| Citation: |
Xiaofeng Guo, Fan Ye, Junyan Ren. A 9 b/12 b 50 MS/s experimental ADC with continuous approximation architecture in 65 nm CMOS[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(10): 105003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/10/105003
****
X F Guo, F Ye, J Y Ren. A 9 b/12 b 50 MS/s experimental ADC with continuous approximation architecture in 65 nm CMOS[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(10): 105003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/10/105003.
|
A 9 b/12 b 50 MS/s experimental ADC with continuous approximation architecture in 65 nm CMOS
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/10/105003
More Information
-
Abstract
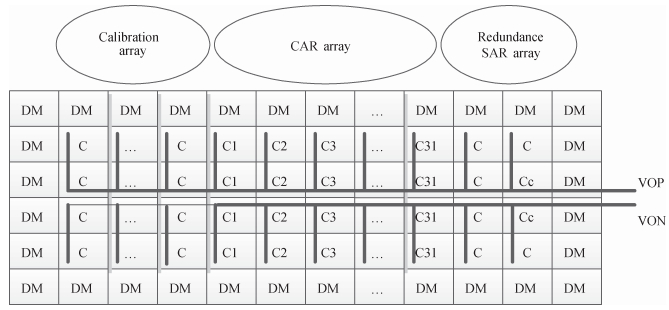
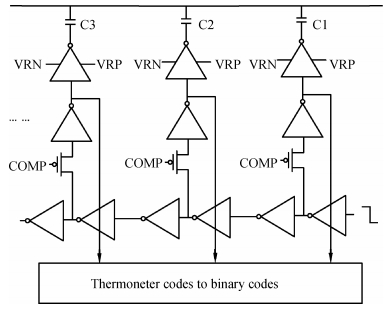
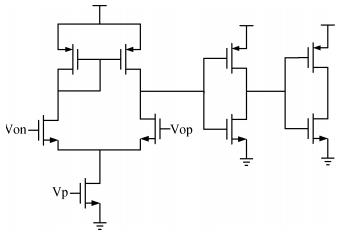
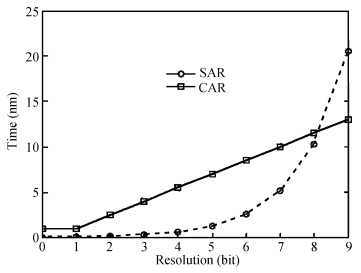
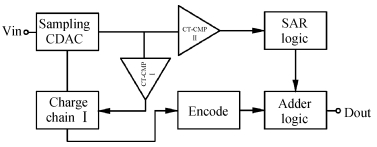
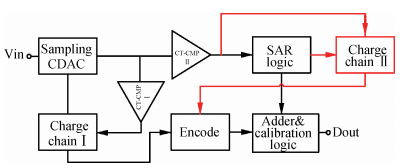
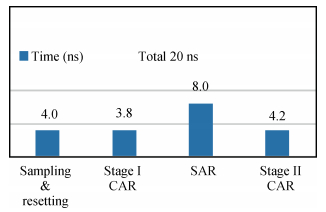
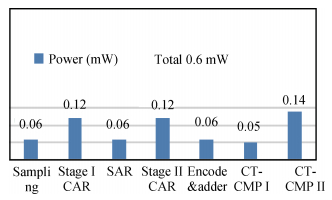
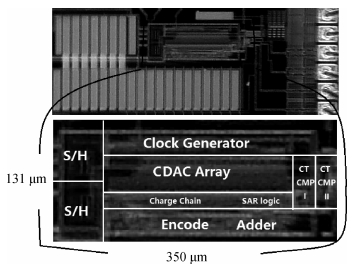
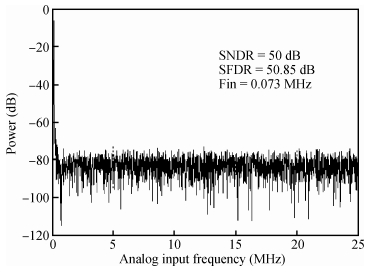
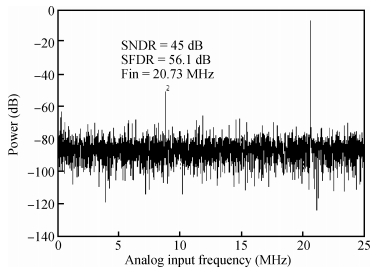
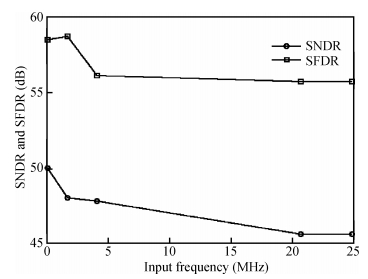
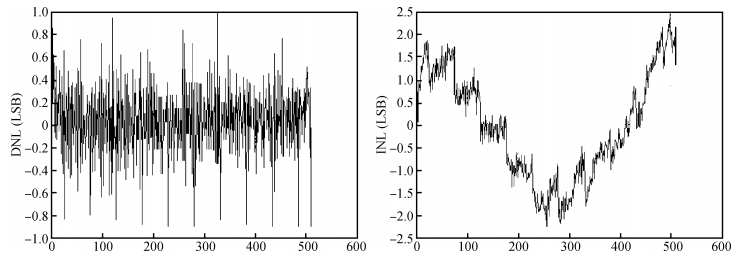
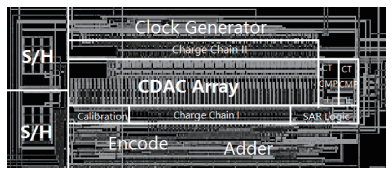
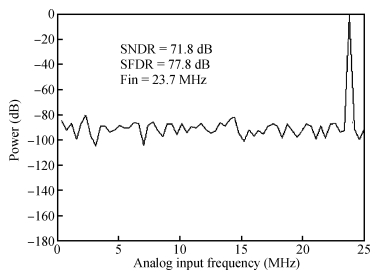
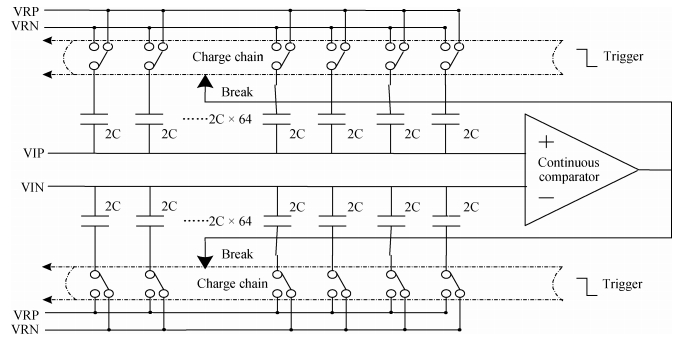
A 9 bits 50 MS/s 0.5 mW continuous approximation mixed successive approximation (CAR&SAR) ADC is presented. A 12 bits 50 MS/s 0.6 mW CAR&CAR ADC is presented. In the field of low power and high performance ADC, CAR is a new architecture different from SAR. It is faster and easier to get high accuracy. Here we will introduce CAR and its circuit implementation, and the 9 bits experimental ADC is designed to verify CARADC's feasibility. Meanwhile, its resolution can be extended to 12 bits with adding an extra CAR, and then the performance is raised to 0.6 mW 50 MS/s 72 dB SNDR at TT corner and the Walden FOM is 3.6 fj/conv-step. The 9 b ADC was fabricated by using TSMC 1P9M 65 nm CMOS technology. The ADC achieves 50 dB SNDR and the realized Walden FOM is 34 fj/conv-step. The simulation and measurement results prove that CAR is available in the low power and high performance ADC and it even outperforms SAR. The ADC core occupies an active area of 0.045 mm2.-
Keywords:
- low-power and high-performance ADC,
- CAR,
- SAR,
- digital sloop ADC,
- hybrid ADC
-
References
[1] Van der Goes F, Ward C, Astgimath S, et al. A 1.5 mW 68 dB-SNDR 80MS/s 2-times interleaved SAR-assisted pipelined ADC in 28 nm CMOS. IEEE International Solid State Circuit Conference (ISSCC), 2014: 200[2] Murmann B. ADC performance survey 1997-2015, [Online]. Available: http://web.stanford.edu/~murmann/adcsurvey.html http://web.stanford.edu/~murmann/adcsurvey.html[3] Lim Y, Flynn M P. A 1 mW 71.5 dB SNDR 50 MS/s 13 b fully differential ring amplifier based SAR-assisted pipeline ADC in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE International Solid State Circuit Conference (ISSCC), 2015: 458[4] Liu C C, Chang S J, Huang G Y, et al. A 10-bit 50-MS/s SAR ADC with a monotonic capacitor switching procedure. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(4): 731 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2042254[5] Liu C C. A 0.35 mW 12 b 100 MS/s SAR-assisted digital slope ADC in 28 nm CMOS. IEEE International Solid State Circuit Conference (ISSCC), 2016: 649[6] Li Dong, Meng Qiao, Li Fei. A 10 bit 50 MS/s SARADC with partial split capacitor switching scheme in 0.18 μm CMOS. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(1): 015004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/1/015004[7] Chen Huabin, Ye Fan, Ren Junyan. An analog front end with a 12-bit 3.2-MS/s SAR ADC for a power line communication system. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(11): 115008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/115008[8] Harpe P, Zhou C, Philips K, et al. A 0.8-mW 5-bit 250-MS/s time-interleaved asynchronous digital slope ADC. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(11): 2450 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2164031[9] Liu C C. A 10-bit 320-MS/s low-cost SAR ADC for IEEE 802.11ac applications in 20-nm CMOS. IEEE A-SSCC, 2014: 77[10] Huang G Y, Chang S J, Liu C C, et al. A 10-bit 30-MS/s SARADC using a switchback switching method. IEEE Trans VLSI Syst, 2013, 21(3): 584 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2012.2190117[11] Qiao Ning, Zhang Guoquan, Yang Bo, et al. A 10-bit 50-MS/s reference-free low power SAR ADC in 0.18 μm SOI CMOS technology. Journal of Semiconductors, 2012, 33(9): 095005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/33/9/095005 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: