| Citation: |
Shuo Li, Wenxu Yin, Weitao Zheng, Xiaoyu Zhang. Size matters: quantum confinement-driven dynamics in CsPbI3 quantum dot light-emitting diodes[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2025, 46(4): 042103. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24120018
****
S Li, W X Yin, W T Zheng, and X Y Zhang, Size matters: quantum confinement-driven dynamics in CsPbI3 quantum dot light-emitting diodes[J]. J. Semicond., 2025, 46(4), 042103 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24120018
|
Size matters: quantum confinement-driven dynamics in CsPbI3 quantum dot light-emitting diodes
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/24120018
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.24120018
More Information-
Abstract
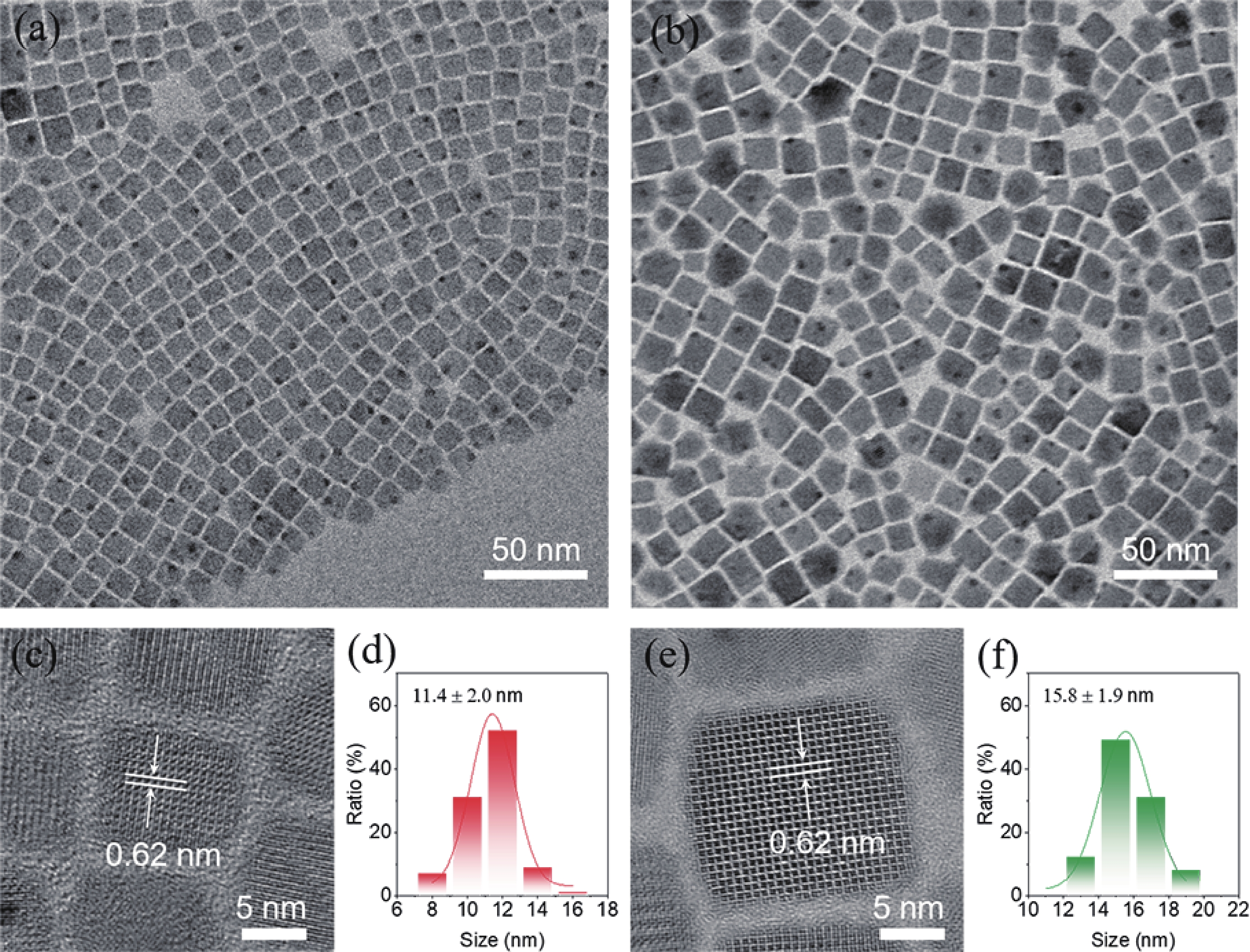
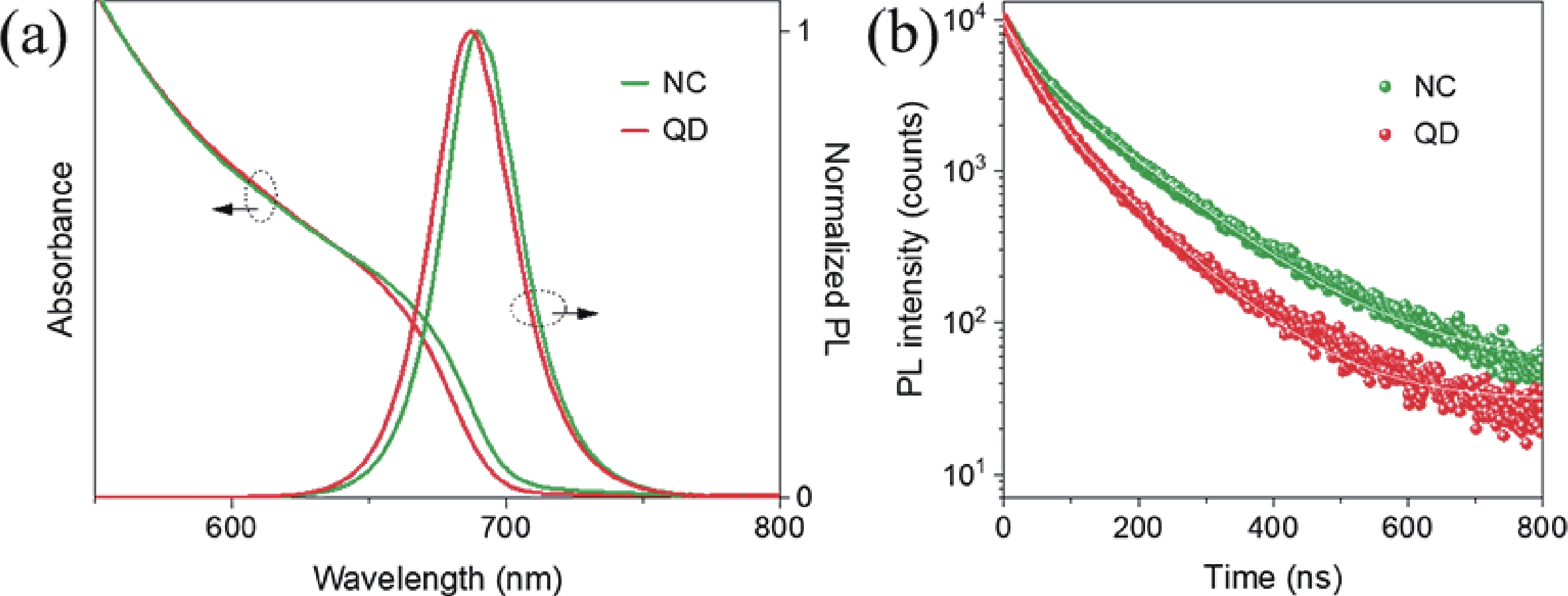
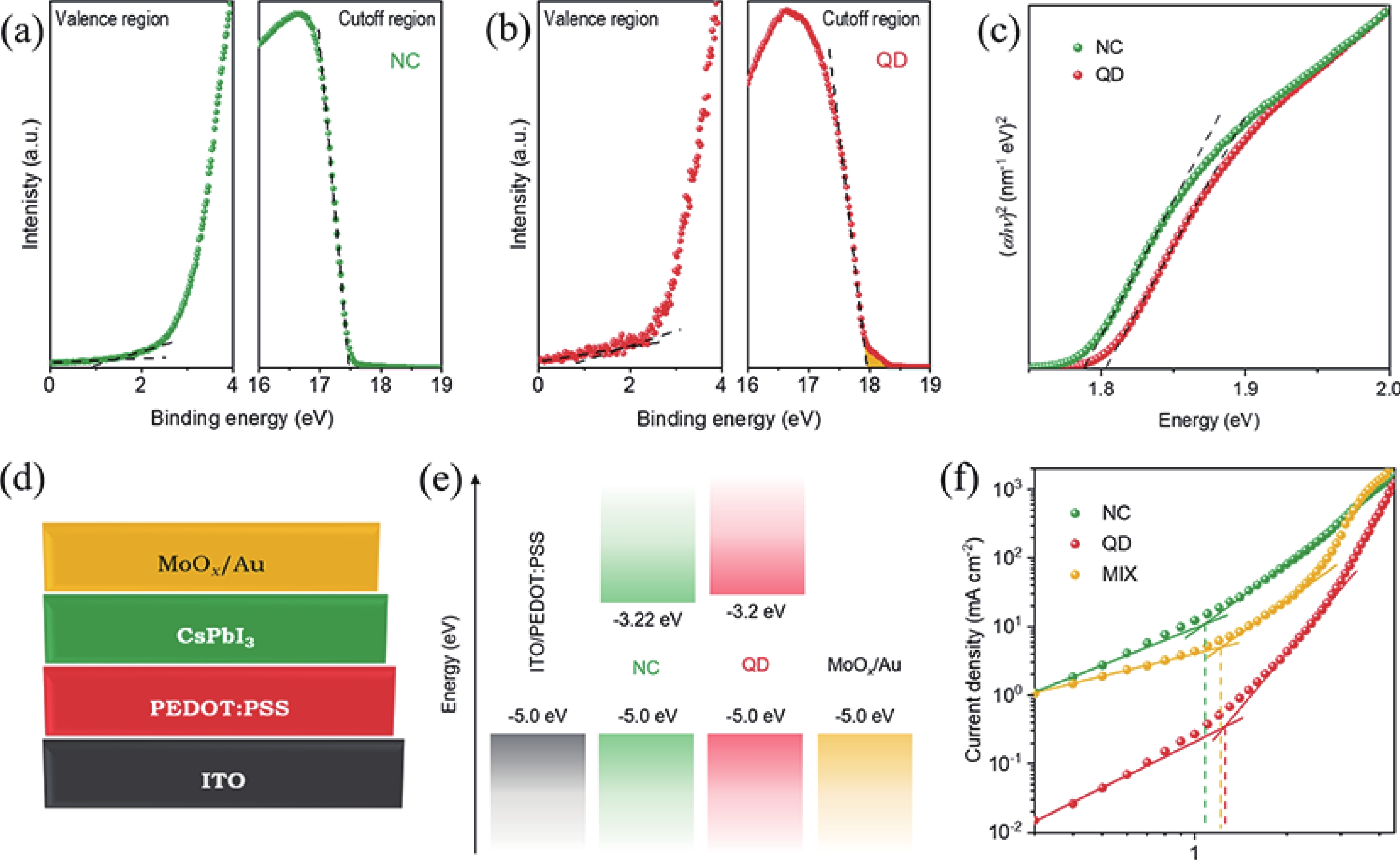
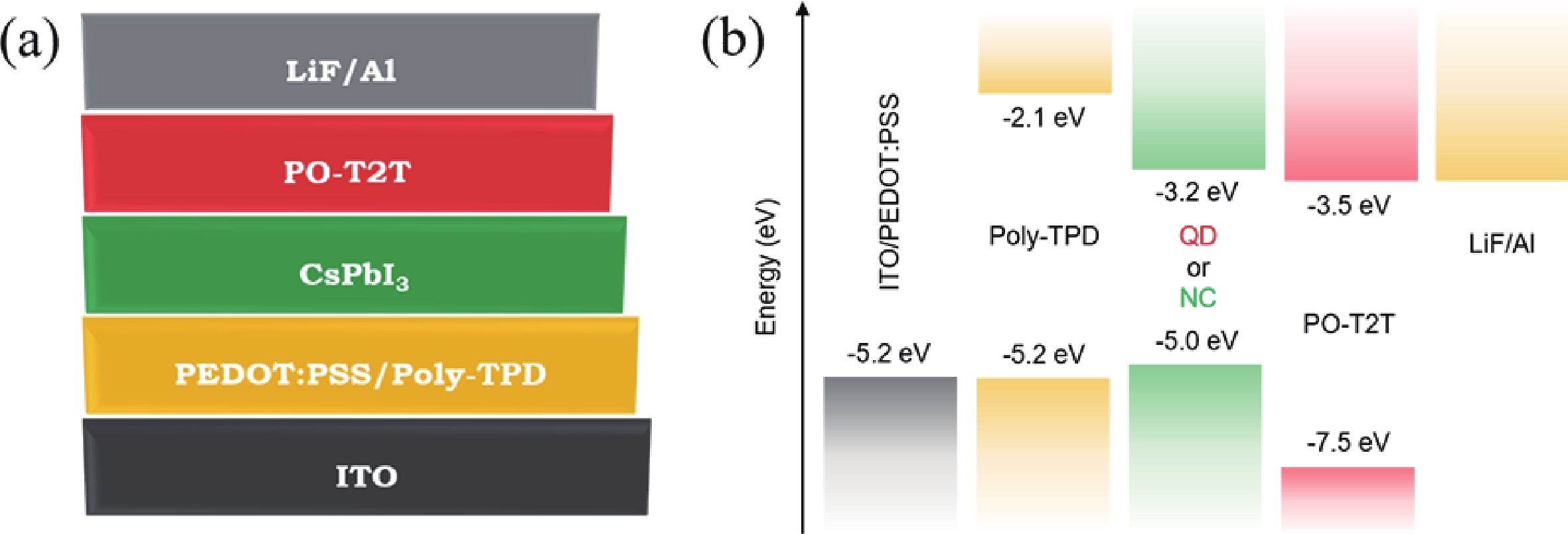
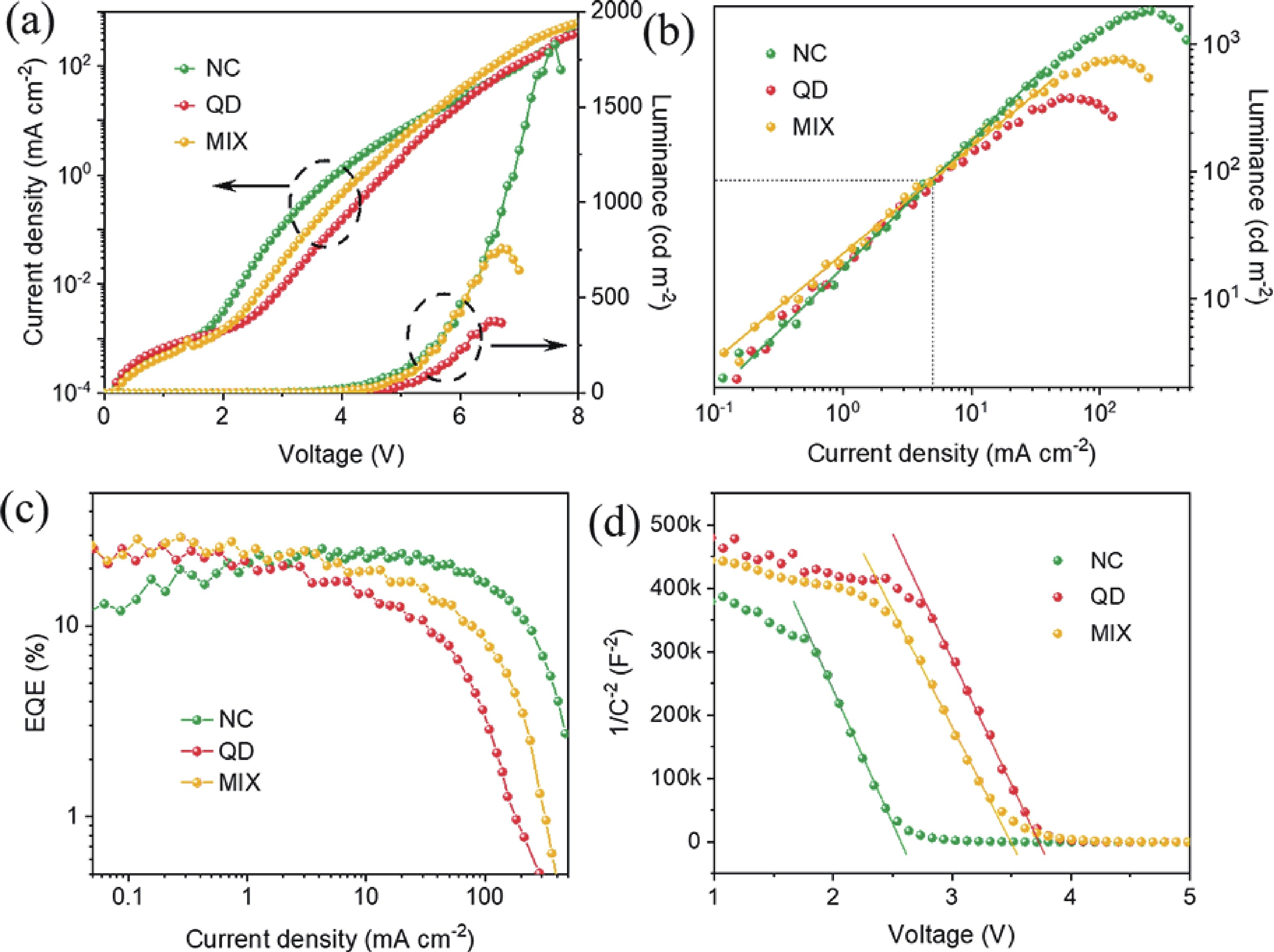
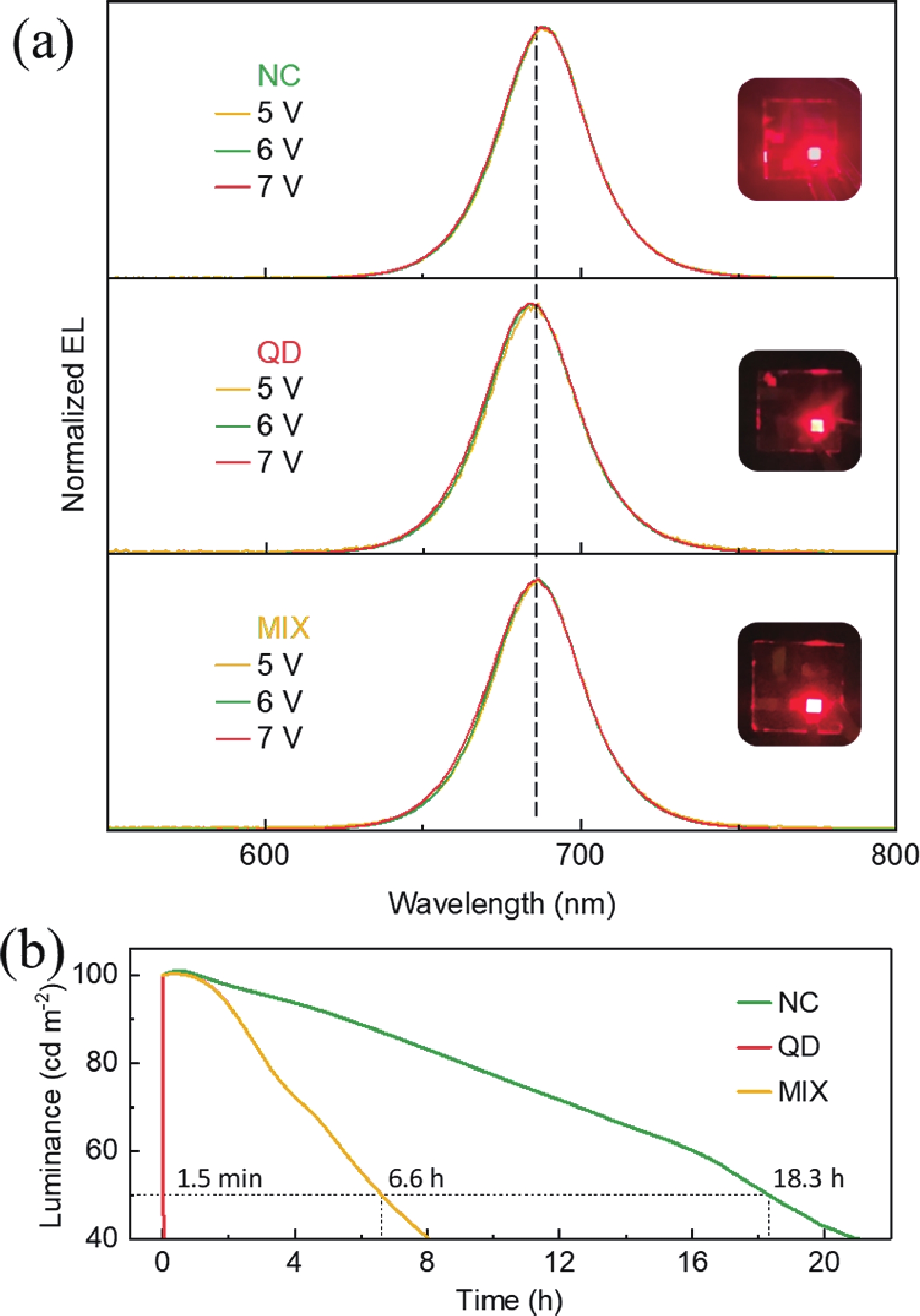
The quantum confinement effect fundamentally alters the optical and electronic properties of quantum dots (QDs), making them versatile building blocks for next-generation light-emitting diodes (LEDs). This study investigates how quantum confinement governs the charge transport, exciton dynamics, and emission efficiency in QD-LEDs, using CsPbI3 QDs as a model system. By systematically varying QD sizes, we reveal size-dependent trade-offs in LED performance, such as enhanced efficiency for smaller QDs but increased brightness and stability for larger QDs under high current densities. Our findings offer critical insights into the design of high-performance QD-LEDs, paving the way for scalable and energy-efficient optoelectronic devices.-
Keywords:
- quantum confinement effect,
- CsPbI3,
- quantum dot,
- light-emitting diode
-
References
[1] Alivisatos A P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science, 1996, 271(5251), 933 doi: 10.1126/science.271.5251.933[2] Chen O, Zhao J, Chauhan V P, et al. Compact high-quality CdSe-CdS core-shell nanocrystals with narrow emission linewidths and suppressed blinking. Nat Mater, 2013, 12(5), 445 doi: 10.1038/nmat3539[3] Cho K S, Lee E K, Joo W J, et al. High-performance crosslinked colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Nat Photonics, 2009, 3(6), 341 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2009.92[4] Dai X L, Deng Y Z, Peng X G, et al. Quantum-dot light-emitting diodes for large-area displays: Towards the dawn of commercialization. Adv Mater, 2017, 29(14), 1607022 doi: 10.1002/adma.201607022[5] Li X Y, Zhao Y B, Fan F J, et al. Bright colloidal quantum dot light-emitting diodes enabled by efficient chlorination. Nat Photonics, 2018, 12(3), 159 doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0105-8[6] Shirasaki Y, Supran G J, Bawendi M G, et al. Emergence of colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting technologies. Nat Photonics, 2013, 7(1), 13 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.328[7] Yang Y X, Zheng Y, Cao W R, et al. High-efficiency light-emitting devices based on quantum dots with tailored nanostructures. Nat Photonics, 2015, 9(4), 259 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2015.36[8] Yoo J, Lee K, Yang U J, et al. Highly efficient printed quantum dot light-emitting diodes through ultrahigh-definition double-layer transfer printing. Nat Photonics, 2024, 18(10), 1105 doi: 10.1038/s41566-024-01496-x[9] Wang Y K, Wan H Y, Teale S, et al. Long-range order enabled stability in quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nature, 2024, 629(8012), 586 doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07363-7[10] Gao P L, Chen Z N, Chen S M. Electron-induced degradation in blue quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater, 2024, 36(7), e2309123 doi: 10.1002/adma.202309123[11] Kim D C, Seung H, Yoo J, et al. Intrinsically stretchable quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nat Electron, 2024, 7(5), 365 doi: 10.1038/s41928-024-01152-w[12] Su Y R, Ma W B, Yang Y. Perovskite semiconductors for direct X-ray detection and imaging. J Semicond, 2020, 41(5), 051204 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/5/051204[13] Tamarat P, Prin E, Berezovska Y, et al. Universal scaling laws for charge-carrier interactions with quantum confinement in lead-halide perovskites. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1), 229 doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-35842-4[14] Chi W G, Banerjee S K. Application of perovskite quantum dots as an absorber in perovskite solar cells. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2022, 61(9), e202112412 doi: 10.1002/anie.202112412[15] Li Y M, Deng M, Zhang X Y, et al. Stable and efficient CsPbI3 quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with strong quantum confinement. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1), 5696 doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50022-8[16] Bera D, Qian L, Tseng T K, et al. Quantum dots and their multimodal applications: A review. Materials, 2010, 3(4), 2260 doi: 10.3390/ma3042260[17] Polavarapu L, Nickel B, Feldmann J, et al. Advances in quantum-confined perovskite nanocrystals for optoelectronics. Adv Energy Mater, 2017, 7(16), 1700267 doi: 10.1002/aenm.201700267[18] Li W Z, Fan J D, Ding L M. Multidimensional perovskites enhance solar cell performance. J Semicond, 2021, 42(2), 020201 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/2/020201[19] Ye F J, Yang W Q, Luo D Y, et al. Applications of cesium in the perovskite solar cells. J Semicond, 2017, 38(1), 011003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/1/011003[20] Bae W K, Park Y S, Lim J, et al. Controlling the influence of Auger recombination on the performance of quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Nat Commun, 2013, 4(1), 2661 doi: 10.1038/ncomms3661[21] Li Q Y, Wu K F, Zhu H M, et al. Charge transfer from quantum-confined 0D, 1D, and 2D nanocrystals. Chem Rev, 2024, 124(9), 5695 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00742[22] Liu X F, Zhang Q, Xing G C, et al. Size-dependent exciton recombination dynamics in single CdS nanowires beyond the quantum confinement regime. J Phys Chem C, 2013, 117(20), 10716 doi: 10.1021/jp312850w[23] Kovalenko M V, Protesescu L, Bodnarchuk M I. Properties and potential optoelectronic applications of lead halide perovskite nanocrystals. Science, 2017, 358(6364), 745 doi: 10.1126/science.aam7093[24] Lu M, Zhang Y, Wang S X, et al. Metal halide perovskite light-emitting devices: Promising technology for next-generation displays. Adv Funct Materials, 2019, 29(30), 1902008 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201902008[25] Han T H, Jang K Y, Dong Y T, et al. A roadmap for the commercialization of perovskite light emitters. Nat Rev Mater, 2022, 7(10), 757 doi: 10.1038/s41578-022-00459-4[26] Han B N, Shan Q S, Zhang F J, et al. Giant efficiency and color purity enhancement in multicolor inorganic perovskite light-emitting diodes via heating-assisted vacuum deposition. J Semicond, 2020, 41(5), 052205 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/5/052205[27] Du J S, Shin D, Stanev T K, et al. Halide perovskite nanocrystal arrays: Multiplexed synthesis and size-dependent emission. Sci Adv, 2020, 6(39), eabc4959 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abc4959[28] Jiang Y Z, Wei K Y, Sun C J, et al. Unraveling size-dependent ion-migration for stable mixed-halide perovskite light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater, 2023, 35(39), e2304094 doi: 10.1002/adma.202304094[29] Kim Y H, Wolf C, Kim Y T, et al. Highly efficient light-emitting diodes of colloidal metal-halide perovskite nanocrystals beyond quantum size. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(7), 6586 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b07617[30] Feng A B, Jiang X M, Zhang X Y, et al. Shape control of metal halide perovskite single crystals: From bulk to nanoscale. Chem Mater, 2020, 32(18), 7602 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c02269[31] Jiang X M, Xia S Q, Zhang J, et al. Exploring organic metal halides with reversible temperature-responsive dual-emissive photoluminescence. ChemSusChem, 2019, 12(24), 5228 doi: 10.1002/cssc.201902481[32] Li H J, Feng Y F, Zhu M Y, et al. Nanosurface-reconstructed perovskite for highly efficient and stable active-matrix light-emitting diode display. Nat Nanotechnol, 2024, 19(5), 638 doi: 10.1038/s41565-024-01652-y[33] Wang Y, Zhang T Y, Kan M, et al. Bifunctional stabilization of all-inorganic α-CsPbI3 perovskite for 17% efficiency photovoltaics. J Am Chem Soc, 2018, 140(39), 12345 doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b07927[34] Hu Y Q, Bai F, Liu X B, et al. Bismuth incorporation stabilized α-CsPbI3 for fully inorganic perovskite solar cells. ACS Energy Lett, 2017, 2(10), 2219 doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.7b00508[35] Aleiner I L, Brouwer P W, Glazman L I. Quantum effects in coulomb blockade. Phys Rep, 2002, 358(5), 309 doi: 10.1016/S0370-1573(01)00063-1[36] Patel S R, Cronenwett S M, Stewart D R, et al. Statistics of coulomb blockade peak spacings. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 80(20), 4522 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.4522[37] Kong L M, Zhang X Y, Zhang C X, et al. Stability of perovskite light-emitting diodes: Existing issues and mitigation strategies related to both material and device aspects. Adv Mater, 2022, 34(43), e2205217 doi: 10.1002/adma.202205217[38] Jeong J E, Park J H, Jang C H, et al. Multifunctional charge transporting materials for perovskite light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater, 2020, 32(51), e2002176 doi: 10.1002/adma.202002176 -
Supplements
 24120018SI.pdf
24120018SI.pdf

-
Proportional views




 Shuo Li received his bachelor's degree from Inner Mongolia University in 2020, and he is currently pursuing a PhD in the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Jilin University under the supervision of Professor Zhang Xiaoyu. He is mainly engaged in the stability research of metal halide perovskite light-emitting diodes.
Shuo Li received his bachelor's degree from Inner Mongolia University in 2020, and he is currently pursuing a PhD in the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Jilin University under the supervision of Professor Zhang Xiaoyu. He is mainly engaged in the stability research of metal halide perovskite light-emitting diodes. Xiaoyu Zhang serves as a doctoral supervisor at the School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jilin University. His research is centered on quantum dot materials and their applications in optoelectronic devices. To date, he has published 124 SCI papers, with 14 of these being recognized as ESI highly cited papers. His work has garnered over 10 000 citations, and he maintains an H-index of 50.
Xiaoyu Zhang serves as a doctoral supervisor at the School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jilin University. His research is centered on quantum dot materials and their applications in optoelectronic devices. To date, he has published 124 SCI papers, with 14 of these being recognized as ESI highly cited papers. His work has garnered over 10 000 citations, and he maintains an H-index of 50.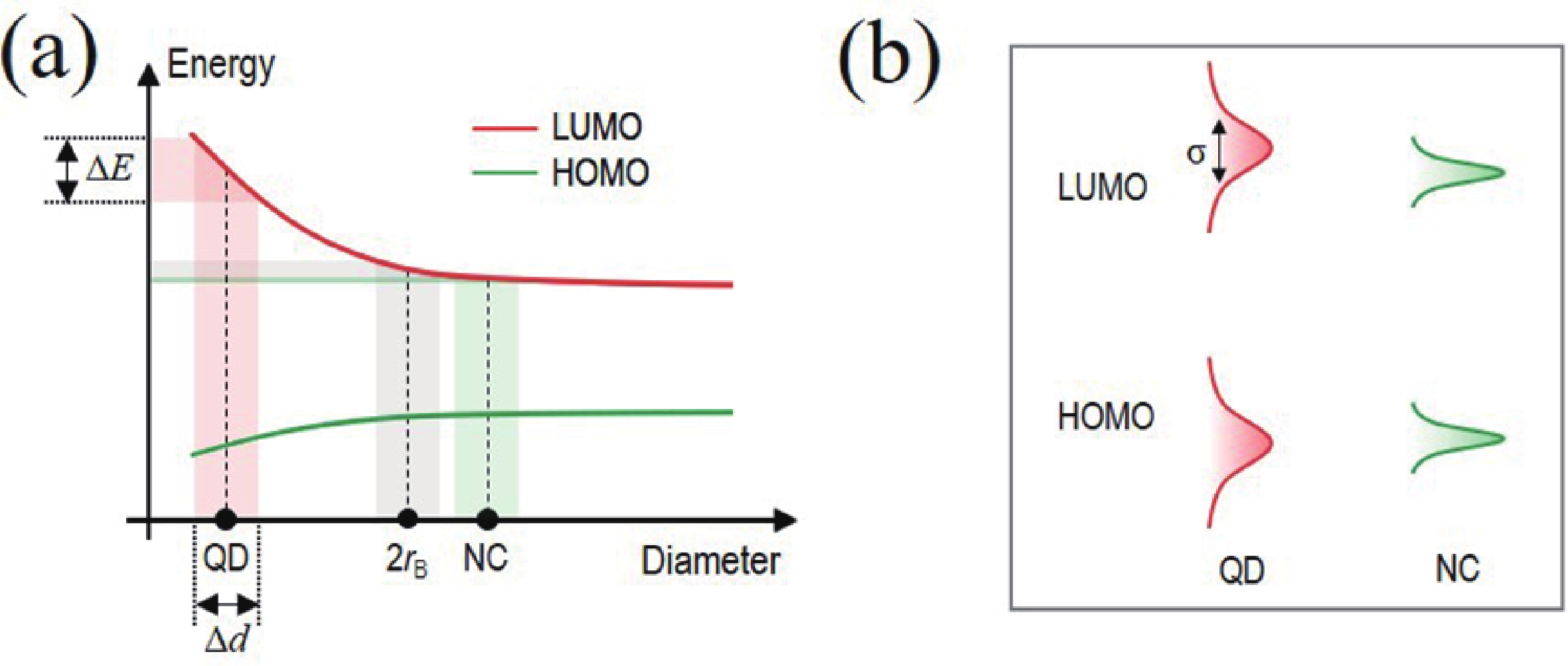
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: