| Citation: |
Meixin Feng, Qian Sun, Jianping Liu, Zengcheng Li, Yu Zhou, Hongwei Gao, Shuming Zhang, Hui Yang. Al-free cladding-layer blue laser diodes with a low aspect ratio in far-field beam pattern[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2018, 39(8): 084004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/8/084004
****
M X Feng, Q Sun, J P Liu, Z C Li, Y Zhou, H W Gao, S M Zhang, H Yang, Al-free cladding-layer blue laser diodes with a low aspect ratio in far-field beam pattern[J]. J. Semicond., 2018, 39(8): 084004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/8/084004.
|
Al-free cladding-layer blue laser diodes with a low aspect ratio in far-field beam pattern
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/8/084004
More Information
-
Abstract
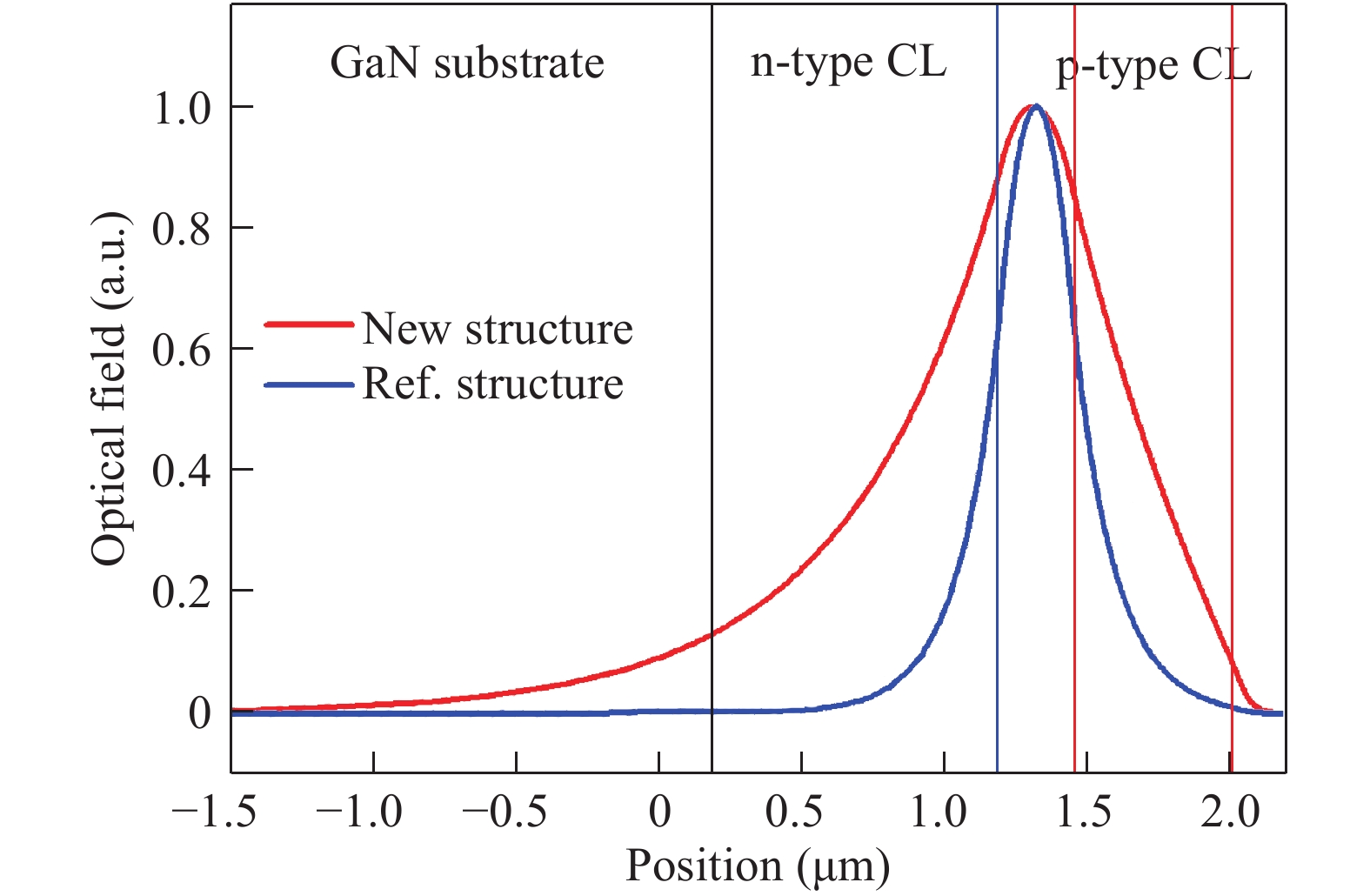
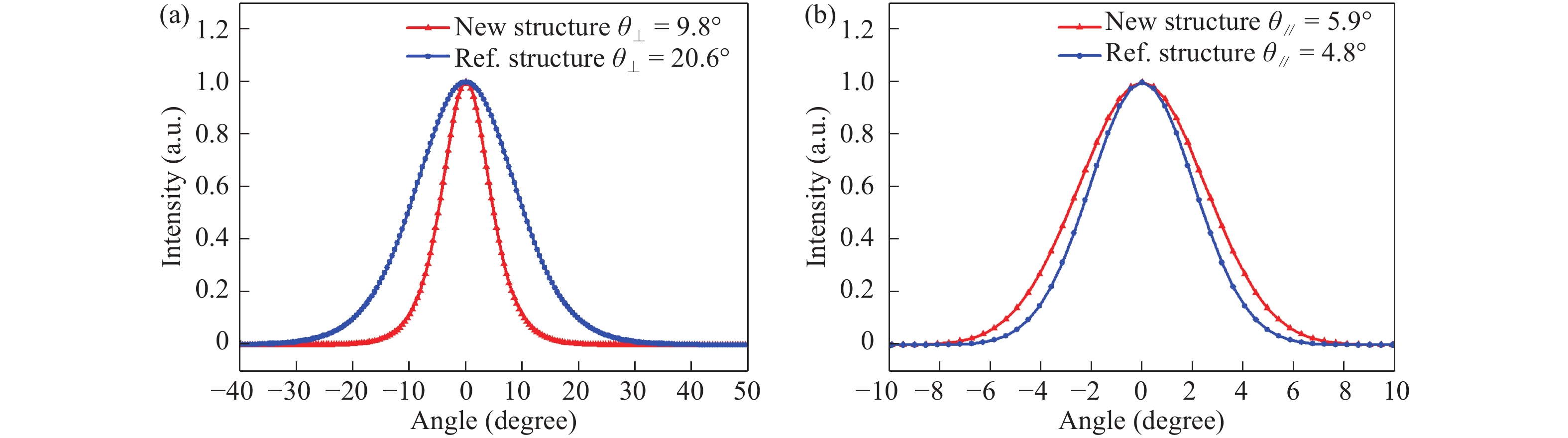
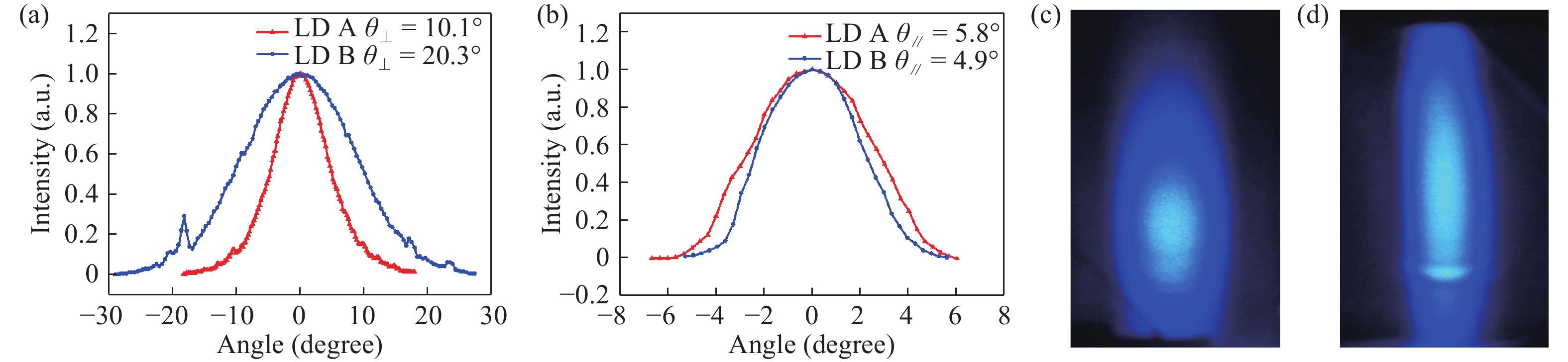
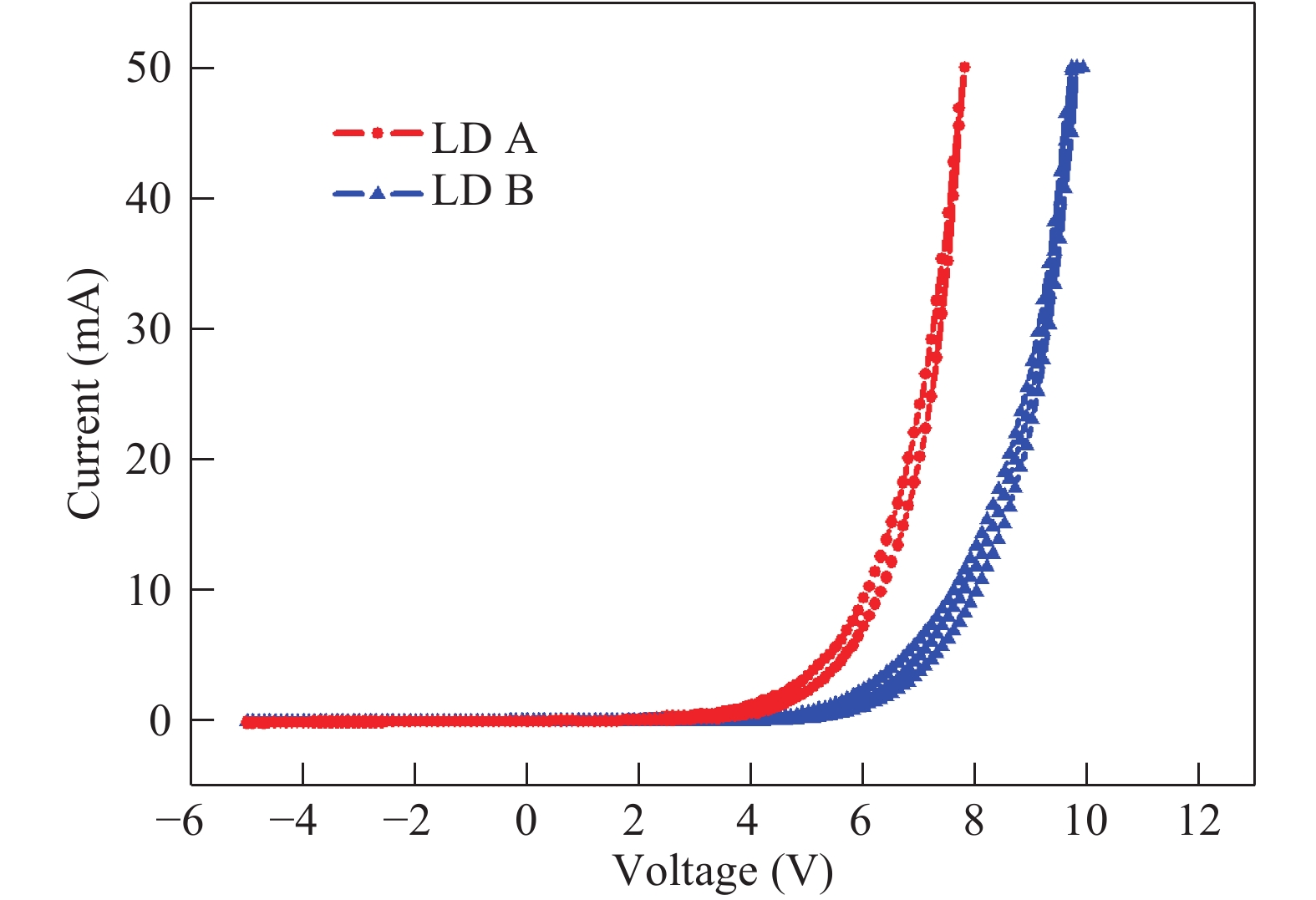
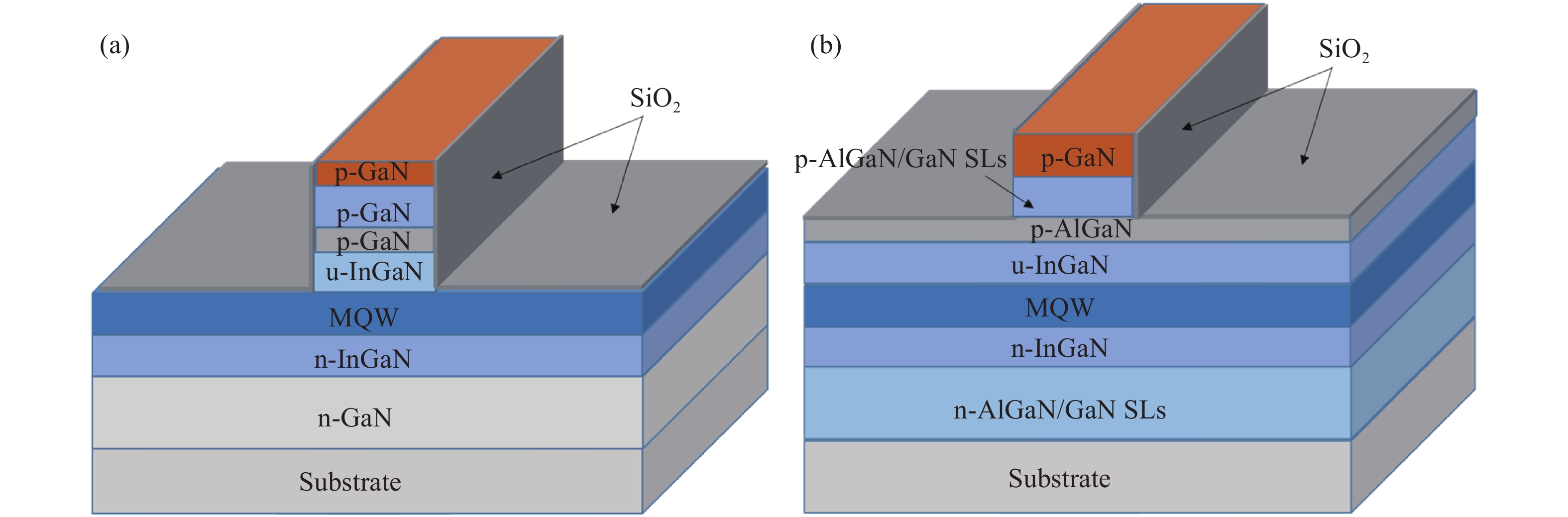
c-plane GaN-based blue laser diodes (LDs) were fabricated with Al-free cladding layers (CLs) and deepened etching depth of mesa structure, so the aspect ratio of the far-field pattern (FFP) of the laser beam can be reduced to as low as 1.7, which is nearly the same as conventional AlGaInP-based red LDs. By using GaN CLs, the radiation angle of the laser beam θ⊥ is only 10.1° in the direction perpendicular to the junction plane. After forming a deeply etched mesa, the beam divergence angle parallel to the junction plane of FFP, θ//, increases from 4.9° to 5.8°. After using the modified structure, the operation voltage of LD is effectively reduced by 2 V at an injection current of 50 mA, but the threshold current value increases. The etching damage may be one of the main reasons responsible for the increase of the threshold current. -
References
[1] Nakamura S, Senoh M, Nagahama S, et al. InGaN-based multi-quantum-well-structure laser diodes. Jpn J Appl Phys, 1996, 35: L74 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.35.L74[2] Nakamura S, Senoh M, Nagahama S, et al. High-power, long-lifetime InGaN/GaN/AlGaN based laser diodes grown on pure GaN substrates. Jpn J Appl Phys, 1998, 37: L309 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.37.L309[3] Kawaguchi M, Imafuji O, Nozaki S, et al. Optical-loss suppressed InGaN laser diodes using undoped thick waveguide structure. Proc SPIE, 2016, 9748: 974818 doi: 10.1117/12.2212011[4] Asano T, Takeya M, Tojyo T, et al. High-power 400-nm-band AlGaInN-based laser diodes with low aspect ratio. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 80: 3497 doi: 10.1063/1.1478157[5] Asano T, Tojyo T, Mizuno T, et al. 100-mW kink-free blue-violet laser diodes with low aspect ratio. IEEE J Quantum Electr, 2003, 39: 135 doi: 10.1109/JQE.2002.806213[6] Ito S, Yamasaki Y, Omi S, et al. AlGaInN violet laser diodes grown on GaN substrates with low aspect ratio. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2004, 43: 96 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.43.96[7] Tojyo T, Asano T, Takeya M, et al. GaN-based high power blue-violet laser diodes. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2001, 40: 3206 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.40.3206[8] Hiroyama R, Inoue D, Nomura Y, et al. High-power 660-nm-band algainp laser diodes with a small aspect ratio for beam divergence. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2002, 41: 1154 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.41.1154[9] Ryu H Y, Ha K H, Lee S N, et al. High-performance blue InGaN laser diodes with single-quantum-well active layers. IEEE Photonic Tech L, 2007, 19: 1717 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2007.905215[10] Braun H, Lauterbach C, Schwarz U T, et al. Experimental and theoretical study of substrate modes in (Al,In)GaN laser diodes. Phys Status Solidi C, 2007, 4: 2772 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1610-1642[11] Laino V, Roemer F, Witzigmann B, et al. Substrate modes of (Al,In)GaN semiconductor laser diodes on SiC and GaN substrates. IEEE J Quantum Electr, 2007, 43: 16 doi: 10.1109/JQE.2006.884769[12] Lermer T, Schillgalies M, Breidenassel A, et al. Waveguide design of green InGaN laser diodes. Phys Status Solidi A, 2010, 207: 1328 doi: 10.1002/pssa.200983410[13] Feezell D F, Schmidt M C, Farrell R M, et al. AlGaN-cladding-free nonpolar InGaN/GaN laser diodes. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2007, 46: L284 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.46.L284[14] Farrell R M, Hsu P S, Haeger D A, et al. Low-threshold-current-density AlGaN-cladding-free m-plane InGaN/GaN laser diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96: 2311132[15] Pourhashemi A, Farrell R M, Hardy M T, et al. Pulsed high-power AlGaN-cladding-free blue laser diodes on semipolar (20-21) GaN substrates. Appl Phys Lett, 2013, 103: 151112 doi: 10.1063/1.4824773[16] Tyagi A, Farrell R M, Kelchner K M, et al. AlGaN-cladding free green semipolar GaN based laser diode with a lasing wavelength of 506.4 nm. Appl Phys Express, 2010, 3: 011002 doi: 10.1143/APEX.3.011002[17] Feng M X, Liu J P, Zhang S M, et al. Design considerations for GaN-based blue laser diodes with InGaN upper waveguide layer. IEEE J Sel Topics Quantum Electron, 2013, 19: 1500705 doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2012.2237015[18] Feng M X, Liu J P, Zhang S M, et al. High efficient GaN-based laser diodes with tunnel junction. Appl Phys Lett, 2013, 103: 043508 doi: 10.1063/1.4816598[19] Redaelli L, Martens M, Piprek J, et al. Effect of ridge waveguide etch depth on laser threshold of InGaN MQW laser diodes. Proc SPIE, 2012, 8262: 826219[20] Sizov D S, Bhat R, Heberle A, et al. Internal optical waveguide loss and p-type absorption in blue and green InGaN quantum well laser diodes. Appl Phys Express, 2010, 3: 122104 doi: 10.1143/APEX.3.122104[21] Huang C Y, Lin Y D, Tyagi A, et al. Optical waveguide simulations for the optimization of InGaN-based green laser diodes. J Appl Phys, 2010, 107: 023101 doi: 10.1063/1.3275325[22] Ladroue J, Meritan A, Boufnichel M, et al. Deep GaN etching by inductively coupled plasma and induced surface defects. J Vac Sci Technol A, 2010, 28: 1226 doi: 10.1116/1.3478674[23] Qiu R, Lu H, Chen D, et al. Optimization of inductively coupled plasma deep etching of GaN and etching damage analysis. Appl Surf Sci, 2011, 257: 2700 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.048 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: