| Citation: |
Lixue Kuang, Baoyong Chi, Lei Chen, Wen Jia, Zhihua Wang. A fully-differential phase-locked loop frequency synthesizer for 60-GHz wireless communication[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(12): 125002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/12/125002
****
L X Kuang, B Y Chi, L Chen, W Jia, Z H Wang. A fully-differential phase-locked loop frequency synthesizer for 60-GHz wireless communication[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(12): 125002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/12/125002.
|
A fully-differential phase-locked loop frequency synthesizer for 60-GHz wireless communication
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/12/125002
More Information
-
Abstract
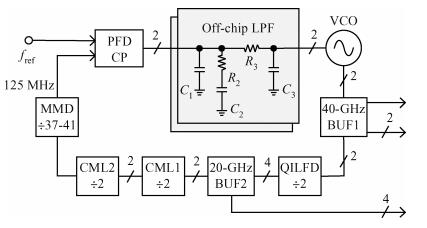
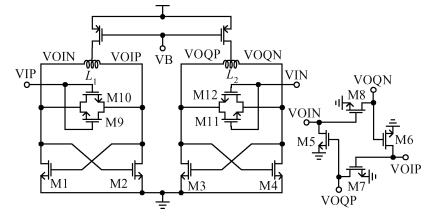
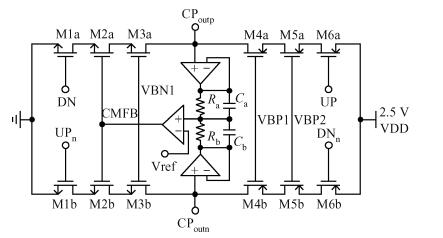
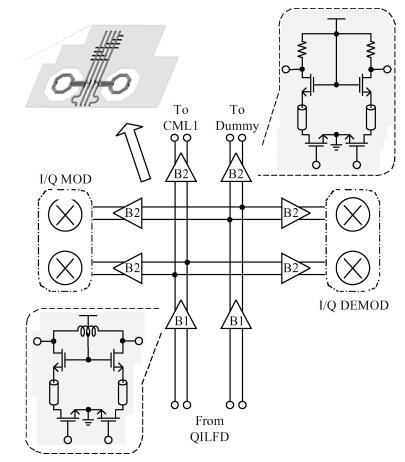
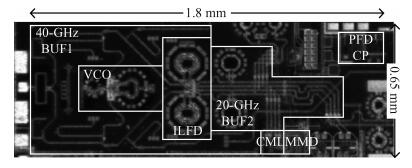
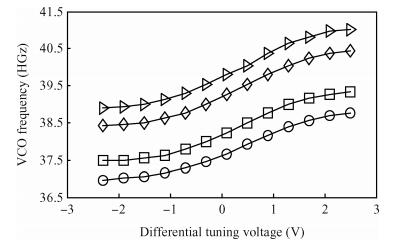
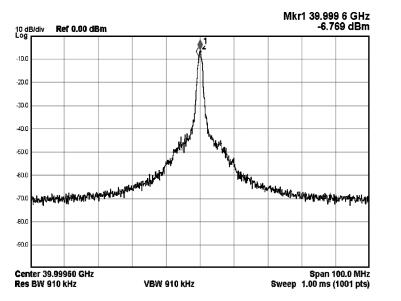
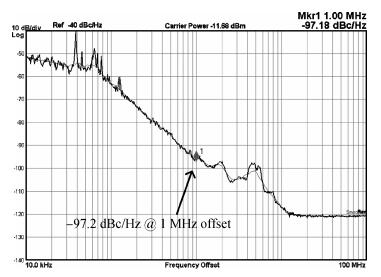
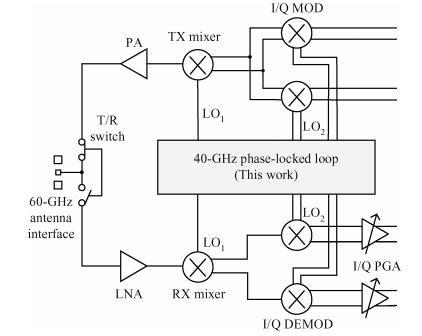
A 40-GHz phase-locked loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer for 60-GHz wireless communication applications is presented. The electrical characteristics of the passive components in the VCO and LO buffers are accurately extracted with an electromagnetic simulator HFSS. A differential tuning technique is utilized in the voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) to achieve higher common-mode noise rejection and better phase noise performance. The VCO and the divider chain are powered by a 1.0 V supply while the phase-frequency detector (PFD) and the charge pump (CP) are powered by a 2.5 V supply to improve the linearity. The measurement results show that the total frequency locking range of the frequency synthesizer is from 37 to 41 GHz, and the phase noise from a 40 GHz carrier is -97.2 dBc/Hz at 1 MHz offset. Implemented in 65 nm CMOS, the synthesizer consumes a DC power of 62 mW, including all the buffers. -
References
[1] Mitomo T, Tsutsumi Y, Hoshino H, et al. A 2 Gb/s-throughput CMOS transceiver chipset with in-package antenna for 60 GHz short-range wireless communication. IEEE ISSCC Dige Tec Papers, 2012:266[2] Okada K, Kondou K, Miyahara M, et al. Full four-channel 6.3-Gb/s 60-GHz CMOS transceiver with low-power analog and digital baseband circuitry. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 48(1):46 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2012.2218066[3] Saito N, Tsukizawa T, Shirakata N, et al. A fully integrated 60-GHz CMOS transceiver chipset based on WiGig/IEEE 802.11ad with built-in self calibration for mobile usage. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 48(12):3146 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2013.2279573[4] Lee J, Liu M, Wang H. A 75-GHz phase-locked loop in 90-nm CMOS technology. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(6):1414 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.922719[5] Lee J Y, Kim H, Yu H K. A 52 GHz millimeter-wave pll synthesizer for 60 GHz WPAN radio. IEEE European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference Proceeding, 2008:155[6] Zhou Chunyuan, Zhang Lei, Wang Hongrui, et al. A CMOS frequency generation module for 60-GHz applications. Journal of Semiconductors, 2012, 33(8):085004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/33/8/085004[7] Hammad M C, Mahmoudi R, van Zeijl Paul T M, et al. A 40-GHz phase-locked loop for 60-GHz sliding-IF transceivers in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2010:1[8] Pellerano S, Mukhopadhyay R, Ravi A, et al. A 39.1-to-41.6 GHz Δ-Σ fractional-N frequency synthesizer in 90 nm CMOS. IEEE ISSCC Dige Tec Papers, 2008:484[9] Richard O, Siligaris A, Badets F, et al. A 17.5-to-20.94 GHz and 35-to-41.88 GHz PLL in 65 nm CMOS for wireless HD applications. IEEE ISSCC Dige Tec Papers, 2010:252[10] Scheir K, Vandersteen G, Rolain Y, et al. A 57-to-66 GHz quadrature PLL in 45 nm digital CMOS. IEEE ISSCC Dige Tec Papers, 2009:494 doi: 10.1109/ISSCC.2009.4977524[11] Yi X, Boon C, Liu H, et al. A 57.9-to-68.3 GHz 24.6 mW frequency synthesizer with in-phase injection-coupled QVCO in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 49(2):347[12] Kuang Lixue, Chi Baoyong, Chen Lei, et al. An integrated 60 GHz 5 Gb/s QPSK transmitter with on-chip T/R switch and fully-differential PLL frequency synthesizer in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2013:413 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: