| Citation: |
Kh. S. Karimov, M. Saleem, M. Mahroof-Tahir, R. Akram, M.T. Saeed Chanee, A.K. Niaz. Resistive humidity sensor based on vanadium complex films[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(9): 094001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/9/094001
****
Kh. S. Karimov, M. Saleem, M. Mahroof-Tahir, R. Akram, M. T. S. Chanee, A.K. Niaz. Resistive humidity sensor based on vanadium complex films[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(9): 094001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/9/094001.
|
Resistive humidity sensor based on vanadium complex films
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/9/094001
More Information
-
Abstract
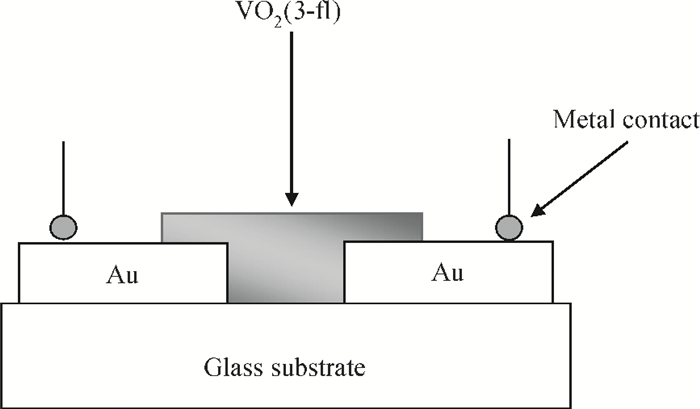
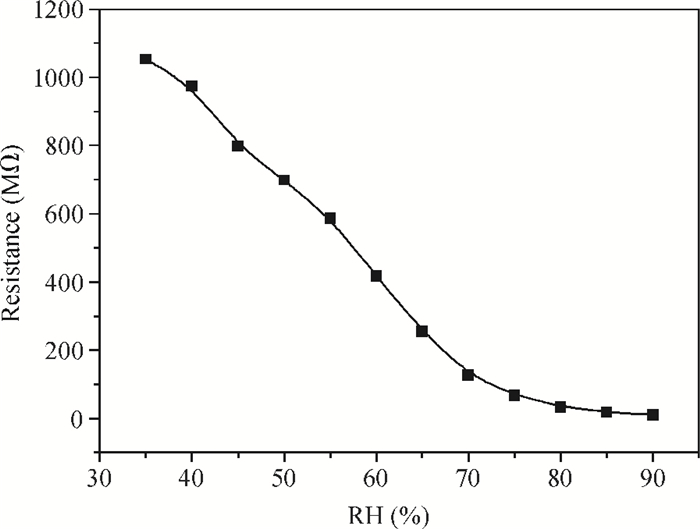
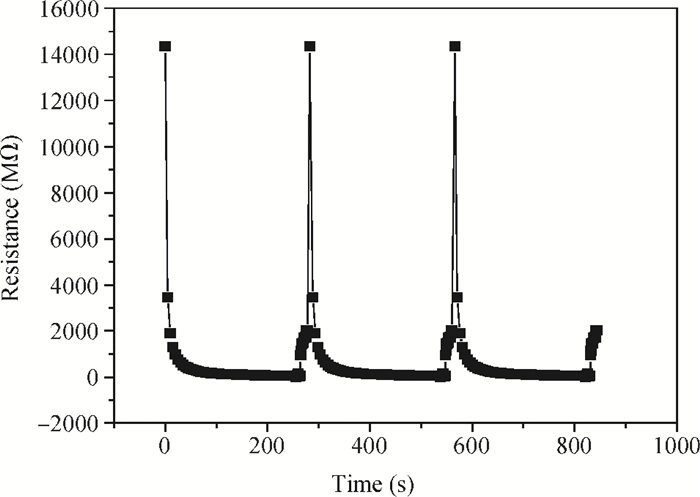
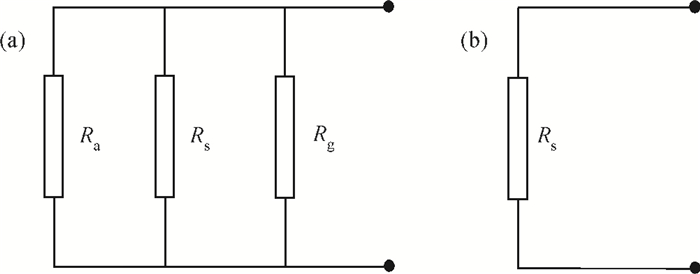
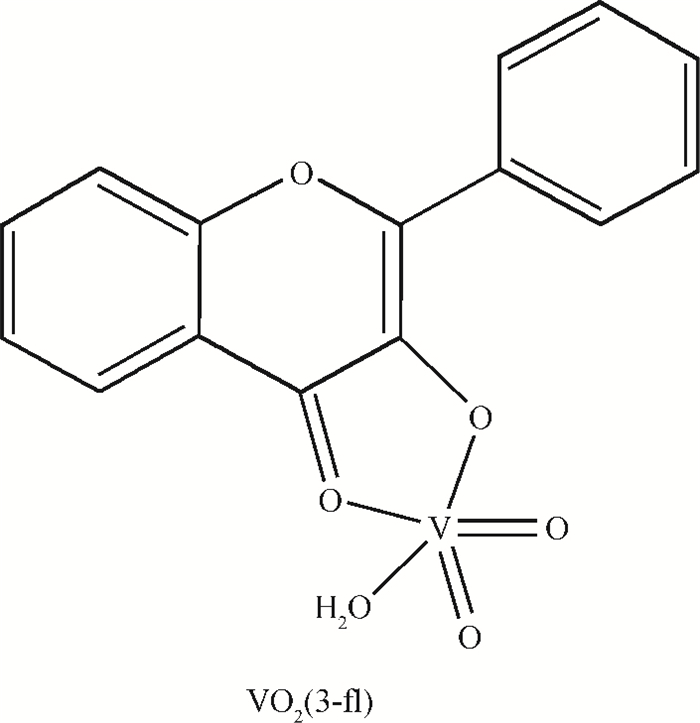
A resistive-type relative humidity (RH) sensor based on vanadium complex (VO2(3-fl)) film is reported in this study. Gold electrodes were deposited on the glass substrates in a co-planar structure. A thin film of vanadium complex was coated as a humidity-sensing material on the top of the pre-patterned electrodes. The humidity-sensing principle of the sensor was based on the conductivity change of coated sensing element upon adsorption/desorption of water vapor. The resistance of the humidity sensor measured at 1 kHz decreased linearly with increasing the humidity in the range of 35%-70% RH. The overall resistance of the sensor decreases 11 times. An equivalent circuit for the VO2(3-fl) based resistive-type humidity sensor was developed. The properties of the sensor studied in this work make it beneficial for use in the instruments for environmental monitoring of humidity.-
Keywords:
- vanadium complex,
- thin film,
- humidity sensor,
- resistance
-
References
[1] Jain S, Chakane S, Samui A B, et al. Humidity sensing with weak acid-doped polyaniline and its composites. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2003, 96:124[2] Maddanimath T, Mulla I S, Sainkar S R, et al. Humidity sensing properties of surface functionalised polyethylene and polypropylene films. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2002, 81:141[3] Lee C W, Rhee H W, Gong M S. Humidity sensor using epoxy resin containing quaternary ammonium salts. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2001, 73:124[4] Lee C W, Park H S, Kim J G, et al. Polymeric humidity sensor using organic/inorganic hybrid polyelectrolytes. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2005, 109:315[5] Kulwicki B M. Humidity sensors. J Amer Ceramic Soc, 1991, 74:697 doi: 10.1111/jace.1991.74.issue-4[6] Karimov Kh S, Qazi I, Khan T A, et al. Humidity and illumination organic semiconductor copper phthalocyanine sensor for environmental monitoring. Environ Monit Assess, 2008, 141:323 doi: 10.1007/s10661-007-9898-5[7] Harsányi G. Polymeric sensing films:new horizons in sensorics. Mater Chem Phys, 1996, 43:199 doi: 10.1016/0254-0584(95)01629-9[8] Anchisini R, Faglia G, Gallazzi M C, et al. Polyphosphazene membrane as a very sensitive resistive and capacitive humidity sensor. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 1996, 35:99[9] Tai W P, Kim J G, Oh J H, et al. Preparation and humidity sensing behaviors of nanostructured potassium tantalate:titania films. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2005, 105:199[10] Faia P M, Furtado C S, Ferreira A J. Humidity sensing properties of a thick-film titania prepared by a slow spinning process. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2004, 101:183[11] Misra P, Shukla R K, Bali L M, et al. EPR studies of some thick film ferrates, aluminates and their correlation with humidity sensitivity. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2003, 94:210[12] Przyluski J, Wieczorek W. Proton polymeric electrolytes-a review. Synthetic Metals, 1991, 45:323 doi: 10.1016/0379-6779(91)91788-C[13] Ahmad Z, Sayyad M H, Saleem M, et al. Humidity-dependent characteristics of methyl-red thin film-based Ag/methyl-red/Ag surface-type cell. Physica E, 2008, 41:18 doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2008.05.018[14] Lv X, Li Y, Li P, et al. A resistive-type humidity sensor based on crosslinked polyelectrolyte prepared by UV irradiation. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2009, 135:581[15] Su P G, Ho C J, Sun Y L, et al. A micromachined resistive-type humidity sensor with a composite material as sensitive film. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2006, 113:837[16] Yoo K P, Lim L T, Min N K, et al. Novel resistive-type humidity sensor based on multiwall carbon nanotube/polyimide composite films. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2010, 145:120[17] Kim D U, Gong M S. Thick films of copper-titanate resistive humidity sensor. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2005, 110:321[18] Shimizu K I, Chinzei I, Nishiyama H, et al. Doped-vanadium oxides as sensing materials for high temperature operative selective ammonia gas sensors. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2009, 141:410[19] Wang C T, Chen M T. Vanadium-promoted tin oxide semiconductor carbon monoxide gas sensors. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2010, 150:360[20] Carotta M C, Ferroni M, Gherardi S, et al. Thick-film gas sensors based on vanadium-titanium oxide powders prepared by sol-gel synthesis. J Europ Ceram Soci, 2004, 24:1409 doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(03)00418-7[21] Lavacchi A, Cortigiani B, Rovida G, et al. Composition and structure of tin/vanadium oxide surfaces for chemical sensing applications A. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2000, 71:123[22] Zakharova G S, Volkov V L. Intercalation compounds based on vanadium (V) oxide xerogel. Russian Chem Revi, 2003, 72:311 doi: 10.1070/RC2003v072n04ABEH000762[23] Schilling O, Colbow K. A mechanism for sensing reducing gases with vanadium pentoxide films. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 1994, 21:151[24] Mitzi D B, Chondroudis K, Kagan C R. Organic-inorganic electronics. IBM J Res Develop, 2001, 45:29 doi: 10.1147/rd.451.0029[25] Rittersma Z. Recent achievements in miniaturised humidity sensors-a review of transduction techniques. Sens Actuat A:Physical, 2002, 96:196[26] Geng W, Wang R, Li X, et al. Humidity sensitive property of Li-doped mesoporous silica SBA-15. Sens Actuat B:Chem, 2007, 127:323[27] Ernsberger F M. The nonconformist ion. J Amer Ceram Soc, 1983, 66:747 doi: 10.1111/jace.1983.66.issue-11 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: