| Citation: |
Zhifang Lei, Guangyu Chen, Shibin Gu, Lingling Dai, Rong Yang, Yuan Meng, Ted Guo, Liwei Li. Development of aluminum-doped ZnO films for a-Si:H/μc-Si:H solar cell applications[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(6): 063004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/6/063004
****
Z F Lei, G Y Chen, S B Gu, L L Dai, R Yang, Y Meng, T Guo, L W Li. Development of aluminum-doped ZnO films for a-Si:H/μc-Si:H solar cell applications[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(6): 063004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/6/063004.
|
Development of aluminum-doped ZnO films for a-Si:H/μc-Si:H solar cell applications
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/6/063004
More Information
-
Abstract
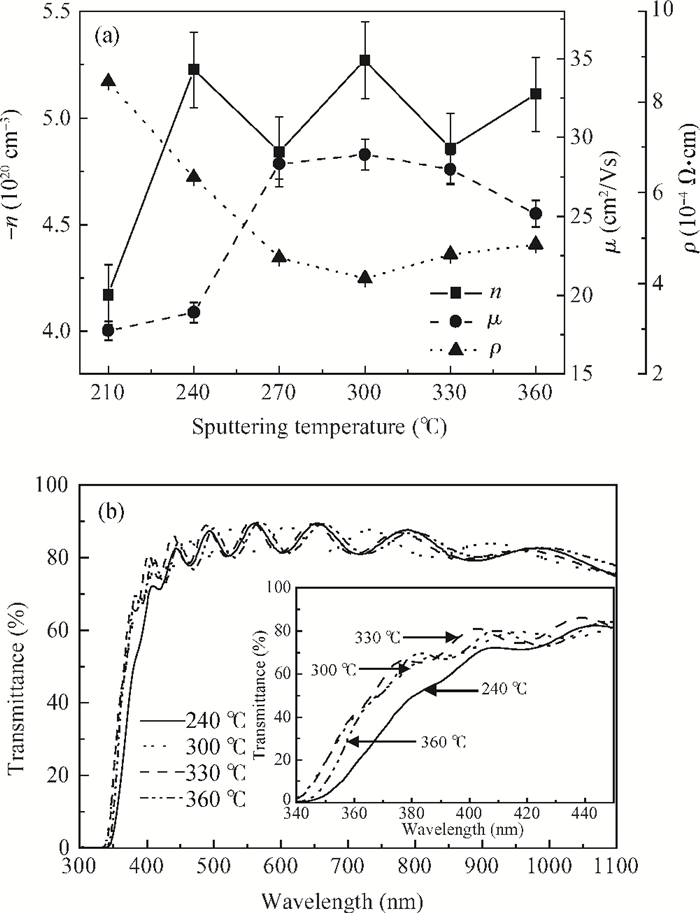
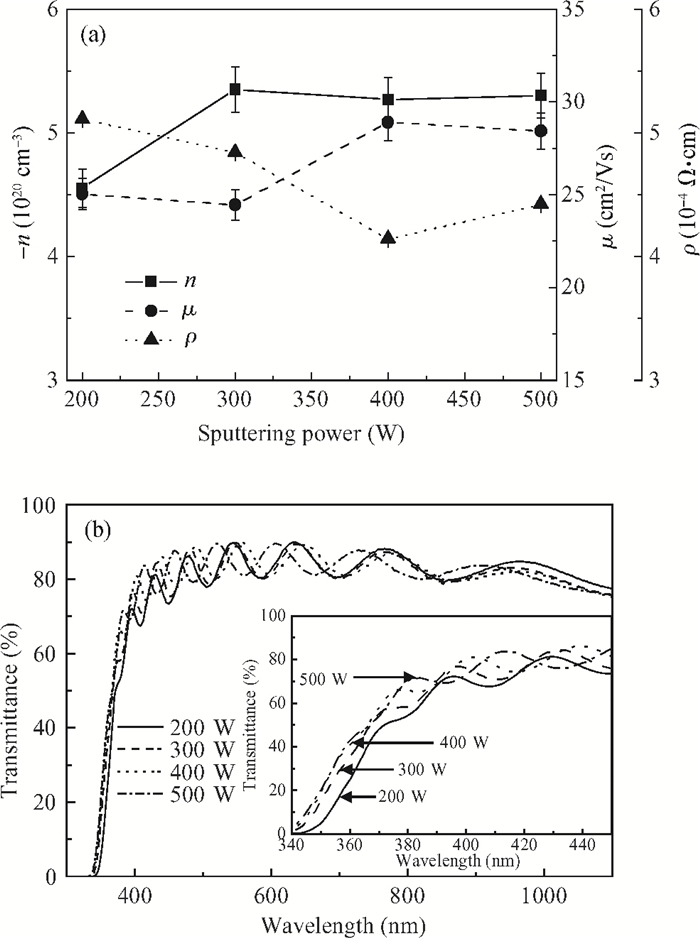
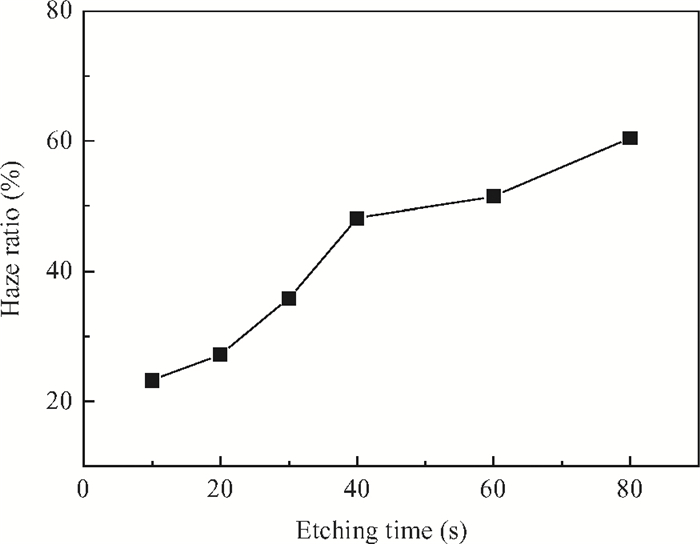
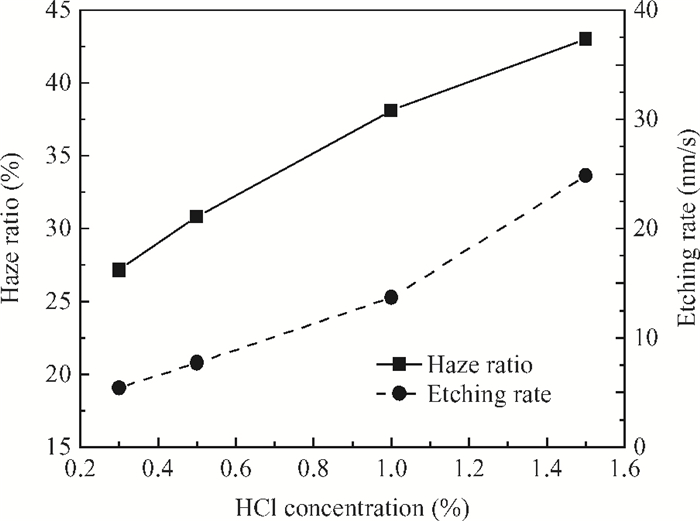
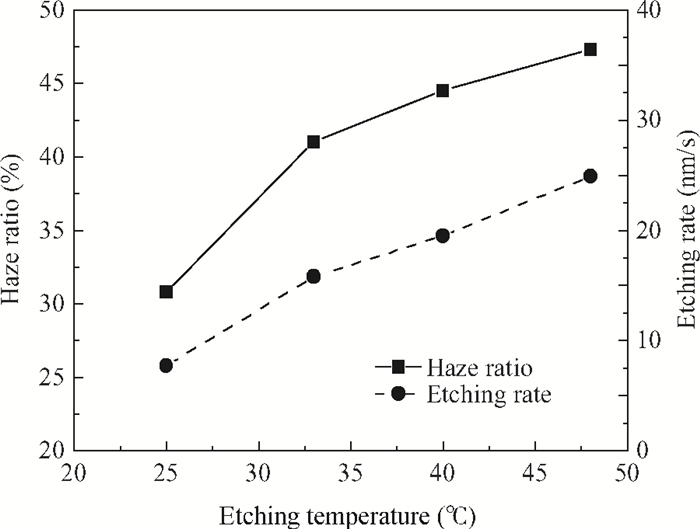
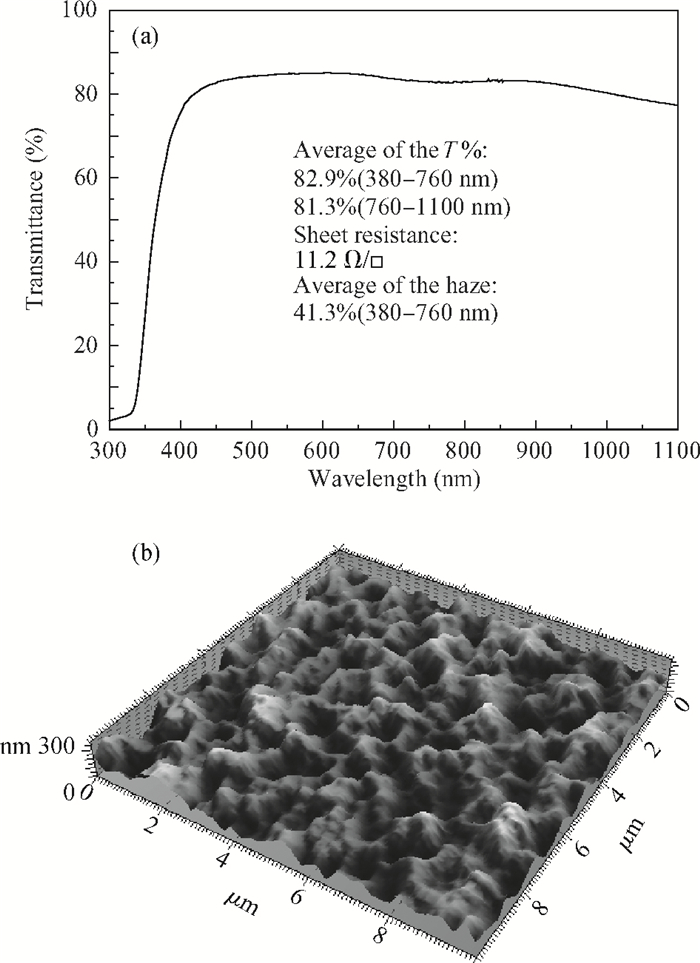
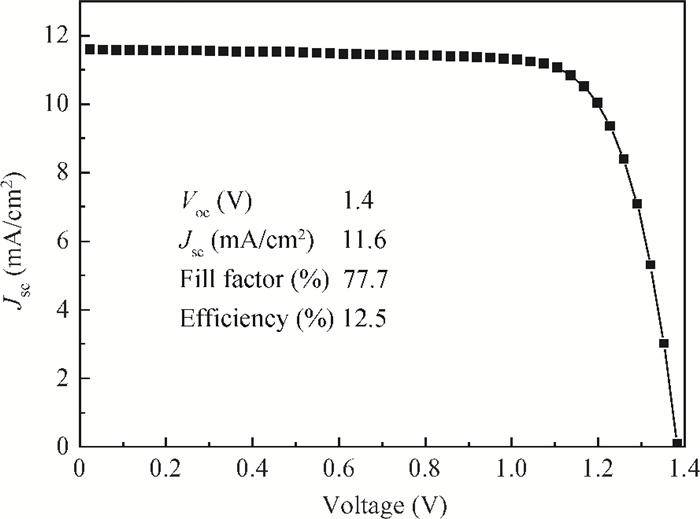
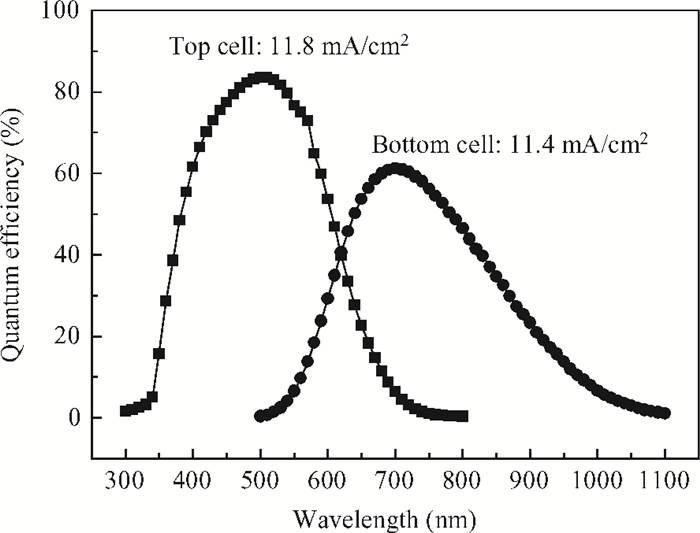
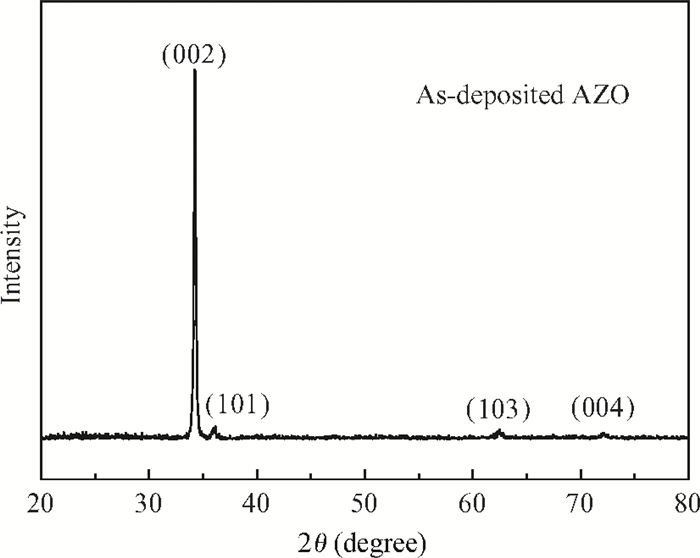
This study deals with the optimization of direct current (DC) sputtered aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) thin films and their incorporation into a-Si:H/μc-Si:H tandem junction thin film solar cells aiming for high conversion efficiency. Electrical and optical properties of AZO films, i.e. mobility, carrier density, resistivity, and transmittance, were comprehensively characterized and analyzed by varying sputtering deposition conditions, including chamber pressure, substrate temperature, and sputtering power. The correlations between sputtering processes and AZO thin film properties were first investigated. Then, the AZO films were textured by diluted hydrochloric acid wet etching. Through optimization of deposition and texturing processes, AZO films yield excellent electrical and optical properties with a high transmittance above 81% over the 380-1100 nm wavelength range, low sheet resistance of 11 Ω/$\square$ and high haze ratio of 41.3%. In preliminary experiments, the AZO films were applied to a-Si:H/μc-Si:H tandem thin film solar cells as front contact electrodes, resulting in an initial conversion efficiency of 12.5% with good current matching between subcells. -
References
[1] Kuo S Y, Chen W C, Lai F I, et al. Effects of doping concentration and annealing temperature on properties of highly-oriented Al-doped ZnO films. J Cryst Growth, 2006, 287:78 doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2005.10.047[2] Lee K E, Wang M, Kim E J, et al. Structural, electrical and optical properties of sol-gel AZO thin films. Curr Appl Phys, 2009, 9:683 doi: 10.1016/j.cap.2008.06.006[3] Elm M T, Henning T, Klar P J, et al. Effects of artificially structured micrometer holes on the transport behavior of Al-doped ZnO layers. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93:232101 doi: 10.1063/1.3040312[4] Jung K, Choi W K, Yoon S J, et al. Electrical and optical properties of Ga doped zinc oxide thin films deposited at room temperature by continuous composition spread. Appl Surf Sci, 2010, 256:6219 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.03.144[5] Yang W F, Liu Z G, Zhang F, et al. Structural, electrical, and optical properties of transparent conductive Al-doped ZnO films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Journal of Semiconductors, 2008, 29:2311 http://www.jos.ac.cn/bdtxbcn/ch/reader/view_abstract_new.aspx?volume=29&start_page=2311[6] Agashe C, Kluth O, Schope G, et al. Modified Thornton model for magnetron sputtered zinc oxide:film structure and etching behaviour. Thin solid films, 2003, 442:80 doi: 10.1016/S0040-6090(03)00949-0[7] Calnan S, Hupkes J, Rech B, et al. High deposition rate aluminum-doped zinc films with highly efficient light trapping for silicon thin film solar cells. Thin solid films, 2008, 516:1242 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2007.06.006[8] Ellmer K. Magnetron sputtering of transparent conductive zinc oxide:relation between the sputtering parameters and the electronic properties. J Phys D Appl Phys, 2000, 33:17 doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/33/4/201[9] Zhang H F, Yang S G, Liu H F, et al. Preparation and characterization of transparent conducting ZnO:W films by DC magnetron sputtering. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32:043002 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/4/043002[10] Hooh J, Kim K K, Seong T Y. Effects of deposition temperatures and annealing conditions on the microstructural, electrical and optical properties of polycrystalline Al-doped ZnO thin films. Appl Surf Sci, 2011, 257:2731 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.053[11] Zhou H B, Zhang H Y, Tan M L, et al. Effects of substrate temperature on the efficiency of hydrogen incorporation on the properties of Al-doped ZnO films. Superlattice Microst, 2012, 51:644 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2012.03.003[12] Moon Y K, Bang B, Kim S H, et al. Effects of working pressure on the electrical and optical properties of aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films. J Mater Sci-Mater El, 2008, 19:528 doi: 10.1007/s10854-007-9375-5[13] Kar J P, Kin S, Shin B, et al. Influence of sputtering pressure on morphological, mechanical and electrical properties of Al-doped ZnO films. Solid State Electron, 2010, 54:1447 doi: 10.1016/j.sse.2010.07.002[14] Shin B K, Lee T I, Kar J P, et al. Effect of deposition power on structural and electrical properties of Al-doped ZnO films using pulsed direct-current magnetron sputtering with single cylindrical target. Mat Sci Semicon Proc, 2011, 14:23 doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2010.12.013[15] Kuo S Y, Liu K C, Lai F I, et al. Effects of RF power on the structural, optical and electrical properties of Al-doped zinc oxide films. Microelectron Reliab, 2010, 50:730 doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2010.01.042[16] Rech B, Remann T, Donker M N, et al. Challenges in microcrystalline silicon based solar cell technology. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 511/512:548 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2005.12.161[17] Chang P K, Lu C H, Yeh C H, et al. High efficiency a-Si:H/a-Si:H solar cell with a tunnel recombination junction and a n-type μ c-Si:H layer. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520:3684 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2011.12.083 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: