| Citation: |
Zengru Zhao, Gaofeng Wang. Shallow impurity states in AlxGa1-xAs cylindrical quantum wire[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(8): 082002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/8/082002
****
Z R Zhao, G F Wang. Shallow impurity states in AlxGa1-xAs cylindrical quantum wire[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(8): 082002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/8/082002.
|
Shallow impurity states in AlxGa1-xAs cylindrical quantum wire
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/8/082002
More Information
-
Abstract
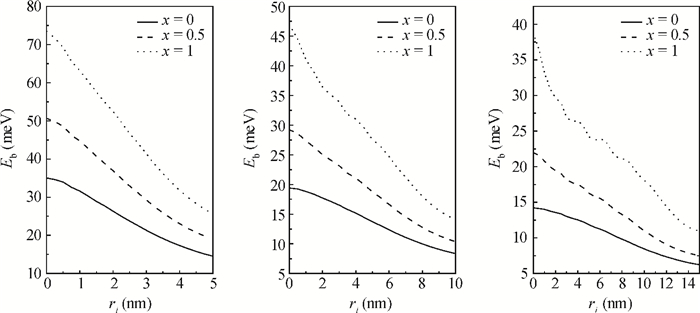
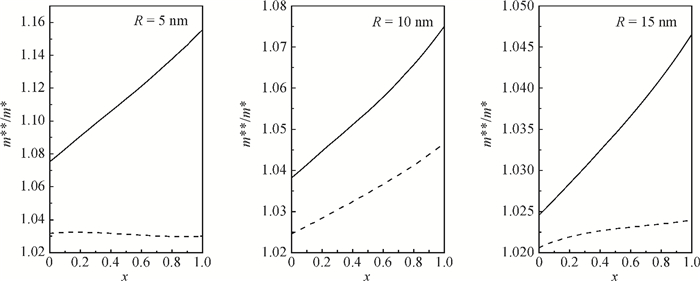
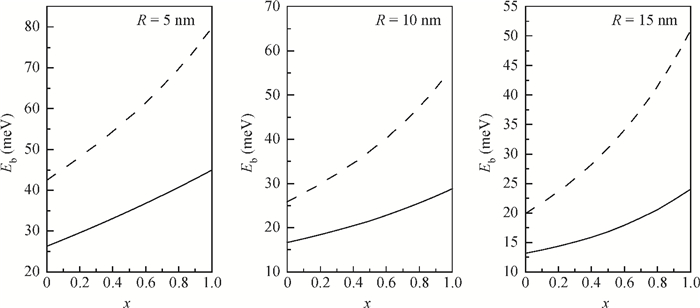
Polarons bound to a shallow Coulomb impurity center in cylindrical quantum wire is studied by a variational approach. The binding energies of the shallow impurity states in AlxGa1-xAs cylindrical quantum wire are calculated as functions of the composition x and the impurity position. It is confirmed that the binding energies are reduced obviously by the influence of the electron-phonon interaction and the binding energies are increased with increasing the composition x.-
Keywords:
- quantum wire,
- electron-phonon interaction,
- impurity states
-
References
[1] Lin Z C, Lin S D. Lee C P. Ordering of stacked InAs/GaAs quantum-wires in InAlAs/InGaAs matrix on (100) InP substrates. Phys E, 2008, 40:512 doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2007.07.005[2] Wang S, Kang Y, Han C J. Transverse Stark effect in the optical absorption in a square semiconducting quantum wire. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34:102001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/10/102001[3] Santhi M, Peter A J. The binding energy of excitons in a cylindrical quantum wire under the influence of laser field intensity. Physica E, 2010, 42:1643 doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2010.01.016[4] Graham A M, Corfdir P, Heiss M, et al. Exciton localization mechanisms in wurtzite/zinc-blende GaAs nanowires. Phys Rev B, 2013, 87:125304 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.87.125304[5] Zhao Z R, Liang X X. Stark effects on bound polarons in polar cylindrical quantum wires with finite confining potential. J Appl Phys, 2009, 105:083704 doi: 10.1063/1.3095509[6] Wang X F, Lei X L. Polar-optic phonons and high-field electron transport in cylindrical GaAs/AlAs quantum wires. Phys Rev B, 1994, 49:4780 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.49.4780[7] Li S S, Xia J B. Binding energy of a hydrogenic donor impurity in a rectangular parallelepiped-shaped quantum dot:quantum confinement and Stark effects. J Appl Phys, 2007, 101:093716 doi: 10.1063/1.2734097[8] Zhao C L, Cai C Y, Xiao J L. The influences of an anisotropic parabolic potential on the quantum dot qubit. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(11):112002 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/11/112002[9] Yin J W, Li W P, Yu Y F. Properties of a polaron in a quantum dot:a squeezed-state variational approach. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(1):012001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/1/012001[10] Zhang L, Shi J J, Tansley T L. Polar vibration spectra of interface optical phonons and electron-interface optical phonon interactions in a wurtzite GaN-AlN nanowire. Phys Rev B, 2005, 71:245324 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.71.245324[11] Bouhassoune M, Charrour R, Fliyou M, et al. Binding energy of shallow impurities in a polar quantum well wire. Phys B, 2001, 304:389 doi: 10.1016/S0921-4526(01)00391-X[12] Moukhliss S, Fliyou M, Sbai N E. Binding energy of the donor-confined LO phonon system in quantum well wire structures. Phys Status Solidi B, 1998, 206:593 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3951[13] Pokatilov E P, Fomin V M, Balaban S N, et al. Impurity-bound hole polaron in a cylindrical quantum wire. Phys Status Solidi B, 1998, 210:879 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3951[14] Osório F A P, Degani M H, Hipólito O. Bound impurity in GaAs-Ga1-κAlκAs quantum-well wires. Phys Rev B, 1988, 37:1402 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.37.1402[15] Xie H J, Chen B, Ma K. Bound polaron in a cylindrical quantum wire of a polar crystal. Phys Rev B, 2000, 61:4827 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.61.4827[16] Buonocore F, Ladonisi G, Ninno D, et al. Bound impurity in GaAs-Ga1-κAlκAs quantum-well wires. Phys Rev B, 2002, 65:205415 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.65.205415[17] Chen Y S, Shockley W, Reaeson G L. Lattice vibration spectra of GaAsxP1-x single crystals. Phys Rev, 1966, 151:648 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.151.648[18] Bellessa J, Symonds C, Meynaud C, et al. Exciton/plasmon polaritons in GaAs/Al0.93Ga0.07As heterostructures near a metallic layer. Phys Rev B, 2008, 78:205326 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.78.205326[19] Reyes-Gomez E, Raigoza N, Oliveira L E. Effects of hydrostatic pressure and aluminum concentration on the conduction-electron g factor in GaAs-(Ga, Al)As quantum wells under in-plane magnetic fields. Phys Rev B, 2008, 77:115308 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.77.115308[20] Chang I F, Mitra S S. Long wavelength optical phonons in mixed crystals. Adv Phys, 1971, 20:359 doi: 10.1080/00018737100101271[21] Liang X X, Yang J S. Effective-phonon approximation of polarons in ternary mixed crystals. Solid State Commun, 1996, 100:629 doi: 10.1016/0038-1098(96)00480-2[22] Zhao Z R, Liang X X. On the ion-and electron-phonon interaction effects on impurity states in polar cylindrical quantum wires. J Appl Phys, 2008, 103:053704 doi: 10.1063/1.2844455[23] Platzman P. Ground-state energy of bound polarons. Phys Rev, 1962125:1961 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.125.1961[24] Adachi S. GaAs, AlAs, and AlxGa1-xAs:material parameters for use in research and device applications. J Appl Phys, 1985, 58:R1 doi: 10.1063/1.336070 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: