| Citation: |
Daiguo Xu, Shiliu Xu, Xi Li, Jie Pu. A 10-bit 110 MHz SAR ADC with asynchronous trimming in 65-nm CMOS[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(4): 045003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/4/045003
****
D G Xu, S L Xu, X Li, J Pu. A 10-bit 110 MHz SAR ADC with asynchronous trimming in 65-nm CMOS[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(4): 045003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/4/045003.
|
A 10-bit 110 MHz SAR ADC with asynchronous trimming in 65-nm CMOS
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/4/045003
More Information
-
Abstract
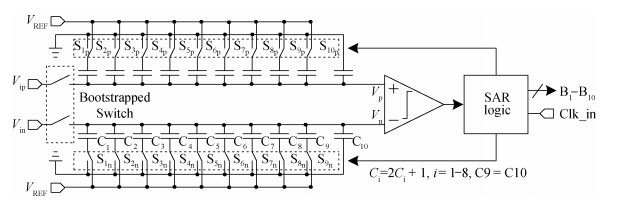
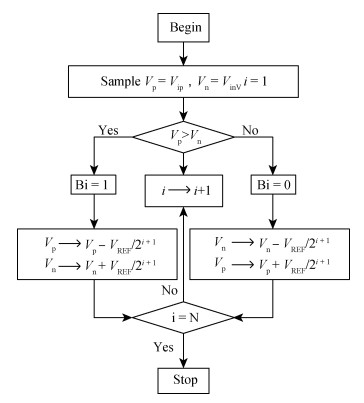
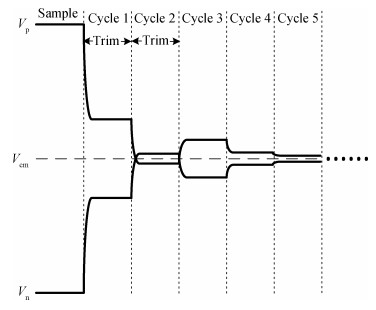
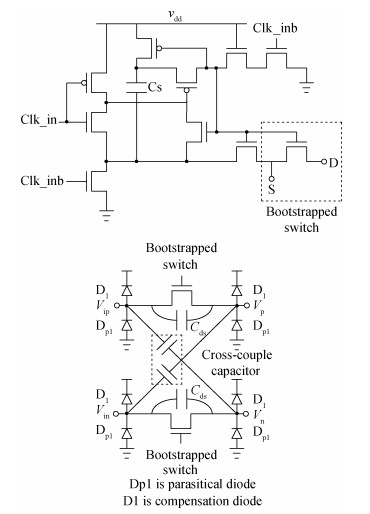
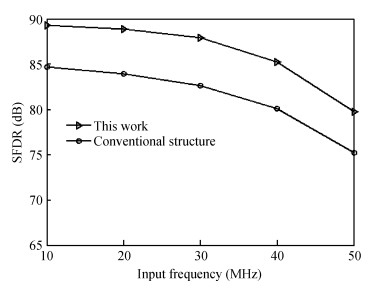
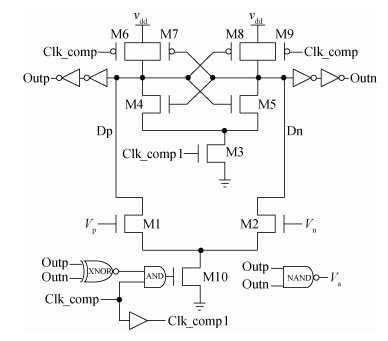
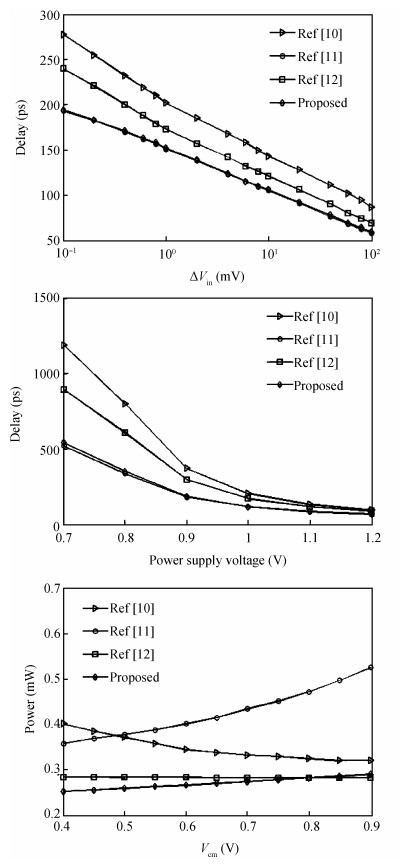
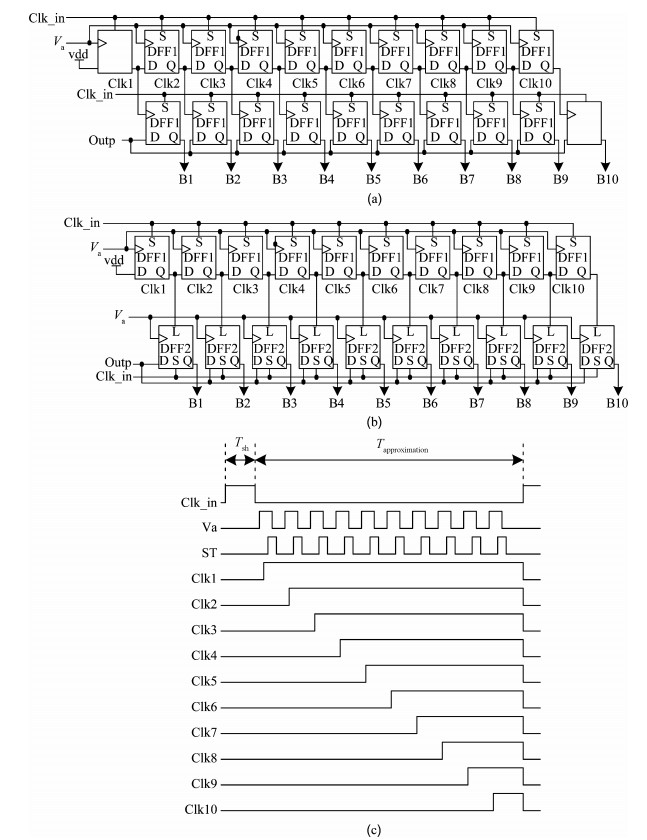
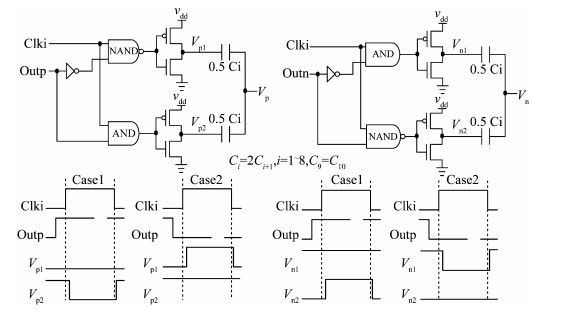
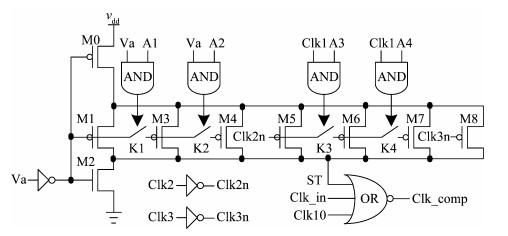
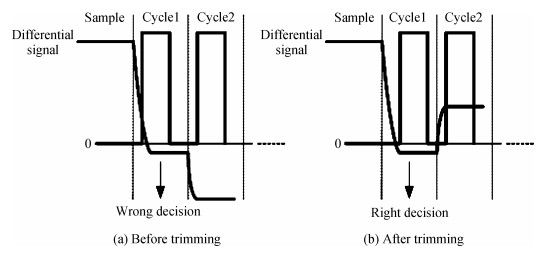
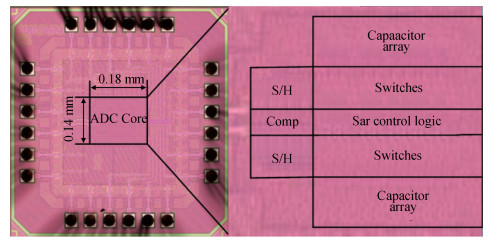
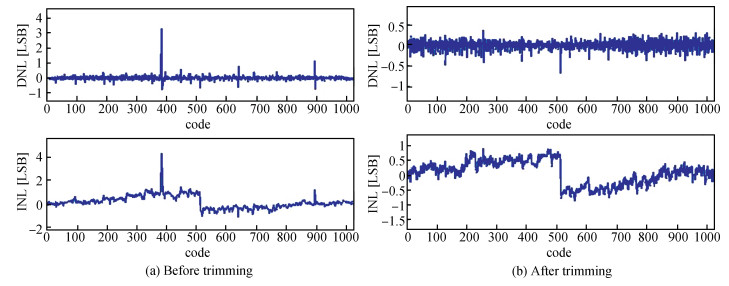
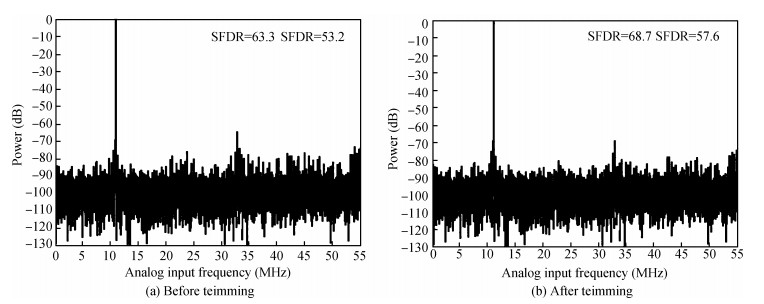
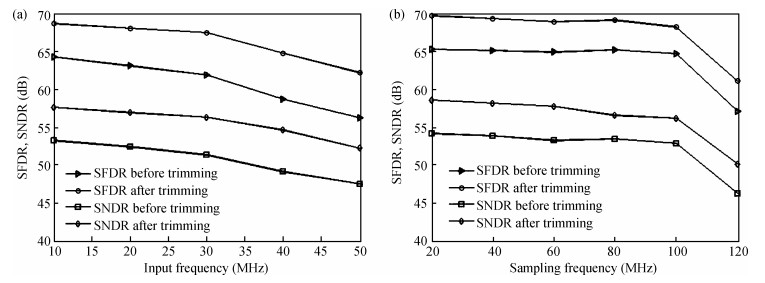
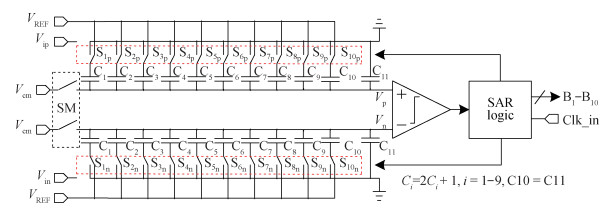
A 10-bit 110 MHz SAR ADC with asynchronous trimming is presented. In this paper, a high linearity sampling switch is used to produce a constant parasitical barrier capacitance which would not change with the range of input signals. As a result, the linearity of the SAR ADC will increase with high linearity sampled signals. Farther more, a high-speed and low-power dynamic comparator is proposed which would reduce the comparison time and save power consumption at the same time compared to existing technology. Additionally, the proposed comparator provides a better performance with the decreasing of power supply. Moreover, a highspeed successive approximation register is exhibited to speed up the conversion time and will reduce about 50% register delay. Lastly, an asynchronous trimming method is provided to make the capacitive-DAC settle up completely instead of using the redundant cycle which would prolong the whole conversion period. This SAR ADC is implemented in 65-nm CMOS technology the core occupies an active area of only 0.025 mm2 and consumes 1.8 mW. The SAR ADC achieves SFDR > 68 dB and SNDR > 57 dB, resulting in the FOM of 28 fJ/conversion-step. From the test results, the presented SAR ADC provides a better FOM compared to previous research and is suitable for a kind of ADC IP in the design SOC. -
References
[1] Kuttner F. A 1.2-V 10-b 20-Msample/s nonbinary successive approximation ADC in 0.13-μm CMOS. ISSCC, 2002: 176[2] Craninckx J, Van der Plas G. A 65 fJ/conversion-step 0-to-50 MS/s 0-to-0.7 mW 9b charge-sharing SAR ADC in 90 nm digital CMOS. ISSCC, 2007: 246 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/4255259_A_65fJconversion-step_0-to-50MSs_0-to-07mW_9b_charge-sharing_SAR_ADC_in_90nm_digital_CMOS[3] Giannini V, Nuzzo P, Chironi V, et al. An 820 μW 9b 40 MS/s noise-tolerant dynamic-SAR ADC in 90 nm digital CMOS. ISSCC, 2008: 238[4] Liu C C, Chang S J, Huang G Y, et al. A 0. 92 mW 10-bit 50-MS/s SAR ADC in 0. 13 μm CMOS process. Symp on VLSI Circuits, 2009: 236[5] Xiang J X, Chen C X, Ye F, et al. A 6-b 600 MS/s SAR ADC with a new switching procedure of 2-b/stage and self-locking comparators. J Semicond, 2015, 36(5): 055009 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/5/055009[6] Lee S, Chandrakasan A P, Lee H S. A 1 GS/s 10 b 18.9 mW time-interleaved SAR ADC with background timing skew calibration. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2014, 49(12): 2846 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2014.2362851[7] Cho S H, Lee C K, Kwon J K. A 550-μW 10 b-40 MS/s SAR ADC with multistep addition-only digital error correction. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(8): 1881 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2151450[8] Yoshioka M, Ishikawa K, Takayama T, et al. A 10 b 50 MS/s 820 μW SAR ADC with on-chip digital calibration. International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2010: 384[9] Liu C C, Chang S J, Huang G Y. A10-b 50-MS/s SAR ADC with a monotonic capacitor switching procedure. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(4): 731 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2042254[10] Chan C H, Zhu Y, Chio U F, et al. A reconfigurable low-noise dynamic comparator with offset calibration in 90 nm CMOS. IEEE A-SSCC, 2011: 233 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/254033850_A_reconfigurable_low-noise_dynamic_comparator_with_offset_calibration_in_90nm_CMOS[11] Abbas M, Furukawa Y, Komatsu S, et al. Clocked comparator for high-speed applications in 65 nm technology. IEEE A-SSCC, 2010: 1 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224220030_Clocked_Comparator_for_High-Speed_Applications_in_65nm_Technology[12] Gao J F, Li G J, Li Q. High-speed low-power common-mode insensitive dynamic comparator. Electron Lett, 2015, 51(2): 134 doi: 10.1049/el.2014.3272[13] Liu W, Wei T C, Li B, et al. A reference voltage in capacitor-resister hybrid SAR ADC for front-end readout system of CZT detector. J Semicond, 2016, 37(1): 015005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/1/015005[14] Wang Y, Xue C Y, Li F L, et al. A low power 11-bit 100 MS/s SAR ADC IP. J Semicond, 2015, 36(2): 025003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/2/025003[15] Morie T, Miki T, Matsukawa K, et al. A 71dB SNDR 50MS/s 4.2mW CMOS SAR ADC by SNR enhancement techniques utilizing noise. Proc IEEE ISSCC, 2013: 273 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261197890_A_71dB-SNDR_50MSs_42mW_CMOS_SAR_ADC_by_SNR_enhancement_techniques_utilizing_noise[16] Yu M Y, Li T, Yang J Q, et al. A 1 V 186-μW 50-MS/s 10-bit subrange SAR ADC in 130-nm CMOS process. J Semicond, 2016, 37(7): 075005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/7/075005[17] Huang G Y, Chang S J, Liu C C, et al. 10-bit 30 MS/s SAR ADC using a switchback switching method. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr (VLSI) Syst, 2013, 21(3): 584 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2012.2190117[18] Lin Y Z, Liu C C, Huang G Y, et al. A 9-bit 150-MS/s subrange ADC based on SAR architecture in 90-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2013, 60(3): 570 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2012.2215756[19] Li D, Meng Q, Li F. A 10 bit 50 MS/s SAR ADC with partial split capacitor switching scheme in 0.18 μm CMOS. J Semicond, 2016, 37(1): 015004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/1/015004[20] Wong S S, Chio U F, Zhu Y, et al. A 2.3 mW 10-bit 170 MS/s two-step binary-search assisted time-interleaved SAR ADC. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2013, 48(8): 1783 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2013.2258832 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: