| Citation: |
Zhiqiang You, Fei Hu, Liming Huang, Peng Liu, Jishun Kuang, Shiying Li. A long lifetime, low error rate RRAM design with self-repair module[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(11): 115004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/11/115004
****
Z Q You, F Hu, L M Huang, P Liu, J S Kuang, S Y Li. A long lifetime, low error rate RRAM design with self-repair module[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(11): 115004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/11/115004.
|
A long lifetime, low error rate RRAM design with self-repair module
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/11/115004
More Information
-
Abstract
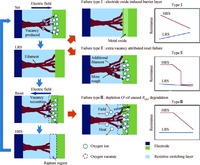
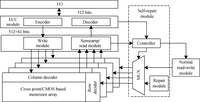
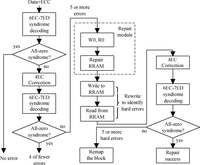
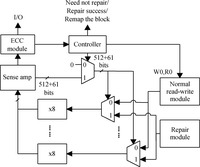
Resistive random access memory (RRAM) is one of the promising candidates for future universal memory. However, it suffers from serious error rate and endurance problems. Therefore, exploring a technical solution is greatly demanded to enhance endurance and reduce error rate. In this paper, we propose a reliable RRAM architecture that includes two reliability modules: error correction code (ECC) and self-repair modules. The ECC module is used to detect errors and decrease error rate. The self-repair module, which is proposed for the first time for RRAM, can get the information of error bits and repair wear-out cells by a repair voltage. Simulation results show that the proposed architecture can achieve lowest error rate and longest lifetime compared to previous reliable designs.-
Keywords:
- self-repair,
- ECC,
- RRAM,
- memristor
-
References
[1] Strukov D B, Snider G S, Stewart D R, et al. The missing memristor found. Nature, 2008, 453:80 doi: 10.1038/nature06932[2] Niu D, Xiao Y, Xie Y. Low power memristor-based ReRAM design with error correcting code. 17th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, 2012:79 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1966433652&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[3] Sun Pengxiao, Liu Su, Li Ling, et al. Simulation study of conductive filament growth dynamics in oxide-electrolyte-based ReRAM. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(10):104007 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/104007[4] Chen Y S, Lee H Y, Chen P S, et al. Challenges and opportunities for HfOx based resistive random access memory. 2011 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), 2011:31.3.1 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1495239691&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[5] Schechter S, Loh G H, Straus K, et al. Use ECP, not ECC, for hard failures in resistive memories. ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, ACM, 2010, 38(3):141 doi: 10.1145/1816038[6] Yoon D H, Muralimanohar N, Chang J, et al. FREE-p:protecting non-volatile memory against both hard and soft errors. 2011 IEEE 17th International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), 2011:466 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2155462575&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[7] Ghofrani A, Lastras-Montano M A, Cheng K T. Towards data reliable crossbar-based memristive memories. 2013 IEEE International Test Conference (ITC), 2013:14.3.1 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1965970229&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[8] Chen B, Lu Y, Gao B, et al. Physical mechanisms of endurance degradation in TMO-RRAM. 2011 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), 2011:12.3.1 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2018068167&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[9] Huang P Y, Chen B, Wang Y J, et al. Analytic model of endurance degradation and its practical applications for operation scheme optimization in metal oxide based RRAM. 2013 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), 2013:22.5.1 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2083980649&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[10] Chen Y Y, Govoreanu B, Goux L, et al. Balancing set/reset pulse for endurance in 1T1R bipolar RRAM. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2012, 59(12):3243 doi: 10.1109/TED.2012.2218607[11] Kim S Y, Baek J M, Seo D J, et al. Power-efficient fast write and hidden refresh of ReRAM using an ADC-based sense amplifier. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ, 2013, 60(11):776 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2050500844&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[12] Lu Jinglong, Luo Jing, Zhao Hongpeng, et al. Optimal migration route of Cu in HfO2. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(1):013001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/1/013001[13] Zhao Yuanyang, Wang Jiayu, Xu Jianbin, et al. Metal dopants in HfO2-based RRAM:first principle study. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(4):042002 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/042002[14] Liu P, You Z, Kuang J, et al. Logic operation-based DFT method and 1R memristive crossbar march-like test algorithm. IEICE Electronics Express, 2015, 12(23):20150839 doi: 10.1587/elex.12.20150839 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: