| Citation: |
Suge Yue, Xiaolin Zhang, Yuanfu Zhao, Lin Liu. Modeling and simulation of single-event effect in CMOS circuit[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(11): 111002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/11/111002
****
S G Yue, X L Zhang, Y F Zhao, L Liu. Modeling and simulation of single-event effect in CMOS circuit[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(11): 111002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/11/111002.
|
Modeling and simulation of single-event effect in CMOS circuit
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/11/111002
More Information
-
Abstract
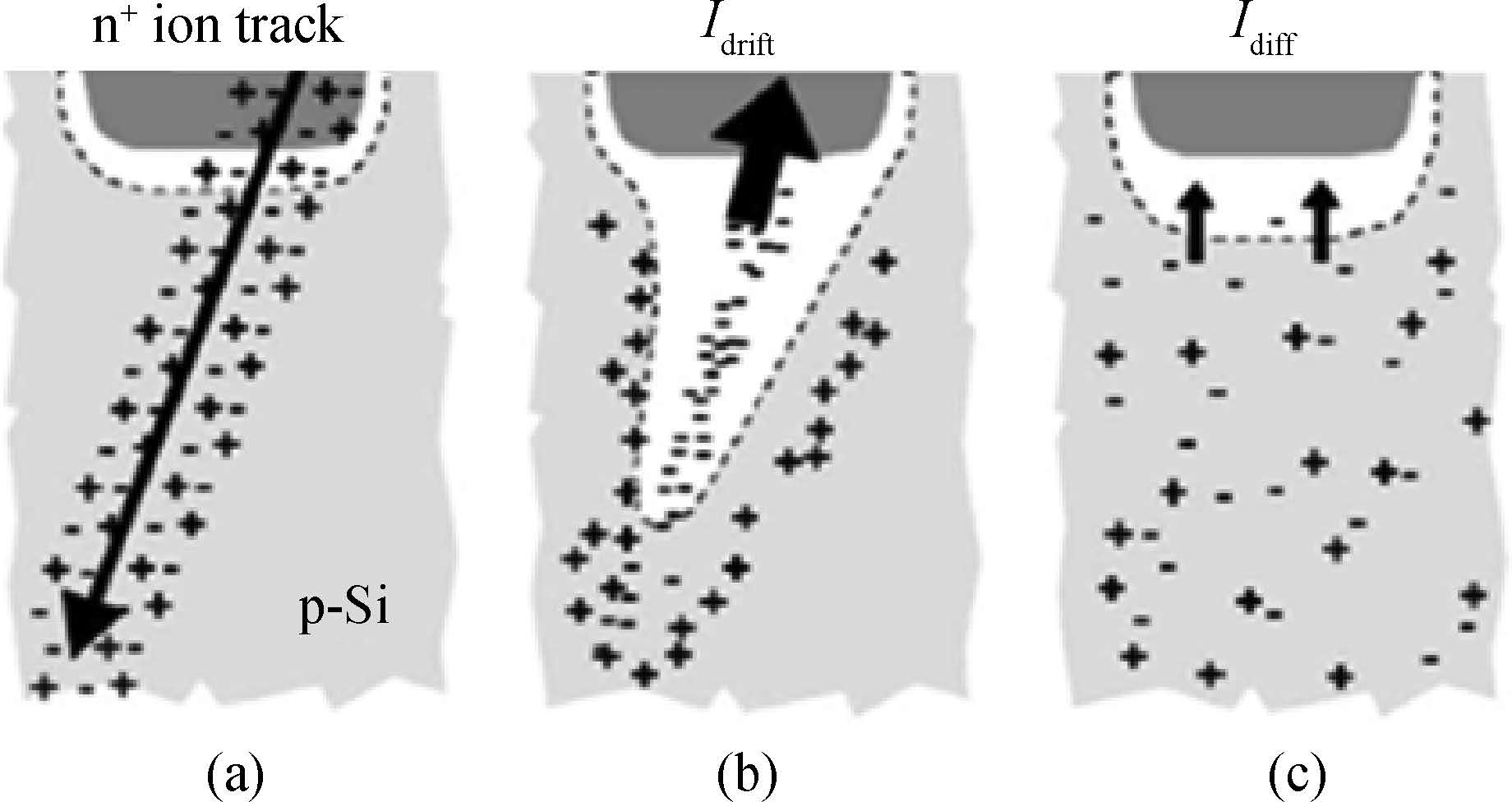
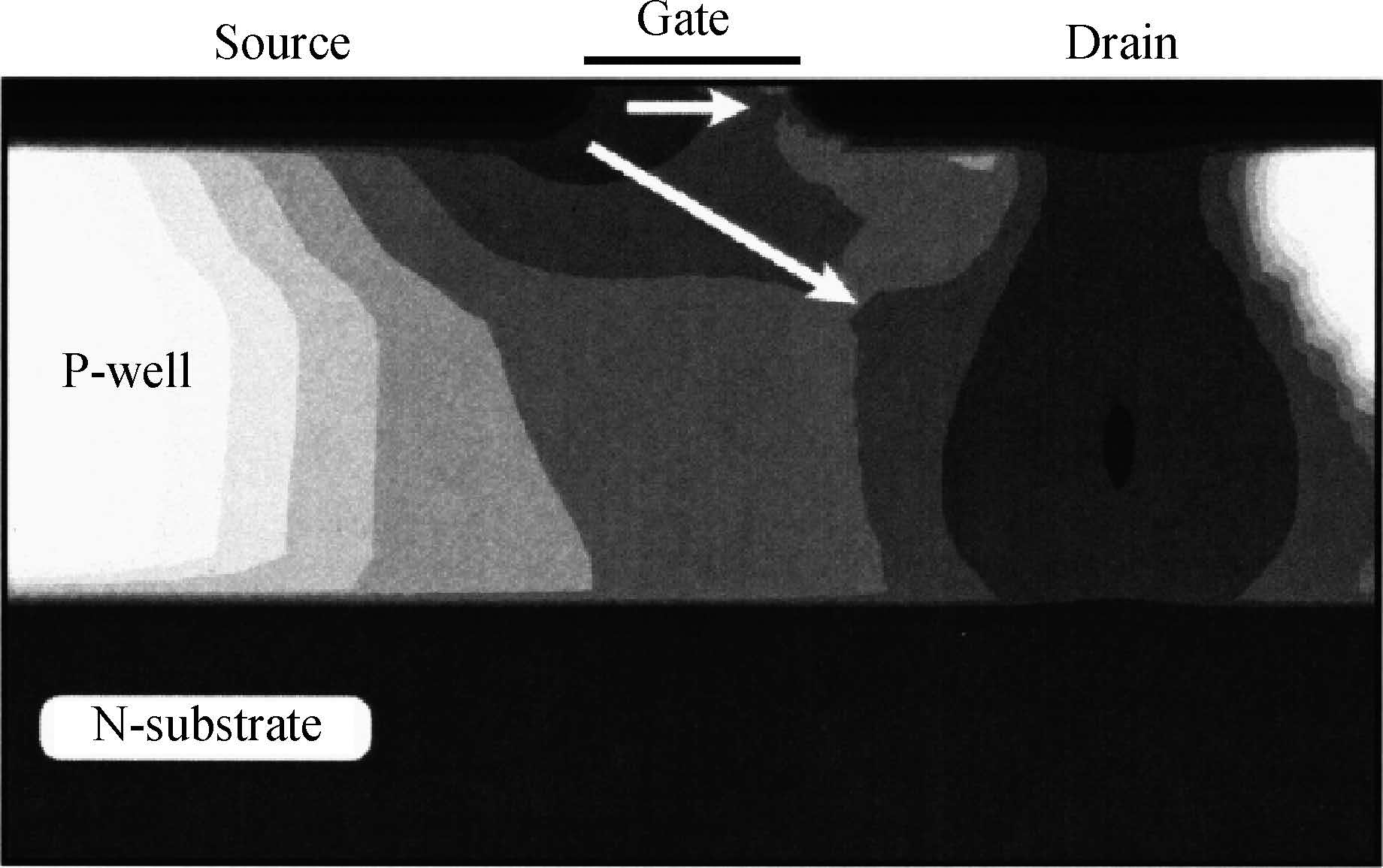
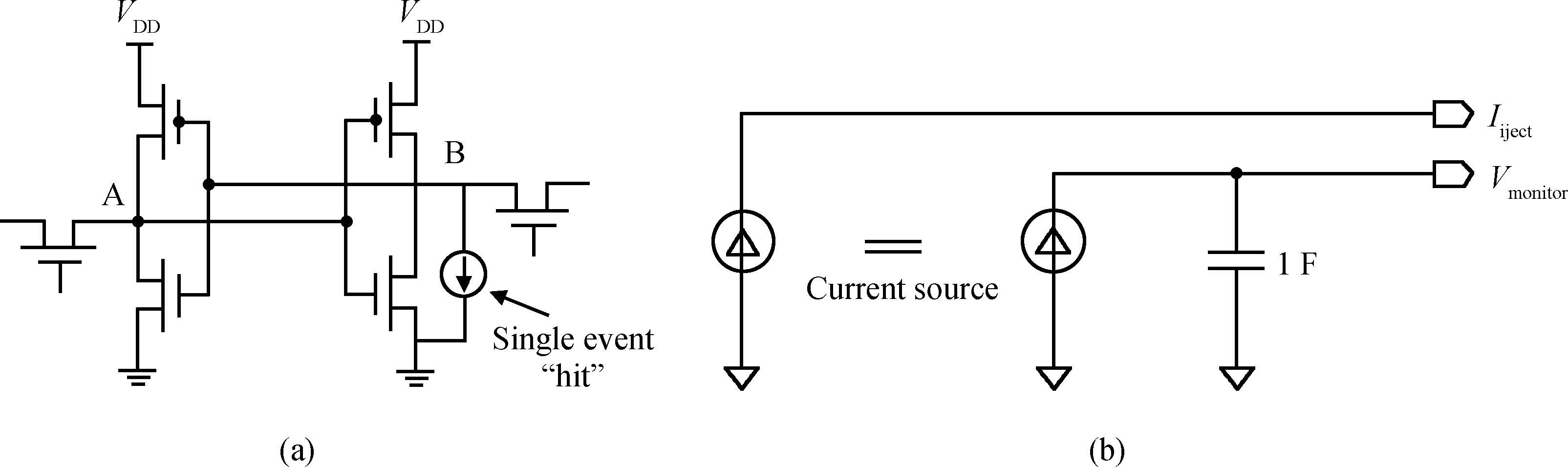
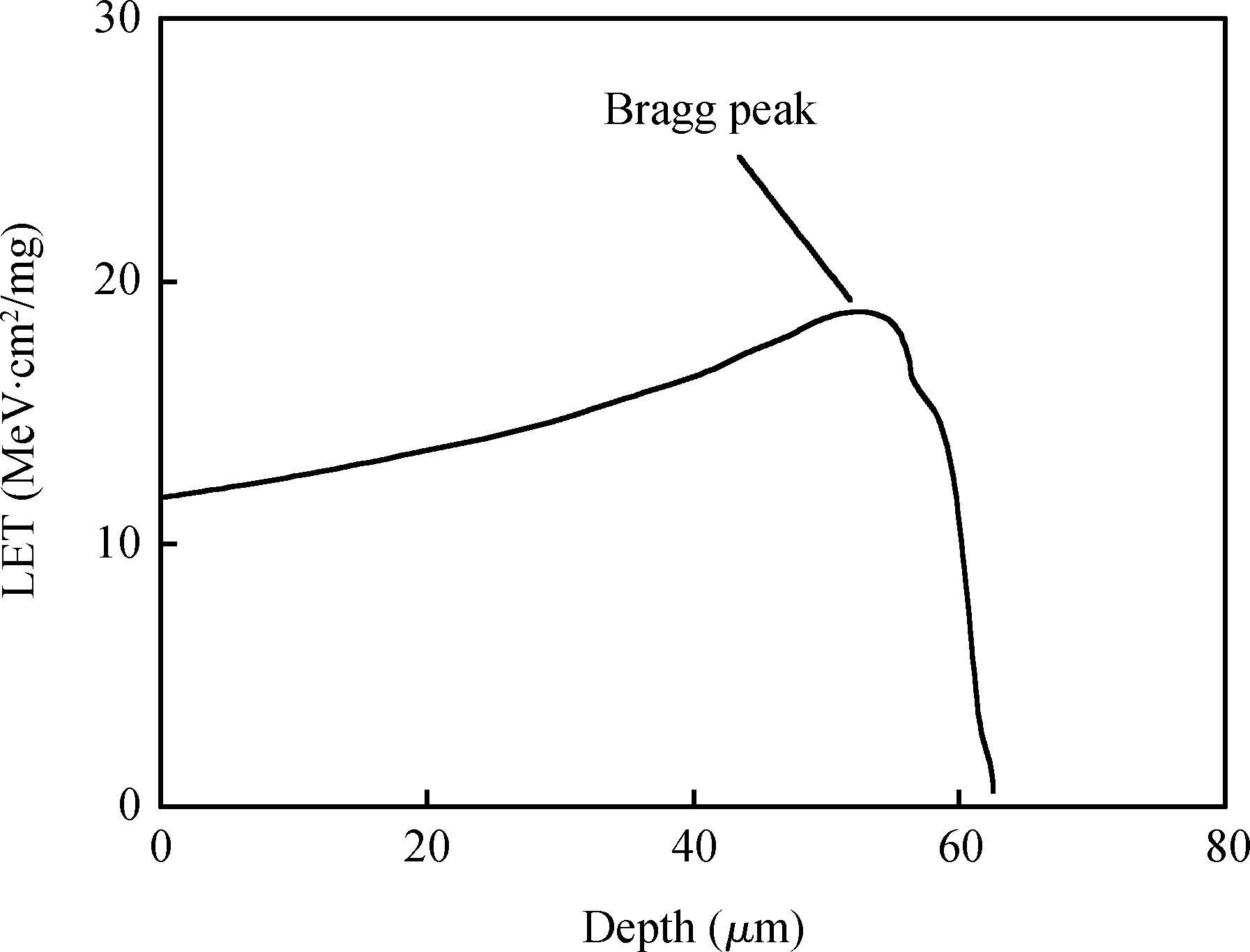
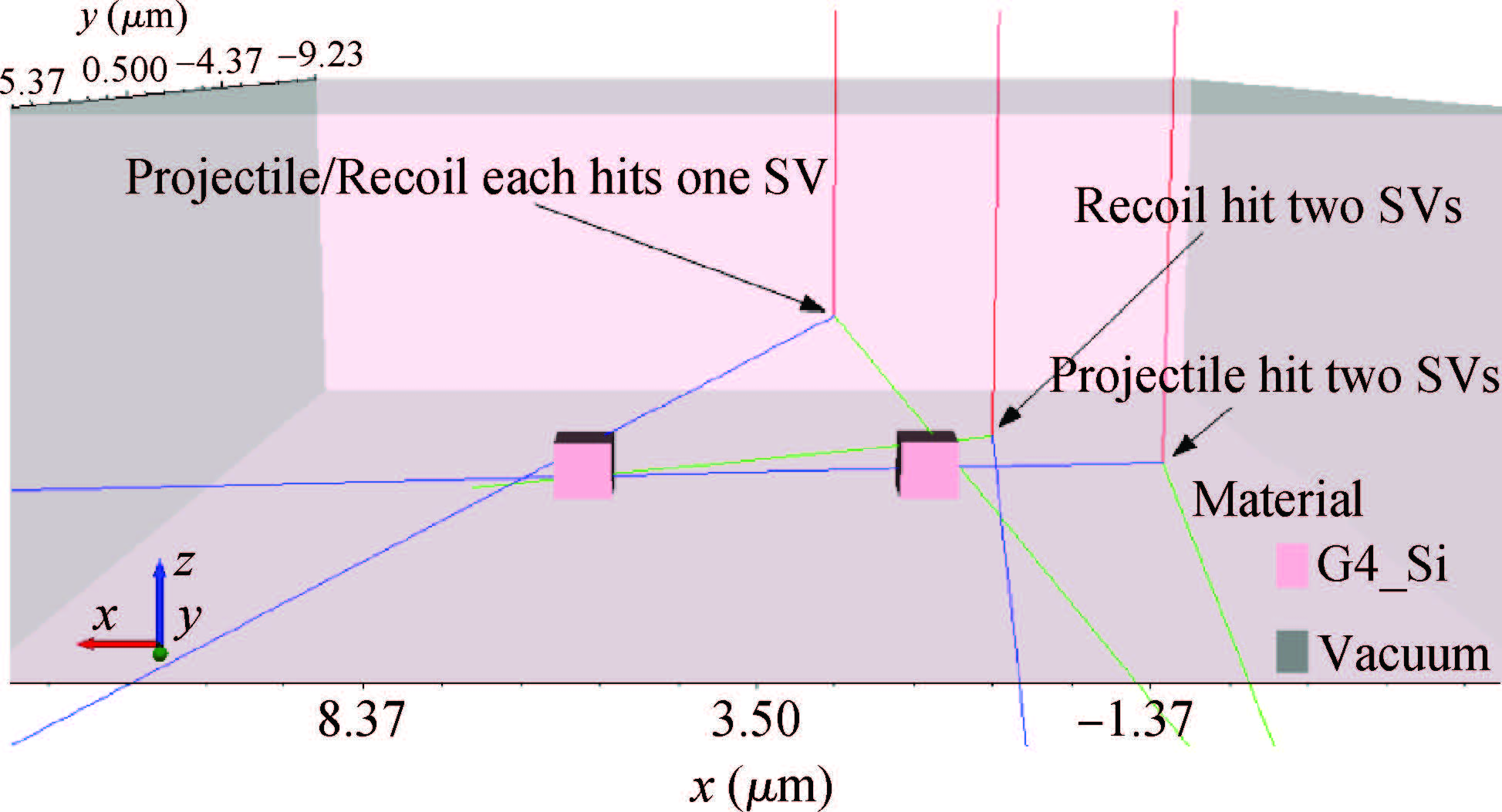
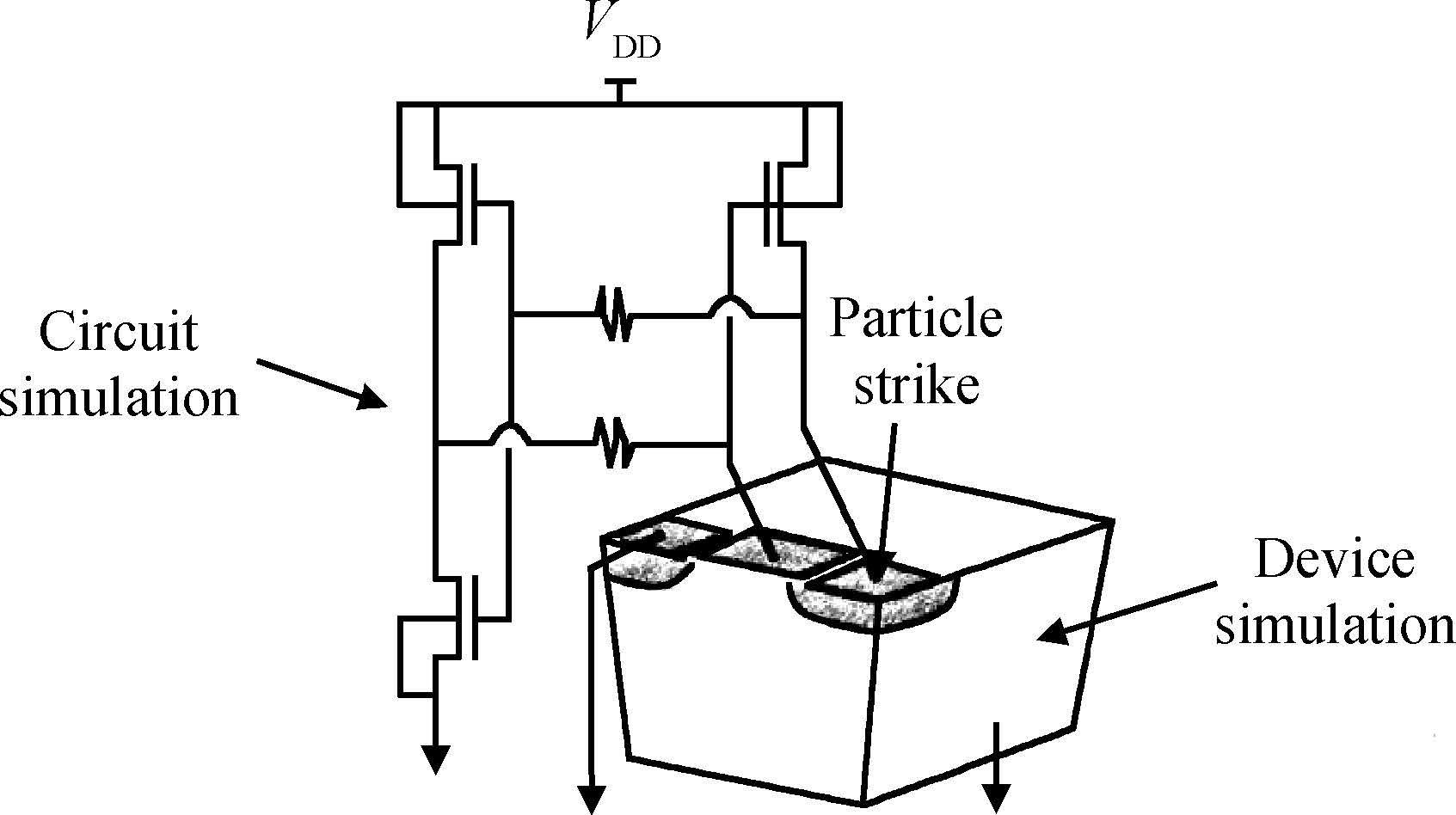
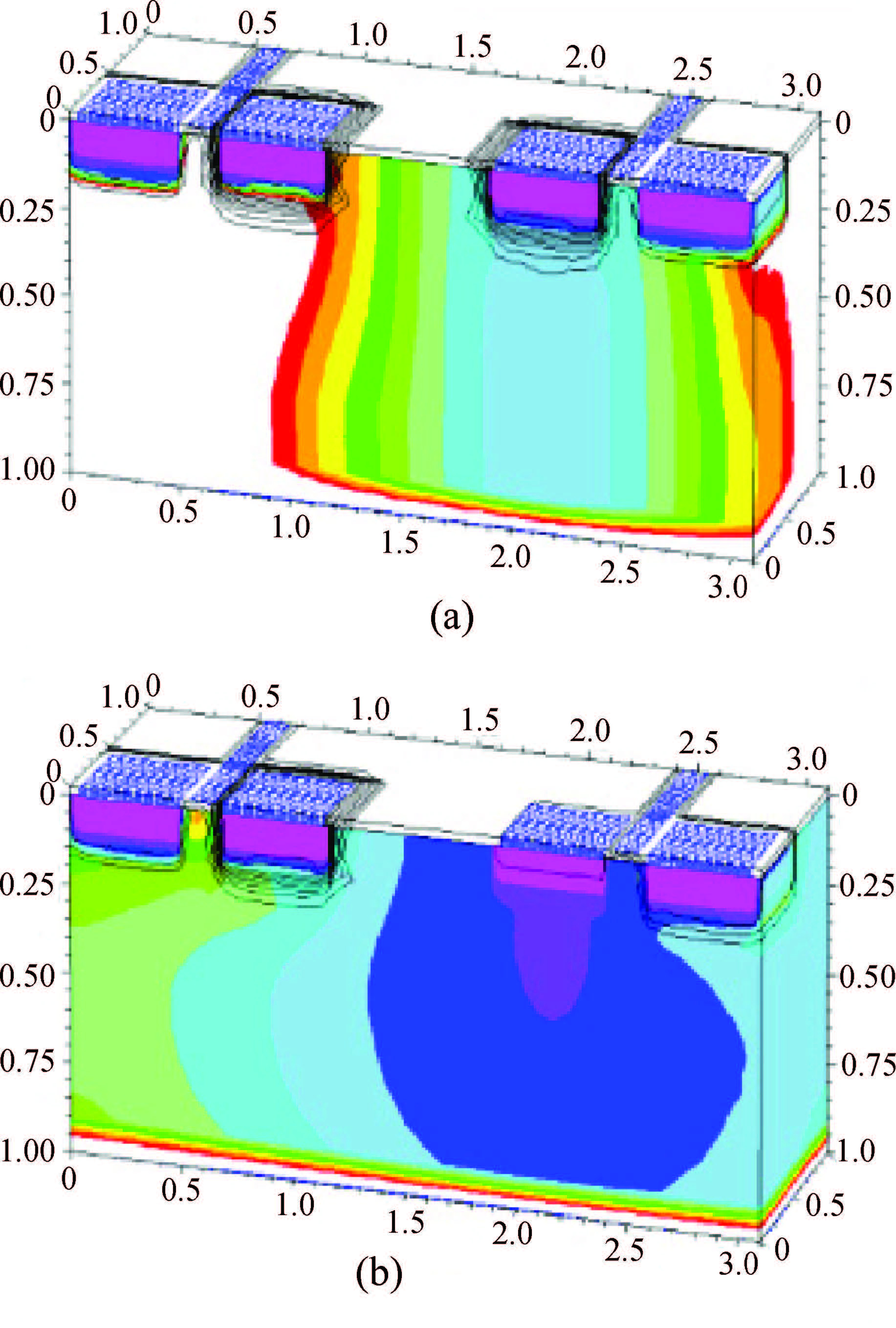
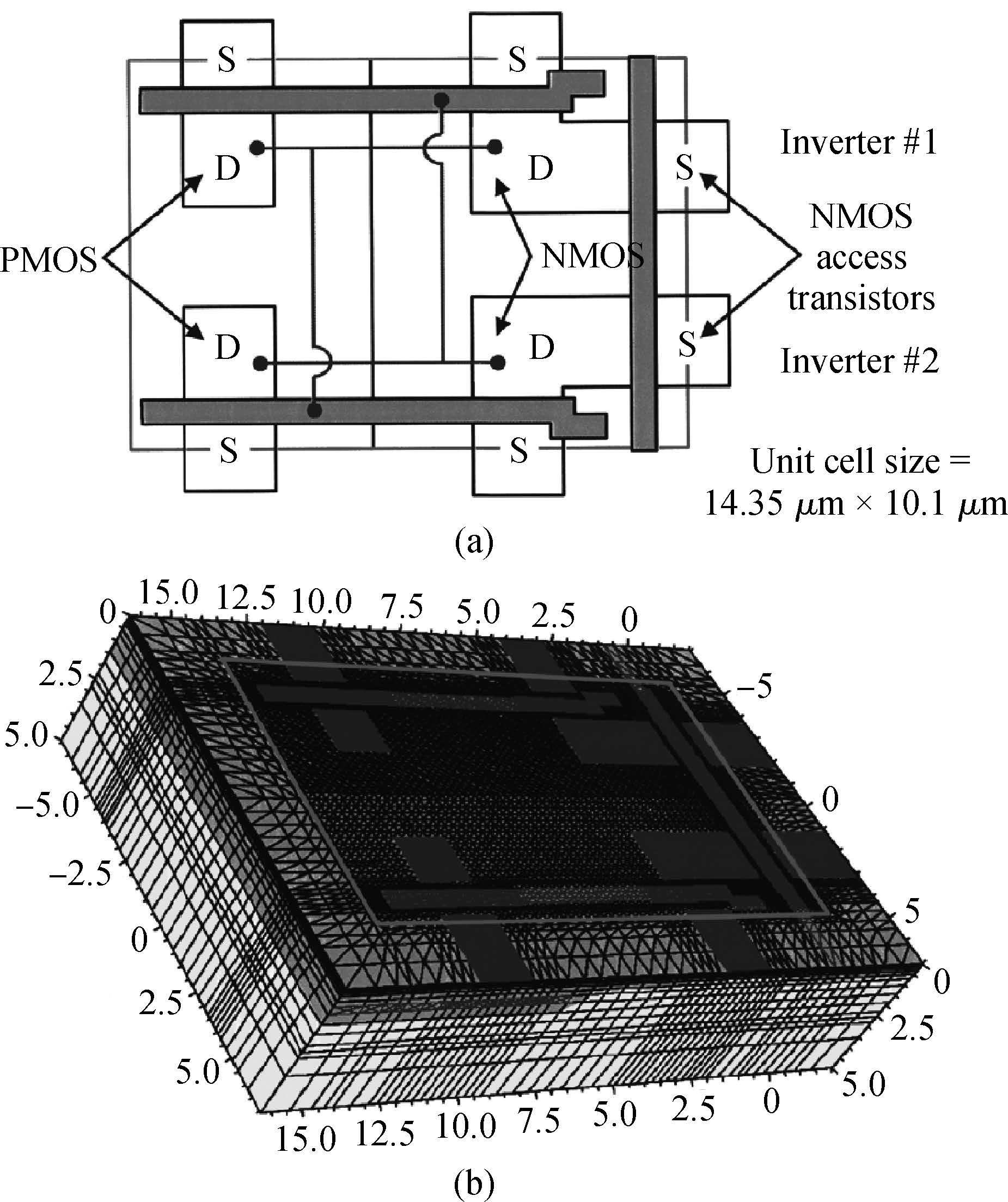
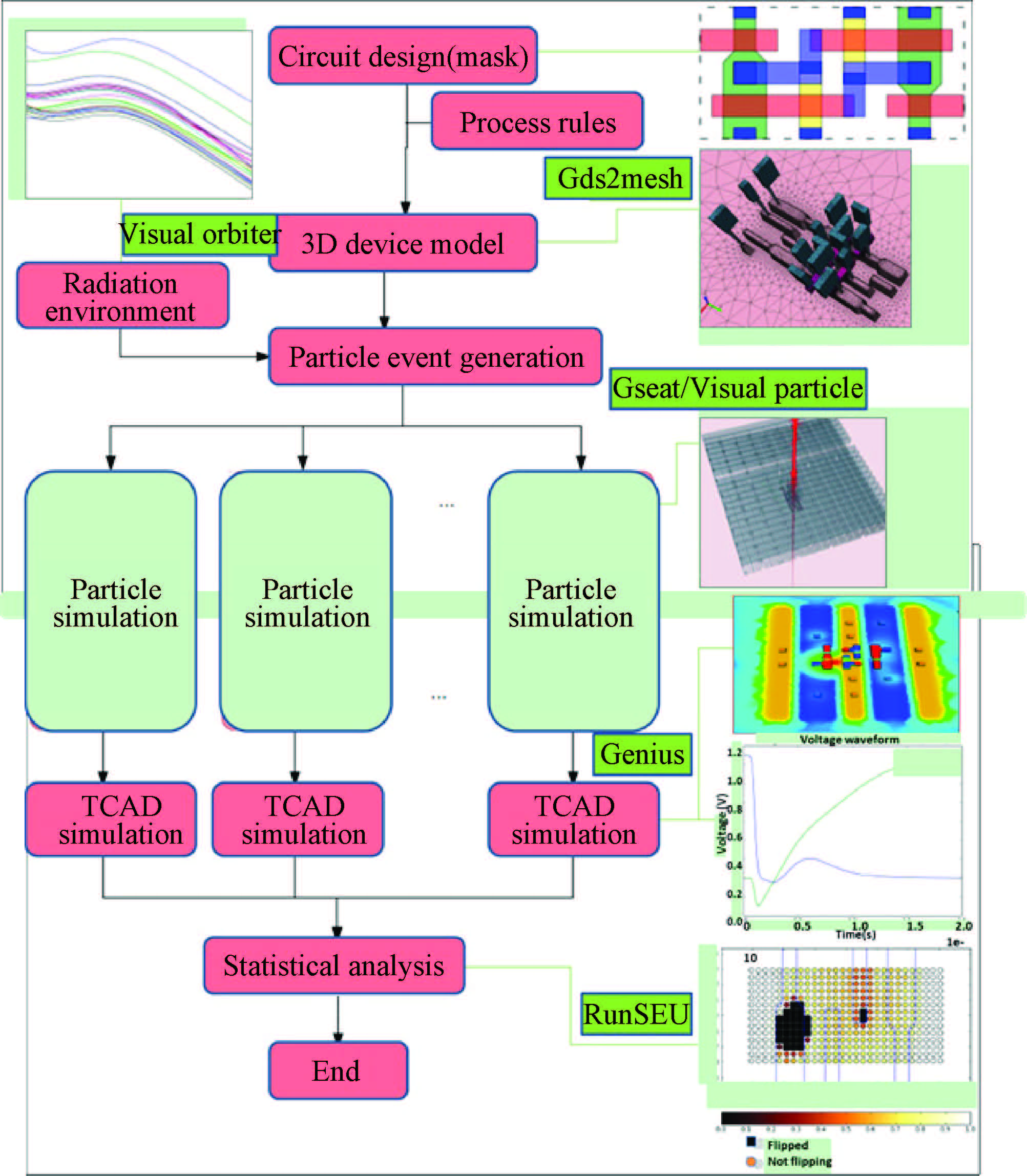
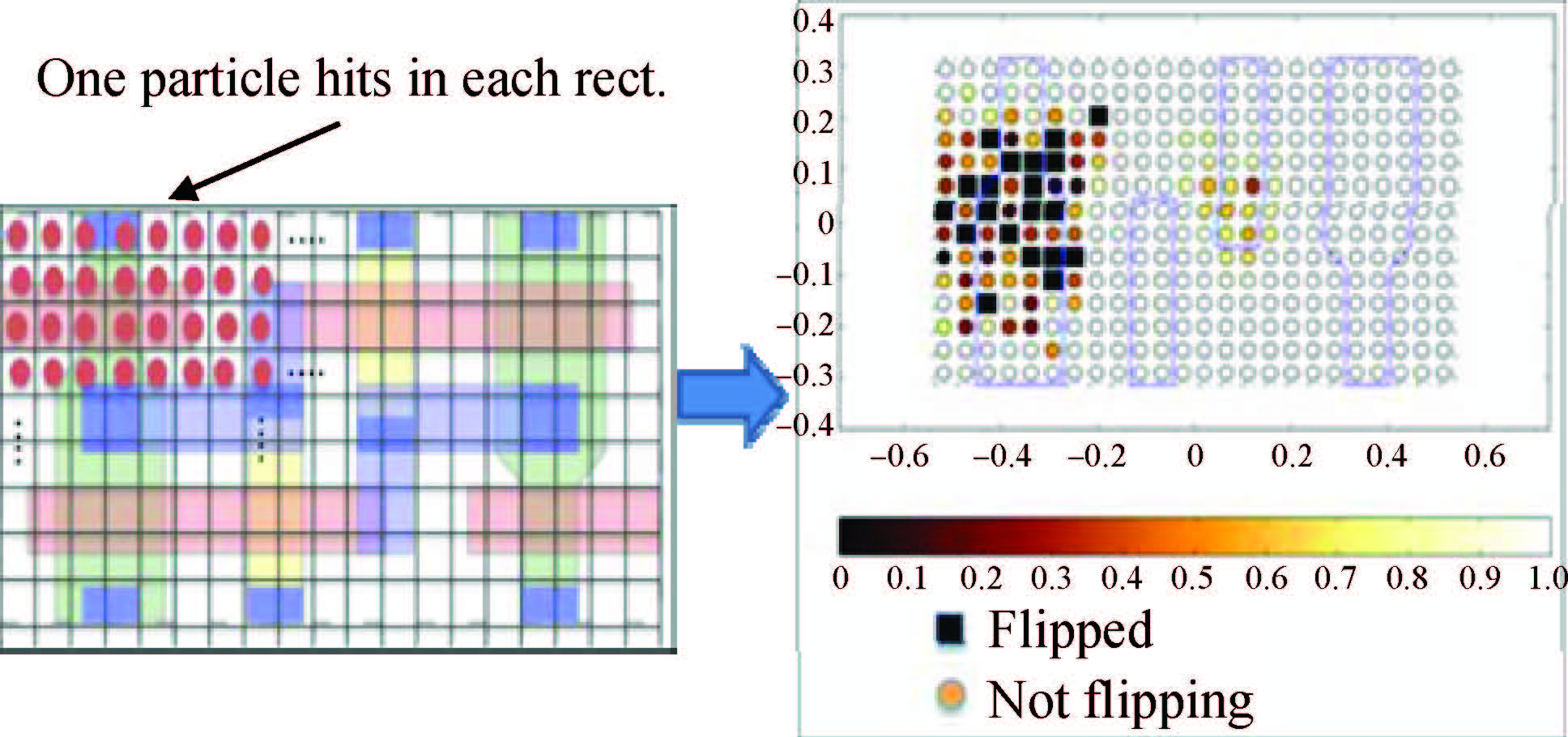
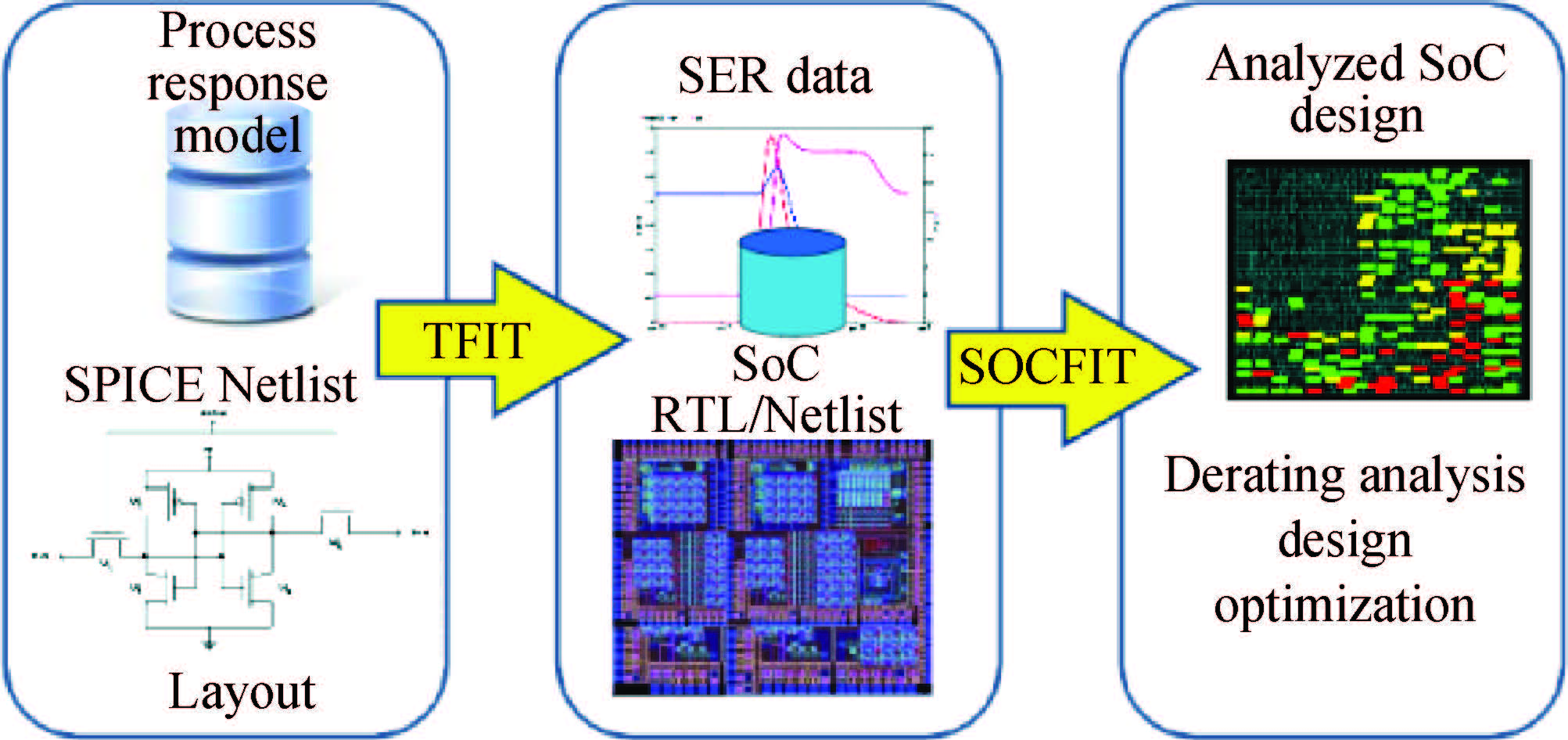
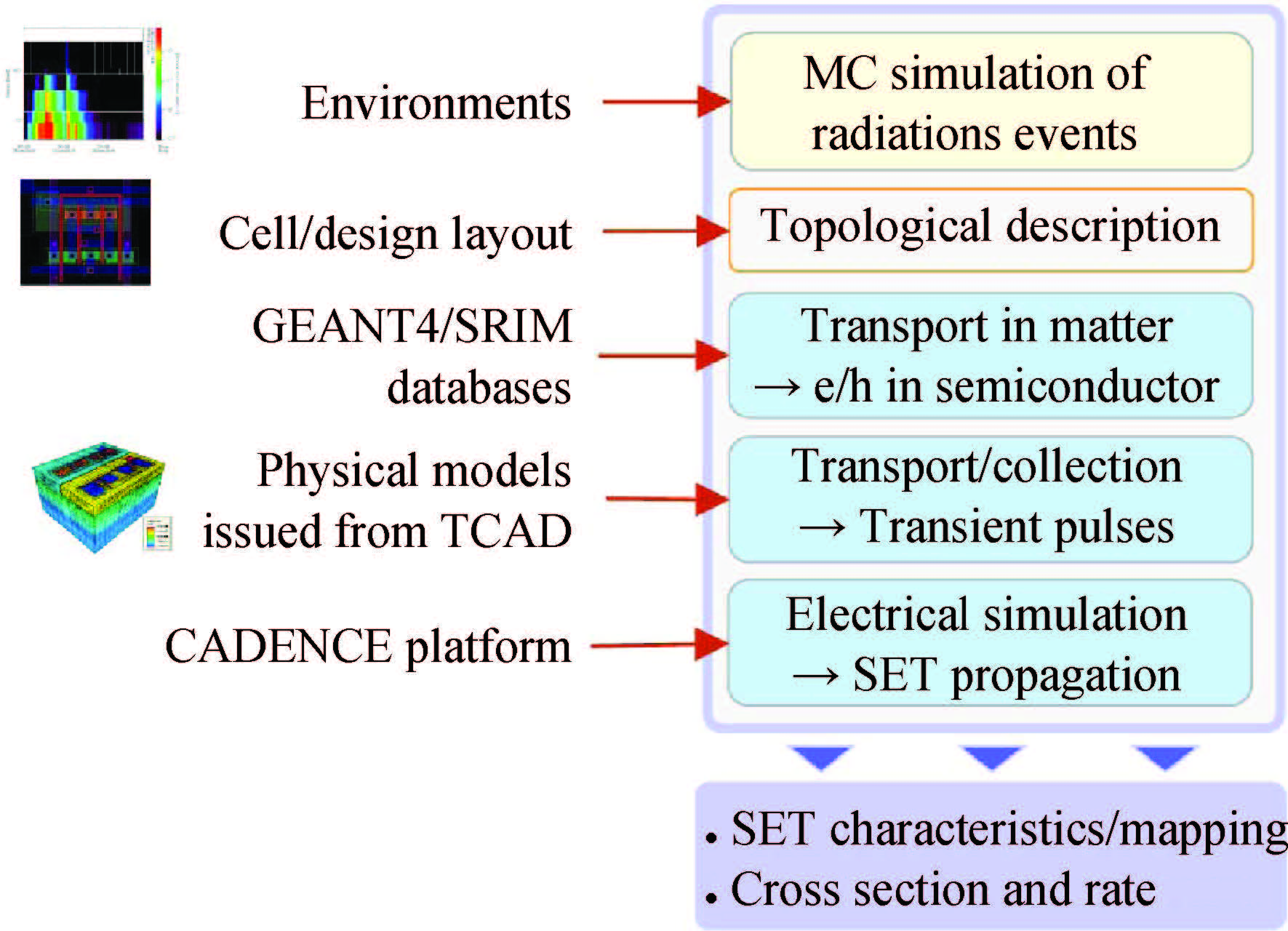
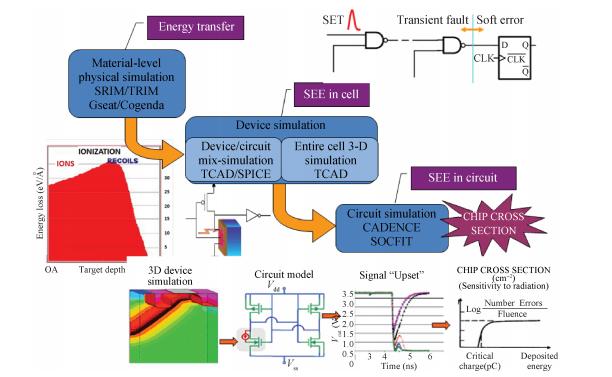
This paper reviews the status of research in modeling and simulation of single-event effects (SEE) in digital devices and integrated circuits. After introducing a brief historical overview of SEE simulation, different level simulation approaches of SEE are detailed, including material-level physical simulation where two primary methods by which ionizing radiation releases charge in a semiconductor device (direct ionization and indirect ionization) are introduced, device-level simulation where the main emerging physical phenomena affecting nanometer devices (bipolar transistor effect, charge sharing effect) and the methods envisaged for taking them into account are focused on, and circuit-level simulation where the methods for predicting single-event response about the production and propagation of single-event transients (SETs) in sequential and combinatorial logic are detailed, as well as the soft error rate trends with scaling are particularly addressed. -
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] [34] [35] [36] [37] [38] [39] [40] [41] [42] [43] [44] [45] [46] [47] [48] [49] [50] [51] [52] [53] [54] [55] [56] [57] [58] [59] [60] [61] [62] [63] [64] [65] [66] [67] [68] [69] [70] [71] [72] [73] [74] [75] [76] [77] [78] [79] [80] [81] [82] [83] [84] [85] [86] [87] [88] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: