| Citation: |
Lulu Zheng, Xianglong Bi, Xuhong Ma, Guibin Liu, Binbin Liu, Kang Zhou, Hua Li. Experimental study on phase noise of terahertz quantum cascade laser frequency comb and dual-comb sources[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2024, 45(12): 122401. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24060028
****
L L Zheng, X L Bi, X H Ma, G B Liu, B B Liu, K Zhou, and H Li, Experimental study on phase noise of terahertz quantum cascade laser frequency comb and dual-comb sources[J]. J. Semicond., 2024, 45(12), 122401 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24060028
|
Experimental study on phase noise of terahertz quantum cascade laser frequency comb and dual-comb sources
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/24060028
More Information
-
Abstract
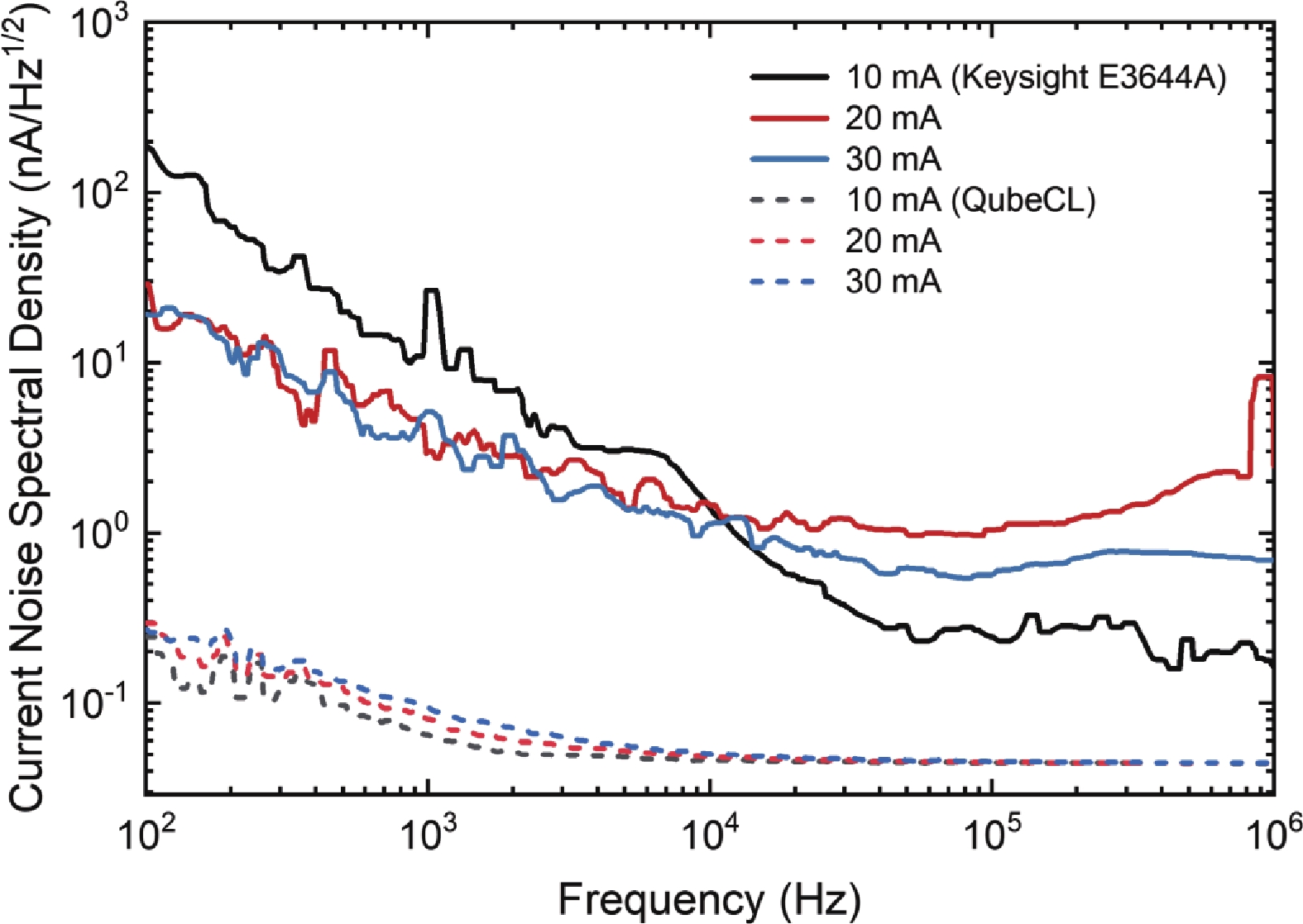
Frequency combs with equally spaced frequency lines show great potentials for applications in spectroscopy, imaging, communications, and so on. In the terahertz frequency region, the quantum cascade laser (QCL) is an ideal radiation source for frequency comb and dual-comb operation. The systematic evaluation of phase noise characteristics of terahertz QCL frequency comb and dual-comb sources is of great importance for high precision measurements. In this work, we present detailed measurements and analysis of the phase noise characteristics of terahertz QCL frequency comb and dual-comb sources emitting around 4.2 THz with repetition frequencies of ~6.2 GHz. The measurement results for the current noise of the direct current (DC) sources (that are used to electrically pump the terahertz QCLs) indicate that at 100 Hz, the current noise for DC-1 and DC-2 is 0.3895 and 0.0982 nA/Hz1/2, respectively. Such levels of current noise can be safely disregarded. The phase noise of radio frequency (RF) generators (that are employed for injection locking and phase locking), intermode beatnotes, and dual-comb signals with and without phase-locked loop (PLL) are all measured and compared. The experimental results show that in the free-running mode, the phase noise of the intermode beatnote signals is always lower than that of the dual-comb signals across all frequencies. Additionally, the phase noise induced by the RF generators is negligible. By employing the phase locking technique, the phase noise of the intermode beatnote and dual-comb signals in the low offset frequency band can be significantly suppressed. At an offset frequency of 100 Hz, the measured phase noise values of the dual-comb line without and with phase locking are 15.026 and −64.801 dBc/Hz, respectively.-
Keywords:
- terahertz,
- quantum cascade laser,
- frequency comb,
- dual-comb,
- phase noise
-
References
[1] Yang Y, Burghoff D, Hayton D J, et al. Terahertz multiheterodyne spectroscopy using laser frequency combs. Optica, 2016, 3, 499 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.3.000499[2] Zhang X C, Xu J Z. Introduction to THz wave photonics. Boston, MA: Springer US, 2010[3] Tonouchi M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nat Photonics, 2007, 1, 97 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.3[4] Faist J, Villares G, Scalari G, et al. Quantum cascade laser frequency combs. Nanophotonics, 2016, 5, 272 doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2016-0015[5] Diddams S A. The evolving optical frequency comb. J Opt Soc Am B, 2010, 27, B51 doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.27.000B51[6] Wilken T, Curto G L, Probst R A, et al. A spectrograph for exoplanet observations calibrated at the centimetre-per-second level. Nature, 2012, 485, 611 doi: 10.1038/nature11092[7] Baltuska A, Udem T, Uiberacker M, et al. Attosecond control of electronic processes by intense light fields. Nature, 2003, 421, 611 doi: 10.1038/nature01414[8] Hyun S, Kim Y J, Kim Y, et al. Absolute distance measurement using the frequency comb of a femtosecond laser. CIRP Ann, 2010, 59, 555 doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2010.03.039[9] Li H. Semiconductor-based terahertz frequency combs. J Semicond, 2019, 40, 050402 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/5/050402[10] Wang C J, Li Z P, Liao X Y, et al. Improved comb and dual-comb operation of terahertz quantum cascade lasers utilizing a symmetric thermal dissipation. Opt Express, 2021, 29, 29412 doi: 10.1364/OE.433938[11] Schiller S. Spectrometry with frequency combs. Opt Lett, 2002, 27, 766 doi: 10.1364/OL.27.000766[12] Khalatpour A, Paulsen A K, Deimert C, et al. High-power portable terahertz laser systems. Nat Photonics, 2021, 15, 16 doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-00707-5[13] Li L H, Chen L, Freeman J R, et al. Multi-Watt high-power THz frequency quantum cascade lasers. Electron Lett, 2017, 53, 799 doi: 10.1049/el.2017.0662[14] He T J, Liu S P, Li W, et al. Study of quantum well mixing induced by impurity-free vacancy in the primary epitaxial wafers of a 915 nm semiconductor laser. J Semicond, 2023, 44, 102302 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/10/102302[15] Liao X Y, Li Z P, Zhou K, et al. Broadband terahertz quantum cascade laser dual-comb sources under off-resonant microwave injection. Adv Photonics Res, 2022, 3, 2100361 doi: 10.1002/adpr.202100361[16] Zhao Y R, Li Z P, Zhou K, et al. Active stabilization of terahertz semiconductor dual-comb laser sources employing a phase locking technique. Laser Photonics Rev, 2021, 15, 2000498 doi: 10.1002/lpor.202000498[17] Xu Y F, Li W J, Ma Y, et al. Phase-locked single-mode terahertz quantum cascade lasers array. J Semicond, 2024, 45, 062401 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/23120010[18] Rösch M, Scalari G, Beck M, et al. Octave-spanning semiconductor laser. Nat Photonics, 2015, 9, 42 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.279[19] Zhou K, Li H, Wan W J, et al. Ridge width effect on comb operation in terahertz quantum cascade lasers. Appl Phys Lett, 2019, 114, 191101 doi: 10.1063/1.5092436[20] Guan W, Liao X Y, Li Z P, et al. Frequency tuning behaviour of terahertz quantum cascade lasers revealed by a laser beating scheme. Opt Express, 2021, 29, 21269 doi: 10.1364/OE.427326[21] Tombez L, Di Francesco J, Schilt S, et al. Frequency noise of free-running 46 μm distributed feedback quantum cascade lasers near room temperature. Opt Lett, 2011, 36, 3109 doi: 10.1364/OL.36.003109[22] Li H, Yan M, Wan W J, et al. Graphene-coupled terahertz semiconductor lasers for enhanced passive frequency comb operation. Adv Sci, 2019, 6, 1900460 doi: 10.1002/advs.201900460[23] Wan W J, Li H, Zhou T, et al. Homogeneous spectral spanning of terahertz semiconductor lasers with radio frequency modulation. Sci Rep, 2017, 7, 44109 doi: 10.1038/srep44109[24] Li H, Li Z P, Wan W J, et al. Toward compact and real-time terahertz dual-comb spectroscopy employing a self-detection scheme. ACS Photonics, 2020, 7, 49 doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.9b01427[25] Guan W, Li Z P, Wu S M, et al. Relative phase locking of a terahertz laser system configured with a frequency comb and a single-mode laser. Adv Photon Nexus, 2023, 2, 026006 doi: 10.1117/1.APN.2.2.026006[26] Guan W, Li Z P, Zhou K, et al. Repetition frequency locking of a terahertz quantum cascade laser emitting at 4.2 THz. Terahertz Sci Technol, 2020, 13, 32 doi: 10.1051/tst/2020131032 -
Proportional views




 Lulu Zheng received her bachelor's degree from Hebei University of Technology in 2022. Now she is a master’s student at Shanghai Institute of Microsystems and Information Technology (SIMIT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Her research focuses on phase noise analysis of terahertz quantum cascade laser frequency combs.
Lulu Zheng received her bachelor's degree from Hebei University of Technology in 2022. Now she is a master’s student at Shanghai Institute of Microsystems and Information Technology (SIMIT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Her research focuses on phase noise analysis of terahertz quantum cascade laser frequency combs. Hua Li received his PhD from Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology (SIMIT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) in 2009. From 2009 to 2015, he worked at Technical University of Munich, University of Tokyo, and University Paris 7 as a postdoctoral research fellow. Since 2015, he has been with SIMIT, CAS as a professor. His research group focuses on physics, devices, and applications of semiconductor lasers, frequency comb, and dual-comb sources emitting in the terahertz frequency range.
Hua Li received his PhD from Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology (SIMIT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) in 2009. From 2009 to 2015, he worked at Technical University of Munich, University of Tokyo, and University Paris 7 as a postdoctoral research fellow. Since 2015, he has been with SIMIT, CAS as a professor. His research group focuses on physics, devices, and applications of semiconductor lasers, frequency comb, and dual-comb sources emitting in the terahertz frequency range.
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: