| Citation: |
Jing Wen, Yumei Wen, Ping Li, Sanshan Wang. Junction-temperature estimation in AlGaInP light-emitting diodes using the luminescence spectra method[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(6): 064010. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/6/064010
****
J Wen, Y M Wen, P Li, S S Wang. Junction-temperature estimation in AlGaInP light-emitting diodes using the luminescence spectra method[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(6): 064010. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/6/064010.
|
Junction-temperature estimation in AlGaInP light-emitting diodes using the luminescence spectra method
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/6/064010
More Information
-
Abstract
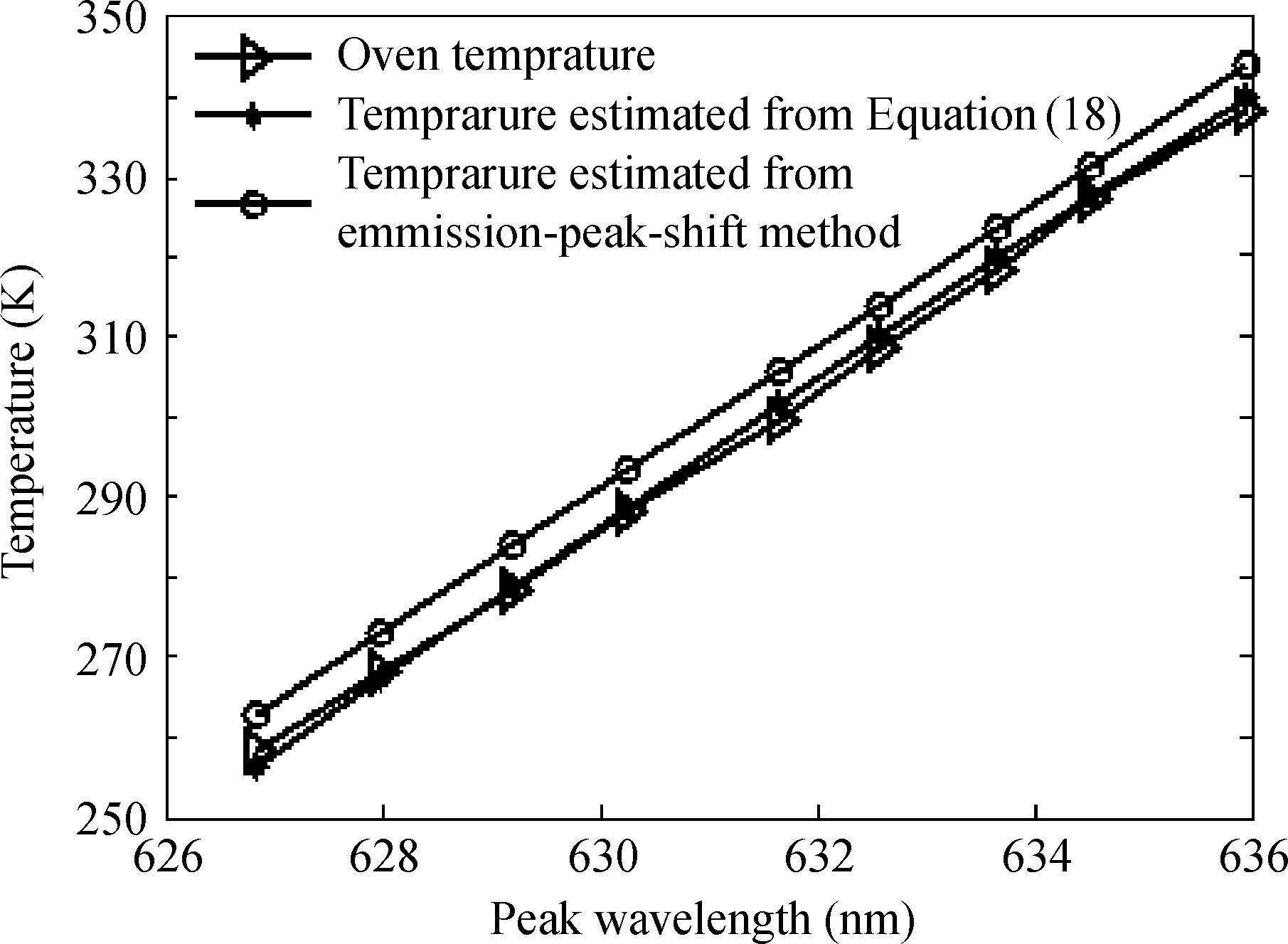
This study proposes a practical method to estimate the junction temperature of AlGaInP LEDs using the luminescence spectra method. The peak wavelength shift of LEDs is due to the energy band gap shrinking. The temperature dependence of the bandgap of AlGaInP LEDs is derived from those of the underlying binary compounds AlP, GaP, and InP. Based on this, a theoretical model for the dependence of the peak wavelength on junction temperature is developed. Experimental results on the junction temperature of AlGaInP red light-emitting diodes are presented. Excellent agreement between the theoretical and experimental temperature dependence of the peak wavelength is found.-
Keywords:
- light emitting diode,
- junction temperature,
- luminescence,
- bandgap
-
References
[1] Zuo Zhiyuan, Xia Wei, Wang Gang, et al. Wafer-bonding AlGaInP light emitting diodes with pyramidally patterned metal reflector. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(2):024011[2] Liu Yu'an, Lou Wenlang. Correlation between dark current RTS noise and defects for AlGaInP multiple-quantum-well laser diode. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(2):024009[3] Gessmann T, Schubert E F. High-efficiency AlGaInP light-emitting diodes for solid-state lighting applications. J Appl Phys, 2004, 95(5):2203[4] Todoroki S, Sawai M, Aiki K. Temperature distribution along the striped active region in high-power GaAlAs visible lasers. J Appl Phys, 1985, 58(3):1124[5] Abdelkader H I, Hausien H H, Martin J D. Temperature rise and thermal rise-time measure-meters of a semiconductor laser diode. Rev Sci Instrum, 1992, 63(3):2004[6] Murata S, Nakada H. Adding a heat by pass improves the thermal characteristics of a 50 pm spaced a-beam laser diode array. J Appl Phys, 1992, 72:2514[7] Epperlein P W. Mapping of local temperatures on mirrors of GaAs/AlGaAs laser diodes. Proceedings of 17th International Symposium of Gallium Arsenide and Related Compounds, IOP Conference Series, 1990, 112:633[8] Epperlein P W, Bona G L. Influence of the vertical structure on the mirror facet temperature of visible GaInP quantum well laser. Appl Phys Lett, 1993, 24:3074[9] Hall D C, Goldberg L, Mehuys D. Technique for lateral temperature profiling in optoelectronic devices using a photoluminescence microprobe. Appl Phys Lett, 1992, 61(4):384[10] Chhajed S, Xi Y, Gessmann T, et al. Junction temperature in light-emitting diodes assessed by different methods. Proceedings of SPIE, Light-Emitting Diodes:Research, Manufacturing, and Applications Ⅸ, 2005, 5739:16[11] Willardson R K, Beer A C. Semiconductors and semimetals. Vol. 8. NewYork:Academic Press, 1972[12] Varshni Y P. Temperature dependence of the energy gap in semiconductors. Physica, 1967, 34(6):149[13] Sarkar N, Ghosh S. The temperature dependence of the band gap shrinkage due to the electron-phonon interaction in AlxGa1-xAs. J Phys:Cond Matt, 2006, 18(5):1687[14] Fan H Y. Temperature dependence of the energy gap in semiconductor. Phys Rev, 1951, 82:900[15] Vina L, Logothetidis S, Cardona M. Temperature dependence of the dielectric function of germanium. Phys Rev B, 1984, 30(4):1979[16] Malikova L, Huang Y S, Pollak F H, et al. Temperature dependence of the energies and broadening parameters of the excitonic interband transitions in Ga0.95Al0.05N. Solid State Commun, 1997, 103:273[17] Manoogian A,Wooley J C. Temperature dependence of the energy gap in semiconductors. Can J Phys, 1984, 62(21):285[18] Krijn M P C M. Hetero junction band offsets and effective masses in Ⅲ-Ⅴ quaternary alloys. Semicond Sci Technol, 1991, 6(1):27[19] Adachi S. Band gaps and refractive indices of AlGaAsSb, GaInAsSb, and InPAsSb:Key properties for a variety of the 2-4-μm optoelectronic device applications. J Appl Phys, 1987, 61(10):4869[20] Glisson T H, Hauser J R, Littlejohn M A, et al. Energy bandgap and lattice constant contours of Ⅲ-Ⅴ quaternary alloys. J Electron Mater, 1978, 7(1):1[21] Vurgaftman I, Meyer J R, Ram-Mohan L R. Band parameters for Ⅲ-Ⅴ compound semiconductors and their alloys. J Appl Phys, 2001, 89(11):5815[22] Pavesi L, Piazza F, Rudra A, et al. Temperature dependence of the InP band gap from a photoluminescence study. Phys Rev B, 1991, 44(16):9052[23] Passler R. Dispersion-related description of temperature dependencies of band gaps in semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 2002, 66(8):085201[24] Passler R. Parameter sets due to fittings of the temperature dependencies of fundamental band gaps in semiconductors. Physica Status Solidi B, 1999, 216(2):975 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad:














