| Citation: |
Karolis Stašys, Andrejus Geižutis, Jan Devenson. Enhanced thermal emission from metal-free, fully epitaxial structures with epsilon-near-zero InAs layers[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2024, 45(2): 022101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/2/022101
****
K Stašys, A Geižutis, J Devenson. Enhanced thermal emission from metal-free, fully epitaxial structures with epsilon-near-zero InAs layers[J]. J. Semicond, 2024, 45(2): 022101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/2/022101
|
Enhanced thermal emission from metal-free, fully epitaxial structures with epsilon-near-zero InAs layers
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/2/022101
More Information
-
Abstract
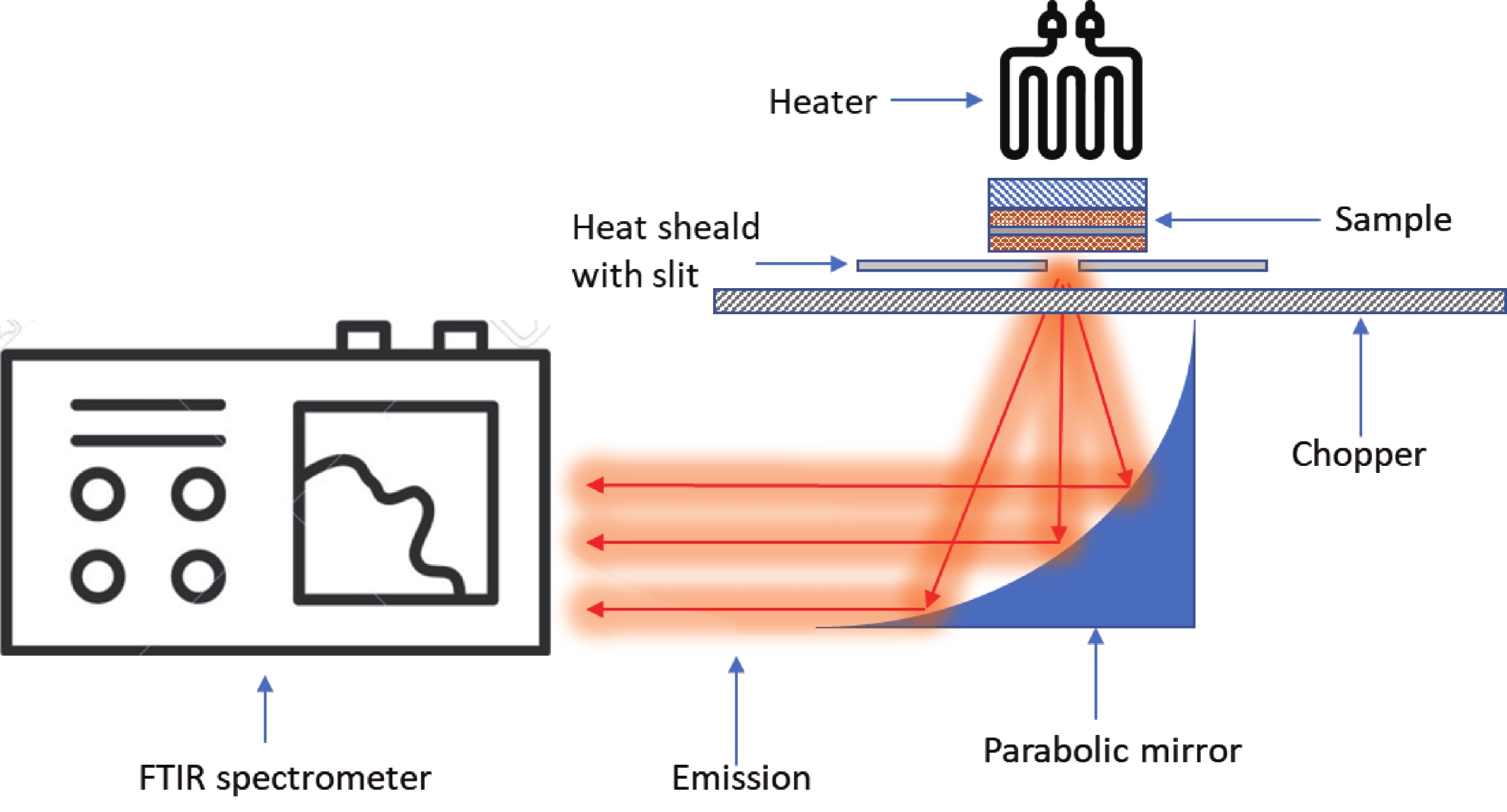
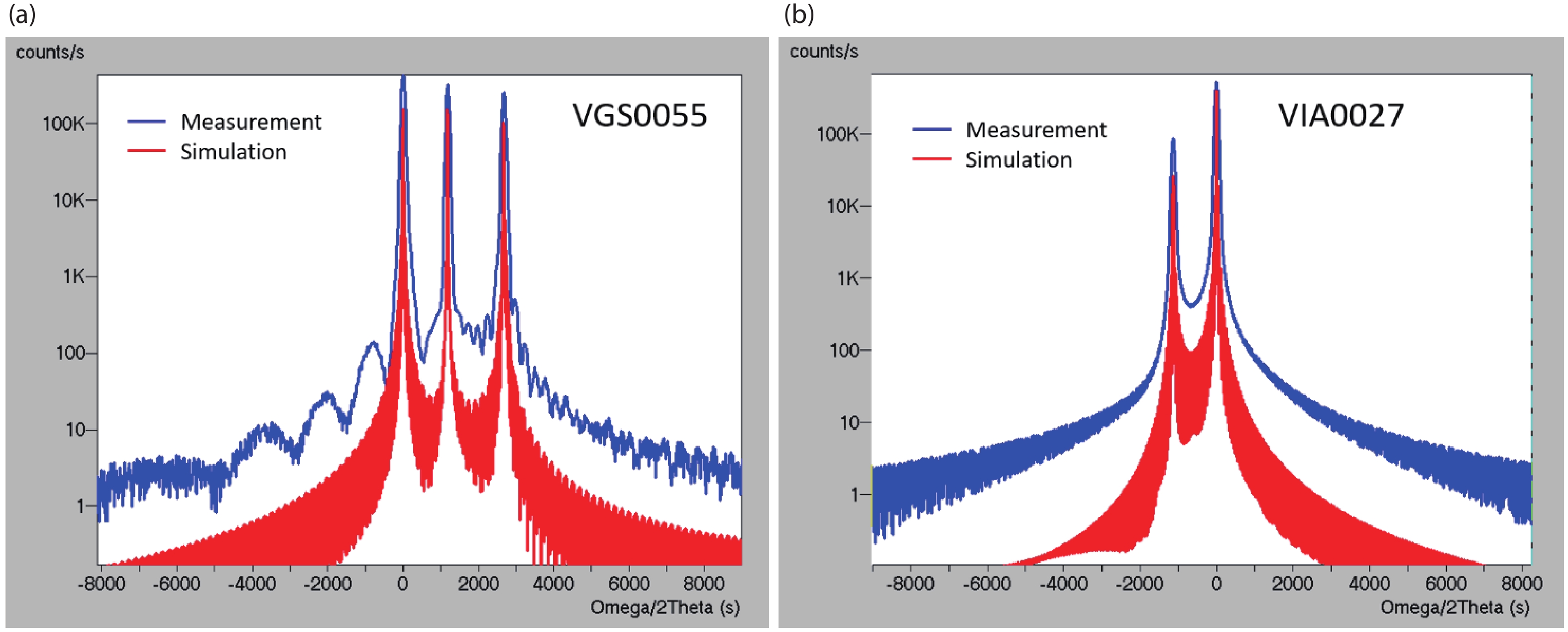
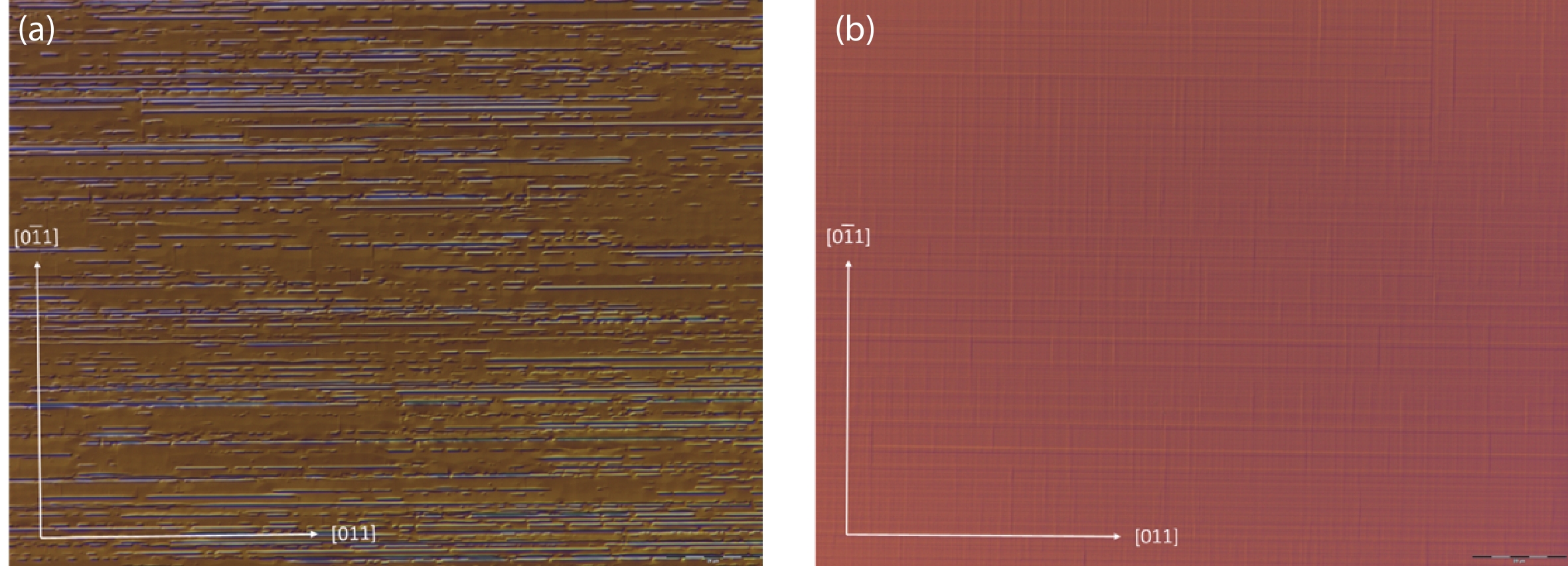
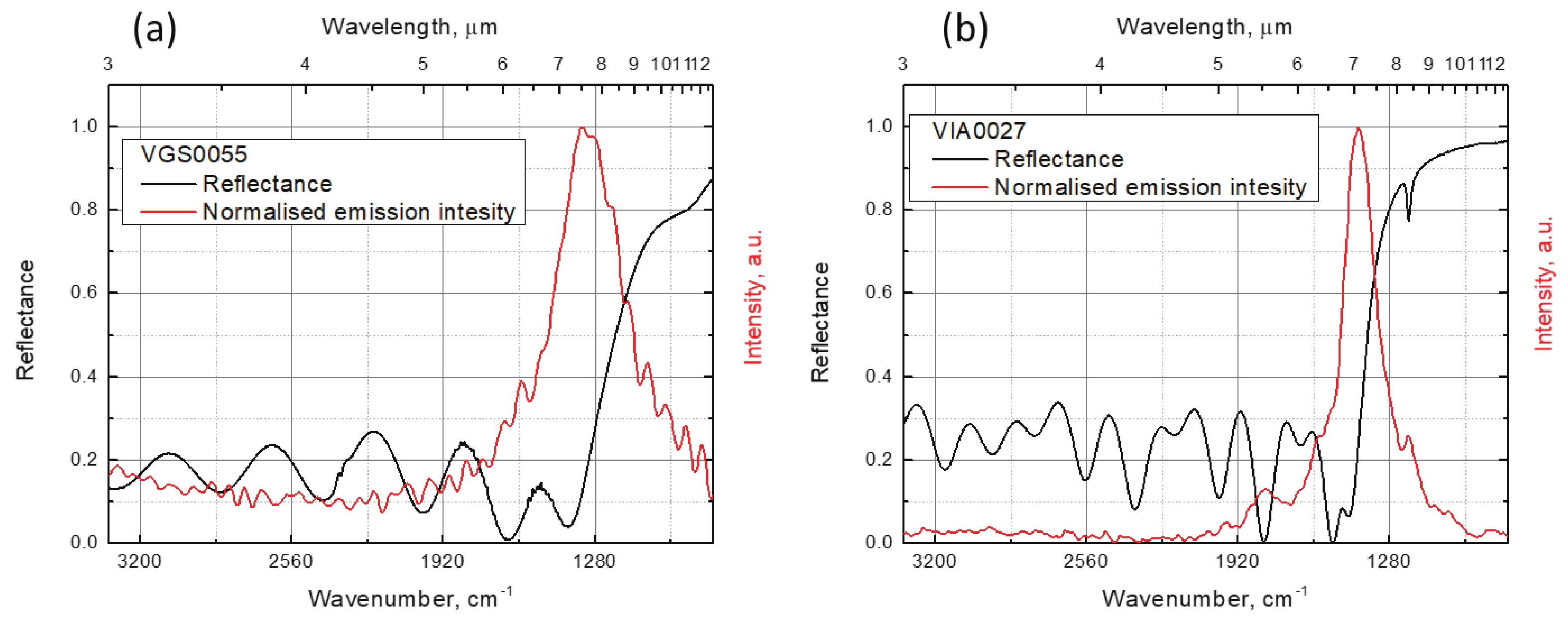
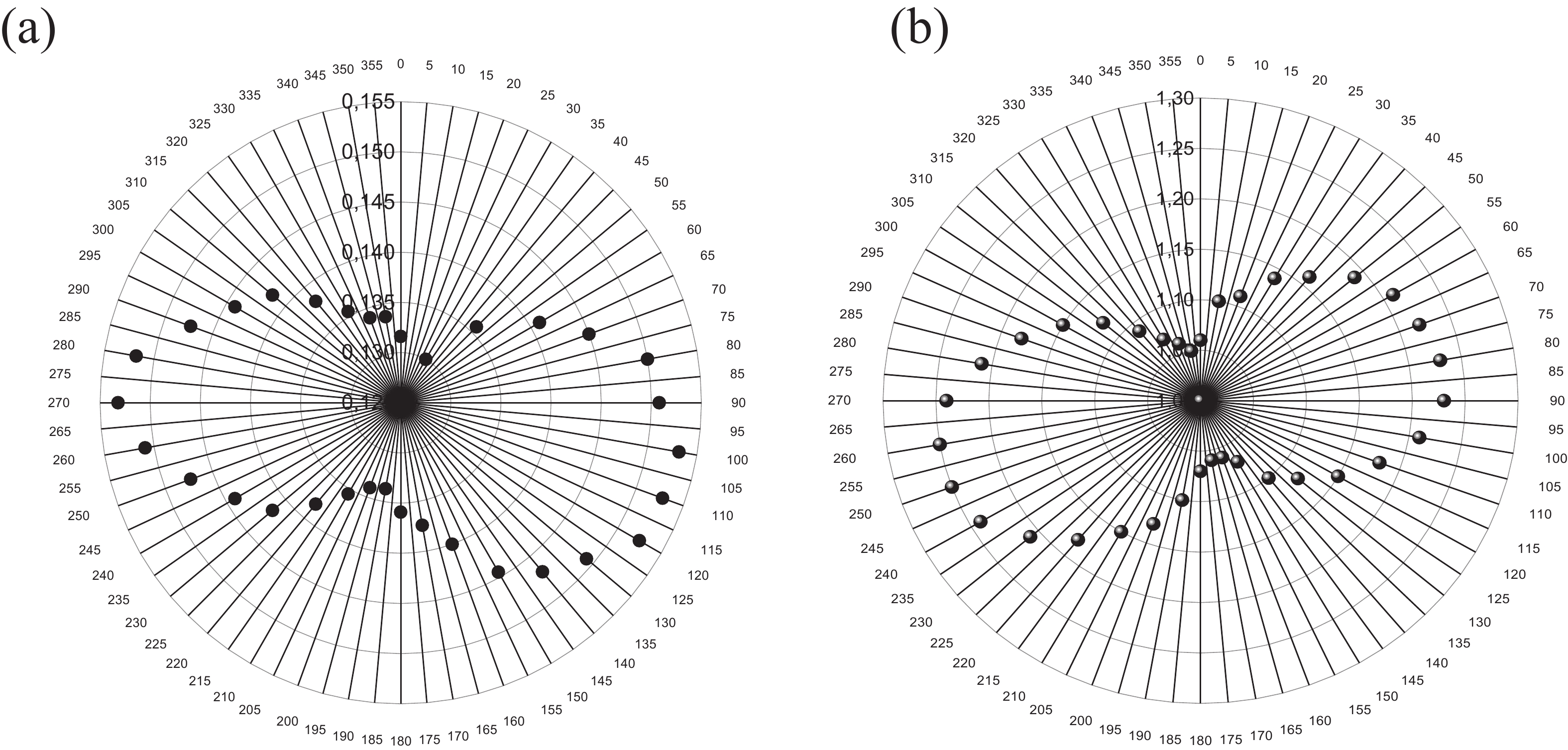
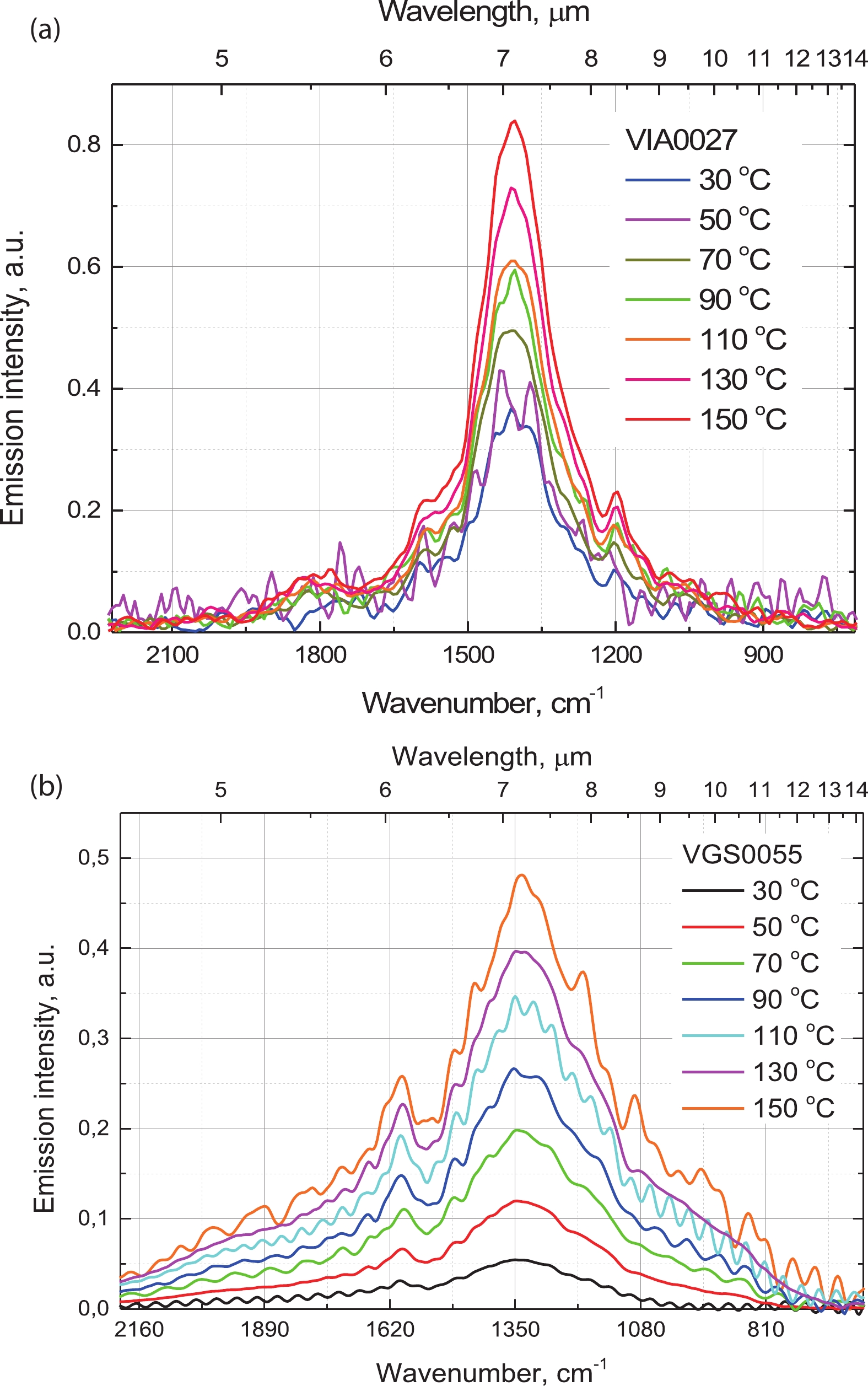
We introduce a novel method to create mid-infrared (MIR) thermal emitters using fully epitaxial, metal-free structures. Through the strategic use of epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) thin films in InAs layers, we achieve a narrow-band, wide-angle, and p-polarized thermal emission spectra. This approach, employing molecular beam epitaxy, circumvents the complexities associated with current layered structures and yields temperature-resistant emission wavelengths. Our findings contribute a promising route towards simpler, more efficient MIR optoelectronic devices. -
References
[1] Willer U, Saraji M, Khorsandi A, et al. Near- and mid-infrared laser monitoring of industrial processes, environment and security applications. Opt Lasers Eng, 2006, 44, 699 doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2005.04.015[2] Faist J, Capasso F, Sivco D L, et al. Quantum cascade laser. Science, 1994, 264, 553 doi: 10.1126/science.264.5158.553[3] Liu X X, Li Z W, Wen Z J, et al. Large-area, lithography-free, narrow-band and highly directional thermal emitter. Nanoscale, 2019, 11, 19742 doi: 10.1039/C9NR06181A[4] Lu G Y, Nolen J R, Folland T G, et al. Narrowband polaritonic thermal emitters driven by waste heat. ACS Omega, 2020, 5, 10900 doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00600[5] Wu J Y, Xie Z T, Sha Y H, et al. Epsilon-near-zero photonics: Infinite potentials. Photon Res, 2021, 9, 1616 doi: 10.1364/PRJ.427246[6] Jun Y C, Luk T S, Robert Ellis A, et al. Doping-tunable thermal emission from plasmon polaritons in semiconductor epsilon-near-zero thin films. Appl Phys Lett, 2014, 105, 13 doi: 10.1063/1.4896573[7] Hwang J S, Xu J, Raman A P. Simultaneous control of spectral and directional emissivity with gradient epsilon-near-zero InAs photonic structures. Adv Mater, 2023, 35, 2302956 doi: 10.1002/adma.202302956[8] Argyropoulos C, Le K Q, Mattiucci N, et al. Broadband absorbers and selective emitters based on plasmonic Brewster metasurfaces. Phys Rev B, 2013, 87, 205112 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.87.205112[9] Law S, Liu R Y, Wasserman D. Doped semiconductors with band-edge plasma frequencies. J Vac Sci Technol B, 2014, 32, 325 doi: doi.org/10.1116/1.4891170[10] Liu M Q, Xia S, Wan W J, et al. Broadband mid-infrared non-reciprocal absorption using magnetized gradient epsilon-near-zero thin films. Nat Mater, 2023, 22, 1196 doi: 10.1038/s41563-023-01635-9[11] Shiba M, Ikariyama R, Takushima M, et al. Properties of low-temperature-grown InAs and their changes upon annealing. J Cryst Growth, 2007, 301/302, 256 doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2006.11.140[12] Ciattoni A, Marini A, Rizza C, et al. Polariton excitation in epsilon-near-zero slabs: Transient trapping of slow light. Phys Rev A, 2013, 87, 053853 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.87.053853 -
Proportional views




 Karolis Stašys got his MSc degree from Vilnius University in 2014. Now he is a PhD student at State research institute Center for Physical Sciences and Technology under the supervision of Assoc. Prof. Jan Devenson. His research focuses on development of emitters and detectors for mid infrared range using molecular beam epitaxy.
Karolis Stašys got his MSc degree from Vilnius University in 2014. Now he is a PhD student at State research institute Center for Physical Sciences and Technology under the supervision of Assoc. Prof. Jan Devenson. His research focuses on development of emitters and detectors for mid infrared range using molecular beam epitaxy.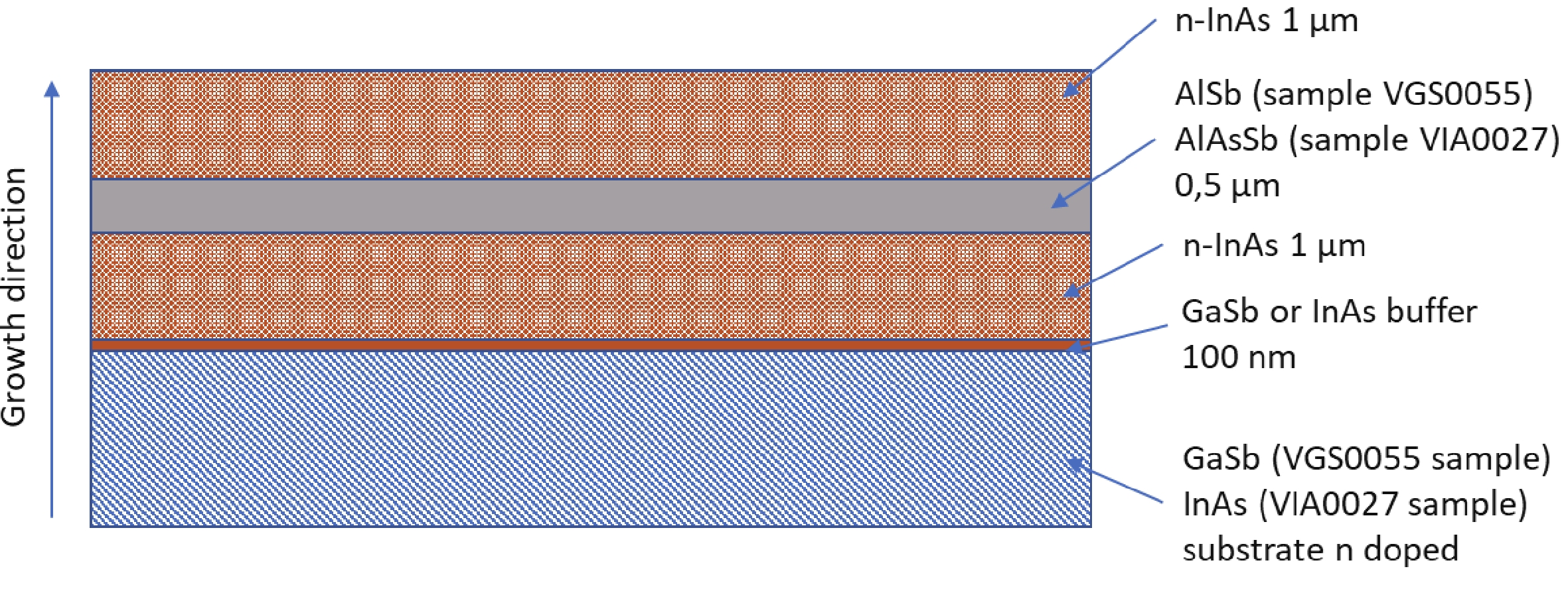
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: