| Citation: |
Kaixuan Chen, Gengxin Chen, Ziliang Ruan, Xuancong Fan, Junwei Zhang, Ranfeng Gan, Jie Liu, Daoxin Dai, Changjian Guo, Liu Liu. Four-channel CWDM transmitter chip based on thin-film lithium niobate platform[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2022, 43(11): 112301. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/11/112301
****
K X Chen, G X Chen, Z L Ruan, X C Fan, J W Zhang, R F Gan, J Liu, D X Dai, C J Guo, L Liu. Four-channel CWDM transmitter chip based on thin-film lithium niobate platform[J]. J. Semicond, 2022, 43(11): 112301. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/11/112301
|
Four-channel CWDM transmitter chip based on thin-film lithium niobate platform
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/11/112301
More Information
-
Abstract
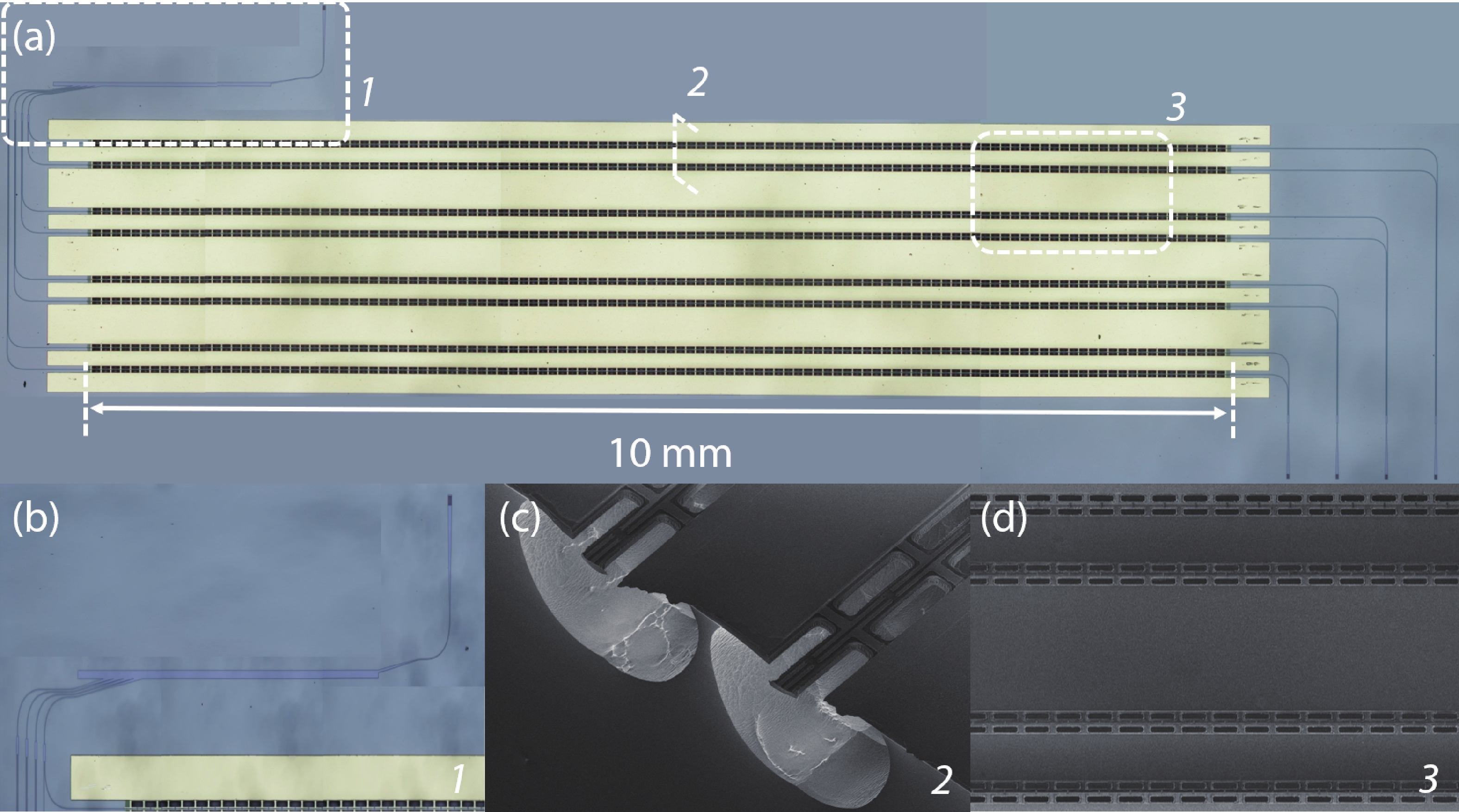
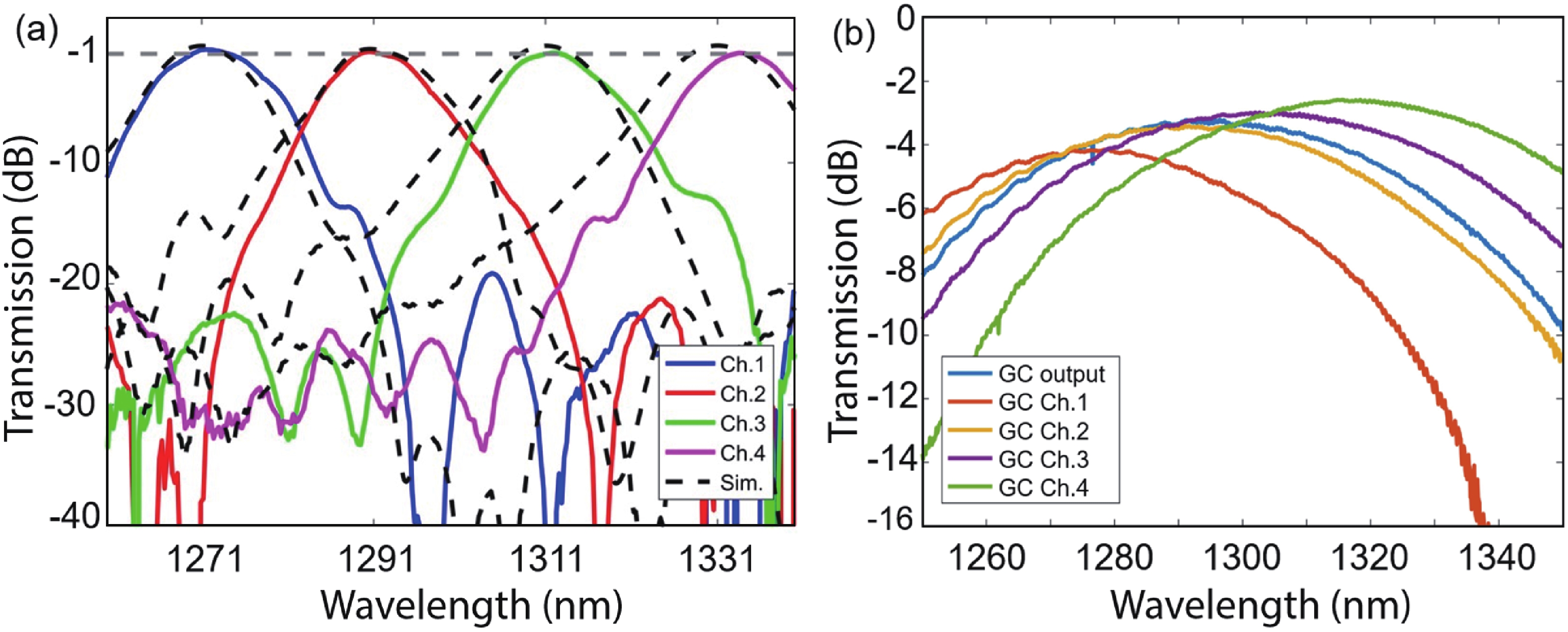
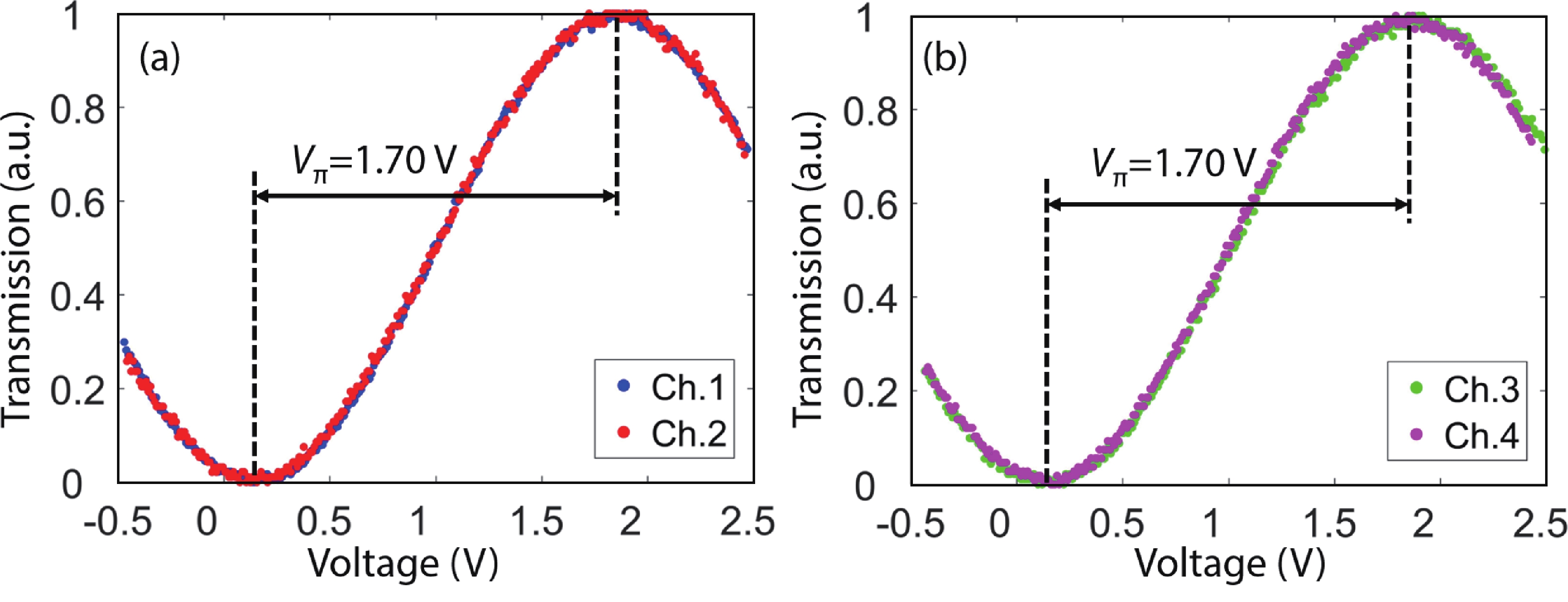
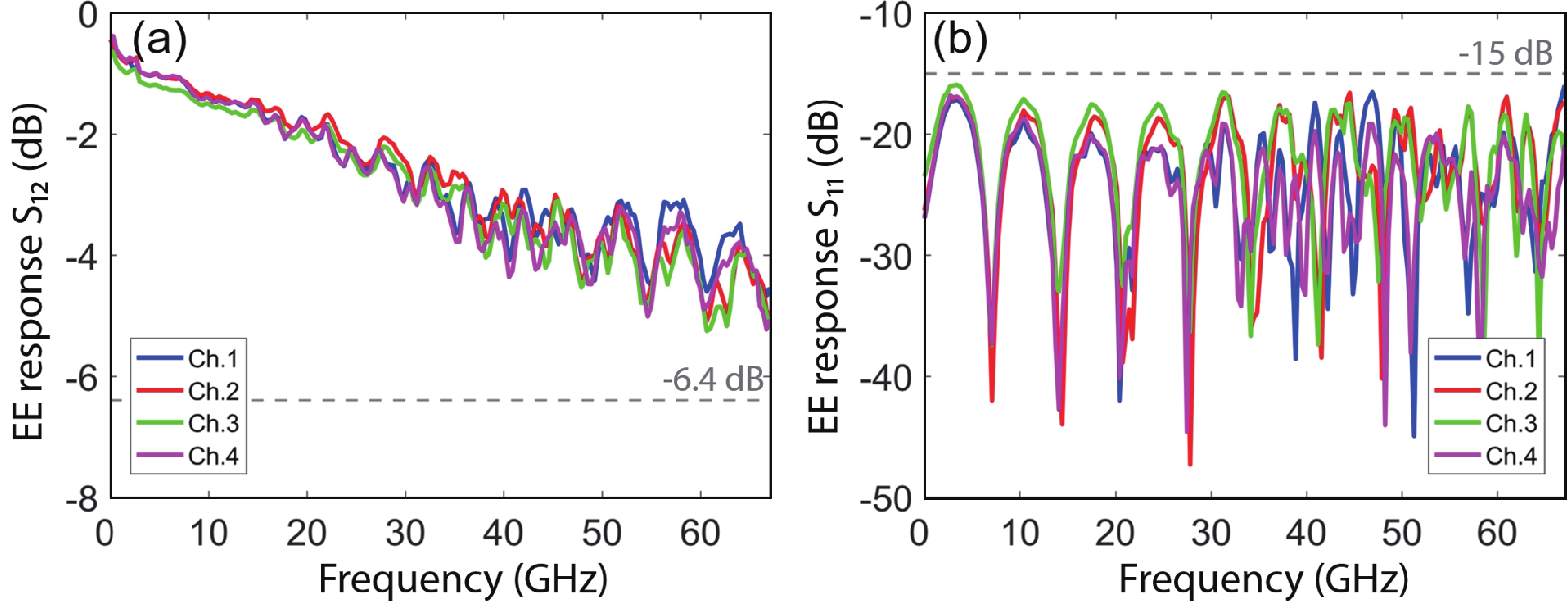
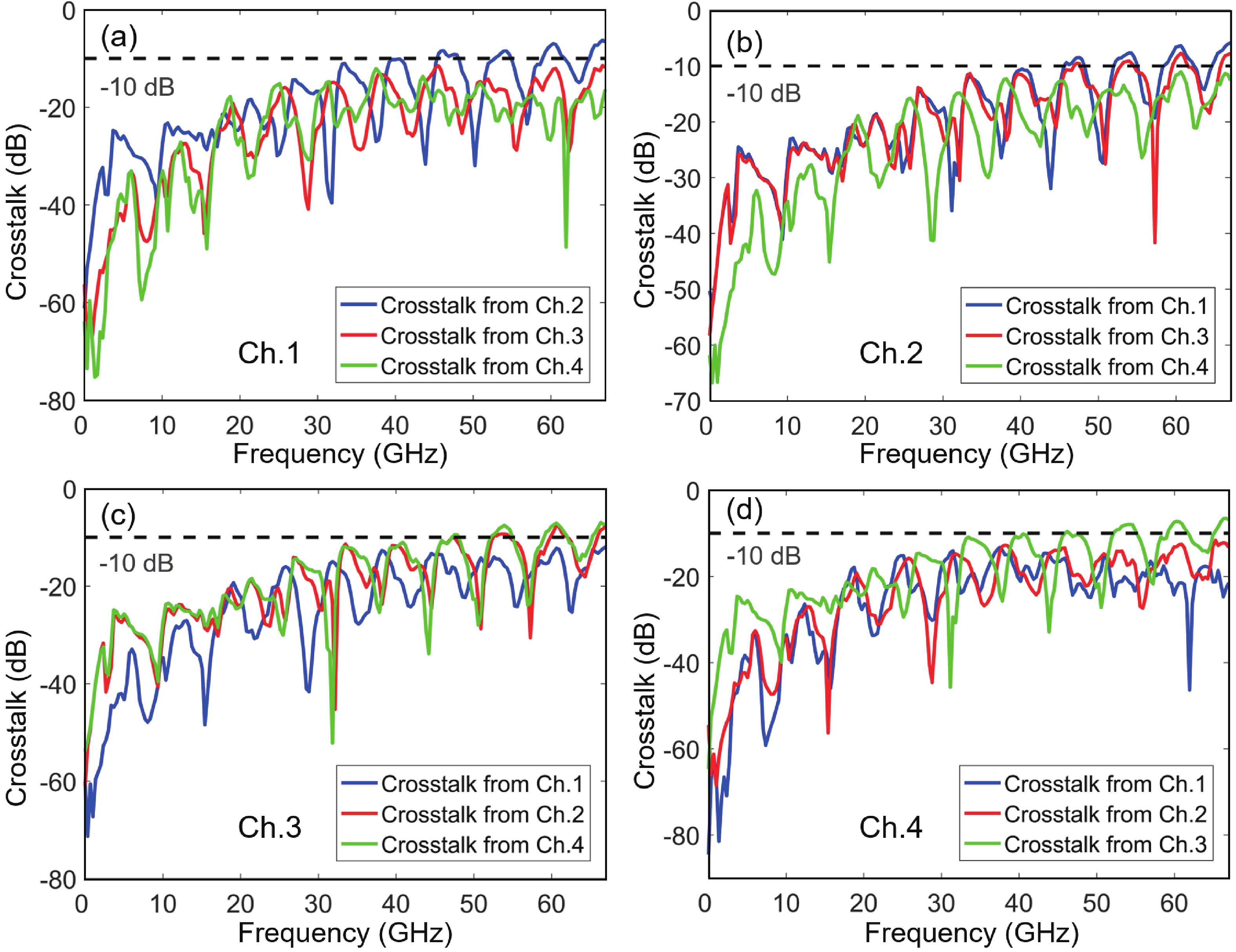
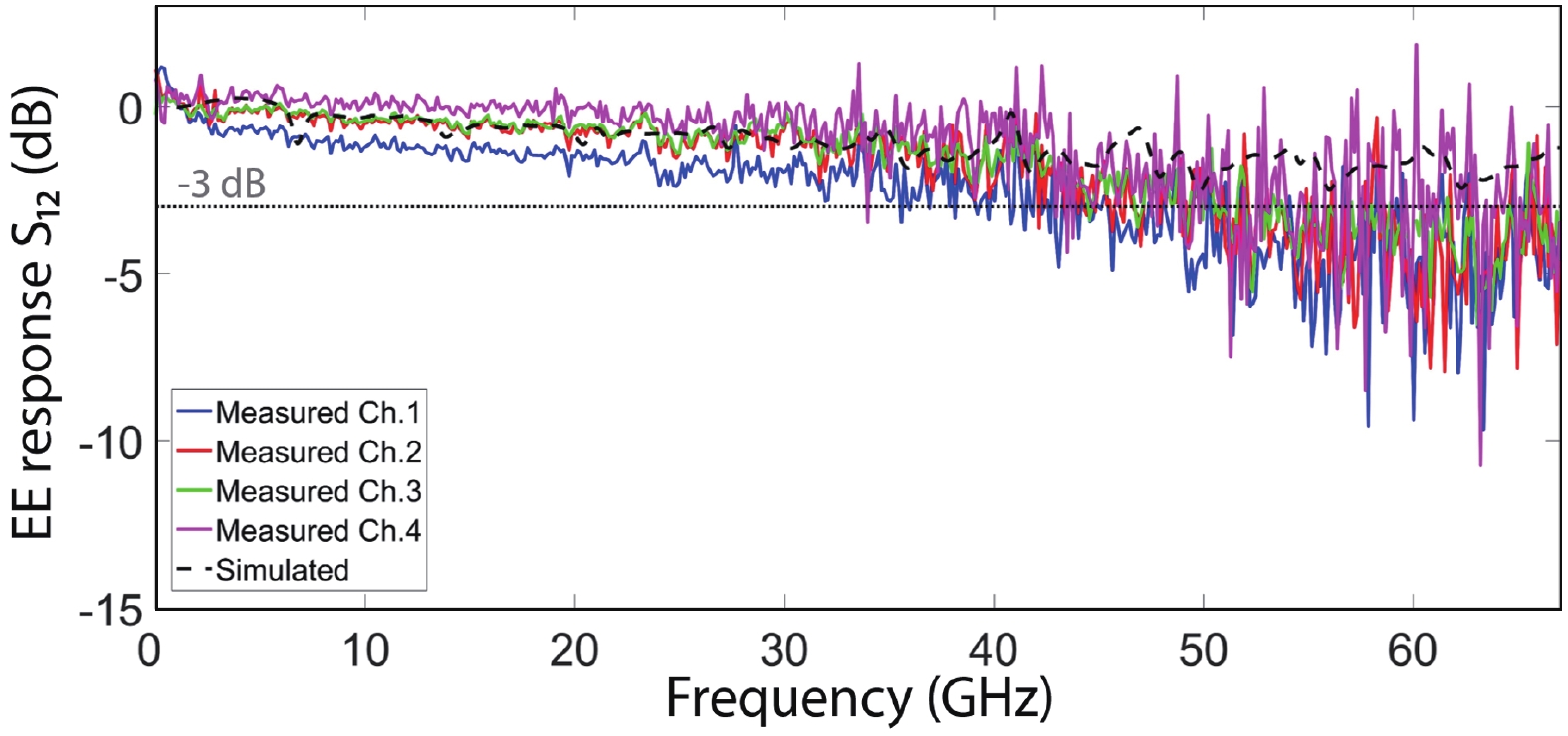
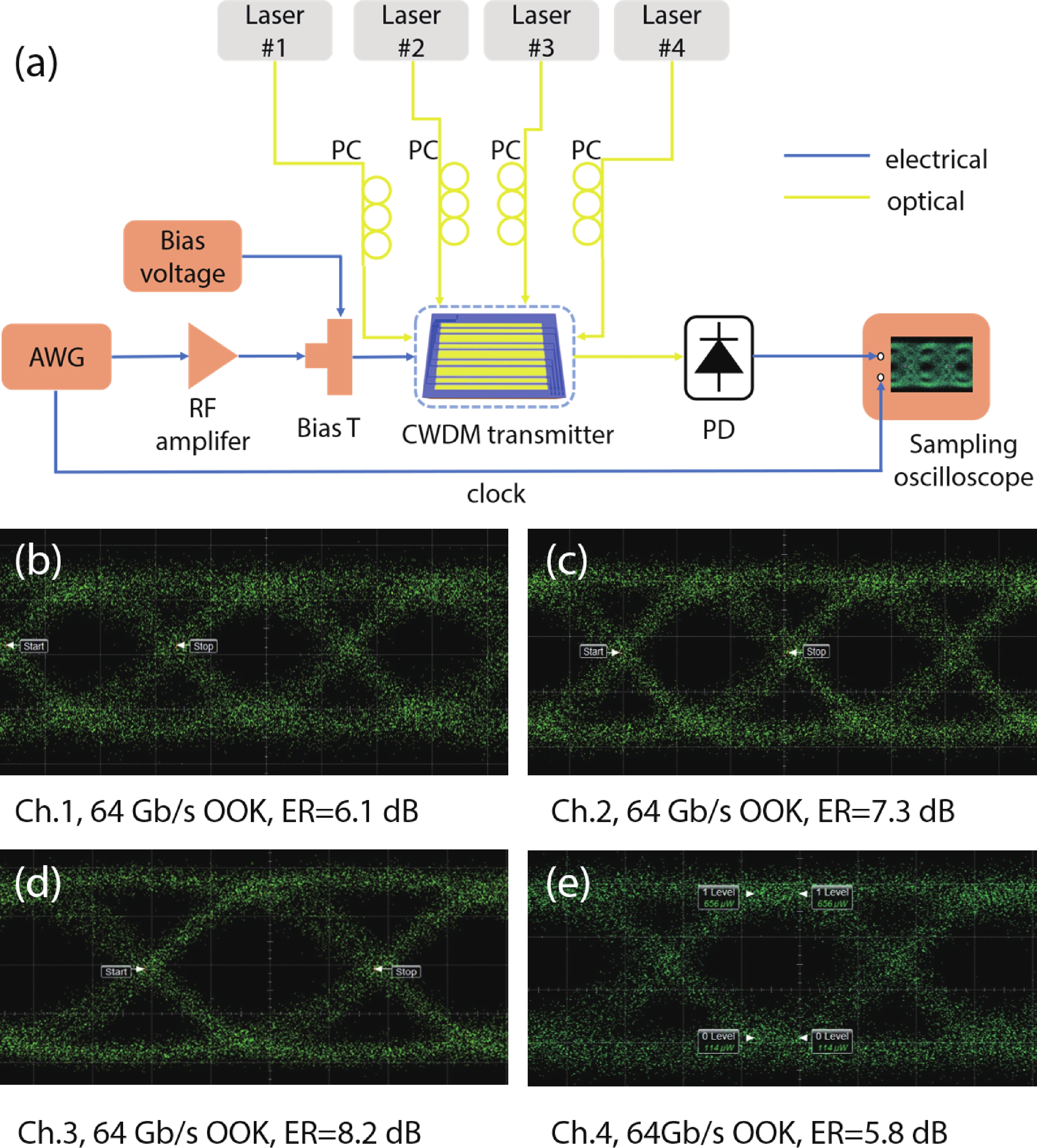
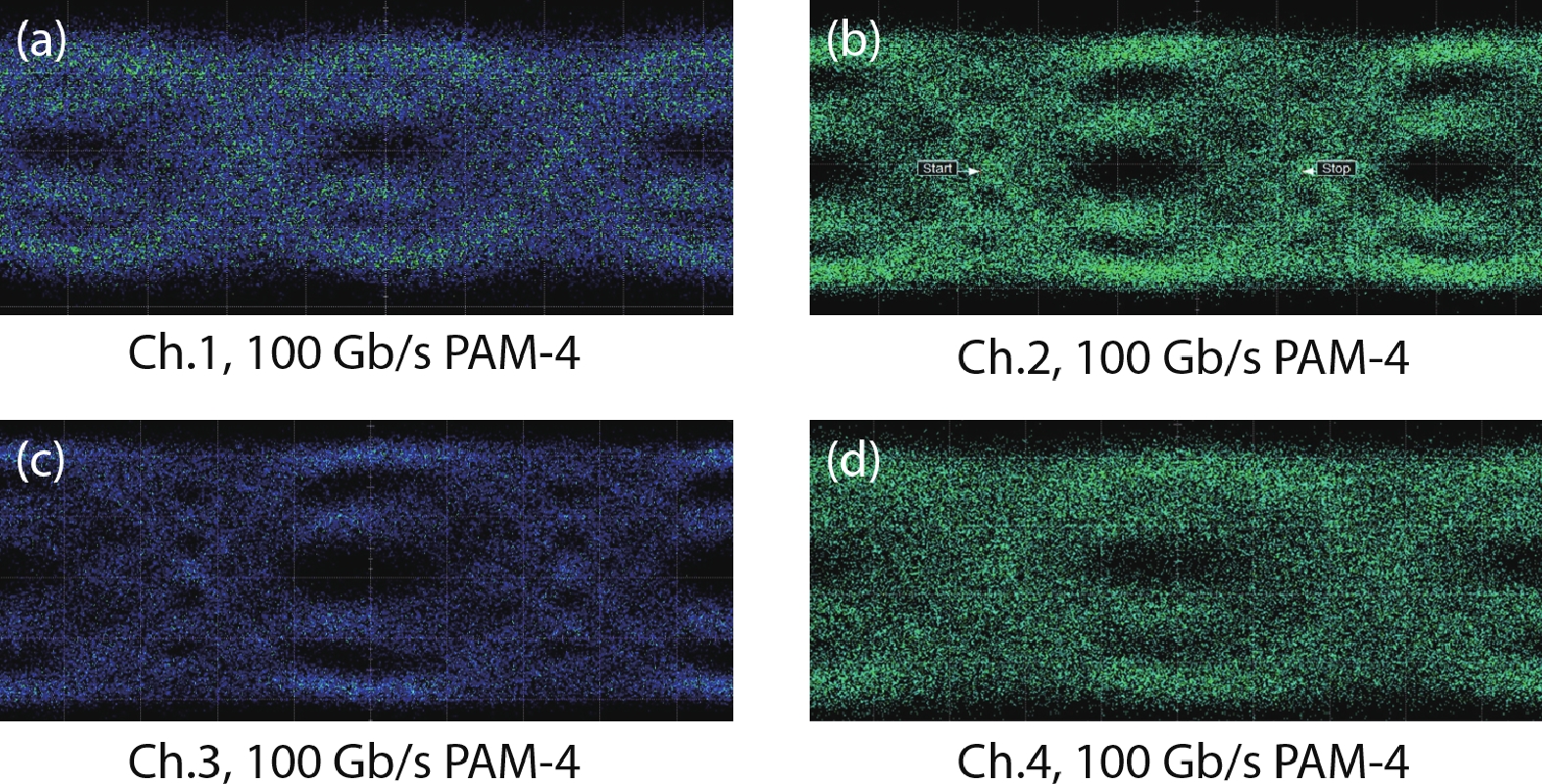
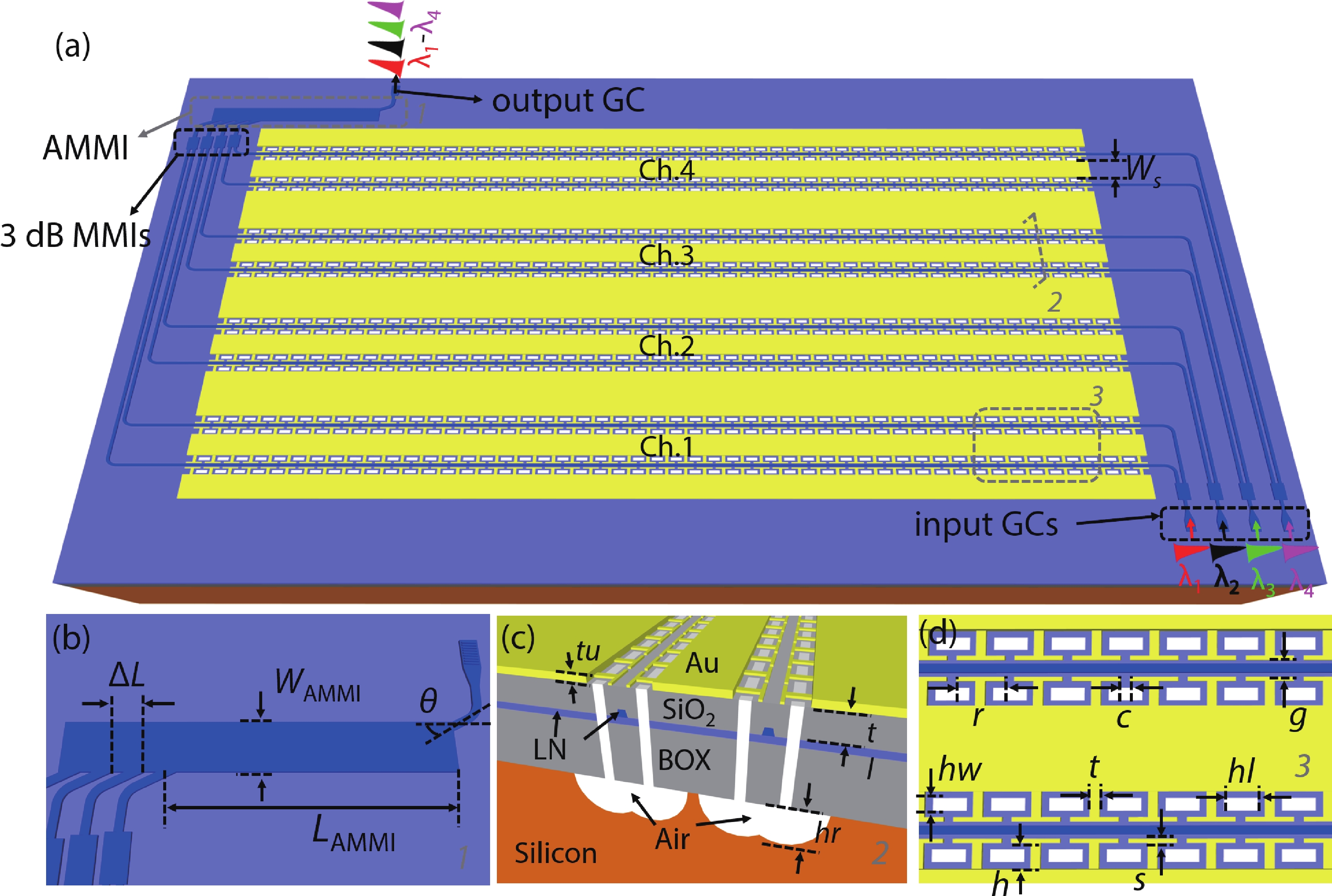
Multi-lane integrated transmitter chips are key components in future compact optical modules to realize high-speed optical interconnects. Thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) photonics have emerged as a promising platform for achieving high-performance chip-scale optical systems. Combining a coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) devices using fabrication-tolerant angled multimode interferometer structure and high-performance electro-optical modulators, we demonstrate monolithic on-chip four-channel CWDM transmitter on the TFLN platform for the first time. The four-channel CWDM transmitter enables high-speed transmissions of 100 Gb/s data rate per wavelength channel (i.e., an aggregated date rate of 400 Gb/s). -
References
[1] Winzer P J, Neilson D T, Chraplyvy A R. Fiber-optic transmission and networking: the previous 20 and the next 20 years. Opt Express, 2018, 26(18), 24190 doi: 10.1364/OE.26.024190[2] Liu J, Ye Y, Deng L, et al. Integrated four-channel directly modulated O-band optical transceiver for radio over fiber application. Opt Express, 2018, 26(17), 21490 doi: 10.1364/OE.26.021490[3] Arima R, Yamashita T, Yahagi T, et al. Demonstration of world-first 103 Gbit/s transmission over 40 km single mode fiber by 1310 nm LAN-WDM optical transceiver for 100GbE. National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference, 2011, JWA9 doi: 10.1364/NFOEC.2011.JWA9[4] Fujisawa T, Kanazawa S, Ishii H, et al. 1.3-μm × 25-Gb/s monolithically integrated light source for metro area 100-Gb/s ethernet. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2011, 23(6), 356 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2011.2106117[5] Kanazawa S, Fujisawa T, Ohki A, et al. A compact EADFB laser array module for a future 100-Gb/s Ethernet transceiver. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron, 2011, 17(5), 1191 doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2011.2124446[6] Ramaswamy A, Roth J, Norberg E J, et al. A WDM 4× 28Gbps integrated silicon photonic transmitter driven by 32nm CMOS driver ICs. Optical Fiber Communication Conference, 2015, Th5B.5[7] Murao T, Yasui N, Shinada T, et al. Integrated spatial optical system for compact 28-Gb/s × 4-lane transmitter optical subassemblies. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2014, 26(22), 2275 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2014.2350971[8] Zhang H, Li M, Zhang Y, et al. 800 Gbit/s transmission over 1 km single-mode fiber using a four-channel silicon photonic transmitter. Photonics Res, 2020, 8(11), 1776 doi: 10.1364/PRJ.396815[9] Mardoyan H, Jorge F, Ozolins O, et al. 204-GBaud on-off keying transmitter for inter-data center communications. Optical Fiber Communication Conference, 2018, Th4A.4[10] Zhong K, Zhou X, Huo J, et al. Digital signal processing for short-reach optical communications: A review of current technologies and future trends. J Lightwave Technol, 2018, 36(2), 377 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2018.2793881[11] Motaghiannezam S. Optical PAM4 signaling and system performance for DCI applications. Optical Fiber Communication Conference, 2019, M3A.1 doi: 10.1364/OFC.2019.M3A.1[12] Zhu D, Shao L, Yu M, et al. Integrated photonics on thin-film lithium niobate. Adv Opt Photonics, 2021, 13(2), 242 doi: 10.1364/AOP.411024[13] Wooten E L, Kissa K M, Yi-Yan A, et al. A review of lithium niobate modulators for fiber-optic communications systems. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron, 2000, 6(1), 69 doi: 10.1109/2944.826874[14] Saravi S, Pertsch T, Setzpfandt F. Lithium niobate on insulator: An emerging platform for integrated quantum photonics. Adv Opt Mater, 2021, 9(22), 2100789 doi: 10.1002/adom.202100789[15] Marpaung D, Yao J, Capmany J. Integrated microwave photonics. Nat Photonics, 2019, 13(2), 80 doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0310-5[16] Wang C, Zhang M, Chen X, et al. Integrated lithium niobate electro-optic modulators operating at CMOS-compatible voltages. Nature, 2018, 562(7725), 101 doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0551-y[17] Jian J, Xu M, Liu L, et al. High modulation efficiency lithium niobate Michelson interferometer modulator. Opt Express, 2019, 27(13), 18731 doi: 10.1364/OE.27.018731[18] Pohl D, Messner A, Kaufmann F, et al. 100-Gbd waveguide Bragg grating modulator in thin-film lithium niobate. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2020, 33(2), 85 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2020.3044648[19] Xu M, He M, Zhu Y, et al. Integrated thin film lithium niobate Fabry–Perot modulator. Chin Opt Lett, 2021, 19(6), 060003 doi: 10.3788/COL202119.060003[20] Shams-Ansari A, Renaud D, Cheng R, et al. Electrically-pumped high-power laser transmitter integrated on thin-film lithium niobate. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2111.08473, 2021[21] Chen G, Ruan Z, Wang Z, et al. Four-channel CWDM device on a thin-film lithium niobate platform using an angled multimode interferometer structure. Photonics Res, 2022, 10(1), 8 doi: 10.1364/PRJ.438816[22] Chen G, Chen K, Gan R, et al. High performance thin-film lithium niobate modulator on a silicon substrate using periodic capacitively loaded traveling-wave electrode. APL Photonics, 2022, 7(2), 026103 doi: 10.1063/5.0077232[23] Wang J, Chen P, Dai D, et al. Polarization coupling of X-cut thin film lithium niobate based waveguides. IEEE Photonics J, 2020, 12(3), 1 doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2020.2995317[24] Kharel P, Reimer C, Luke K, et al. Breaking voltage–bandwidth limits in integrated lithium niobate modulators using micro-structured electrodes. Optica, 2021, 8(3), 357 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.416155[25] Ying P, Tan H, Zhang J, et al. Low-loss edge-coupling thin-film lithium niobate modulator with an efficient phase shifter. Opt Lett, 2021, 46(6), 1478 doi: 10.1364/OL.418996 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: