| Citation: |
Qiuyang He, Yue Xu, Feifei Zhao. An accurate simulation model for single-photon avalanche diodes including important statistical effects[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(10): 104007. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/10/104007
****
Q Y He, Y Xu, F F Zhao. An accurate simulation model for single-photon avalanche diodes including important statistical effects[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(10): 104007. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/10/104007.
|
An accurate simulation model for single-photon avalanche diodes including important statistical effects
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/10/104007
More Information
-
Abstract
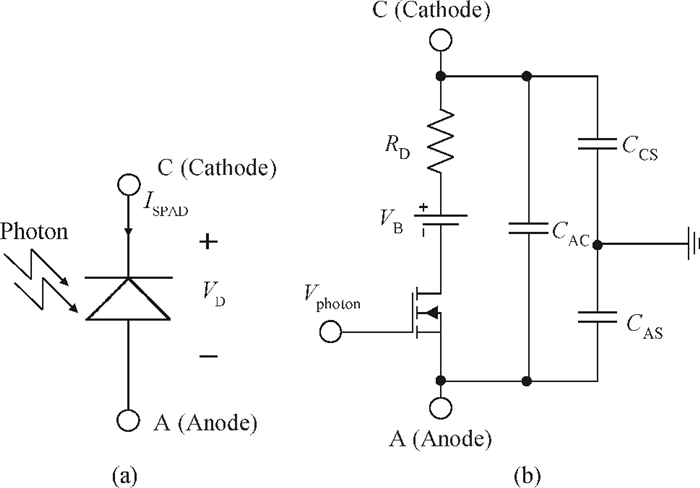
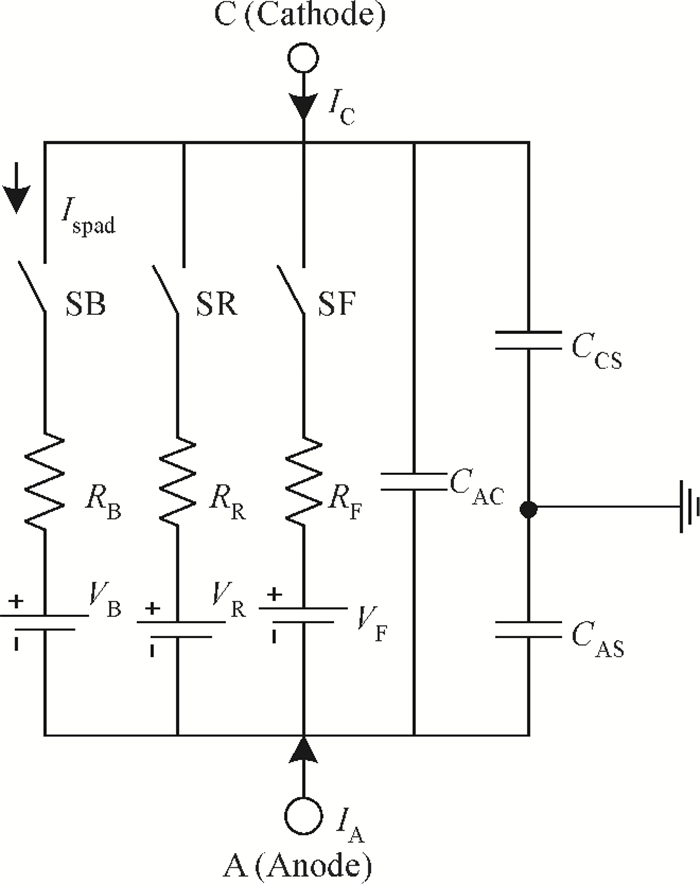
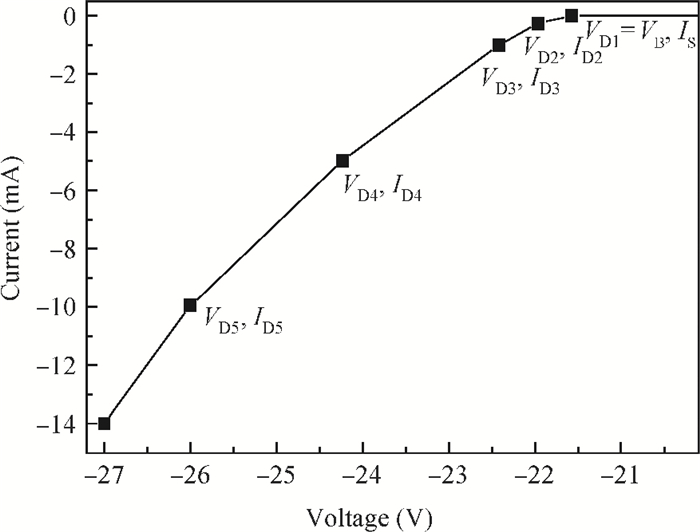
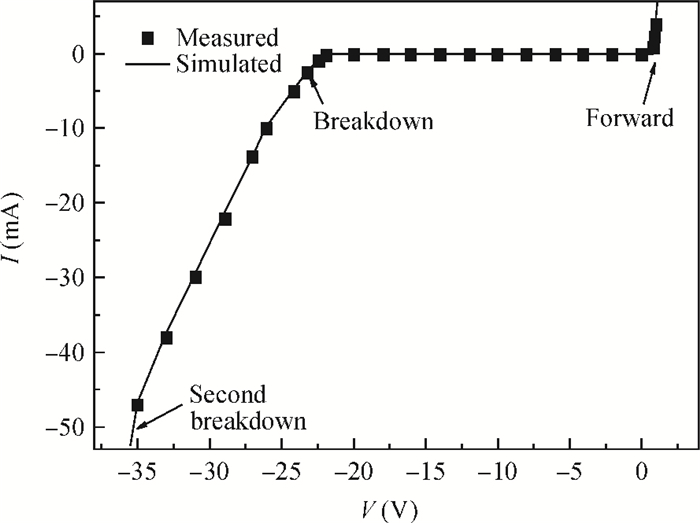
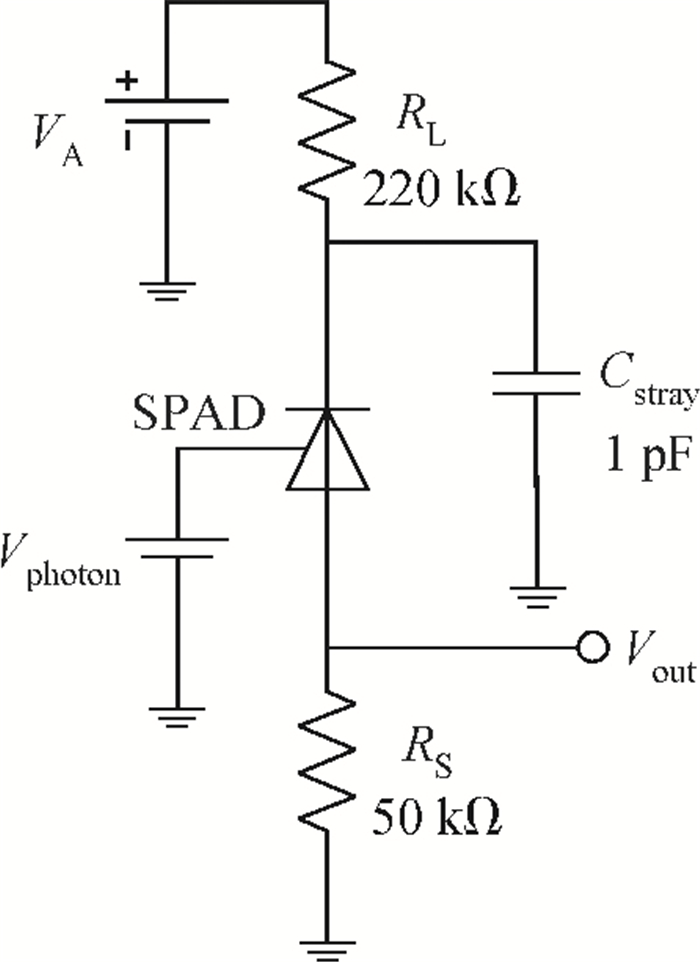
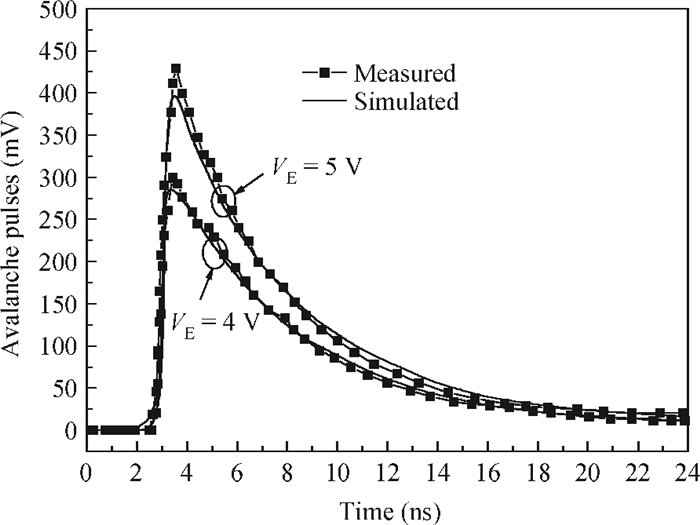
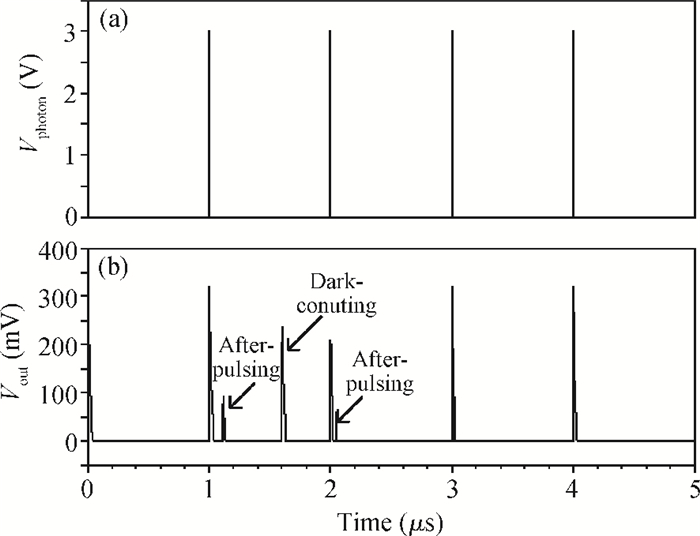
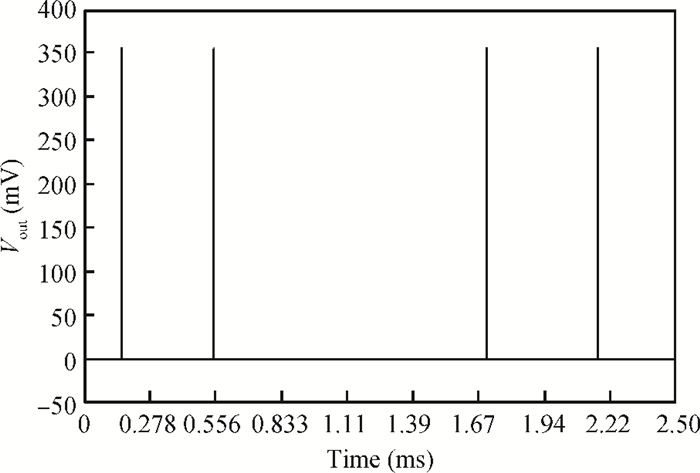
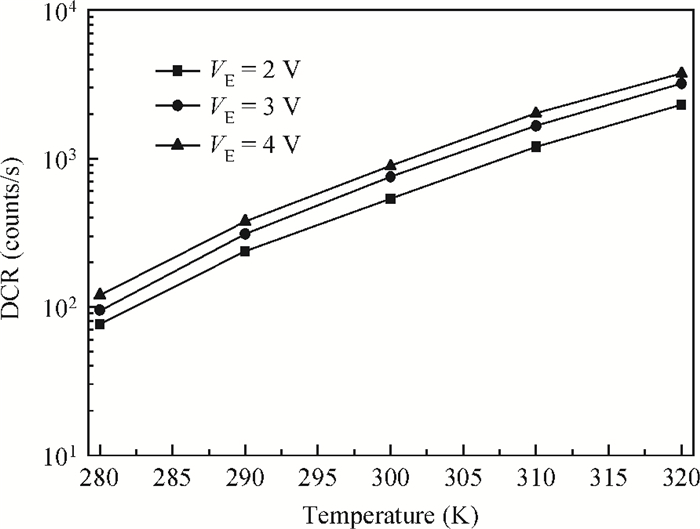
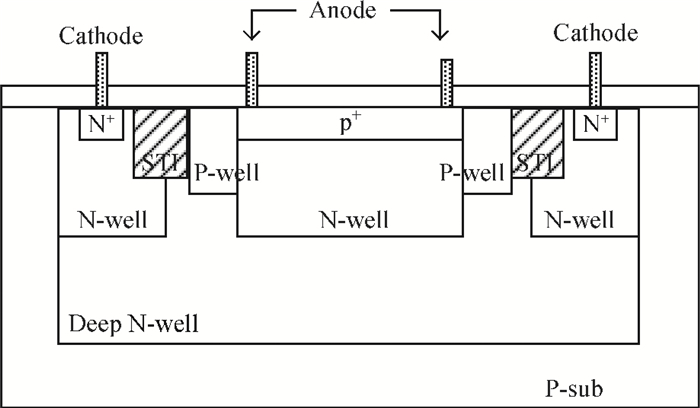
An accurate and complete circuit simulation model for single-photon avalanche diodes (SPADs) is presented. The derived model is not only able to simulate the static DC and dynamic AC behaviors of an SPAD operating in Geiger-mode, but also can emulate the second breakdown and the forward bias behaviors. In particular, it considers important statistical effects, such as dark-counting and after-pulsing phenomena. The developed model is implemented using the Verilog-A description language and can be directly performed in commercial simulators such as Cadence Spectre. The Spectre simulation results give a very good agreement with the experimental results reported in the open literature. This model shows a high simulation accuracy and very fast simulation rate. -
References
[1] Guerrieri F, Tisa S, Tosi A, et al. Two-dimensional SPAD imaging camera for photon counting. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2010, 2(5):759 doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2010.2066554[2] Rech I, Cova S, Restelli A, et al. Microchips and single-photon avalanche diodes for DNA separation with high sensitivity. Electrophoresis, 2006, 27(19):3797 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1522-2683[3] Felekyan S, Kühnemuth R, Kudryavtsev V, et al. Full correlation from picoseconds to seconds by time-resolved and time-correlated single photon detection. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2005, 76(8):083104 doi: 10.1063/1.1946088[4] Squillante M R, Gordon J S. Recent advances in avalanche photodiode technology. SPIE, 2003, 5071:405 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4137571/[5] Faramarzpour N, Deen M J, Shirani S, et al. Fully integrated single photon avalanche diode detector in standard CMOS 0.18-μm technology. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2008, 55(3):760 doi: 10.1109/TED.2007.914839[6] Richardson J A, Webster E A G, Grant L A, et al. Scaleable single-photon avalanche diode structures in nanometer CMOS technology. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2011, 58(7):2028 doi: 10.1109/TED.2011.2141138[7] Cova S, Ghioni M, Lacaita A, et al. Avalanche photodiodes and quenching circuits for single-photon detection. Appl Opt, 1996, 35(12):1956 doi: 10.1364/AO.35.001956[8] Mita R, Palumbo G. High-speed and compact quenching circuit for single-photon avalanche diodes. IEEE Trans Instrumentation and Measurement, 2008, 57(3):543 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2007.911691[9] Marwick M A, Andreou A G. Single photon avalanche photodetector with integrated quenching fabricated in TSMC 0.18μm 1.8 V CMOS process. Electron Lett, 2008, 44(10):643 doi: 10.1049/el:20080673[10] Cova S, Longoni A, Andreoni A. Towards pocosecond resolution with single-photon avalanche diodes. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1981, 52(3):408 doi: 10.1063/1.1136594[11] Zappa F, Tosi A, Mora A D, et al. Spice modeling of single photon avalanche diodes. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2009, 153(2):197 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2009.05.007[12] Mora A D, Tosi A, Tisa S, et al. Single-photon avalanche diode model for circuit simulations. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2007, 19(23):1922 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2007.908768[13] Mita R, Palumbo G, Fallica P G. Accurate model for single-photon avalanche diodes. Circuits, IET Devices & Systems, 2008, 2(2):207 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4490223/?reload=true&arnumber=4490223[14] Kang Y, Lu H X, Lo Y H. Dark count probability and quantum efficiency of avalanche photodiodes for single-photon detection. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 83(14):2955 doi: 10.1063/1.1616666[15] Ramirez D, Hayat M, Karve G, et al. Detection efficiencies and generalized breakdown probabilities for nano second-gated near infrared single-photon avalanche photodiodes. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 2006, 42(1/2):137 https://www.osapublishing.org/oe/abstract.cfm?uri=oe-22-19-22608#figanchor6[16] Ramirez D A, Hayat M A, Itzler M A. Dependence of the performance of single photon avalanche diodes on the multiplication region width. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 2008, 44(11/12):1188 https://www.infona.pl/resource/bwmeta1.element.ieee-art-000004675825[17] Itzler M A, Ben-Michael R, Hsu C F, et al. Single photon avalanche diodes (SPADs) for 1.5μm photon counting applications. Journal of Modern Optics, 2007, 54(2/3):283 doi: 10.1080/09500340600792291?journalCode=tmop20[18] Finkelstein H, Hsu M J, Esener S C. STI-bounded single-photon avalanche diode in a deep-submicrometer CMOS technology. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2006, 27(11):887 doi: 10.1109/LED.2006.883560[19] Ripamonti G, Zappa F, Cova S. Effects of trap levels in single-photon optical time-domain reflectometry:evaluation and correction. IEEE J Lightwave Technol, 1992, 10(10):1398 doi: 10.1109/50.166782 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: