gain amplifier (PGA) for 60 GHz wireless transceivers is presented. To attain wideband characteristics, a modified Cherry-Hooper amplifier with a negative capacitive neutralization technique is employed as the gain cell while a novel circuit technique for gain adjustment is adopted; this technique can be universally applicable in wideband PGA design and greatly simplifying the design of wideband PGA. By cascading two gain cells and an output buffer stage, the PGA achieves the highest gain of 30 dB with the bandwidth much wider than 3 GHz. The PGA has been integrated into one whole 60 GHz wireless transceiver and implemented in the TSMC 65 nm CMOS process. The measurements on the receiver front-end show that the receiver front-end achieves an 18 dB variable gain range with a > 3 GHz bandwidth, which proves the proposed PGA achieves an 18 dB variable gain range with a bandwidth much wider than 3 GHz. The PGA consumes 10.7 mW of power from a 1.2-V supply voltage with a core area of only 0.025 mm2. -
References
[1] Belousov E, Lomovskaya K. A 84-dB wideband low-power variable gain amplifier. IEEE International Symposium on Signals, Circuits and Systems (ISSCS), 2013[2] Hsieh Y K, Hsieh H H, Lu L H. A wideband programmable-gain amplifier for 60 GHz applications in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE International Symposium on VLSI Design, Automation, and Test (VLSI-DAT), 2013: 1[3] Huang X, Qin X, Qin Y, et al. A 0. 8-3 GHz 40 dB dynamic range CMOS variable-gain amplifier. IEEE 9th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON), 2011: 1030[4] Qin X, Huang X, Qin Y, et al. A 0-35 dB wideband variable gain amplifier in 0. 13μm CMOS. IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology (RFIT), 2011: 61[5] Kitamura R, Tsukizawa T, Saito N. An 84 dB-gain-range and 1 GHz-bandwidth variable gain amplifier using gain flattening capacitors for multi-gigabit radio. IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), 2013: 220[6] Li J, Huang F, Hu X, et al. A 1 GHz, 68 dB CMOS variable gain amplifier with an exponential-function circuit. IEEE International Symposium on Signals Systems and Electronics (ISSSE), 2010, 2: 1 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: