| Citation: |
Hassiba Rahal, Rafiaa Kihal, Abed Mohamed Affoune, Mokhtar Ghers, Faycal Djazi. Electrodeposition and characterization of ZnO thin films using sodium thiosulfate as an additive for photovoltaic solar cells[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(5): 053002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/5/053002
****
H Rahal, R Kihal, A M Affoune, M Ghers, F Djazi. Electrodeposition and characterization of ZnO thin films using sodium thiosulfate as an additive for photovoltaic solar cells[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(5): 053002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/5/053002.
|
Electrodeposition and characterization of ZnO thin films using sodium thiosulfate as an additive for photovoltaic solar cells
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/5/053002
More Information
-
Abstract
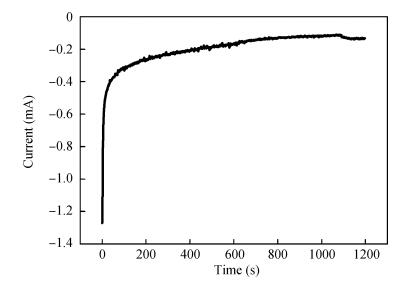
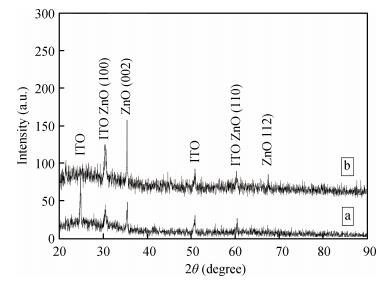
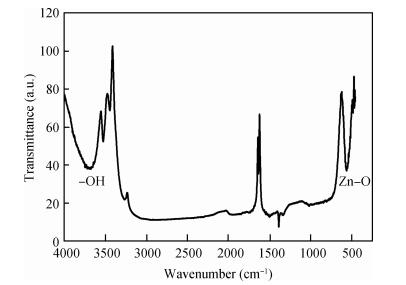
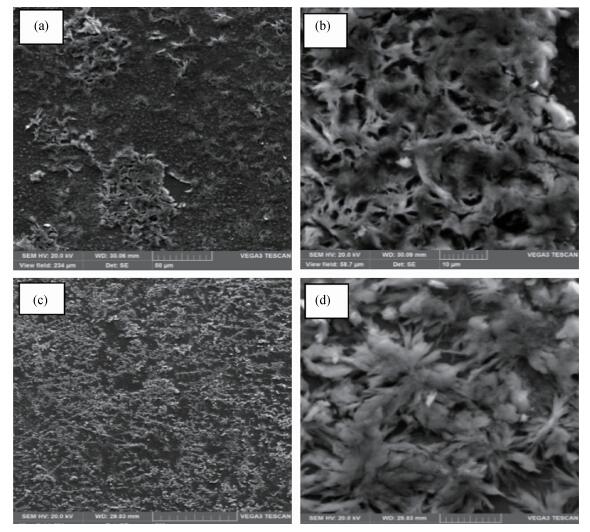
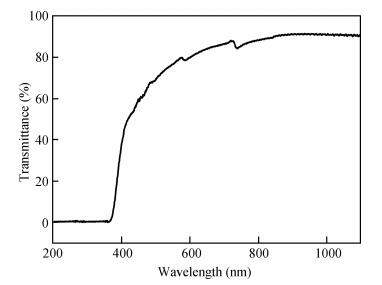
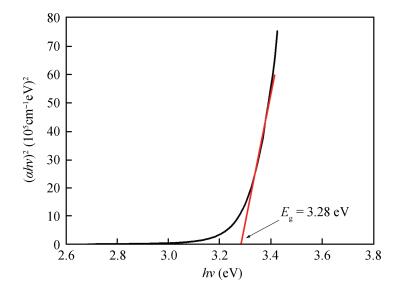
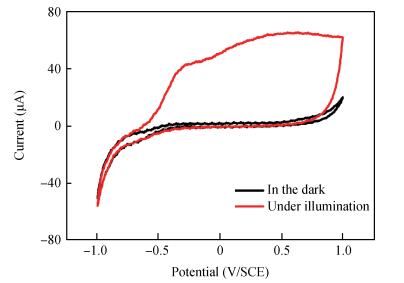
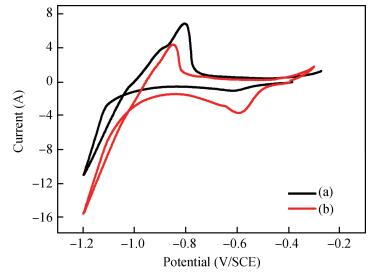
Zinc oxide thin films have been grown by electrodeposition technique onto Cu and ITO-coated glass substrates from an aqueous zinc nitrate solution with addition of sodium thiosulfate at 90℃.The effects of sodium thiosulfate on the electrochemical deposition of ZnO were investigated by cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry techniques.Deposited films were obtained at-0:60 V vs.SCE and characterized by XRD, SEM, FTIR, optical, photoelectrochemical and electrical measurements.Thickness of the deposited film was measured to be 357 nm.X-ray diffraction results indicated that the synthesized ZnO has a pure hexagonal wurtzite structure with a marked preferential orientation along (002) plane.FTIR results confirmed the presence of ZnO films at peak 558 cm-1.SEM images showed uniform, compact morphology without any cracks and films composed of large flower-like ZnO agglomerates with star-shape.Optical properties of ZnO reveal a high optical transmission (>80%) and high absorption coefficient (α>105 cm-1) in visible region.The optical energy band gap was found to be 3.28 eV.Photoelectrochemical measurements indicated that the ZnO films had n-type semiconductor conduction.Electrical properties of ZnO films showed a low electrical resistivity of 6.54 Ω·cm, carrier concentration of-1.3×1017cm-3 and mobility of 7.35 cm2V-1s-1. -
References
[1] Pawar B S, Pawar S M, Shin S W, et al. Effect of complexing agent on the properties of electrochemically deposited Cu2ZnSnS4(CZTS) thin films. Appl Surf Sci, 2010, 257: 1786 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.09.016[2] Arico A S, Silvestro D, Antonucci P L, et al. Electrodeposited thin film ZnTe semiconductors for photovoltaic applications. Adv Perform Mater, 1997, 4: 115 doi: 10.1023/A:1008632602023[3] Sahal M, Hartiti B, Ridah A, et al. Structural, electrical and optical properties of ZnO thin films deposited by sol-gel method. Microelectron J, 2008, 39: 1425 doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2008.06.085[4] Okazaki K, Kubo K, Shimogaki T, et al. Lasing characteristics of ZnO nanosheet excited by ultraviolet laser beam. Adv Mater Lett, 2011, 2(5): 354 doi: 10.5185/amlett[5] Singh S, Chakrabarti P. Comparison of the structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films deposited by three different methods for optoelectronic applications. Superlattices Microstruct, 2013, 64: 283 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2013.09.031[6] Li Y Y, Li Y X, Wu Y L, et al. Preparation and photoluminescent properties of zinc oxide phosphor. J Lumin, 2007, 126: 177 doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2006.06.012[7] Wang X, Ding Y, Li Z, et al. Single-crystal mesoporous ZnO thin films composed of nanowalls. Phys Chem, 2009, 113(5): 1791 http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.332.8214[8] Dunkel C, Graberg T, Smarsly B M, et al. Limits of ZnO electrodeposition in mesoporous tin doped indium oxide films in view of application in dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater, 2014, 7: 3291 doi: 10.3390/ma7043291[9] Shimogaki T, Takahashi M, Yamasaki M, et al. Catalyst-free growth of ZnO nanowires on various-oriented sapphire substrates by pulsed-laser deposition. J Semicond, 2016, 37(2): 1 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDTX201602005.htm[10] Khan Z R, Khan M S, Zulfequar M, et al. Optical and structural properties of ZnO thin films fabricated by sol-gel method. Mater Sci Appl, 2011, 2: 340 http://www.scirp.org/journal/papercitationdetails.aspx?PaperID=4774&JournalID=174[11] Azuma M, Ichimura M. Fabrication of ZnO thin films by the photochemical deposition method. Mate Res Bull, 2008, 43: 3537 doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2008.01.014[12] Sharma S K, Rammohan A, Sharma A. Templated one step electrodeposition of high aspect ratio n-type ZnO nanowire arrays. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2010, 344: 1 doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2009.12.026[13] Kou H, Zhang X, Du Y, et al. Electrochemical synthesis of ZnO nanoflowers and nanosheets on porous Si as photoelectric materials. Appl Surf Sci, 2011, 257: 4643 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.12.108[14] Qin X J, Shao G J, Lin Z. The effect of surfactant on the structure and properties of ZnO films prepared by electrodeposition. Mater Sci Eng, B, 2012, 177: 1678 doi: 10.1016/j.mseb.2012.08.012[15] Yıldırımand A K, Altıokka B. Effect of potential on structural, morphological and optical properties of ZnO thin films obtained by electrodeposition. Mater Sci Eng B, 2015, 120: 107 http://davidpublisher.org/Public/uploads/Contribute/55af5454a5933.pdf[16] Wijesundera R P, Hidaka M, Koga K, et al. Growth and characterisation of potentiostatically electrodeposited Cu2O and Cu thin films. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 500: 241 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2005.11.023[17] Yoshida T, Komatsu D, Shimokawa N, et al. Mechanism of cathodic electrodeposition of zinc oxide thin films from aqueous zinc nitrate baths. Thin Solid Films, 2004, 451: 166 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222841633_Mechanism_of_cathodic_electrodeposition_of_zinc_oxide_thin_films_from_aqueous_zinc_nitrate_baths[18] Wellings J S, Chaure N B, Heavens S N, et al. Growth and characterization of electrodeposited ZnO thin films. Thin Solid Films, 2008, 516: 3893 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2007.07.156[19] Enculescu I, Matei E, Sima M, et al. Influence of polyvinylpyrolidone as an additive in electrochemical preparation of ZnO nanowires and nanostructured thin films. Surf and Interface Anal, 2008, 40: 556 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9918[20] Whang T, Hsieh M, Tsai J. Lactic acid aided electrochemical deposition of c-axis preferred orientation of zinc oxide thin films: Structural and morphological features. Appl Surf Sci, 2011, 257: 9539 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.06.058[21] Fathy N, Ichimura M. Electrochemical deposition of ZnO thin films from acidic solutions. J Cryst Growth, 2006, 294: 191 doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2006.07.008[22] Pauporte Th, Lincot D. Hydrogen peroxide oxygen precursor for zinc oxide electrodeposition Ⅱ-mechanistic aspects. J Electroanal Chem, 2001, 517: 54 doi: 10.1016/S0022-0728(01)00674-X[23] Li G, Dawa C, Bu Q, et al. Electrochemical self-assembly of ZnO nanoporous structures. J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111: 1919 doi: 10.1021/jp066447x[24] Li G, Dawa C, Bu Q, et al. Electrochemical synthesis of orientation-ordered ZnO nanorod bundles. Electrochem Commun, 2007, 9: 863 doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2006.11.029[25] Inamdar A I, Sonavane A C, Sharma S K, et al. Nanocrystalline zinc oxide thin films by novel double pulse single step electro-deposition. J Alloys Compd, 2010, 495: 76 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.01.090[26] Inamdar A I, Mujawar S H, Patil P S. The influences of complexing agents on growth of zinc oxide thin films from zinc acetate bath and associated kinetic parameters. Int J Electrochem Sci, 2007, 2: 797 https://www.researchgate.net/profile/P_Patil/publication/26500104_The_Influences_of_Complexing_agents_on_Growth_of_Zinc_Oxide_Thin_Films_from_Zinc_Acetate_Bath_and_Associated_Kinetic_Parameters/links/02bfe50d017f91d328000000.pdf?origin=publication_detail[27] Wei S, Lian J, Chen X. Effects of seed layer on the structure and property of zinc oxide thin films electrochemically deposited on ITO-coated glass. Appl Surf Sci, 2008, 254: 6605 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.04.039[28] Zhang L, Chen Z, Tang Y. Low temperature cathodic electrodeposition of nanocrystalline zinc oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films, 2005, 492: 24 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2005.06.028[29] El Hichou A, Stein N, Boulanger C. Structural and spectroscopic ellipsometry characterization for electrodeposited ZnO growth at different hydrogen peroxide concentration. Thin Solid Films, 2010, 518: 4150 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2009.11.070[30] Laurent K, Wang B Q, Yu D P, et al. Structural and optical properties of electrodeposited ZnO thin films. Thin Solid Films, 2008, 517: 617 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2008.07.013[31] Gao X, Peng F, Li X, et al. Growth of highly oriented ZnO films by the two-step electrodeposition technique. J Mater Sci, 2007, 42: 9638 doi: 10.1007/s10853-007-1970-6[32] Abdel Haleem A M, Ichimura M. Electrochemical deposition of aluminum oxide thin films from aqueous baths. Mater Lett, 2014, 130: 26 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.05.061[33] Chatman Sh, Ryan B J, Poduska K M. Selective formation of Ohmic junctions and Schottky barriers with electrodeposited ZnO. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92: 1 http://core.ac.uk/display/19524501[34] Ibrahim M A M, Al Radadi R M. Role of Glycine as a complexing agent in nickel electrodeposition from acidic sulphate bath. Int J Electrochem Sci, 2015, 10: 4946 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/282159156_Role_of_Glycine_as_a_Complexing_Agent_in_Nickel_Electrodeposition_from_Acidic_Sulphate_Bath[35] Sulciute A, Valatka E. Electrodeposition photoelectrocatalytic activity of ZnO films on AISI 304 type steel. Mater Sci, 2012, 18(4): 318 http://www.oalib.com/paper/2315788[36] Ali M M. Characterization of ZnO thin films grown by chemical bath deposition. J Basra Res Sci, 2011, 37(3): 49 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268201364_Characterization_of_ZnO_thin_films_grown_by_chemical_bath_deposition[37] Thool G Sh, Singh A K, Singh R S, et al. Facile synthesis of flat crystal ZnO thin films by solution growth method: a microstructural investigation. J Saudi Chem Soc, 2014, 18: 712 doi: 10.1016/j.jscs.2014.02.005[38] Ismail A, Abdullah M J. The structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared at different RF sputtering power. J King Saud Univ Sci, 2013, 25: 209 doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2012.12.004[39] Klink M J, Crouch A M. Preparation of low temperature nanostructured ZnO and RhO2 on titanium substrates, and evaluation for phenol electro-catalytic oxidation. Microchim Acta, 2009, 166: 27 doi: 10.1007/s00604-009-0157-z[40] Pathak T K, Kumar R, Purohit L P. Preparation and optical properties of undoped and nitrogen doped ZnO thin films by RF sputtering. Int J Chem Tech Res, 2015, 7(2): 987 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281401796_Preparation_and_Optical_properties_of_undoped_and_Nitrogen_doped_ZnO_thin_films_by_RF_sputtering[41] Baviskar P K, Tan W, Zhang J, et al. Wet chemical synthesis of ZnO thin films and sensitization to light with N3 dye for solar cell application. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2009, 42: 1[42] Foo K L, Kashif M, Hashim U, et al. Effect of different solvents on the structural and optical properties of zinc oxide thin films for optoelectronic applications. Ceram Int, 2014, 40: 753 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.06.065[43] Chettah H, Abdi D. Effect of the electrochemical technique on nanocrysatlline ZnO electrodeposition, its structural, morphological and photoelectrochemical properties. Thin Solid Films, 2013, 537: 119 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.04.024[44] Chen L, Hsieh C, Zhang X. Electrical properties of CZO films prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Mater, 2014, 7: 7304 doi: 10.3390/ma7117304 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: