| Citation: |
Kai Su, Min Gong, Huaibin Qin, Chen Sun. A multiple transistor combination low-voltage curvature-corrected bandgap reference[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(6): 065010. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/6/065010
****
K Su, M Gong, H B Qin, C Sun. A multiple transistor combination low-voltage curvature-corrected bandgap reference[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(6): 065010. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/6/065010.
|
A multiple transistor combination low-voltage curvature-corrected bandgap reference
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/6/065010
More Information
-
Abstract
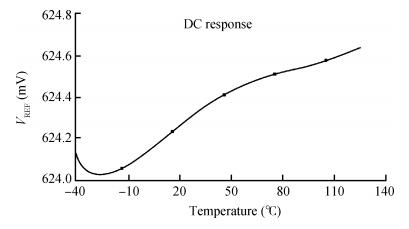
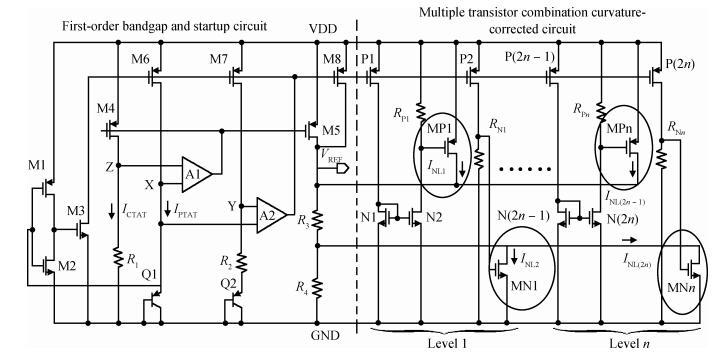
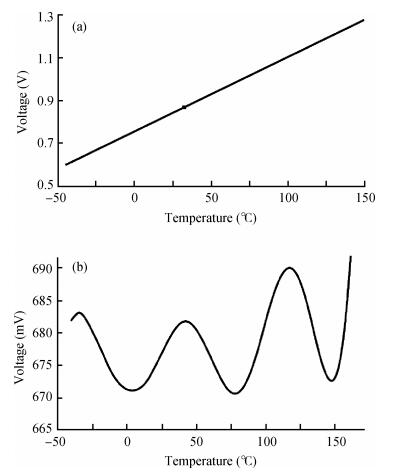
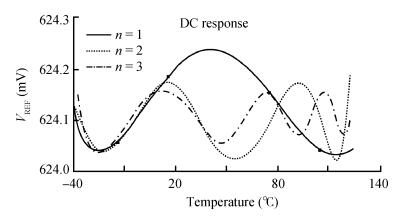
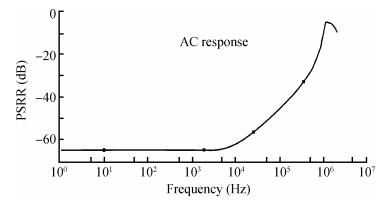
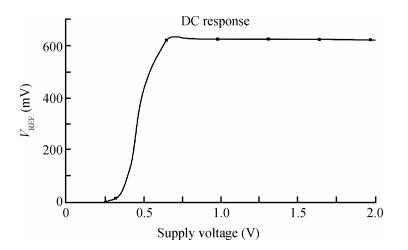
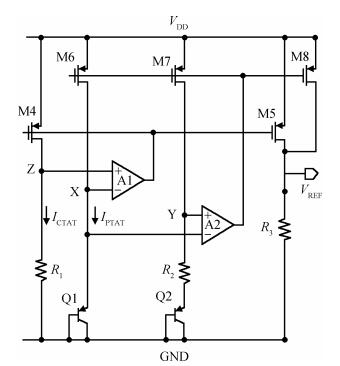
A new bandgap reference (BGR) curvature compensation technology is proposed, which is a kind of multiple transistor combination. On the basis of the existing first-order bandgap reference technology, a compensation current circuit consisting of a sink current branch and a source current branch is added. The BGR was designed and simulated by using Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMIC) 0.18 μm CMOS process. The simulation results showed that when the power supply voltage was 1 V, the temperature coefficient of the BGR was 2.08 ppm/℃ with the temperature range from-40 to 125℃, the power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) was-64.77 dB and the linear regulation was 0.44 mV/V with the supply power changing from 0.85 to 1.8 V. -
References
[1] Magnelli L, Crupi F, Corsonello P, et al. A 2.6 nW, 0.45 V temperature-compensated subthreshold CMOS voltage reference. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(2):465 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2092997[2] Su Q, Yin Y, Deng H. Design of a low voltage high precision CMOS bandgap reference. ICEMI'099th International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments, 2009:2[3] Liu Z, Cheng Y. A sub-1 V CMOS bandgap reference with high-order curvature compensation. IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits, 2009:441[4] Ker M D, Chen J S. New curvature compensated technique for CMOS bandgap reference with sub-1-V operation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ, Analog Digit Signal Process, 2006, 53(8):667 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2006.876377[5] Li Hua, Lu Jian, Jiang Yadong. A curvature-compensated CMOS bandgap voltage reference for high precision applications. Microelectronics, 2009, 39(1):38[6] Jiang Tao, Yang Huazhong. Bandgap reference design by means of multiple point curvature compensation. Chinese Journal of Semiconductors, 2007, 28(4):490[7] Wang Hongyi, Lai Xinquan, Li Yushan, et al. A piecewise-linear compensated bandgap reference. Chinese Journal of Semiconductors, 2004, 25(7):771[8] Ming Xin, Lu Yang, Zhang Bo, et al. A 2.8 ppm/℃ high PSRR BiCMOS bandgap voltage reference. Journal of Semiconductors, 2009, 30(9):095014 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/30/9/095014[9] Banba H, Shiga H, Umezawa A, et al. A CMOS bandgap reference circuit with sub-1-V operation. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1999, 34(5):670 doi: 10.1109/4.760378[10] Razavi B. Design of analog CMOS integrated circuits. Boston:McGraw Hill, 2000[11] Leung K N, Mok P K T. A 2-V 23-μ A 5.3-ppm/℃ curvature-compensated CMOS bandgap voltage reference. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(3):561 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2002.808328 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: