| Citation: |
Zhiqing Geng, Nanjian Wu. A low power wide tuning range baseband filter for multistandard transceivers[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(4): 045006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/4/045006
****
Z Q Geng, N J Wu. A low power wide tuning range baseband filter for multistandard transceivers[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(4): 045006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/4/045006.
|
A low power wide tuning range baseband filter for multistandard transceivers
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/4/045006
More Information
-
Abstract
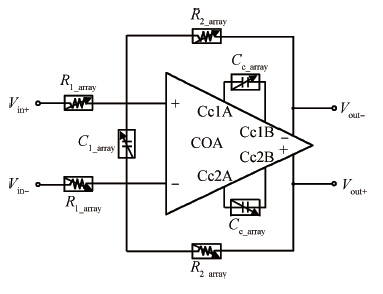
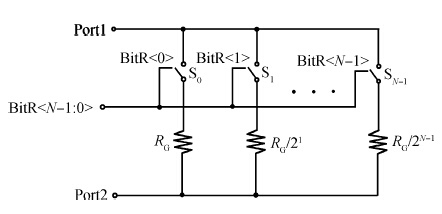
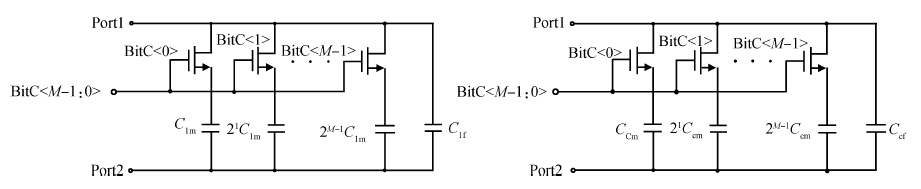
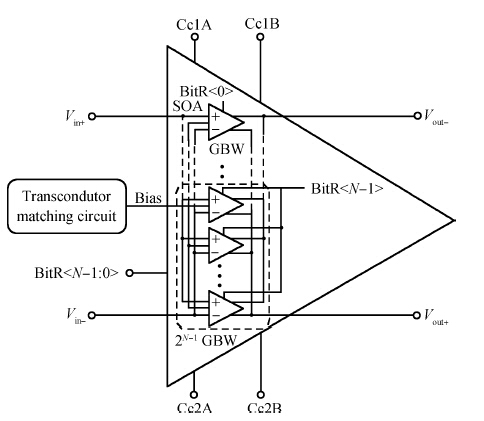
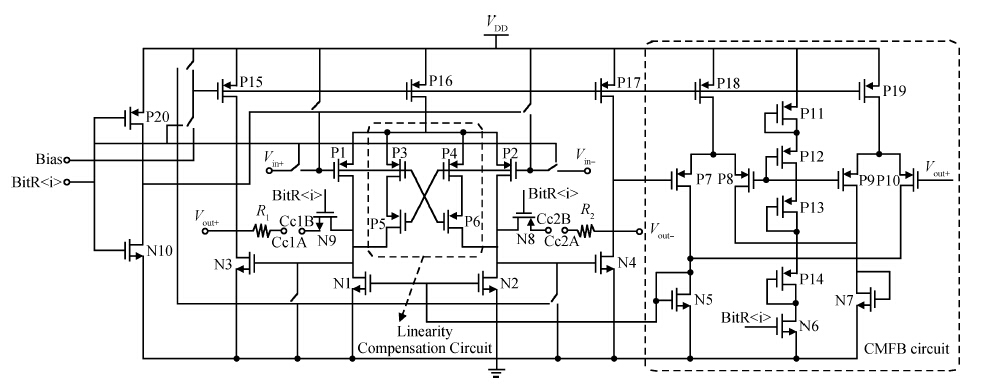
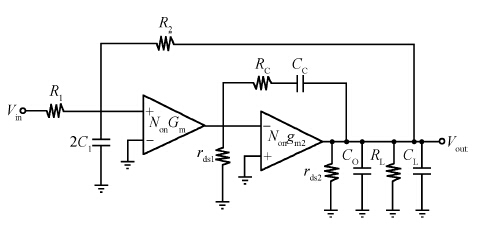
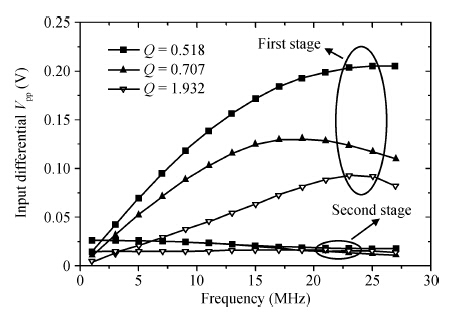
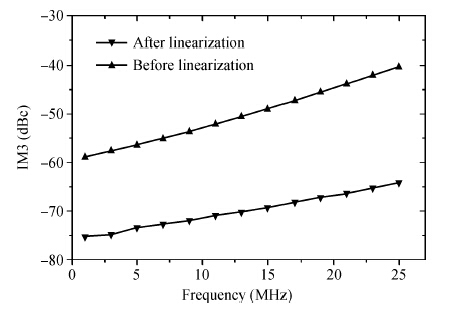
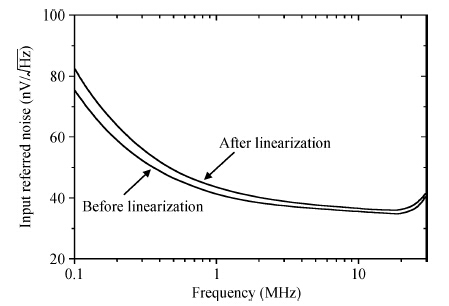
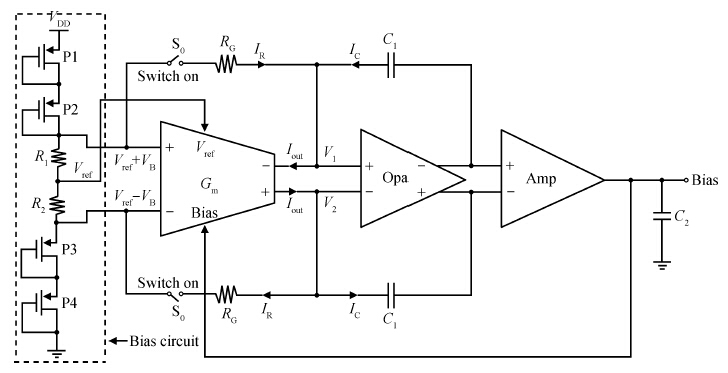
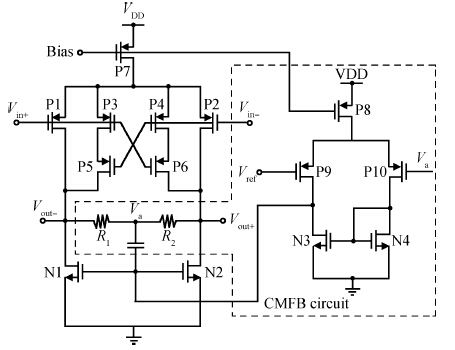
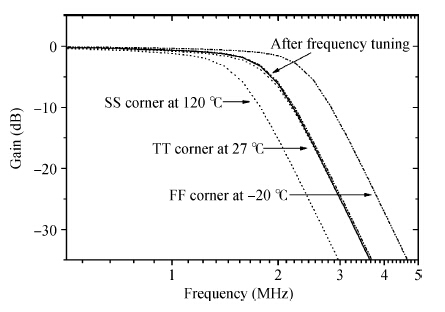
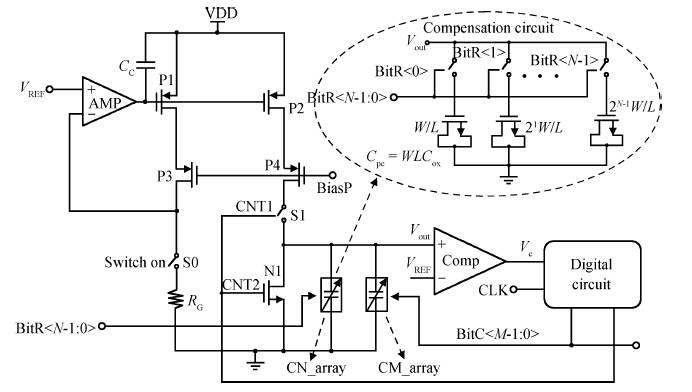
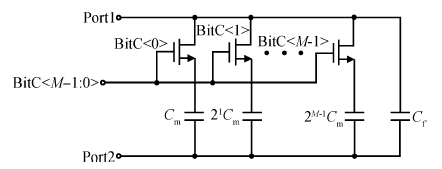
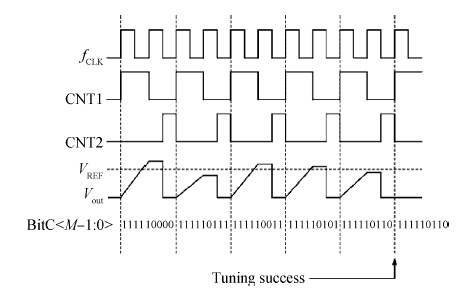
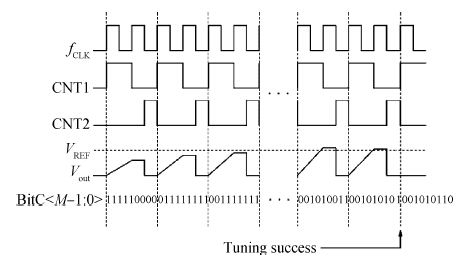
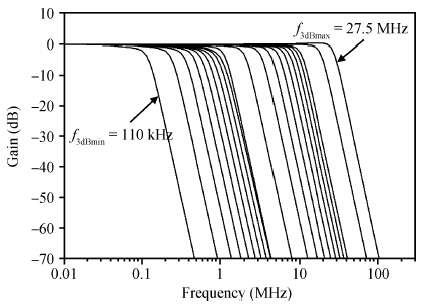
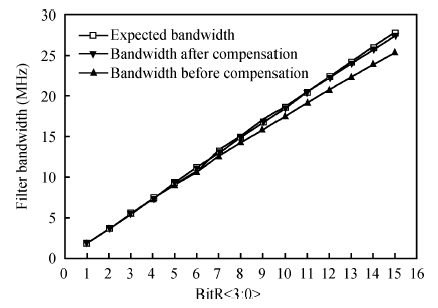
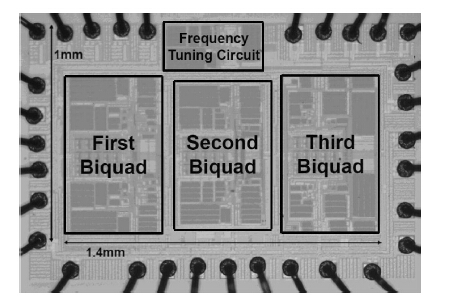
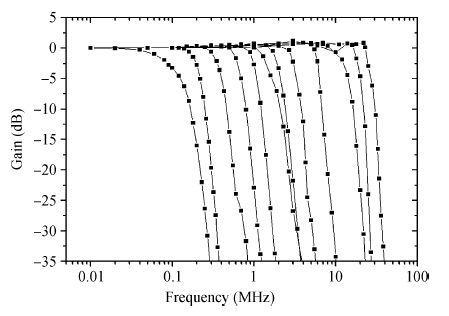
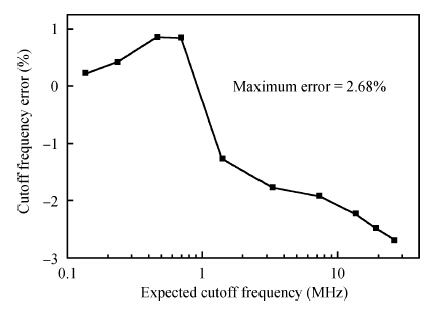
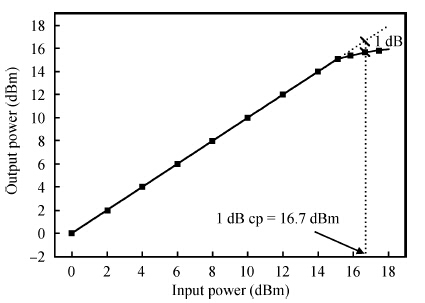
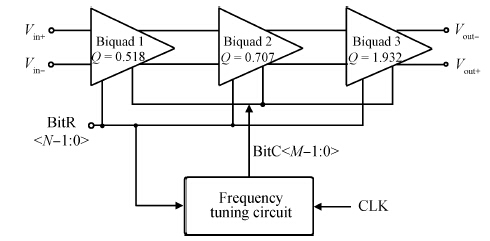
This paper presents the design and implementation of a low power wide tuning range baseband filter with an accurate on-chip tuning circuit for reconfigurable multistandard wireless transceivers. The realized low pass filter (LPF) is a six-order Butterworth type by cascading three stage active-Gm-RC biquadratic cells. A modified linearization technique is used to improve the filter linearity performance at low power consumption. A new process-independent transconductor matching circuit and a new frequency tuning circuit with frequency compensation are proposed to achieve a high precision filter frequency response. The proposed LPF is realized in a 130 nm standard CMOS technology. The measured results show that the LPF exhibits a high bandwidth programmability from 0.1 to 25 MHz with a tuning frequency error less than 2.68% over the wide tuning range. The power consumption is scalable, ranging from 0.52 to 5.25 mA, from a 1.2 V power supply while achieving a 26.3 dBm in-band IIP3.-
Keywords:
- low power,
- baseband filter,
- frequency tuning
-
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: