| Citation: |
Chengfang Liu, He Lin, Dongzhou Ji, Qun Yu, Shuoguo Chen, Ziming Guo, Qian Luo, Xu Liu, Wenyong Lai. Wavelength-tunable organic semiconductor lasers based on elastic distributed feedback gratings[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2023, 44(3): 032601. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/3/032601
****
C F Liu, H Lin, D Z Ji, Q Yu, S G Chen, Z M Guo, Q Luo, X Liu, W Y Lai. Wavelength-tunable organic semiconductor lasers based on elastic distributed feedback gratings[J]. J. Semicond, 2023, 44(3): 032601. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/3/032601
|
Wavelength-tunable organic semiconductor lasers based on elastic distributed feedback gratings
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/3/032601
More Information
-
Abstract
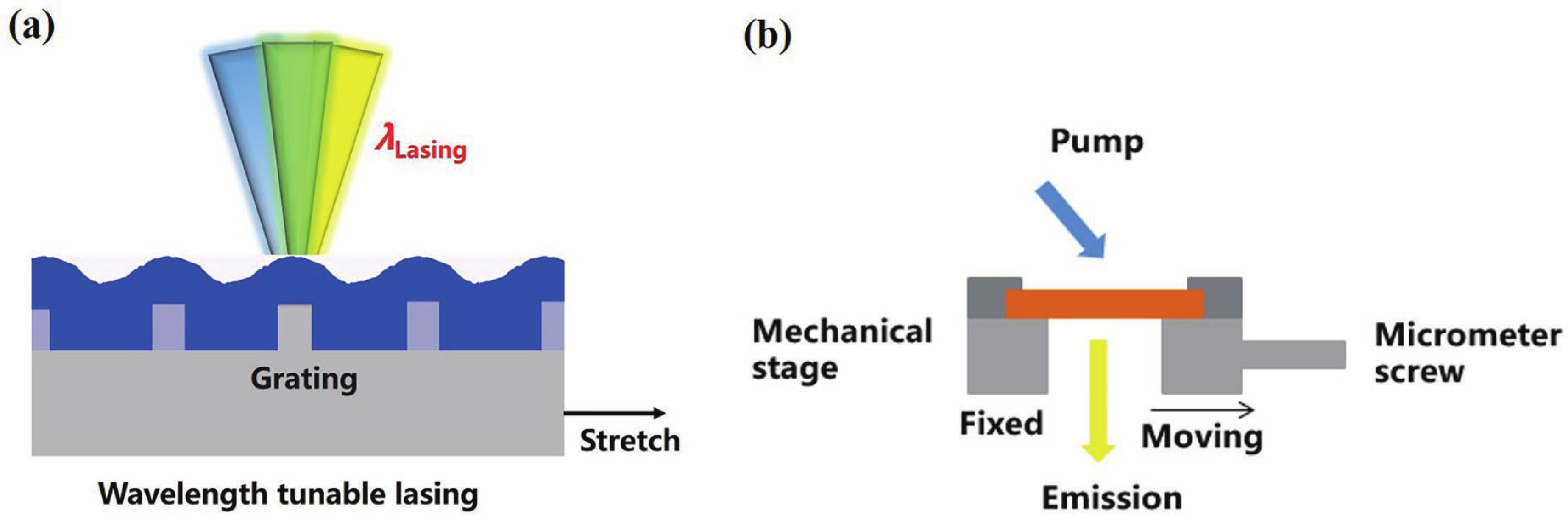
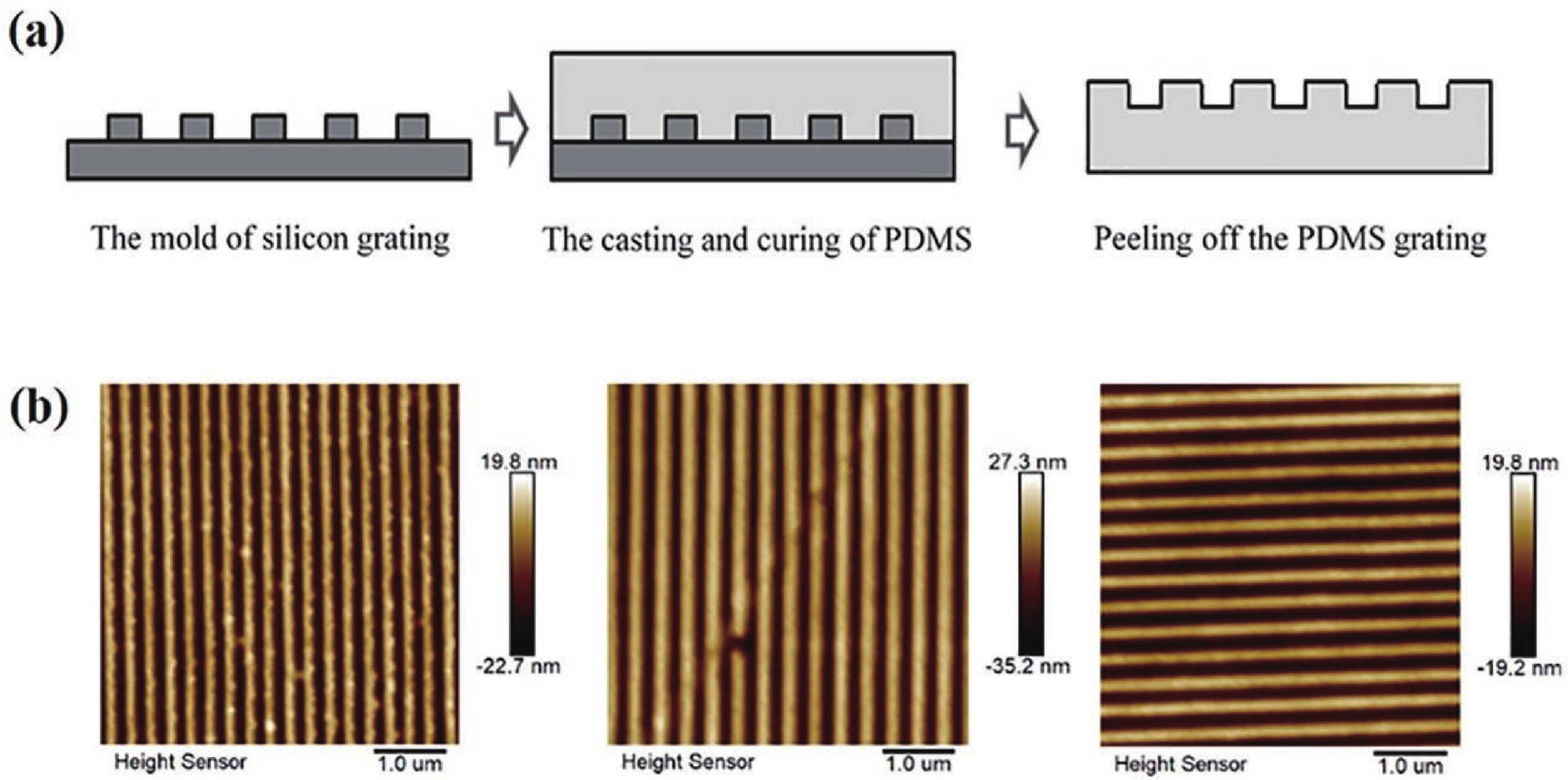
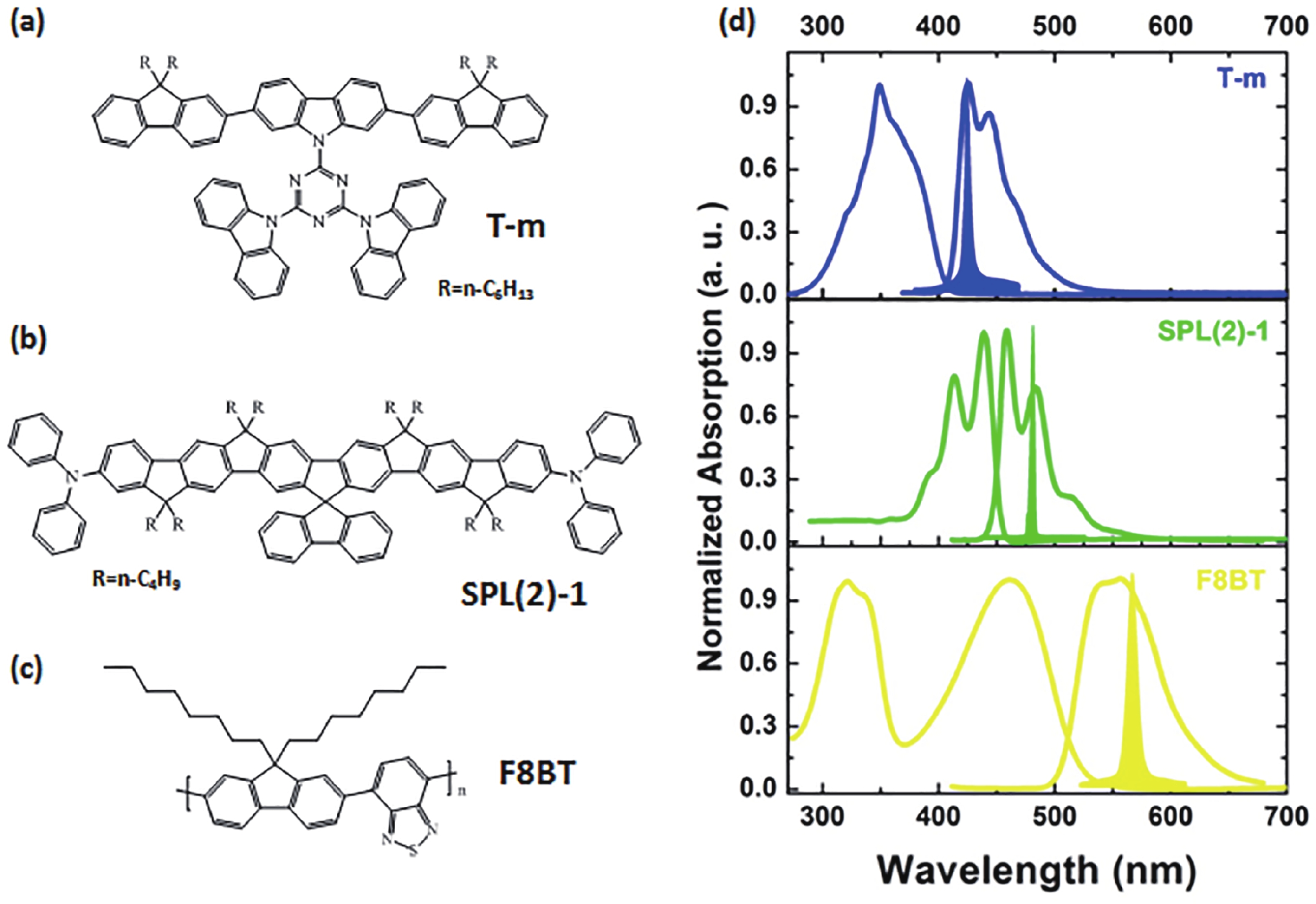
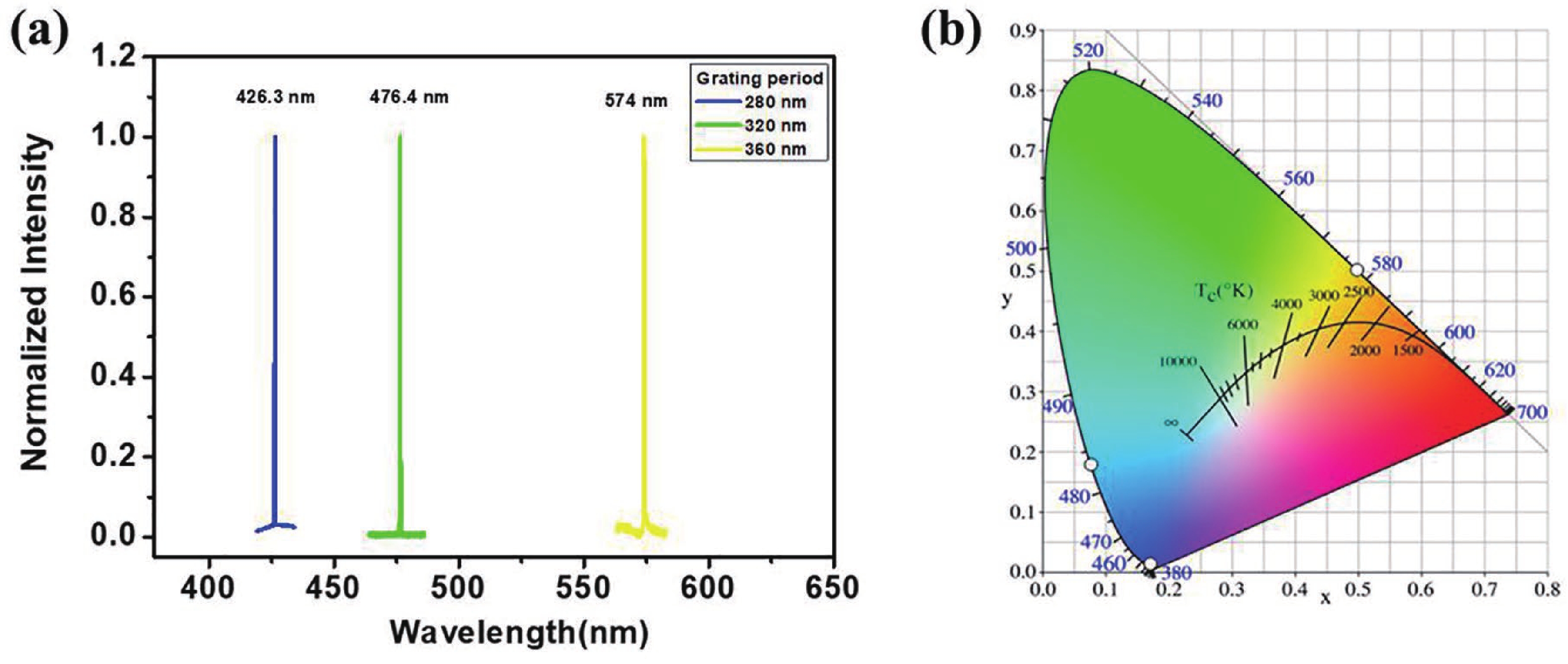
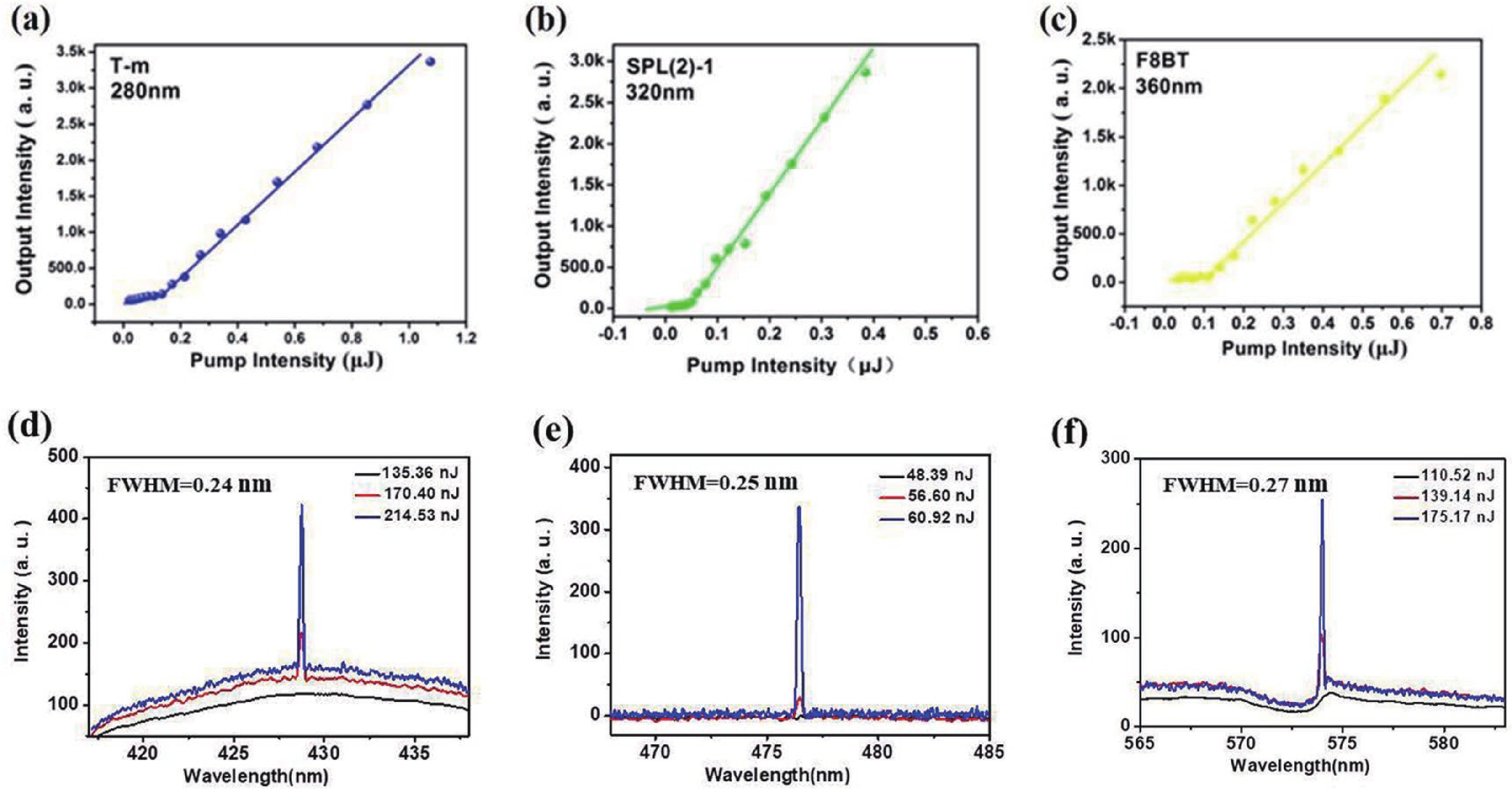
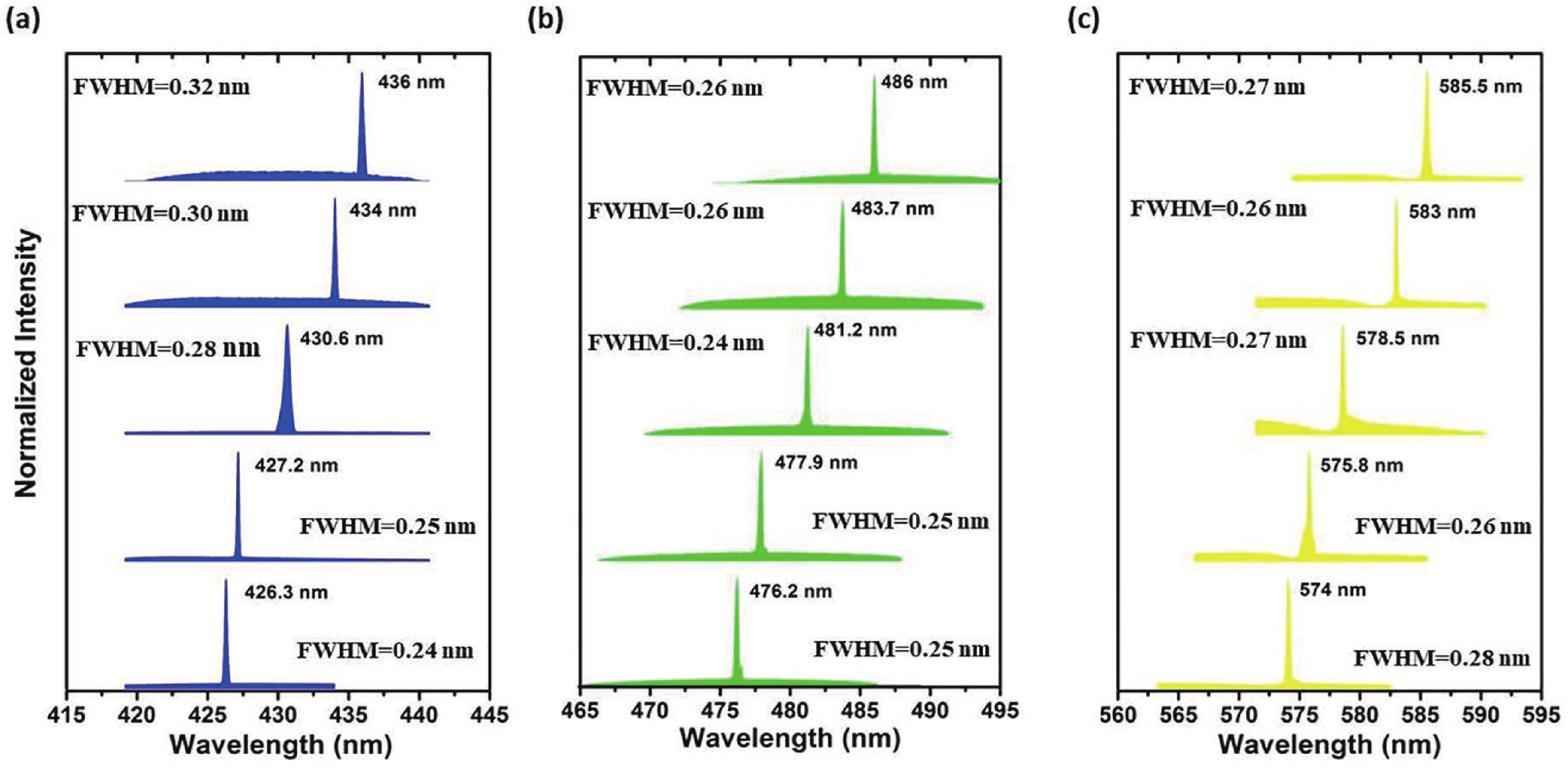
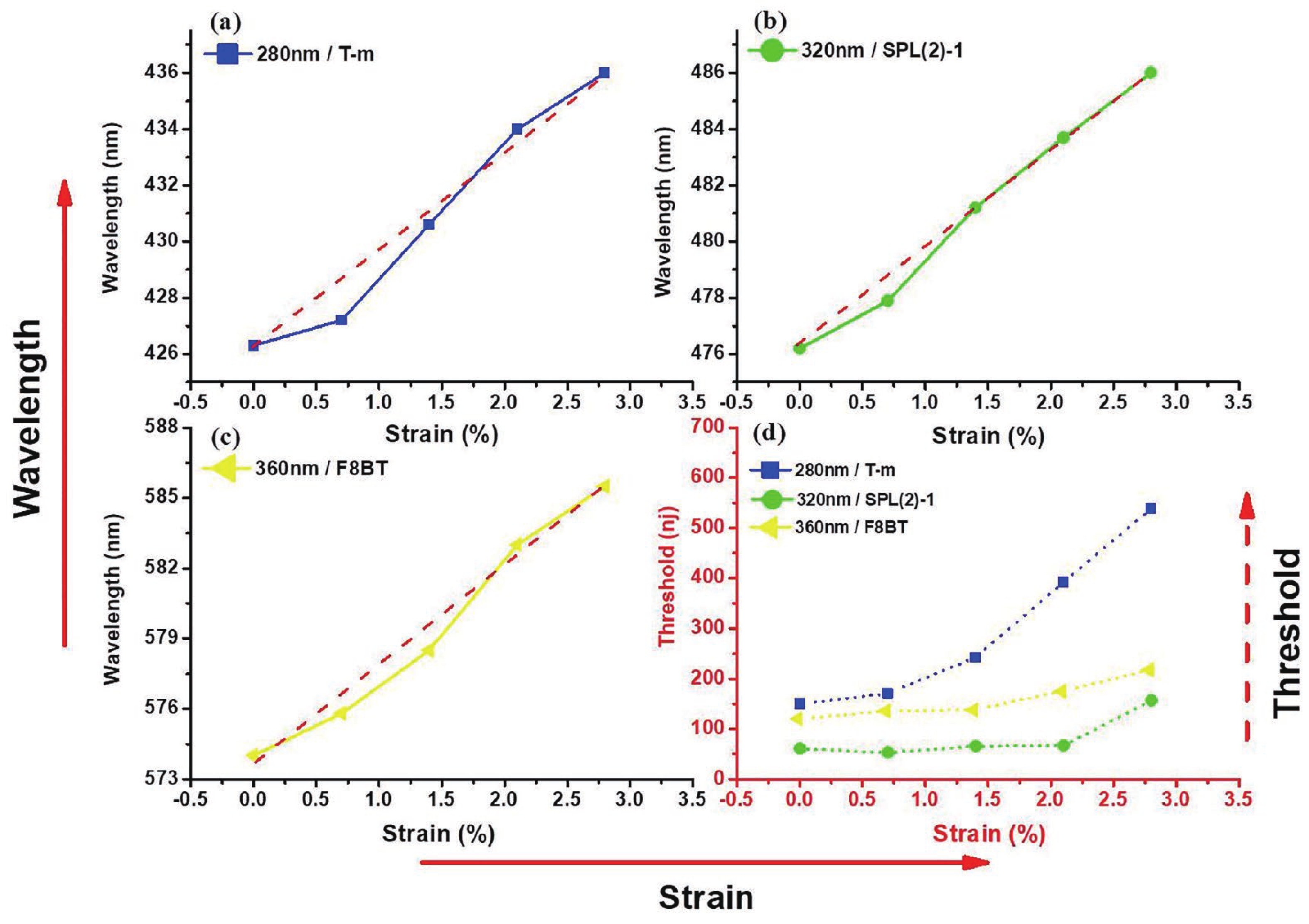
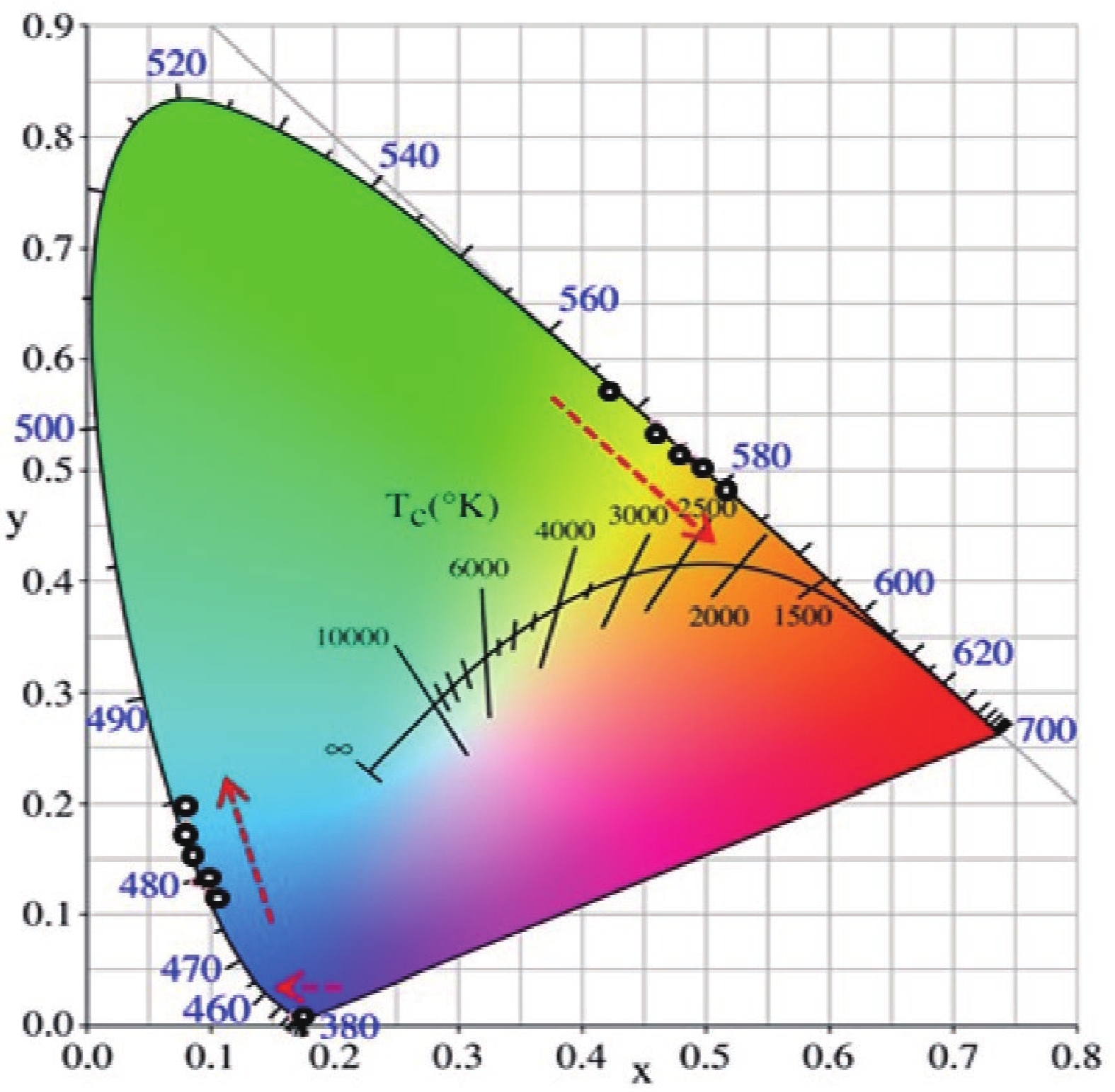
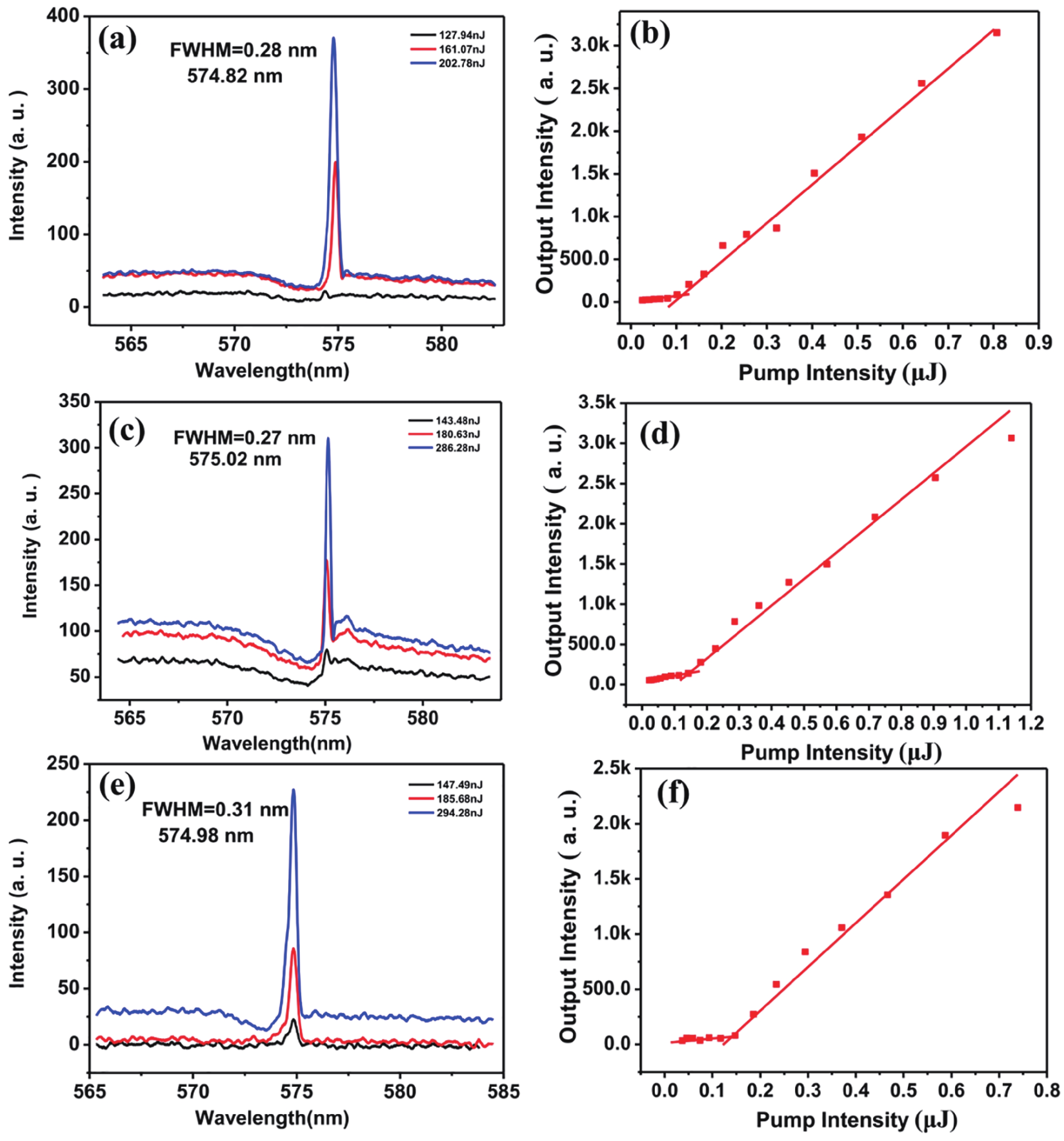
Wavelength-tunable organic semiconductor lasers based on mechanically stretchable polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) gratings were developed. The intrinsic stretchability of PDMS was explored to modulate the period of the distributed feedback gratings for fine tuning the lasing wavelength. Notably, elastic lasers based on three typical light-emitting molecules show comparable lasing threshold values analogous to rigid devices and a continuous wavelength tunability of about 10 nm by mechanical stretching. In addition, the stretchability provides a simple solution for dynamically tuning the lasing wavelength in a spectral range that is challenging to achieve for inorganic counterparts. Our work has provided a simple and efficient method of fabricating tunable organic lasers that depend on stretchable distributed feedback gratings, demonstrating a significant step in the advancement of flexible organic optoelectronic devices. -
References
[1] Jiang Y, Liu Y Y, Liu X, et al. Organic solid-state lasers: a materials view and future development. Chem Soc Rev, 2020, 49, 5885 doi: 10.1039/D0CS00037J[2] Samuel I D W, Turnbull G A. Organic semiconductor lasers. Chem Rev, 2007, 107, 1272 doi: 10.1021/cr050152i[3] Chenais S, Forget S. Recent advances in solid-state organic lasers. Polym Int, 2012, 61, 390 doi: 10.1002/pi.3173[4] Wei G Q, Wang X D, Liao L S. Recent advances in 1D organic solid-state lasers. Adv Funct Mater, 2019, 29, 1902981 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201902981[5] Kuehne A J C, Gather M C. Organic lasers: recent developments on materials, device geometries, and fabrication techniques. Chem Rev, 2016, 116, 12823 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00172[6] Xu J, Ma L, Guo P, et al. Room-temperature dual-wavelength lasing from single-nanoribbon lateral heterostructures. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134, 12394 doi: 10.1021/ja3050458[7] Liu Z, Yin L, Ning H, et al. Dynamical color-controllable lasing with extremely wide tuning range from red to green in a single alloy nanowire using nanoscale manipulation. Nano Lett, 2013, 13, 4945 doi: 10.1021/nl4029686[8] Yang A, Hoang T B, Dridi M, et al. Real-time tunable lasing from plasmonic nanocavity arrays. Nat Commun, 2015, 6, 6939 doi: 10.1038/ncomms7939[9] Ta V D, Yang S, Wang Y, et al. Multicolor lasing prints. Appl Phys Lett, 2015, 107, 221103 doi: 10.1063/1.4936628[10] Dong H Y, Zhang C H, Liu Y, et al. Organic microcrystal vibronic lasers with full-spectrum tunable output beyond the Franck-Condon principle. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2018, 57, 3108 doi: 10.1002/anie.201712524[11] Dong H Y, Zhang C H, Zhao Y S. Controlling the output of organic micro/nanolasers. Adv Optical Mater, 2019, 7, 1900037 doi: 10.1002/adom.201900037[12] Wang X D, Li Z Z, Zhuo M P, et al. Tunable near-infrared organic nanowire nanolasers. Adv Funct Mater, 2017, 27, 1703470 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201703470[13] Dong H Y, Zhang C H, Lin X Q, et al. Dual-wavelength switchable vibronic lasing in single-crystal organic microdisks. Nano Lett, 2017, 17, 91 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03499[14] Qiao C, Zhang C H, Zhou Z H, et al. Optically reconfigurable FRET process for broadband switchable organic single-mode microlasers. CCS Chem, 2022, 4, 250 doi: 10.31635/ccschem.021.202000768[15] Qiao C, Zhang C H, Zhou Z H, et al. Photoisomerization activated intramolecular charge-transfer process for broadband tunable single-mode microlasers. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2020, 59, 15992 doi: 10.1002/anie.202007361[16] Bianco A, Perissinotto S, Garbugli M, et al. Control of optical properties through photochromism: a promising approach to photonics. Laser Photonics Rev, 2011, 5, 711 doi: 10.1002/lpor.201000033[17] Zhang W, Yao J N, Zhao Y S. Organic micro/nanoscale lasers. Acc Chem Res, 2016, 49, 1691 doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00209[18] Lai W Y, Xia R, He Q Y, et al. Enhanced solid-state luminescence and low-threshold lasing from starburst macromolecular materials. Adv Mater, 2009, 21, 355 doi: 10.1002/adma.200800748[19] Xu W D, Yi J P, Lai W Y, et al. Pyrene-capped conjugated amorphous starbursts: synthesis, characterization, and stable lasing properties in ambient atmosphere. Adv Funct Mater, 2015, 25, 4617 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201501337[20] Liu C F, Sang M, Lai W Y, et al. Design and synthesis of monodisperse macromolecular starbursts based on a triazine center with multibranched oligofluorenes as efficient gain media for organic lasers. Macromolecules, 2018, 51, 1325 doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.7b02204[21] Liu C F, Lu T T, Wang J B, et al. Low threshold amplified spontaneous emission from efficient energy transfer in blends of conjugated polymers. J Phys Chem C, 2020, 124, 8576 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c00588[22] Fang M, Huang J, Zhang Y, et al. Pyrene-centered cyanophenyl end-capped starbursts: design, synthesis, stabilized blue electroluminescence and lasing properties. Mater Chem Front, 2017, 1, 668 doi: 10.1039/C6QM00133E[23] Wallikewitz B H, Nikiforov G O, Sirringhaus H, et al. A nanoimprinted, optically tuneable organic laser. Appl Phys Lett, 2012, 100, 10 doi: 10.1063/1.4705303[24] Kjellberg T, Nilsson S, Klinga T J, et al. Investigation on the spectral characteristics of DFB Lasers with different grating configurations made by electron-beam lithography. Lightwave Technol, 1993, 11, 1405 doi: 10.1109/50.241930[25] Pisignano D, Persano L, Visconti P, et al. Oligomer-based organic distributed feedback lasers by room-temperature nanoimprint lithography. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 83, 2545 doi: 10.1063/1.1613362[26] Kallinger C, Hilmer M, Haugeneder A, et al. A flexible conjugated polymer laser. Adv Mater, 1998, 21, 920 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4095(199808)10:12<920::AID-ADMA920>3.0.CO;2-7[27] Weinberger M R, Langer G, Pogantsch A, et al. Continuously color-tunable rubber laser. Adv Mater, 2004, 16, 130 doi: 10.1002/adma.200305681[28] Suzuki K, Takahashi K, Seida Y, et al. A continuously tunable organic solid-state laser based on a flexible distributed-feedback resonator. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2003, 42, L249 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.42.L249[29] Wenger B, Tetreault N, Welland M E, et al. Mechanically tunable conjugated polymer distributed feedback lasers. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 97, 193303 doi: 10.1063/1.3509405[30] Herrnsdorf J, Guilhabert B, Chen Y, et al. Flexible blue-emitting encapsulated organic semiconductor DFB laser. Opt Express, 2010, 18, 25535 doi: 10.1364/OE.18.025535[31] Görrn P, Lehnhardt M, Kowalsky W, et al. Elastically tunable self-organized organic lasers. Adv Mater, 2011, 23, 869 doi: 10.1002/adma.201003108[32] Fang H H, Ding R, Lu S Y, et al. Flexible lasers based on the microstructured single-crystalline ultrathin films. J Mater Chem, 2012, 22, 24139 doi: 10.1039/c2jm35394f[33] Foucher C, Guilhabert B, Kanibolotsky A L, et al. Highly-photostable and mechanically flexible all-organic semiconductor lasers. Opt Mater Express, 2013, 3, 584 doi: 10.1364/OME.3.000584[34] Klinkhammer S, Heussner N, Huska K, et al. Voltage-controlled tuning of an organic semiconductor distributed feedback laser using liquid crystals. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 99, 023307 doi: 10.1063/1.3610473[35] Xu Y, Hai G, Xu HW, et al. Efficient optical gain from near-infrared polymer lasers based on Poly[N-9′-heptadecanyl-2,7-carbazole-alt-5,5-(4′,7′-di-2-thienyl-2′,1′,3′-benzothiadiazole)]. Adv Optical Mater, 2018, 6, 1800263 doi: 10.1002/adom.201800263[36] Dong H Y, Zhang C H, Zhou W, et al. Differential polymer chain scission enables free-standing microcavity laser arrays. Adv Mater, 2022, 34, 2107611 doi: 10.1002/adma.202107611[37] Zhang C H, Dong H Y, Zhang C, et al. Photonic skins based on flexible organic microlaser arrays. Sci Adv, 2021, 7, eahh3530 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abh3530[38] Fan Y Q, Zhang C H, Du Y X, et al. A universal in situ cross-linking strategy enables orthogonal processing of full-color organic microlaser arrays. Adv Funct Mater, 2021, 31, 2103031 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202103031 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad:










 Chengfang Liu:is an associate professor at Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications. She obtained her Ph.D. from the Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2013. She then joined the Key Laboratory for Organic Electronics & Information Displays and Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications. Her current research interests focus on organic devices and thin film growth
Chengfang Liu:is an associate professor at Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications. She obtained her Ph.D. from the Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2013. She then joined the Key Laboratory for Organic Electronics & Information Displays and Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications. Her current research interests focus on organic devices and thin film growth Wenyong Lai:is a full professor at Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications. He received his Ph.D. from Fudan University in 2007. He then joined the State Key Laboratory ofOrganic Electronics & Information Displays and Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications. His research mainly focuses on the design, synthesis, and application of organic and 22 polymer optoelectronic materials for organic/plastic electronics, as well as theexploration of novel materials and processes for printed electronics and flexible electronics
Wenyong Lai:is a full professor at Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications. He received his Ph.D. from Fudan University in 2007. He then joined the State Key Laboratory ofOrganic Electronics & Information Displays and Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications. His research mainly focuses on the design, synthesis, and application of organic and 22 polymer optoelectronic materials for organic/plastic electronics, as well as theexploration of novel materials and processes for printed electronics and flexible electronics



