| Citation: |
Zhiyi Lu, Hongyun Xie, Wenjuan Huo, Wanrong Zhang. 0.9 GHz and 2.4 GHz dual-band SiGe HBT LNA[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(2): 025002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/2/025002
****
Z Y Lu, H Y Xie, W J Huo, W R Zhang. 0.9 GHz and 2.4 GHz dual-band SiGe HBT LNA[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(2): 025002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/2/025002.
|
-
Abstract
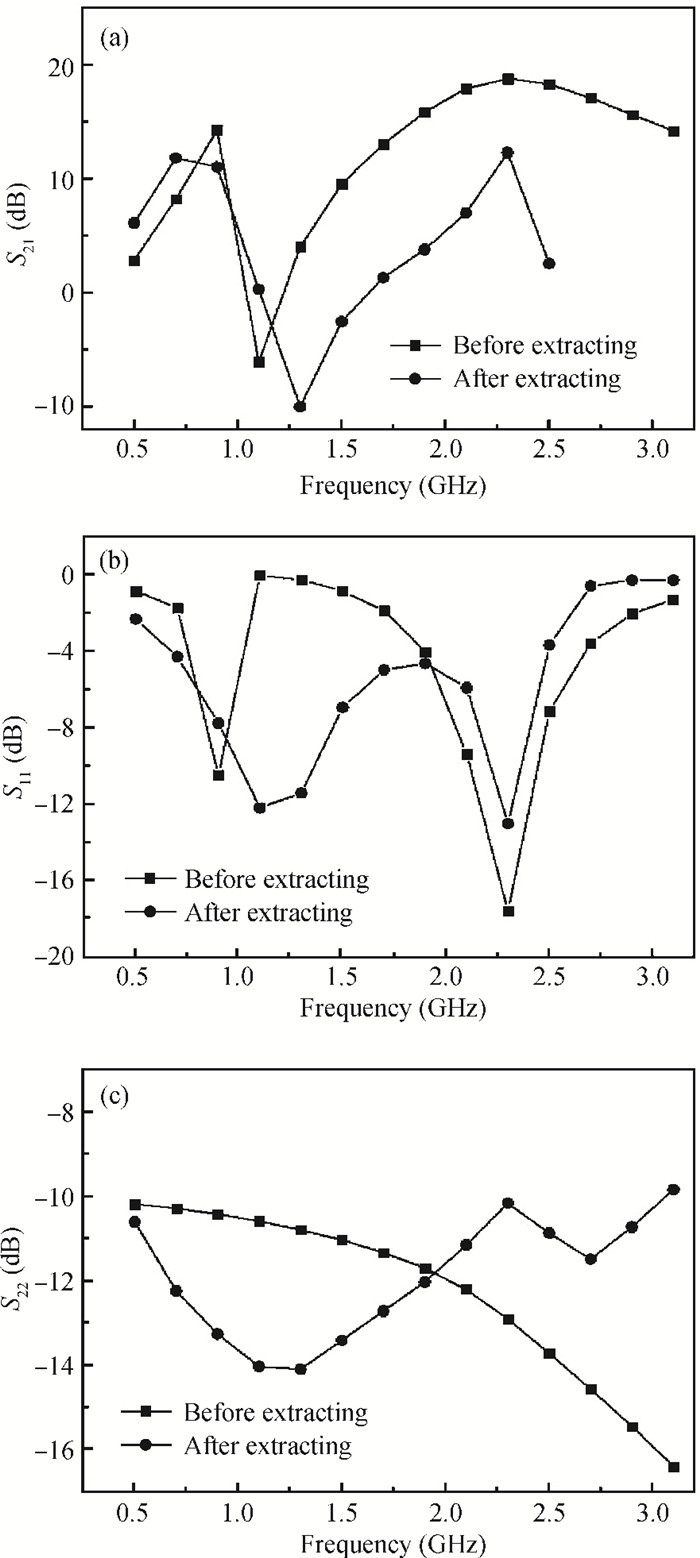
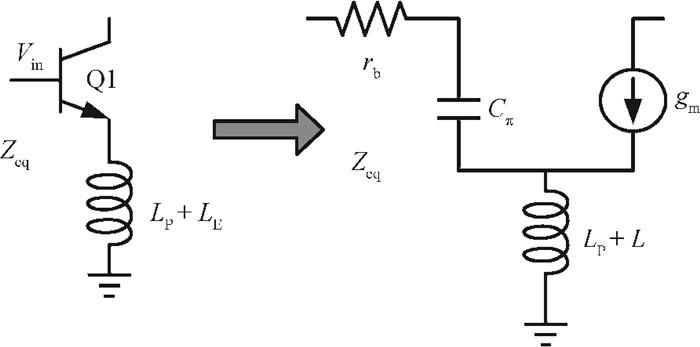
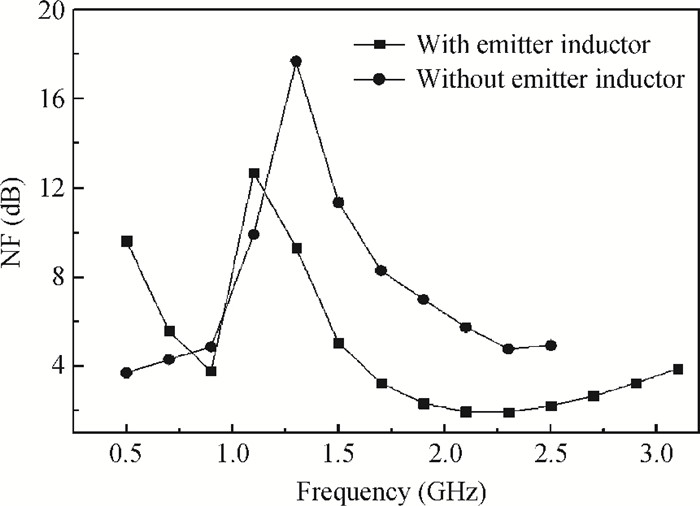
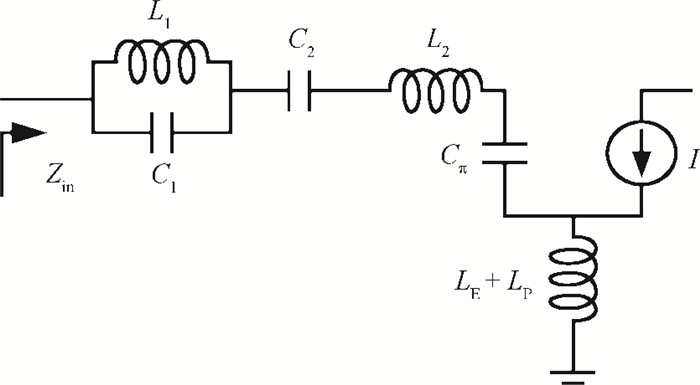
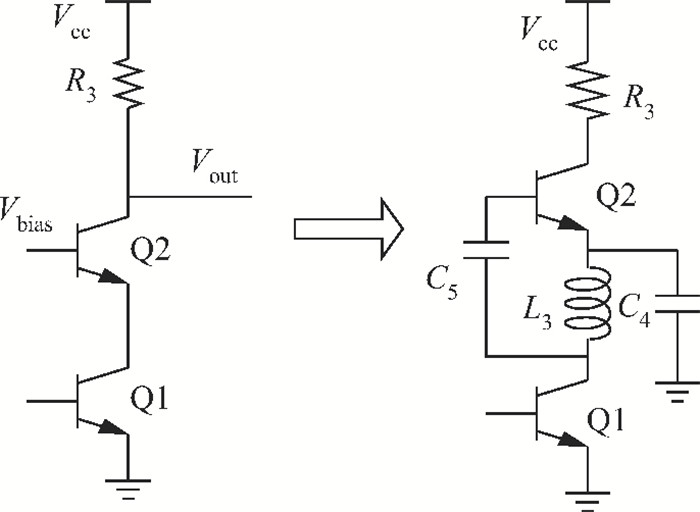
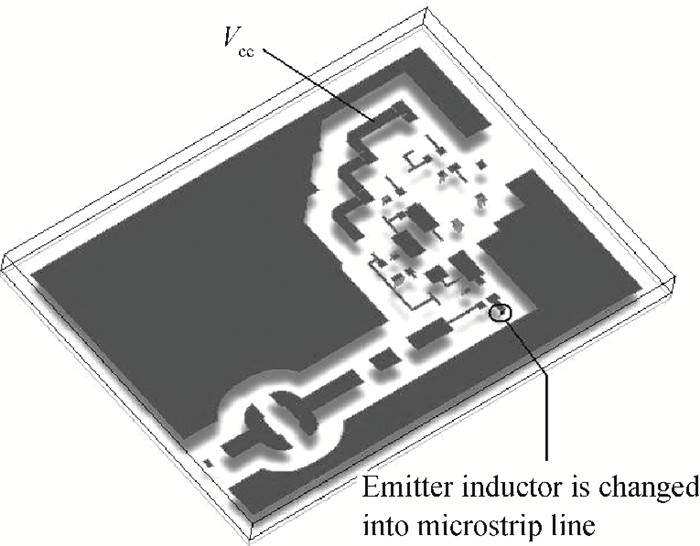
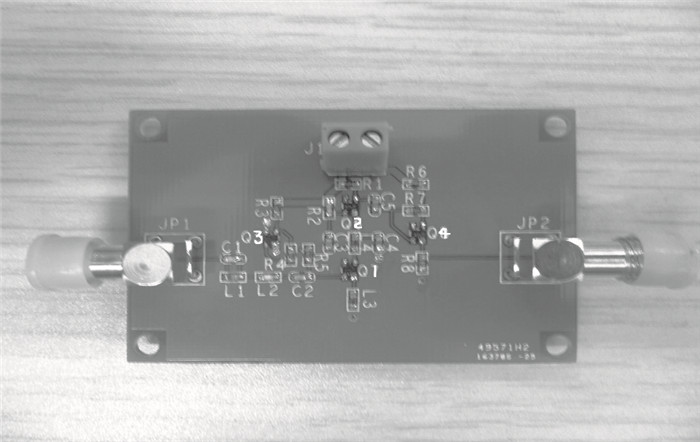
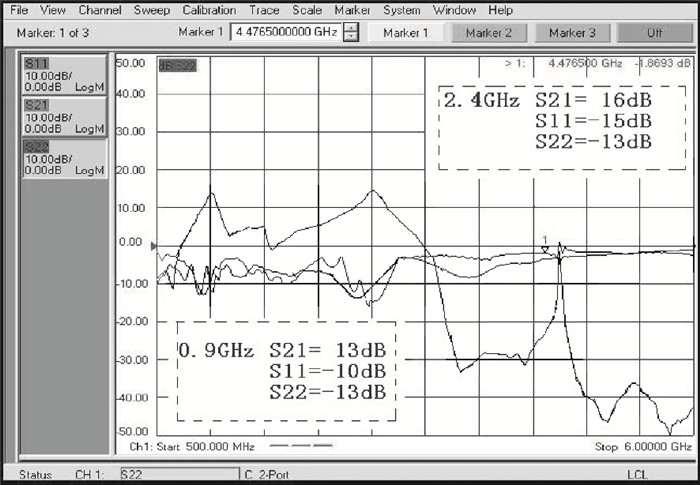
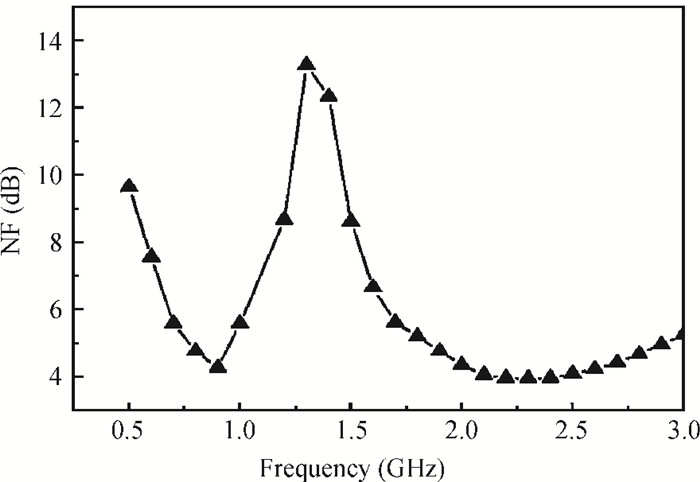
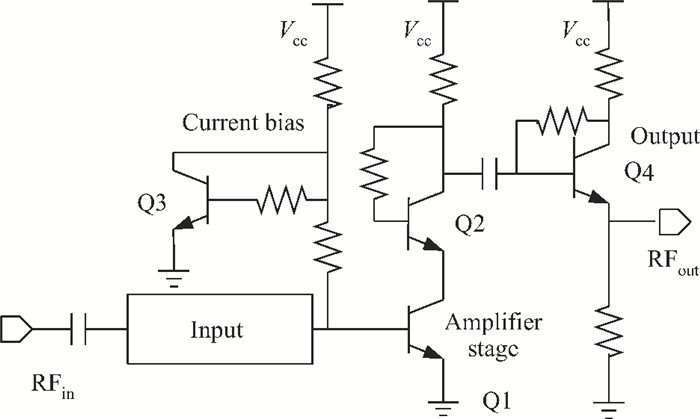
This paper presents design and implementation of a dual-band LNA using a 0.35 μm SiGe HBT process for 0.9 GHz GSM and 2.4 GHz WLAN applications. PCB layout parasitic effects have a vital effect on circuit performance and are accounted for using electro-magnetic (EM) simulation. Design considerations of noise decoupling, input/output impedance matching, and current reuse are described in detail. At 0.9/2.4 GHz, gain and noise figure are 13/16 dB and 4.2/3.9 dB, respectively. Both S11 and S22 are below-10 dB. Power dissipation is 40 mW at 3.5 V supply.-
Keywords:
- current reuse,
- dual-band,
- emitter inductor,
- EM simulation,
- SiGe HBT
-
References
[1] Dao V K, Bui Q D, Park C S, et al. A multi-band 900 MHz/1.8 GHz/5.2 GHz LNA for reconfigurable radio. Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, 2007, 1:69 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4266383/?arnumber=4266383&punumber%3D4266345[2] Amor M B, Douss S, Fakhfakh A, et al. Optimized design of a dual band low noise amplifier for the third generation of wireless system. SSD, 2005, 1:21 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212017316304777[3] Wang R L, Chen S C, Huang C L. Single/multiband COMS low-noise amplifier using concentric switching inductors. Microw Opt Technol Lett, 2012, 54(2):309 doi: 10.1002/mop.v54.2[4] Datta S, Datta K, Dutta A. Fully concurrent dual-band LNA operating in 900 MHz/2.4 GHz bands for multi-standard wireless receiver with sub-2 dB noise figure. ICETET, 2010:731 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5698423/[5] Zhang Q Q, Liu Z F. Design of a concurrent dual-band LNA for GSM900 and GPS system. Microelectronics, 2011, 41(6):824[6] Wang S, Huang B Z. A high-gain CMOS LNA for 2.4/5.2 GHz WLAN applications. Progress in Electromagnetics Research C, 2011, 21:155 doi: 10.2528/PIERC11032705[7] Guo F, Li Z Q. The design of wideband CMOS VGA. Chinese Journal of Semiconductors, 2007, 28(12):1967 https://zh.scientific.net/AMR.1049-1050.682[8] Niknejad A M. Modeling of passive elements with ASITIC. IEEE MTTS Int Microw Symp Digest, 2002, 1(1):149 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1011581/[9] Xie H Y, Lu Z Y, Zhang W R. A dual-band SiGe HBT low noise amplifier. ICSICT, 2010, 1:568 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5667287/[10] Hao Mingli, Shi Yin. A 2.4 GHz power amplifier in 0.35μm SiGe BiCMOS. Journal of Semiconductors, 2010, 31(1):015004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/31/1/015004[11] Lin Y J, Hsu S H, Jin J D, et al. A 3.1-10.6 GHz ultra-wideband CMOS LNA with current reuse technique. IEEE Microw Wireless Compon Lett, 2007, 17(3):232 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2006.890503 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: