| Citation: |
Yaling Zhou, Xiaofeng Wang, Yingchun Fu, Xiaodong Wang, Fuhua Yang. Investigation and solution of low yield problem for phase change memory with lateral fully-confined structure[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(8): 084005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/8/084005
****
Y L Zhou, X F Wang, Y C Fu, X D Wang, F H Yang. Investigation and solution of low yield problem for phase change memory with lateral fully-confined structure[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(8): 084005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/8/084005.
|
Investigation and solution of low yield problem for phase change memory with lateral fully-confined structure
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/8/084005
More Information
-
Abstract
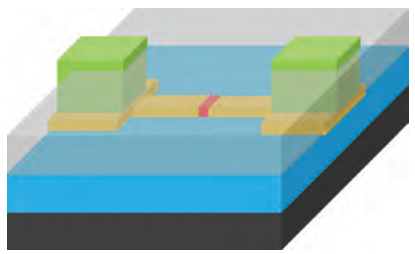
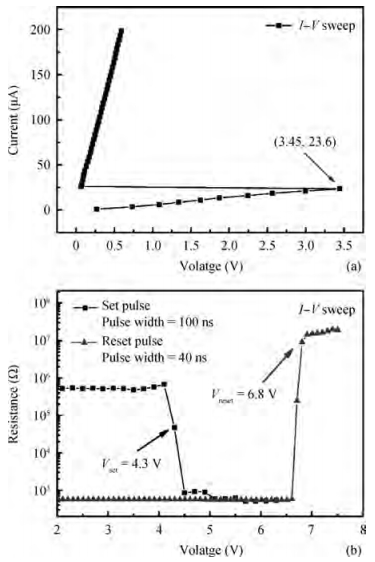
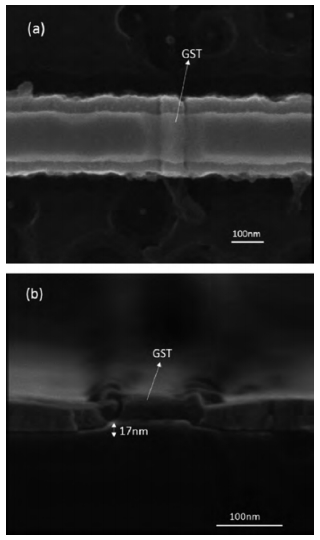
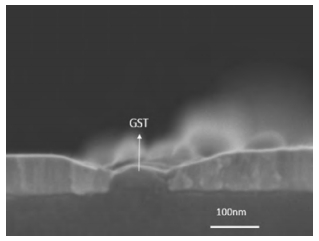
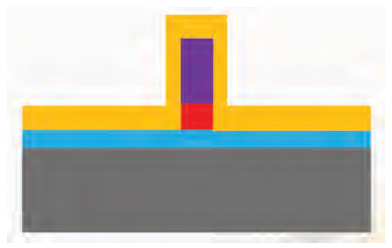
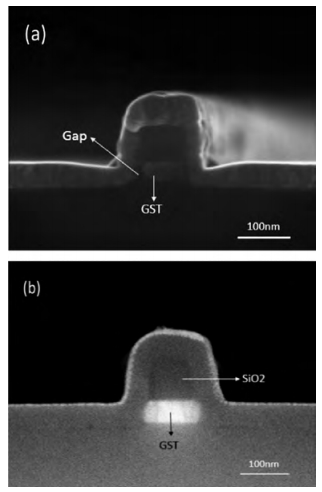
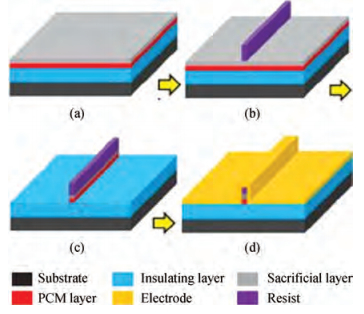
This paper mainly focuses on solving the low yield problem for lateral phase change random access memory with a fully confined phase change material node. Improper over-etching and bad step-coverage of physical vapor deposition were the main reasons for the poor contact quality, which leads to the low yield problem. Process improvement was carried out to better control over-etching within 10 nm. Atomic layer deposition process was used to replace physical vapor deposition to guarantee good step coverage. Contrasting cross-sectional photos taken by scanning electron microscopy showed great improvement in contact quality. The atom layer deposition process was demonstrated to have good prospects in nano-contact for phase change memory application. -
References
[1] Ovshinsk S R. Reversible electrical switching phenomena in disordered structures. Phys Rev Lett, 1968, 21(20): 1450 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.21.1450[2] Lai S. Current status of the phase change memory and its future. Electron Devices Meeting, 2003: 10.1.1 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1488028183&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[3] Yu Bin, Ju Sanghyun, Sun Xuhui, et al. Indium selenide nanowire phase-change memory. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 91(13): 133119 doi: 10.1063/1.2793505[4] Xiong F, Bae M H, Dai Y, et al. Self-aligned nanotube-nanowire phase change memory. Nano Lett, 2013, 13(2): 464 doi: 10.1021/nl3038097[5] Qi P, Javey A, Rolandi M, et al. Miniature organic transistors with carbon nanotubes as quasi-one-dimensional electrodes. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(38): 11774 doi: 10.1021/ja045900k[6] Xiong F, Liao A D, Estrada D, et al. Low-power switching of phase-change materials with carbon nanotube electrodes. Science, 2011, 332(6029): 568 doi: 10.1126/science.1201938[7] Jung Y, Nam S, Agarwal R. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy study of electrically-driven reversible phase change in Ge2Sb2Te5 nanowires. Nano Lett, 2011, 11(3): 1364 doi: 10.1021/nl104537c[8] Ahn J K, Park K W, Jung H J, et al. Phase-change InSbTe nanowires grown in situ at low temperature by metal-organic chemical vapor deposition. Nano Lett, 2010, 10(2): 472 doi: 10.1021/nl903188z[9] Yu Bin, Ju Sanghyun, Sun Xuhui, et al. Indium selenide nanowire phase-change memory. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 91(13): 133119 doi: 10.1063/1.2793505[10] Xiong F, Bae M H, Dai Y, Liao A D, et al. Self-aligned nanotube-nanowire phase change memory. Nano Lett, 2013, 13(2): 464 doi: 10.1021/nl3038097[11] Fu Yingchun, Wang Xiaofeng, Ma Liuhong, et al. High quality metal-quantum dot-metal structure fabricated with a highly compatible self-aligned process. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(12): 123004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/12/123004[12] Yin Y, Miyachi A, Niida D, et al. A novel lateral phase-change random access memory characterized by ultra low reset current and power consumption. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2006, 45(7L): L726 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2069131378&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[13] Merget F, Kim D H, Bolivar P H, et al. Lateral phase change random access memory cell design for low power operation. Microsystem Technologies, 2007, 13(2): 169 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2060507633&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[14] Yin Y, Sone H, Hosaka S. Lateral SbTeN based multi-layer phase change memory for multi-state storage. Microelectron Eng, 2007, 84(12): 2901 doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2007.03.004[15] Yin Y, Ota K, Higano N, et al. Multilevel storage in lateral top-heater phase-change memory. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2008, 29(8): 876 doi: 10.1109/LED.2008.2000793[16] Yang H, Chong C T, Zhao R, et al. GeTe/Sb7Te3 superlatticelike structure for lateral phase change memory. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94(20): 203110 doi: 10.1063/1.3139776 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: