| Citation: |
Jiafeng Wang, Xiangning Fan, Xiaoyang Shi, Zhigong Wang. A fractional-N frequency divider for multi-standard wireless transceiver fabricated in 0.18 μm CMOS process[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(12): 125001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/12/125001
****
J F Wang, X N Fan, X Y Shi, Z G Wang. A fractional-N frequency divider for multi-standard wireless transceiver fabricated in 0.18 μm CMOS process[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(12): 125001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/12/125001.
|
A fractional-N frequency divider for multi-standard wireless transceiver fabricated in 0.18 μm CMOS process
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/12/125001
More Information
-
Abstract
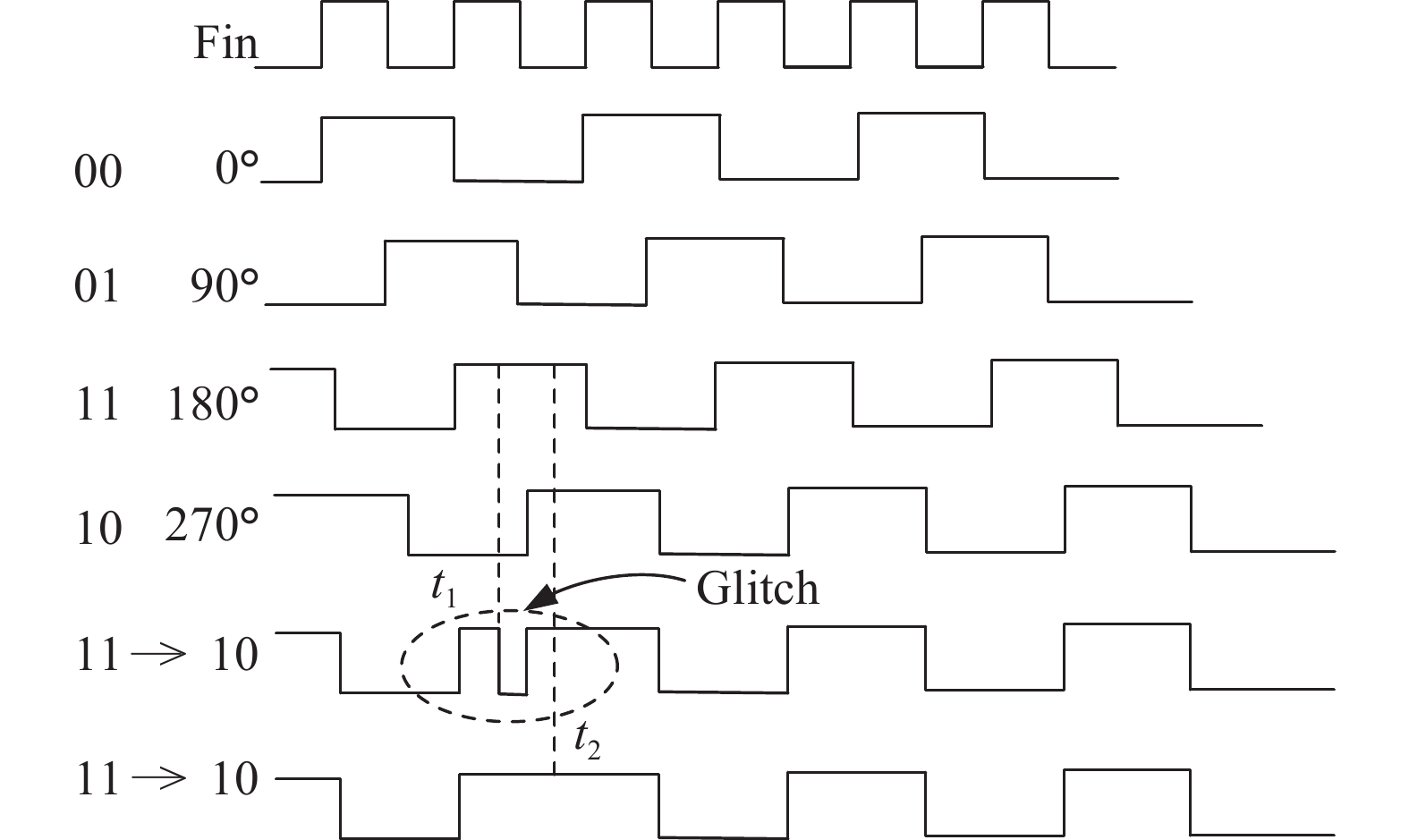
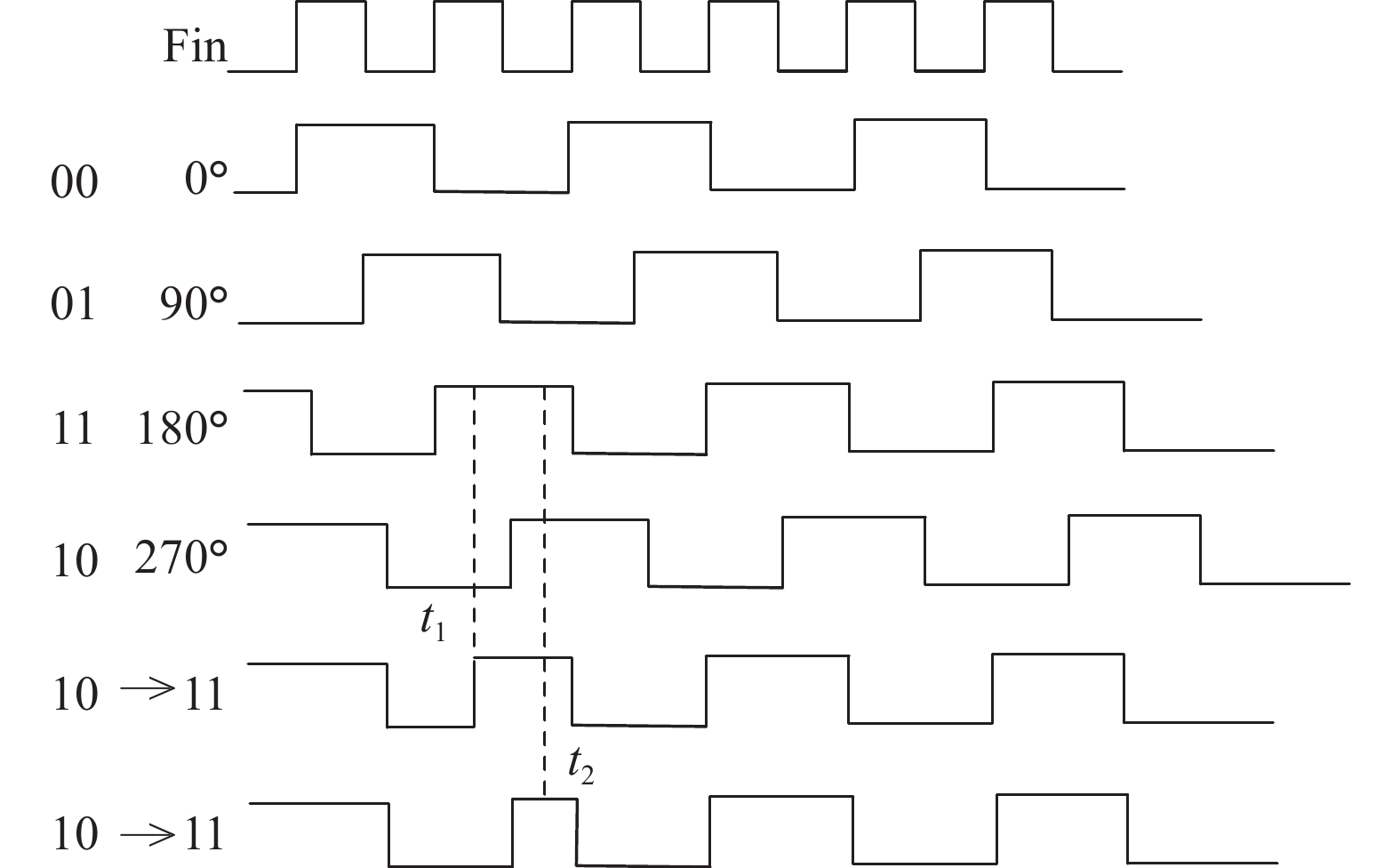
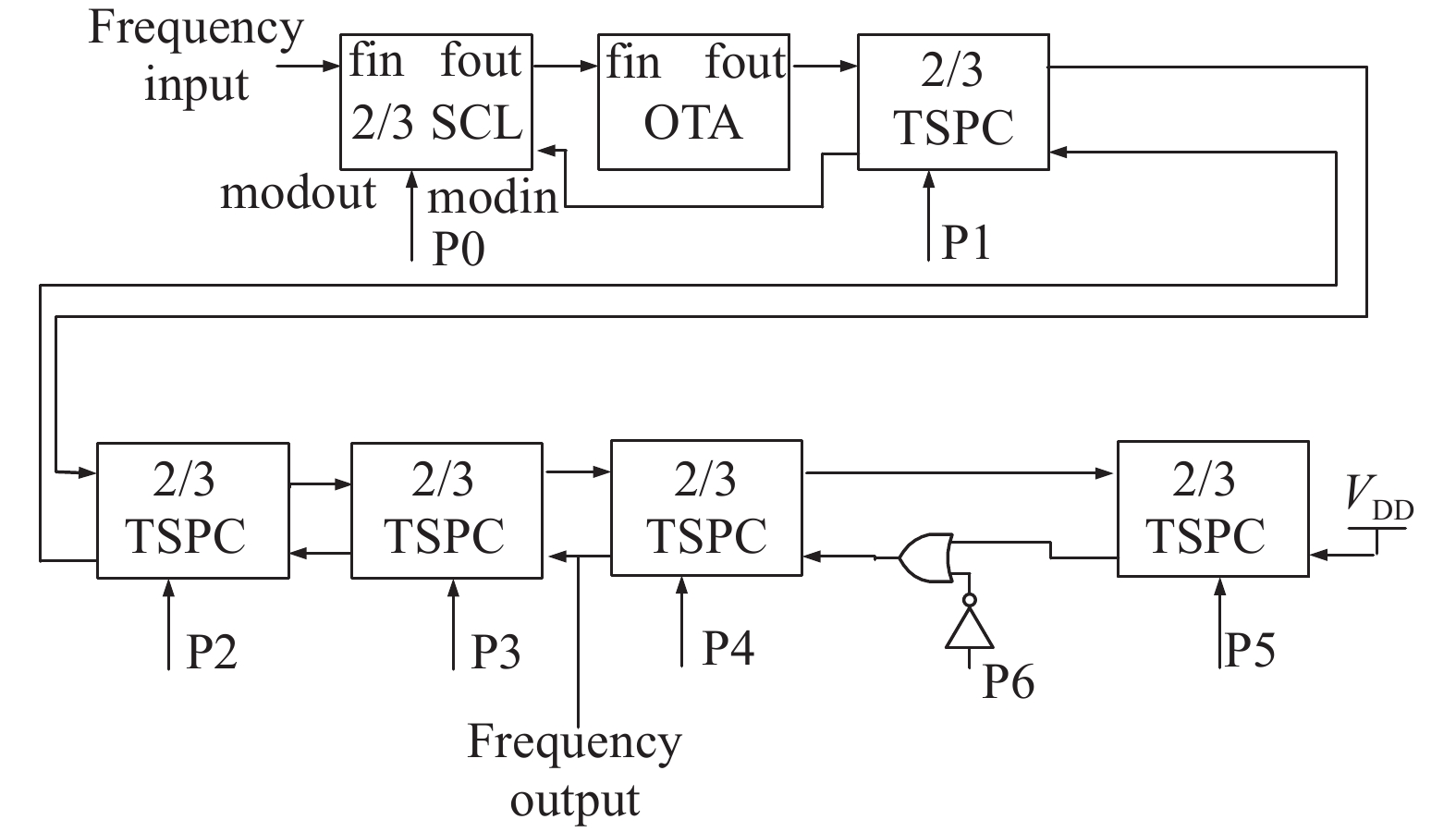
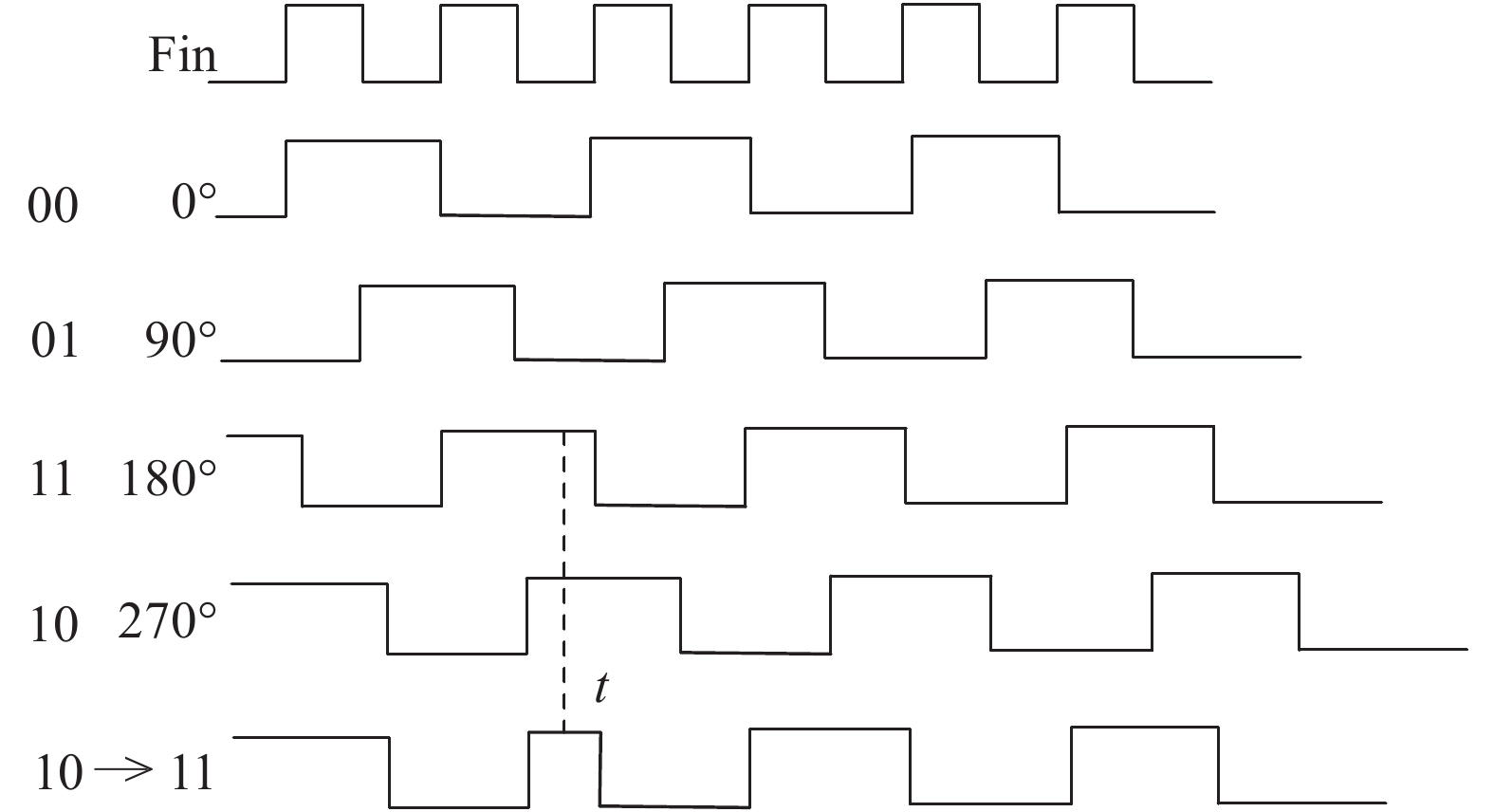
With the rapid evolution of wireless communication technology, integrating various communication modes in a mobile terminal has become the popular trend. Because of this, multi-standard wireless technology is one of the hot spots in current research. This paper presents a wideband fractional-N frequency divider of the multi-standard wireless transceiver for many applications. High-speed divider-by-2 with traditional source-coupled-logic is designed for very wide band usage. Phase switching technique and a chain of divider-by-2/3 are applied to the programmable frequency divider with 0.5 step. The phase noise of the whole frequency synthesizer will be decreased by the narrower step of programmable frequency divider. Δ–Σ modulator is achieved by an improved MASH 1-1-1 structure. This structure has excellent performance in many ways, such as noise, spur and input dynamic range. Fabricated in TSMC 0.18μm CMOS process, the fractional-N frequency divider occupies a chip area of 1130 × 510 μm2 and it can correctly divide within the frequency range of 0.8–9 GHz. With 1.8 V supply voltage, its division ratio ranges from 62.5 to 254 and the total current consumption is 29 mA. -
References
[1] Brandolini M, Rossi P, Manstretta D, et al. Toward multistandard mobile terminals—fully integrated receivers requirements and architectures. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 2005, 53(3): 1026 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2005.843505[2] Shu K, Sánchez-Sinencio E. CMOS PLL synthesizers: analysis and design. Springer, 2005[3] Ed Callaway, Paul Gorday, Lance Hester, et al. A developing standard for low-rate wireless personal area networks. IEEE Commun Mag, 2002, 40(8): 70 doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2002.1024418[4] Jin J, Liu X, Qin P, et al. Quantization noise suppression in fractional-N PLLs utilizing glitch-free phase switching multi-modulus frequency divider. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst, 2012, 59(5): 926 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2012.2189042[5] Shu K, Sanchez-Sinencio E, Silva-Martinez J, et al. A 2.4-GHz monolithic fractional-N frequency synthesizer with robust phase-swtiching prescaler and loop capacitance multiplier. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(6): 866 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.811875[6] Singh U, Green M. Dynamics of high-frequency CMOS dividers. Circuits and Systems. ISCAS, 2002[7] Wang J F, Fan X N, Tang L, et al. A programmable frequency divider for multi-standard wireless receivers. 2014 6th International Conference on Mechanical and Electronics Engineering (ICMEE2014), 2014[8] Yang G, Yao W, Yin J W, et al. A 3.1–4.8 GHz CMOS receover for multi-band OFDM UWB system. J Semicond, 2009, 30: 015005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/30/1/015005[9] Jin J. Design and optimization of CMOS frequency synthesizer in Chinese. Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2012[10] Lu L, Gong Z, Liao Y, et al. A 975-to-1960 MHz, fast-locking fractional-N synthesizer with adaptive bandwidth control and 4/4.5 pre-scaler for digital TV tuners. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Conf (ISSCC) Dig Tech Papers, 2009: 396[11] Amin N M, Wang Z G, Li Z Q, et al. A low power, low noise figure quadrature demodulator for a 60 GHz receiver in 65-nm CMOS technology. J Semiconds, 2015, 36(4): 045005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/4/045005[12] Fitzgibbon B, Kennedy M P, Maloberti F. Hardware reduction in digital delta-sigma modulators via bus-splitting and error masking. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2012, 59(9): 1980 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2012.2185278[13] Yang Y C, Yu S A, Liu Y H, et al. A quantization noise suppression technique for Δ-Σ fractional-N frequency synthesizers. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2006, 41: 2500 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2006.883325[14] Liu L. Δ-Σ fractional-N frequency synthesizer for TD-LTE system. Xidian University, 2011[15] Liu F E, Wang Z G, Li Z Q, et al. A Ka-band wide locking range frequency divider with high injection sensitivity. J Semiconds, 2014, 35(3): 035002 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/3/035002[16] Zhang Y T, Li X P, Zhang M, et al. A 83 GHz InP DHBT static frequency divider. J Semiconds, 2014, 35(4): 045004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/045004[17] Sun Z, Xu Y, Ma G Y, et al. An improved fully integrated, high-speed, dual-modulus divider. J Semiconds, 2014, 35(11): 115005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/115005[18] Zhang J C, Zhang Y M, Lv H L, et al. A broadband regenerative frequency divider in InGaP/GaAs HBT technology. J Semiconds, 2014, 35(7): 075004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/7/075004 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: