| Citation: |
Cuilan Zhao, Chunyu Cai, Jinglin Xiao. Influence of an anisotropic parabolic potential on the quantum dot qubit[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(11): 112002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/11/112002
****
C L Zhao, C Y Cai, J L Xiao. Influence of an anisotropic parabolic potential on the quantum dot qubit[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(11): 112002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/11/112002.
|
Influence of an anisotropic parabolic potential on the quantum dot qubit
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/11/112002
More Information
-
Abstract
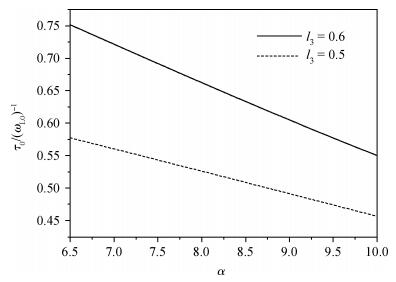
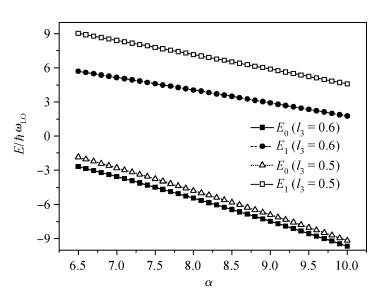
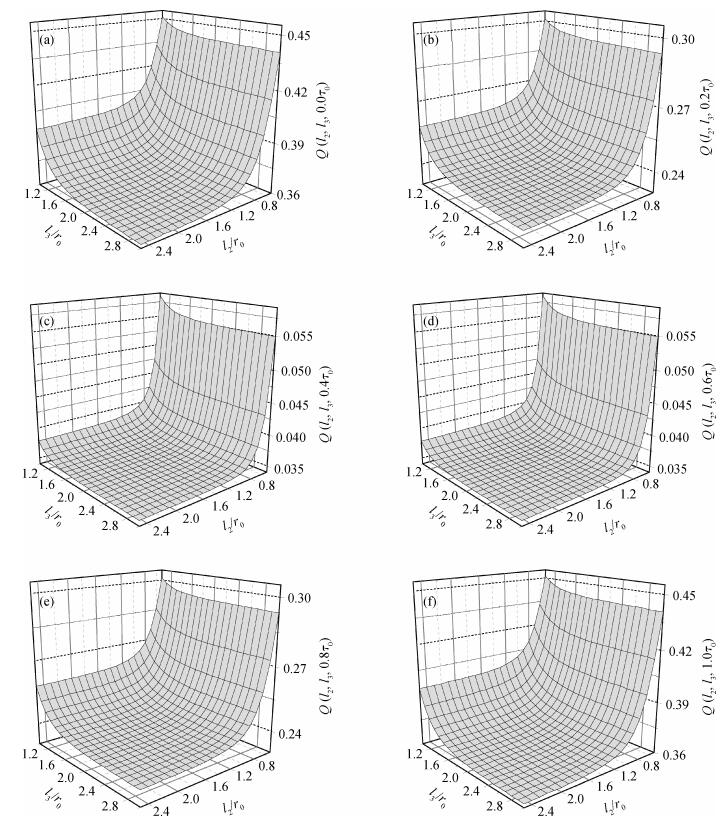
To study the influence of an anisotropic parabolic potential (APP) on the properties of a quantum dot (QD) qubit, we obtain the eigenenergies and eigenfunctions of the ground and first excited state of an electron, which is strongly coupled to the bulk longitudinal optical (LO) phonons, in a QD under the influence of an APP by the celebrated Lee-Low-Pines (LLP) unitary transformation and the Pekar type variational (PTV) methods. Then, this kind of two-level quantum system can be excogitated to constitute a single qubit. When the electron locates at the superposition state of its related eigenfunctions, we get the time evolution of the electron's probability density. Finally, the influence of an APP on the QD qubit is investigated. The numerical calculations indicate that the probability density will oscillate periodically and it is a decreasing function of the effective confinement lengths of the APP in different directions. Whereas its oscillatory period is an increasing one and will diminish with enhancing the electron-phonon (EP) coupling strength. -
References
[1] Brunner R, Shin Y S, Obata T, et al. Two-qubit gate of combined single-spin rotation and interdot spin exchange in a double quantum dot. Phys Rev Lett, 2011, 107(14):146801 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.146801[2] Economou S E, Climente J I, Badolato A, et al. Scalable qubit architecture based on holes in quantum dot molecules. Phys Rev B, 2012, 86(8):085319 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.86.085319[3] Cao G, Wand L, Tu T, et al. Pulse designed coherent dynamics of a quantum dot charge qubit. Chin Phys Lett, 2012, 29(3):030306 doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/29/3/030306[4] Hsieh C Y, Alexandre R, Pawel H. Herzberg circuit and berry's phase in chirality-based coded qubit in a triangular triple quantum dot. Phys Rev B, 2012, 86(11):115312 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.86.115312[5] Kristiaan D G, McMahon P L, Press D, et al. Ultrafast coherent control and suppressed nuclear feedback of a single quantum dot hole qubit. Nat Phys, 2011, 7(11):872 doi: 10.1038/nphys2078[6] Shi Z, Simmons C B, Prance J R, et al. Fast hybrid silicon double-quantum-dot qubit. Phys Rev Lett, 2012, 108(14):140503 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.140503[7] Puri S, Kim N Y, Yamamoto Y. Two-qubit geometric phase gate for quantum dot spins using cavity polariton resonance. Phys Rev B, 2012, 85(24):241403 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.85.241403[8] Seigneur H P, Gonzalez G, Leuenberger M N, et al. Dynamics of entanglement between a quantum dot spin qubit and a photon qubit inside a semiconductor high-Q nanocavity. Adv Math Phys, 2010, 2010:342915 http://emis.library.cornell.edu/journals/HOA/AMP/Volume2010/342915.pdf[9] Wang Z W, Li W P, Yin J W, et al. Properties of parabolic linear bound potential and coulomb bound potential quantum dot qubit. Commun Theor Phys, 2008, 49(2):311 doi: 10.1088/0253-6102/49/2/12[10] Yin J W, Xiao J L, Yu Y F, et al. The influence of electric field on a parabolic quantum dot qubit. Chin Phys B, 2009, 18(2):446 doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/18/2/012[11] Li W P, Yin J W, Yu Y F, et al. The effect of magnetic on the properties of a parabolic quantum dot qubit. J Low Temp Phys, 2010, 160(3):112 doi: 10.1007%2Fs10909-010-0180-9.pdf[12] Chen S H, Xiao J L. Properties of unsymmetrical parabolic confinement potential quantum dot qubit. Commun Theory Phys, 2009, 50(6):1287 doi: 10.1007/s11128-013-0631-8[13] Xiao W, Xiao J L. Coulomb bound potential quantum rod qubit. Superlattice Microst, 2012, 52(4):851 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2012.07.010[14] Lee T D, Low F E, Pines D. The motion of slow electrons in a polar crystal. Phys Rev, 1953, 90(2):297 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.90.297[15] Landau L D, Pekar S I. Polaron effective mass. Zh Eksp Teor Fiz, 1948, 18(5):419 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: