| Citation: |
Qifeng Yao, Yongzhen Huang, Yuede Yang, Jinlong Xiao. Analysis of mode characteristics for microcircular resonators confined by different metallic materials[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(12): 124004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/12/124004
****
Q F Yao, Y Z Huang, Y D Yang, J L Xiao. Analysis of mode characteristics for microcircular resonators confined by different metallic materials[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(12): 124004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/12/124004.
|
Analysis of mode characteristics for microcircular resonators confined by different metallic materials
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/12/124004
More Information
-
Abstract
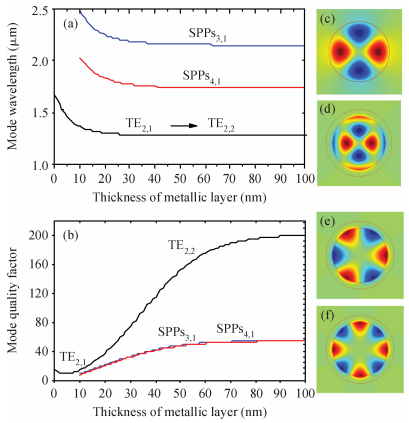
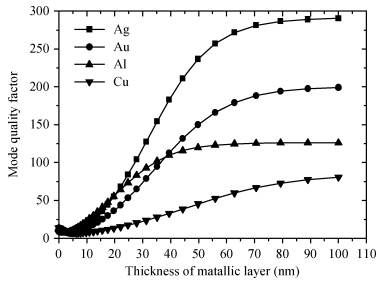
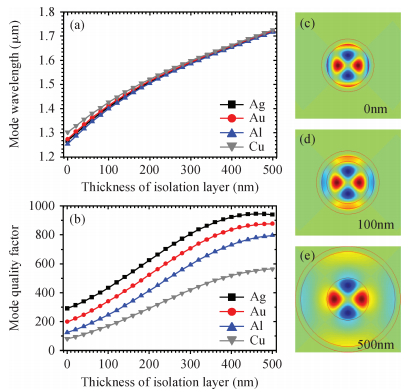
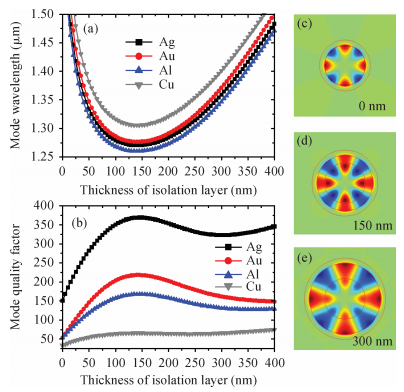
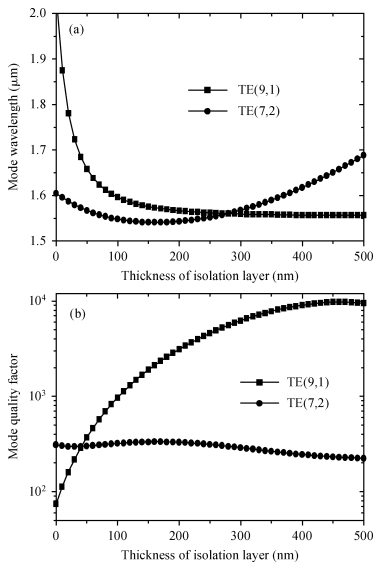
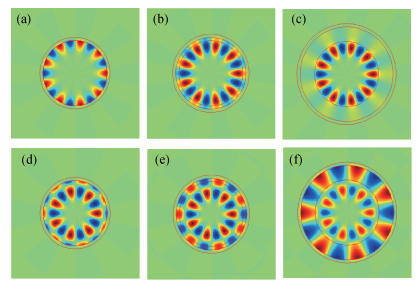
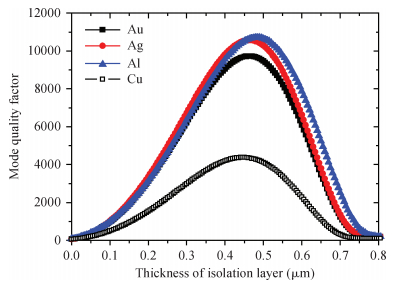
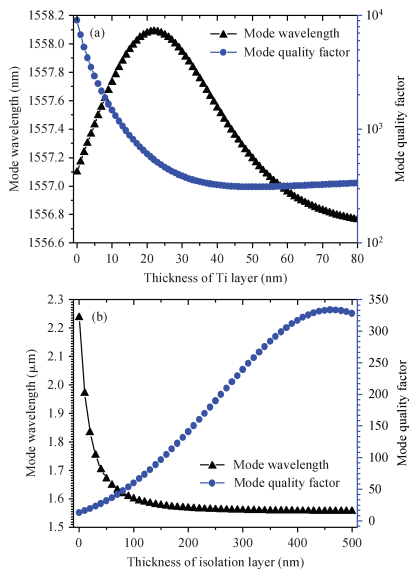
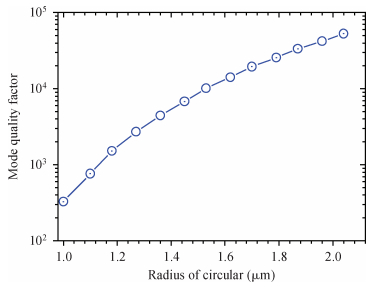
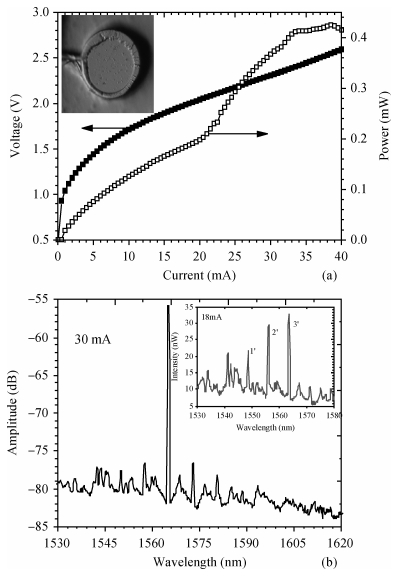
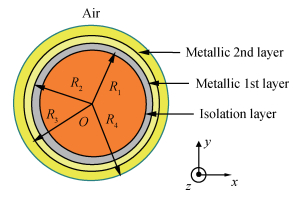
Mode characteristics of metallically confined microcircular resonators are theoretically studied by solving eigenvalue equations for two-dimensional multilayer structures. The influences of conventional metals including Au, Ag, Cu, Al, and Ti, on the mode wavelengths and Q factors of whispering gallery modes (WGMs) are analyzed and compared. The results show silver has the best optical confinement among these metals, and aluminum presents similar behavior to Au. However, Ti, which is usually applied to enhance the adhesion of p-electrode to semiconductors, results in a great dissipation for confined modes. Furthermore, circular microlasers with Al as both p-electrode and optical confinement medium are fabricated, and continuous-wave operations are realized at room temperature for the microlasers with a radius of 15 μm. -
References
[1] Hill M T, Oei Y S, Smalbrugge B, et al. Lasing in metallic-coated nanocavities. Nature Photonics, 2007, 1: 589 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.171[2] Ding K, Liu Z C, Yin L J, et al. Room-temperature continuous wave lasing in deep-subwavelength metallic cavities under electrical injection. Phys Rev B, 2012, 85: 041301(R) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235537357_Room-temperature_continuous_wave_lasing_in_deep-subwavelength_metallic_cavities_under_electrical_injection[3] Chuang S L, Bimberg D. Metal-cavity nanolasers. IEEE Photon J, 2011, 3: 288 doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2011.2138690[4] Nezhad M P, Simic A, Bondarenko O, et al. Room-temperature subwavelength metallo-dielectric lasers. Nature Photonics, 2010, 4: 395 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2010.88[5] Ma R M, Oulton R F, Sorge V J, et al. Room-temperature sub-diffraction-limited plasmon laser by total internal reflection. Nature Material, 2011, 10: 110 doi: 10.1038/nmat2919[6] Hill M T, Marell M, Leong E S P, et al. Lasing in metal-insulator-metal sub-wavelength plasmonic waveguides. Opt Express, 2009, 17: 11107 doi: 10.1364/OE.17.011107[7] Kwon S H, Kang J H, Seassal C, et al. Subwavelength plasmonic lasing from a semiconductor nanodisk with silver nanopan cavity. Nano Lett, 2010, 10: 3679 doi: 10.1021/nl1021706[8] Ning C Z. Semiconductor nanolasers. Phys Status Solidi B, 2010, 247: 774 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2023361355&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[9] Huang J, Kim S H, Scherer A. Design of a surface-emitting, subwavelength metal-clad disk laser in the visible spectrum. Opt Express, 2010, 18: 19581 doi: 10.1364/OE.18.019581[10] Lu C Y, Chuang S L. A surface emitting 3D metal-nanocavity laser: proposal and theory. Opt Express, 2011, 19: 13225 doi: 10.1364/OE.19.013225[11] Krishnamurthy V, Klein B. Theoretical investigation of metal cladding for nanowire and cylindrical micropost lasers. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 2008, 40(1): 67 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/2975124_Theoretical_Investigation_of_Metal_Cladding_for_Nanowire_and_Cylindrical_Micropost_Lasers[12] Mizrahi A, Lomakin V, Slutsky B A, et al. Low threshold gain metal coated laser nanoresonators. Opt Lett, 2008, 33: 1261 doi: 10.1364/OL.33.001261[13] Yang Y D, Huang Y Z, Wang S J. Mode analysis for equilateral-triangle-resonator microlasers with metal confinement layers. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 2009, 45: 1529 doi: 10.1109/JQE.2009.2024006[14] Che K J, Yang Y D, Huang Y Z. Mode characteristics for square resonators with a metal confinement layer. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 2010, 46: 414 doi: 10.1109/JQE.2009.2031616[15] Yao Q F, Huang Y Z, Zou L X, et al. Analysis of mode coupling and threshold gain control for nanocircular resonators confined by isolation and metallic layers. IEEE J Lightw Technol, 2013, 31(5): 786 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2012.2234437[16] Palik E D. Handbook of optical constants of solid. 1st ed. Boston: Academic Press, 1985[17] Vial A, Grimault A S, Macias D, et al. Application to the modeling of improved analytical fit of gold dispersion: extinction spectra with a finite-difference time-domain method. Phys Rev B, 2005, 71: 085416 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.71.085416[18] Wang S J, Lin J D, Huang Y Z, et al. AlGaInAs-InP microcylinder lasers connected with an output waveguide. IEEE Photon Technol Lett, 2010, 22: 1349 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2010.2056361[19] Lin J D, Zou L X, Huang Y Z, et al. Wide angle emission and single mode deformed circular microlasers with a flat side. Appl Opt, 2012, 51: 3930 doi: 10.1364/AO.51.003930[20] Jiao Wenlong, Yuan Weizheng, Chang Honglong. System level simulation of a micro resonant accelerometer with geometric nonlinear beams. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(10): 104007 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/10/104007[21] Zhang Fanfan, Zhou Ping, Chen Qiaoshan, et al. An electro-optic directed decoder based on two cascaded microring resonators. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(10): 104011 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/104011 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: