| Citation: |
Yong Cao, Hailong Zhang, Fengzhen Liu, Meifang Zhu, Gangqiang Dong. Effect of hydrogen on low temperature epitaxial growth of polycrystalline silicon by hot wire chemical vapor deposition[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(2): 023004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/2/023004
****
Y Cao, H L Zhang, F Z Liu, M F Zhu, G Q Dong. Effect of hydrogen on low temperature epitaxial growth of polycrystalline silicon by hot wire chemical vapor deposition[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(2): 023004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/2/023004.
|
Effect of hydrogen on low temperature epitaxial growth of polycrystalline silicon by hot wire chemical vapor deposition
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/2/023004
More Information
-
Abstract
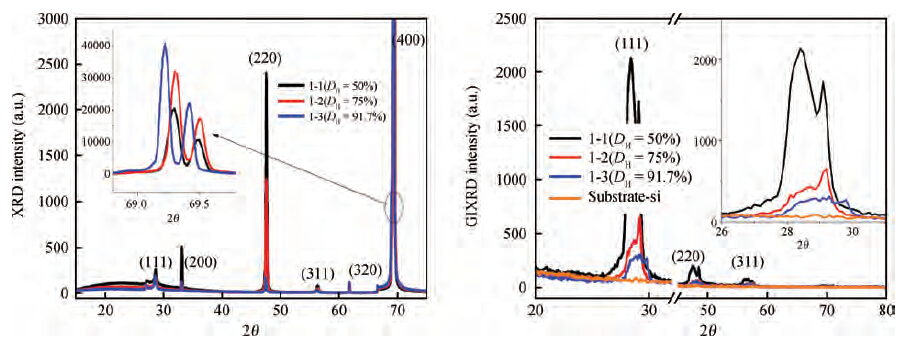
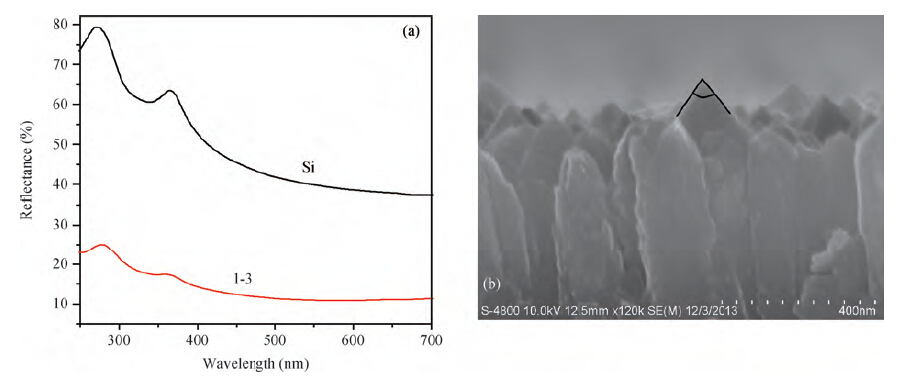
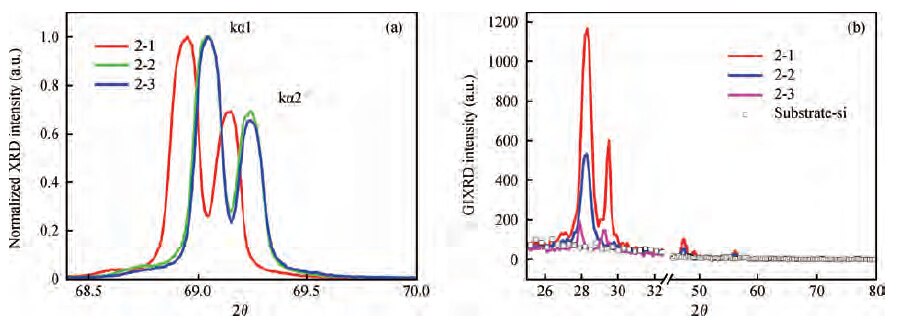
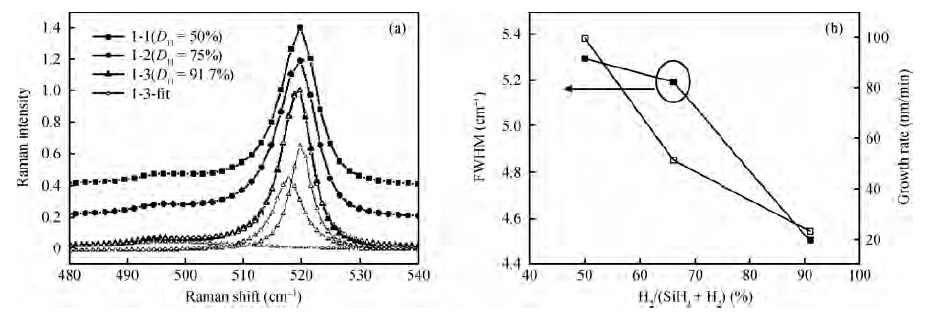
Polycrystalline silicon (poly-Si) films were prepared by hot-wire chemical vapor deposition (HWCVD) at a low substrate temperature of 525 ℃. The influence of hydrogen on the epitaxial growth of ploy-Si films was investigated. Raman spectra show that the poly-Si films are fully crystallized at 525 ℃ with a different hydrogen dilution ratio (50%—91.7%). X-ray diffraction, grazing incidence X-ray diffraction and SEM images show that the poly-Si thin films present (100) preferred orientation on (100) c-Si substrate in the high hydrogen dilution condition. The P-type poly-Si film prepared with a hydrogen dilution ratio of 91.7% shows a hall mobility of 8.78 cm2/(V·s) with a carrier concentration of 1.3 × 1020 cm-3, which indicates that the epitaxial poly-Si film prepared by HWCVD has the possibility to be used in photovoltaic and TFT devices. -
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: