| Citation: |
Depeng Li, Jingrui Ma, Wenbo Liu, Guohong Xiang, Xiangwei Qu, Siqi Jia, Mi Gu, Jiahao Wei, Pai Liu, Kai Wang, Xiaowei Sun. Enhancing performance of inverted quantum-dot light-emitting diodes based on a solution-processed hole transport layer via ligand treatment[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2023, 44(9): 092603. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/9/092603
****
D P Li, J R Ma, W B Liu, G H Xiang, X W Qu, S Q Jia, M Gu, J H Wei, P Liu, K Wang, X W Sun. Enhancing performance of inverted quantum-dot light-emitting diodes based on a solution-processed hole transport layer via ligand treatment[J]. J. Semicond, 2023, 44(9): 092603. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/9/092603
|
Enhancing performance of inverted quantum-dot light-emitting diodes based on a solution-processed hole transport layer via ligand treatment
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/9/092603
More Information
-
Abstract
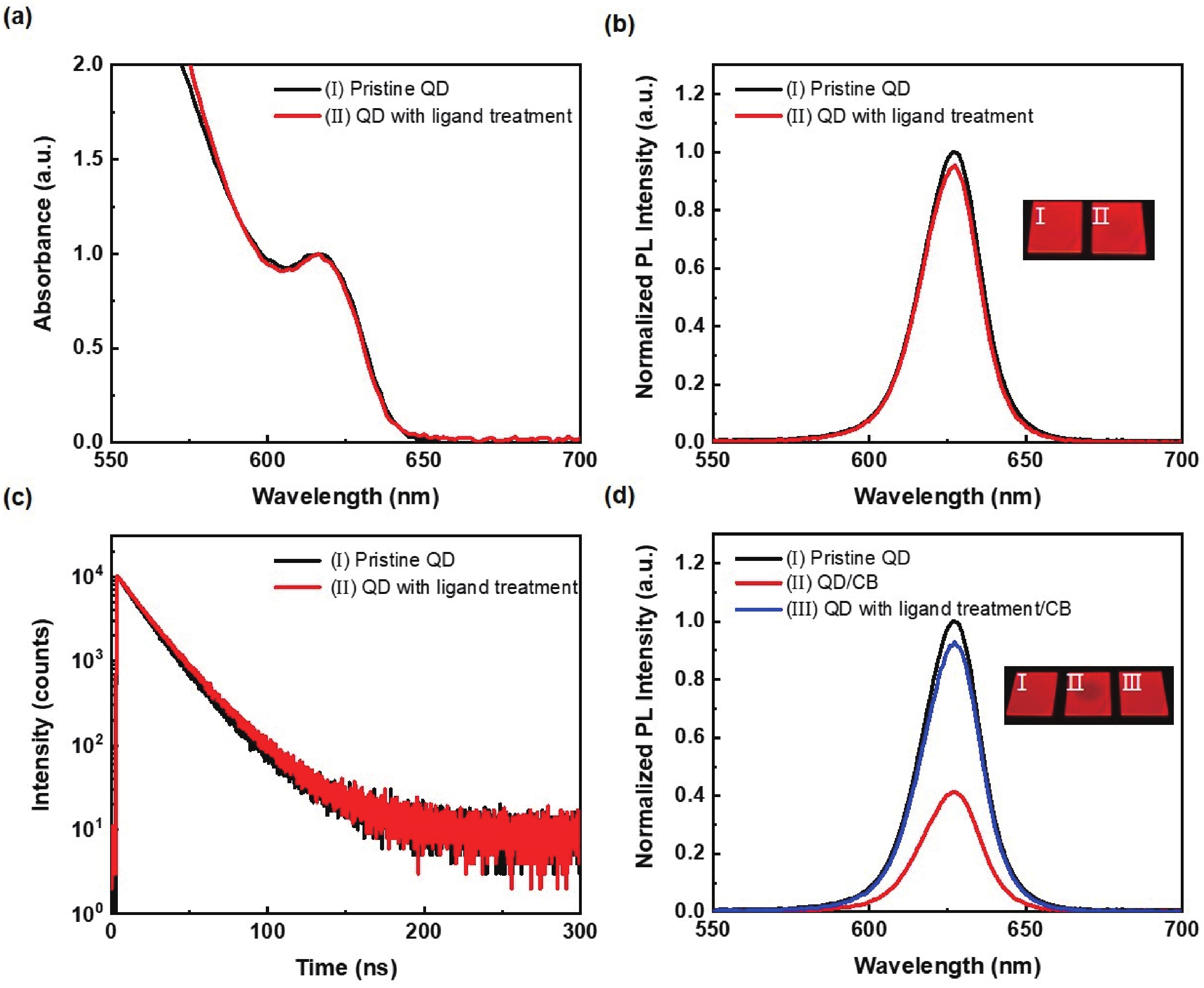
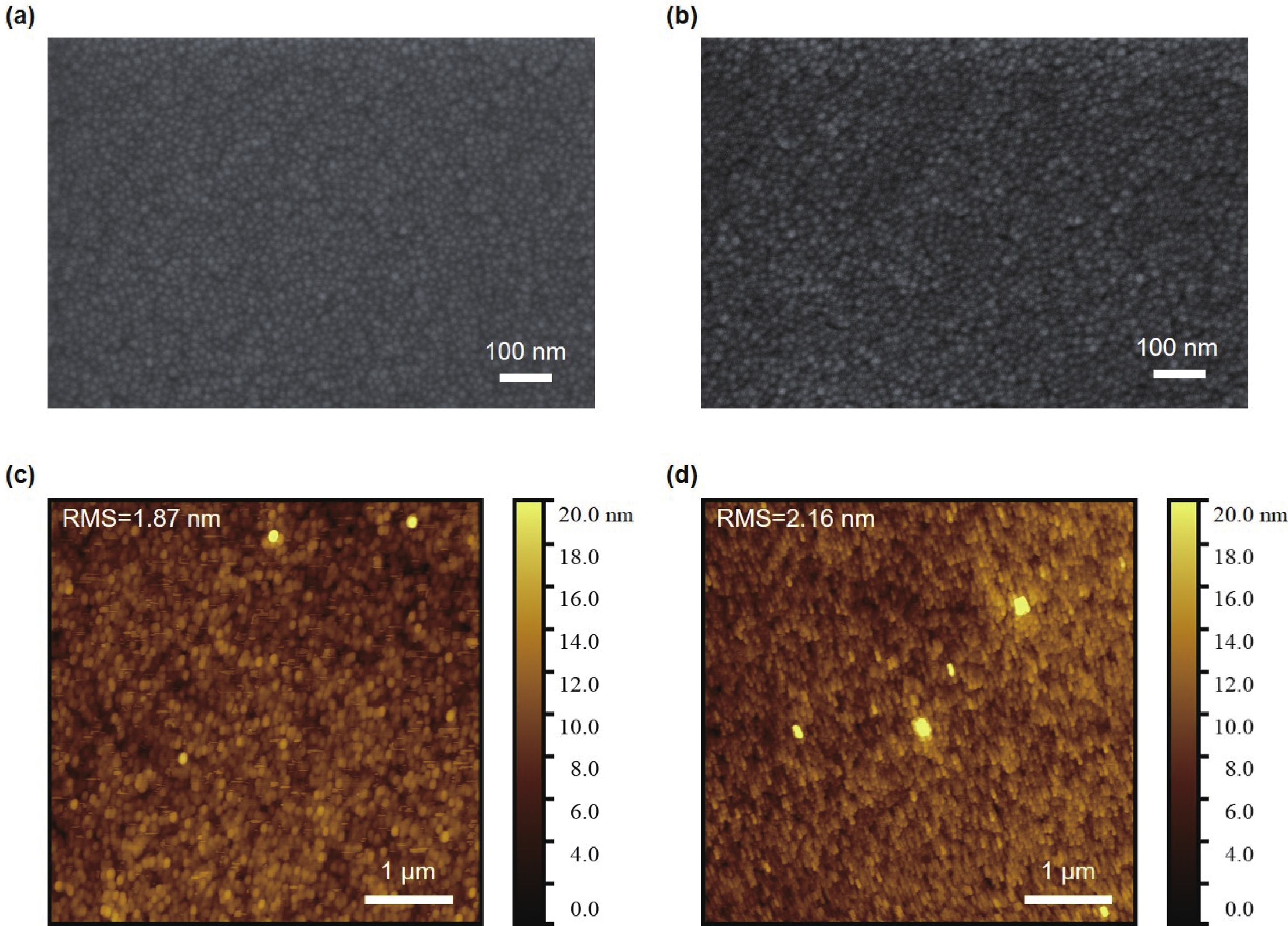
The performance of inverted quantum-dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs) based on solution-processed hole transport layers (HTLs) has been limited by the solvent-induced damage to the quantum dot (QD) layer during the spin-coating of the HTL. The lack of compatibility between the HTL's solvent and the QD layer results in an uneven surface, which negatively impacts the overall device performance. In this work, we develop a novel method to solve this problem by modifying the QD film with 1,8-diaminooctane to improve the resistance of the QD layer for the HTL’s solvent. The uniform QD layer leads the inverted red QLED device to achieve a low turn-on voltage of 1.8 V, a high maximum luminance of 105 500 cd/m2, and a remarkable maximum external quantum efficiency of 13.34%. This approach releases the considerable potential of HTL materials selection and offers a promising avenue for the development of high-performance inverted QLEDs. -
References
[1] Liu Y, Jiang C B, Song C, et al. Highly efficient all-solution processed inverted quantum dots based light emitting diodes. ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 1564 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b08129[2] Kim T H, Cho K S, Lee E K, et al. Full-colour quantum dot displays fabricated by transfer printing. Nature Photon, 2011, 5, 176 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2011.12[3] Hong A, Kim J, Kwak J. Sunlike white quantum dot light-emitting diodes with high color rendition quality. Adv Optical Mater, 2020, 8, 2001051 doi: 10.1002/adom.202001051[4] Bae W K, Lim J, Lee D G, et al. R/G/B/natural white light thin colloidal quantum dot-based light-emitting devices. Adv Mater, 2014, 26, 6387 doi: 10.1002/adma.201400139[5] Lim J, Park Y S, Wu K F, et al. Droop-free colloidal quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nano Lett, 2018, 18, 6645 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b03457[6] Peng Z A, Peng X G. Formation of high-quality CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals using CdO as precursor. J Am Chem Soc, 2001, 123, 183 doi: 10.1021/ja003633m[7] Murray C B, Norris D J, Bawendi M G. Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE (E = sulfur, selenium, tellurium) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J Am Chem Soc, 1993, 115, 8706 doi: 10.1021/ja00072a025[8] Colvin V L, Schlamp M C, Alivisatos A P. Light-emitting diodes made from cadmium selenide nanocrystals and a semiconducting polymer. Nature, 1994, 370, 354 doi: 10.1038/370354a0[9] Liu M X, Yazdani N, Yarema M, et al. Colloidal quantum dot electronics. Nat Electron, 2021, 4, 548 doi: 10.1038/s41928-021-00632-7[10] Meng T T, Zheng Y T, Zhao D L, et al. Ultrahigh-resolution quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Nat Photon, 2022, 16, 297 doi: 10.1038/s41566-022-00960-w[11] Jia S Q, Tang H D, Ma J R, et al. High performance inkjet-printed quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with high operational stability. Adv Opt Mater, 2021, 9, 2101069 doi: 10.1002/adom.202101069[12] Zhao J Y, Chen L X, Li D Z, et al. Large-area patterning of full-color quantum dot arrays beyond 1000 pixels per inch by selective electrophoretic deposition. Nat Commun, 2021, 12, 4603 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24931-x[13] Yang Y X, Zheng Y, Cao W R, et al. High-efficiency light-emitting devices based on quantum dots with tailored nanostructures. Nature Photon, 2015, 9, 259 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2015.36[14] Shen H B, Cao W R, Shewmon N T, et al. High-efficiency, low turn-on voltage blue-violet quantum-dot-based light-emitting diodes. Nano Lett, 2015, 15, 1211 doi: 10.1021/nl504328f[15] Duan X J, Ma J R, Zhang W D, et al. Study of the interfacial oxidation of InP quantum dots synthesized from tris(dimethylamino)phosphine. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2023, 15, 1619 doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c20138[16] Kwak J, Bae W K, Lee D G, et al. Bright and efficient full-color colloidal quantum dot light-emitting diodes using an inverted device structure. Nano Lett, 2012, 12, 2362 doi: 10.1021/nl3003254[17] Zhang H, Chen S M, Sun X W. Efficient red/green/blue tandem quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 21%. ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 697 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b07867[18] Mei G D, Wang W G, Wu D, et al. Full-color quantum dot light-emitting diodes based on microcavities. IEEE Photonics J, 2022, 14, 1 doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2022.3159278[19] Wang L S, Lin J, Lv Y, et al. Red, green, and blue microcavity quantum dot light-emitting devices with narrow line widths. ACS Appl Nano Mater, 2020, 3, 5301 doi: 10.1021/acsanm.0c00695[20] Deng Y Z, Peng F, Lu Y, et al. Solution-processed green and blue quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with eliminated charge leakage. Nat Photon, 2022, 16, 505 doi: 10.1038/s41566-022-00999-9[21] Liu D Q, Cao S, Wang S Y, et al. Highly stable red quantum dot light-emitting diodes with long T95 operation lifetimes. J Phys Chem Lett, 2020, 11, 3111 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c00836[22] Li X Y, Lin Q L, Song J J, et al. Quantum-dot light-emitting diodes for outdoor displays with high stability at high brightness. Adv Optical Mater, 2020, 8, 1901145 doi: 10.1002/adom.201901145[23] Kim J, Roh J, Park M, et al. Recent advances and challenges of colloidal quantum dot light-emitting diodes for display applications. Adv Mater, 2023, 2212220 doi: 10.1002/adma.202212220[24] Hu Q Q, Si J J, Chen D S, et al. High-performance all-solution-processed inverted quantum dot light-emitting diodes enabled by water treatment. Nano Res, 2023, 16, 10215 doi: 10.1007/s12274-023-5635-9[25] Dai X L, Zhang Z X, Jin Y Z, et al. Solution-processed, high-performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature, 2014, 515, 96 doi: 10.1038/nature13829[26] Cao W R, Xiang C Y, Yang Y X, et al. Highly stable QLEDs with improved hole injection via quantum dot structure tailoring. Nat Commun, 2018, 9, 2608 doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04986-z[27] Won Y H, Cho O, Kim T, et al. Highly efficient and stable InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nature, 2019, 575, 634 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1771-5[28] Chen X T, Lin X F, Zhou L K, et al. Blue light-emitting diodes based on colloidal quantum dots with reduced surface-bulk coupling. Nat Commun, 2023, 14, 284 doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-35954-x[29] Kim D, Fu Y, Kim S, et al. Polyethylenimine ethoxylated-mediated all-solution-processed high-performance flexible inverted quantum dot-light-emitting device. ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 1982 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b08142[30] Lee W, Kim B, Choi Y, et al. Polyethylenimine-ethoxylated dual interfacial layers for highly efficient and all-solution-processed inverted quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Opt Express, 2020, 28, 33971 doi: 10.1364/OE.406248[31] Fu Y, Kim D, Moon H, et al. Hexamethyldisilazane-mediated, full-solution-processed inverted quantum dot-light-emitting diodes. J Mater Chem C, 2017, 5, 522 doi: 10.1039/C6TC05119G[32] Lee W, Lee C M, Kim B, et al. Enhancing the efficiency of solution-processed inverted quantum dot light-emitting diodes via ligand modification with 6-mercaptohexanol. Opt Lett, 2021, 46, 1434 doi: 10.1364/OL.414574[33] Kozlov O V, Park Y S, Roh J, et al. Sub–single-exciton lasing using charged quantum dots coupled to a distributed feedback cavity. Science, 2019, 365, 672 doi: 10.1126/science.aax3489[34] Roh J, Park Y S, Lim J, et al. Optically pumped colloidal-quantum-dot lasing in LED-like devices with an integrated optical cavity. Nat Commun, 2020, 11, 271 doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14014-3[35] Qu X W, Xiang G H, Ma J R, et al. Identifying the dominant carrier of CdSe-based blue quantum dot light-emitting diode. Appl Phys Lett, 2023, 122, 113501 doi: 10.1063/5.0142735[36] Rhee S, Jeong B G, Choi M, et al. Versatile use of 1, 12-diaminododecane as an efficient charge balancer for high-performance quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. ACS Photonics, 2023, 10, 500 doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.2c01638[37] Lee S, Choi M J, Sharma G, et al. Orthogonal colloidal quantum dot inks enable efficient multilayer optoelectronic devices. Nat Commun, 2020, 11, 4814 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18655-7[38] Pu C D, Dai X L, Shu Y F, et al. Electrochemically-stable ligands bridge the photoluminescence-electroluminescence gap of quantum dots. Nat Commun, 2020, 11, 937 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14756-5[39] Scholz S, Kondakov D, Lüssem B, et al. Degradation mechanisms and reactions in organic light-emitting devices. Chem Rev, 2015, 115, 8449 doi: 10.1021/cr400704v[40] Mude N N, Kim S J, Lampande R, et al. An efficient organic and inorganic hybrid interlayer for high performance inverted red cadmium-free quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nanoscale Adv, 2022, 4, 904 doi: 10.1039/D1NA00716E[41] Ye Y X, Zheng X R, Chen D S, et al. Design of the hole-injection/hole-transport interfaces for stable quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. J Phys Chem Lett, 2020, 11, 4649 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c01323[42] Davidson-Hall T, Aziz H. Perspective: Toward highly stable electroluminescent quantum dot light-emitting devices in the visible range. Appl Phys Lett, 2020, 116, 010502 doi: 10.1063/1.5134090[43] Ma J R, Tang H D, Qu X W, et al. A dC/dV measurement for quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Chin Phys Lett, 2022, 39, 128401 doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/39/12/128401[44] Xiao X T, Ye T K, Sun J Y, et al. Capacitance–voltage characteristics of perovskite light-emitting diodes: Modeling and implementing on the analysis of carrier behaviors. Appl Phys Lett, 2022, 120, 243501 doi: 10.1063/5.0088231[45] Zhang X W, Xu J W, Xu H R, et al. Elucidation of carrier injection and recombination characteristics with impedance and capacitance in organic light-emitting diodes and the frequency effects. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2013, 46, 055102 doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/46/5/055102[46] Qu X W, Ma J R, Shan C W, et al. Trap state-assisted electron injection in blue quantum dot light-emitting diode. Appl Phys Lett, 2022, 121, 113507 doi: 10.1063/5.0104341[47] Chung D S, Davidson-Hall T, Cotella G, et al. Significant lifetime enhancement in QLEDs by reducing interfacial charge accumulation via fluorine incorporation in the ZnO electron transport layer. Nano Micro Lett, 2022, 14, 1 doi: 10.1007/s40820-021-00751-y[48] Yuan Y, Xue X L, Wang T, et al. Polyethylenimine modified Sol-gel ZnO electron-transporting layers for quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Org Electron, 2022, 100, 106393 doi: 10.1016/j.orgel.2021.106393 -
Supplements
 补充材料 23050021.pdf
补充材料 23050021.pdf

-
Proportional views






 DownLoad:
DownLoad:












 Depeng Li:received his B.E. degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from Southern University of Science and Technology in 2019, Guangdong, China. He is studying a Ph.D. degree in Southern University of Science and Technology currently. His research focuses on Micro-QLED and QLEDs device fabrication
Depeng Li:received his B.E. degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from Southern University of Science and Technology in 2019, Guangdong, China. He is studying a Ph.D. degree in Southern University of Science and Technology currently. His research focuses on Micro-QLED and QLEDs device fabrication Siqi Jia:received his doctoral degree from Jilin University, Changchun, China, in 2022. He is currently a Distinguished Research Fellow at Institute of Advanced Displays and Imaging, Henan Academy of Sciences. His current research interests include inkjet printing technology, optoelectronic materials and device
Siqi Jia:received his doctoral degree from Jilin University, Changchun, China, in 2022. He is currently a Distinguished Research Fellow at Institute of Advanced Displays and Imaging, Henan Academy of Sciences. His current research interests include inkjet printing technology, optoelectronic materials and device Xiaowei Sun:is a Chair Professor and the Executive Dean of the Institute of Nanoscience and Applications in the Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China. He is an academician of the Asia-Pacific Academy of Materials, and the fellow of several other academic societies including Optica (formerly OSA), SPIE, and the Institute of Physics (UK). His main research presently is on high-quality displays based on nanocrystals and naked-eye 3D displays
Xiaowei Sun:is a Chair Professor and the Executive Dean of the Institute of Nanoscience and Applications in the Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China. He is an academician of the Asia-Pacific Academy of Materials, and the fellow of several other academic societies including Optica (formerly OSA), SPIE, and the Institute of Physics (UK). His main research presently is on high-quality displays based on nanocrystals and naked-eye 3D displays





