| Citation: |
Haochun Qi, Xiaoling Zhang, Xuesong Xie, Changzhi Lü, Chengju Chen, Li Zhao. Storage life of power switching transistors based on performance degradation data[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(4): 044006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/044006
****
H C Qi, X L Zhang, X S Xie, C Lü, C J Chen, L Zhao. Storage life of power switching transistors based on performance degradation data[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(4): 044006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/044006.
|
Storage life of power switching transistors based on performance degradation data
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/044006
More Information
-
Abstract
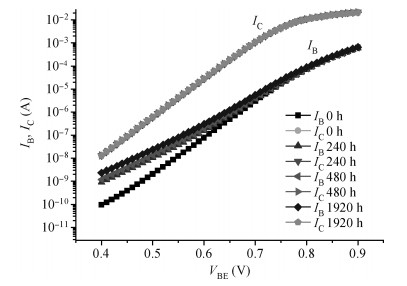
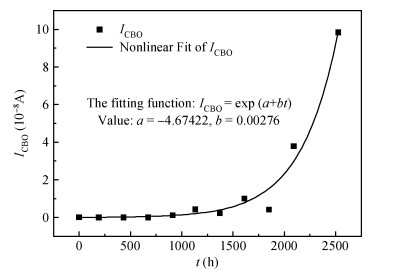
NPN-type small and medium power switching transistors in 3DK series are used to conduct analyses and studies of accelerating degradation. Through three group studies of accelerating degradation in different temperature-humidity constant stresses, the failure sensitive parameters of transistors are identified and the lifetime of samples is extrapolated from the performance degradation data. Average lifetimes in three common distributions are given, when, combined with the Hallberg-Peck temperature-humidity model, the storage lifetime of transistor samples in the natural storage condition is extrapolated between 105-107 h. According to its definition, the accelerating factor is 1462 in 100℃/100% relative humidity (RH) stress condition, and 25℃/25% RH stress condition. Finally, the degradation causes of performance parameters of the test samples are analyzed. The findings can provide certain references for the storage reliability of domestic transistors. -
References
[1] Yang D, En Y, Huang Y. Electronic components storage reliability and evaluation technology. Electron Compon Mater, 2005, 24(7):61 http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZAL200507019.htm[2] Gao Z, Tong L, Gao J, et al. Research on long-term storage test of domestic semiconductor devices. Semicond Technol, 2010, 35(8):800[3] Xu L, Tang Z, Yu X. Quality level analysis of space class transistor 2N2219AL from the USA. Electronic Product Reliability and Environmental Testing, 1999, (01):26[4] Lü C, Zhang X, Xie X. Domestic transistor reliability of long-term storage. Electronic Product Reliability and Environmental Testing, 2009, 27(z1):69[5] Liu Z J, Huang H W, Gan J Y, et al. Polycrystalline ZnO Mott-barrier diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2012, 101:173509 doi: 10.1063/1.4764555[6] Patil N, Das D, Scanff E, et al. Long term storage reliability of antifuse field programmable gate arrays. Microelectron Reliab, 2013, 53(12):2052 doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2013.06.016[7] Sozza A, Dua C, Kerlain A, et al. Long-term reliability of Ti-Pt-Au metallization system for Schottky contact and first-level metallization on SiC MESFET. Microelectron Reliab, 2004, 44(7):1109 doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2004.01.017[8] Rhew K H, Jeon S C, Lee D H, et al. Reliability assessment of 1.55-μm vertical cavity surface emitting lasers with tunnel junction using high-temperature aging tests. Microelectron Reliab, 2009, 49(1):42 doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2008.10.008[9] Ren Jian, Yan Dawei, Gu Xiaofeng. Degradation mechanism of leakage current in AlGaN/GaN high electron mobility transistors. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 15:391 doi: 10.7498/aps.62.157202[10] Zhai Y, Zhang Z, Zhong Q. Degradation reliability evaluation method of products with parameters digression feature. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2013, 25(2):107 http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HJGX201302022.htm[11] Wang Xiaolin, Guo Bo, Cheng Zhijun. Real-time reliability evaluation for product with nonlinear drift-based Wiener process. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 44(8):3203 http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201308018.htm[12] Zhu T, Wang H, Chen J. Reliability prediction method of multiple degradations based on unknown degradation paths. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2013, (02):53 http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CGQJ201302017.htm[13] Qi Haochun, Lü Changzhi, Zhang Xiaoling, et al. Accelerating the life of transistors. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(6):064010 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/6/064010[14] Peck D S. Comprehensive model for humidity testing correlation. Proc 24th Ann Int'l Reliability Physics Symposium, 1986:44 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4208640/authors[15] GJB/Z 123-1999. Aerospace electronic components effective storage period and extended retest guide[16] GJB548B-2005. Test methods and procedures for Microelectronics[17] Meeker M Q, Escobar L A. Statistical methods for reliability data. New York:John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1998[18] Zhao Yu, Yang Jun, Ma Xiaobing. Reliability data analysis tutorial. Beijing:Beihang University Press, 2009[19] Zhao L, Tokei Z, Croes K, et al. Direct observation of the 1/E dependence of time dependent dielectric breakdown in the presence of copper. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98:032107 doi: 10.1063/1.3543850[20] Lloyda J R, Liniger E, Shaw T M. Simple model for time-dependent dielectric breakdown in inter-and intralevel low-k dielectrics. J Appl Phys, 2005, 98:084109 doi: 10.1063/1.2112171[21] Chen F, Bravo B, Chanda K, et al. A comprehensive study of low-k SiCOH TDDB phenomena and its reliability lifetime model development. Proceedings of International Reliability Physics Symposium, 2006:46[22] Zhang R, Xu L, Gao Z. Storage life of demiconductor devices. Semicond Technol, 2007, 32(3):252[23] Liu Mingzhi. Reliability test. Beijing:Electronic Industry Press, 2004:77[24] Gao Guangbo, Li Xuexin. Reliability physics of semiconductor devices. Science Press, 1987, 58-76:224[25] He M, Li H, Wang P I, et al. Bias temperature stress of Al on porous low-k dielectric. Microelectron Reliab, 2011, 51(8):1342 doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2011.03.004 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: