| Citation: |
Qianqian Lei, Erhu Zhao, Fang Yuan, Min Lin, Lianbi Li, Song Feng. I/Q mismatch calibration based on digital baseband[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(7): 075007. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/075007
****
Q Q Lei, E H Zhao, F Yuan, M Lin, L B Li, S Feng. I/Q mismatch calibration based on digital baseband[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(7): 075007. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/075007.
|
I/Q mismatch calibration based on digital baseband
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/075007
More Information
-
Abstract
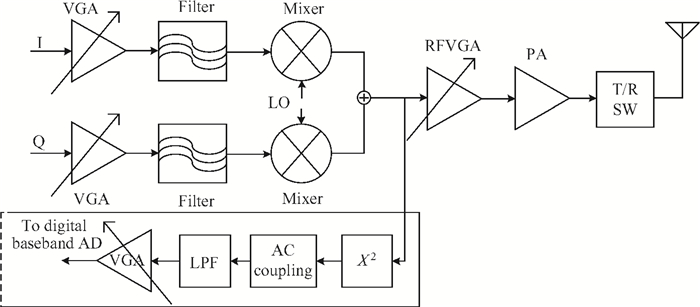
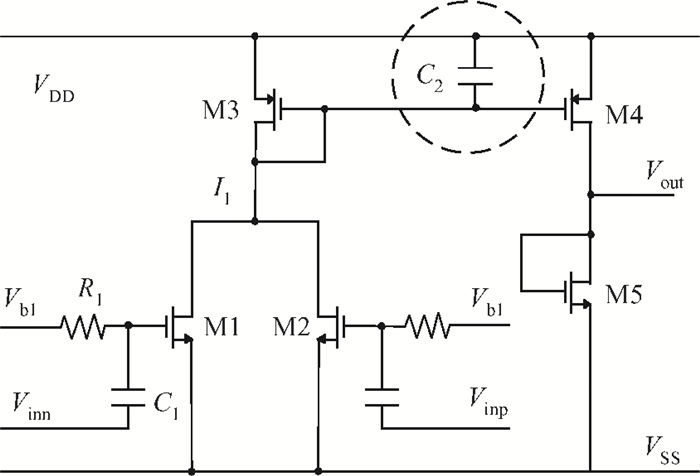
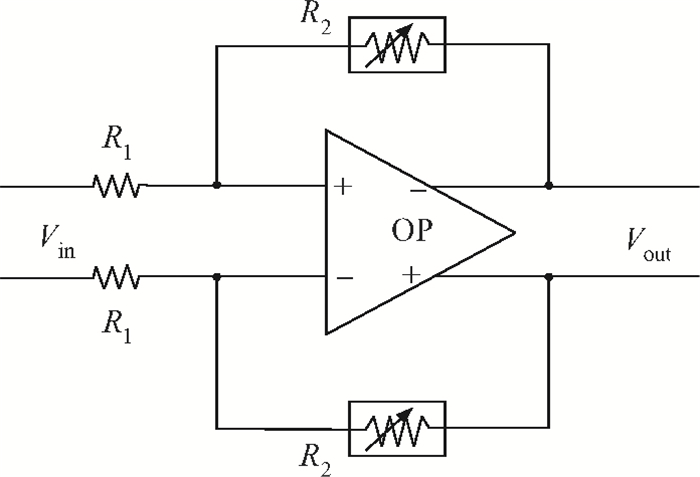
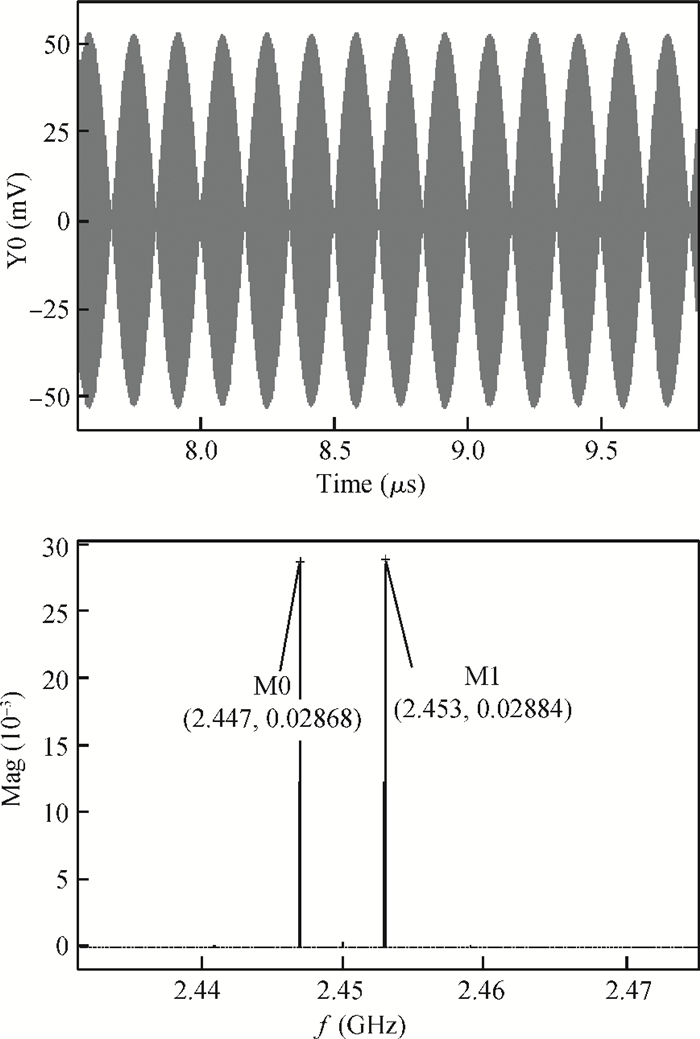
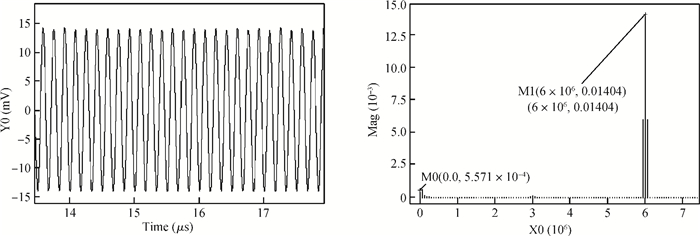
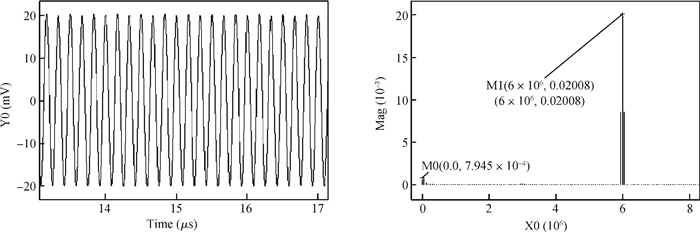
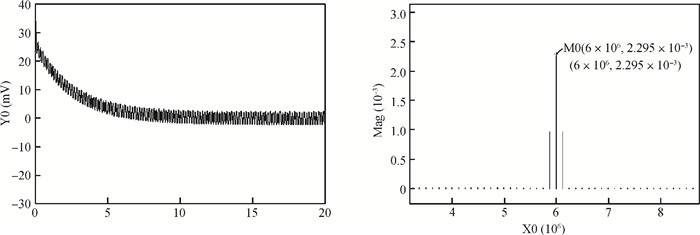
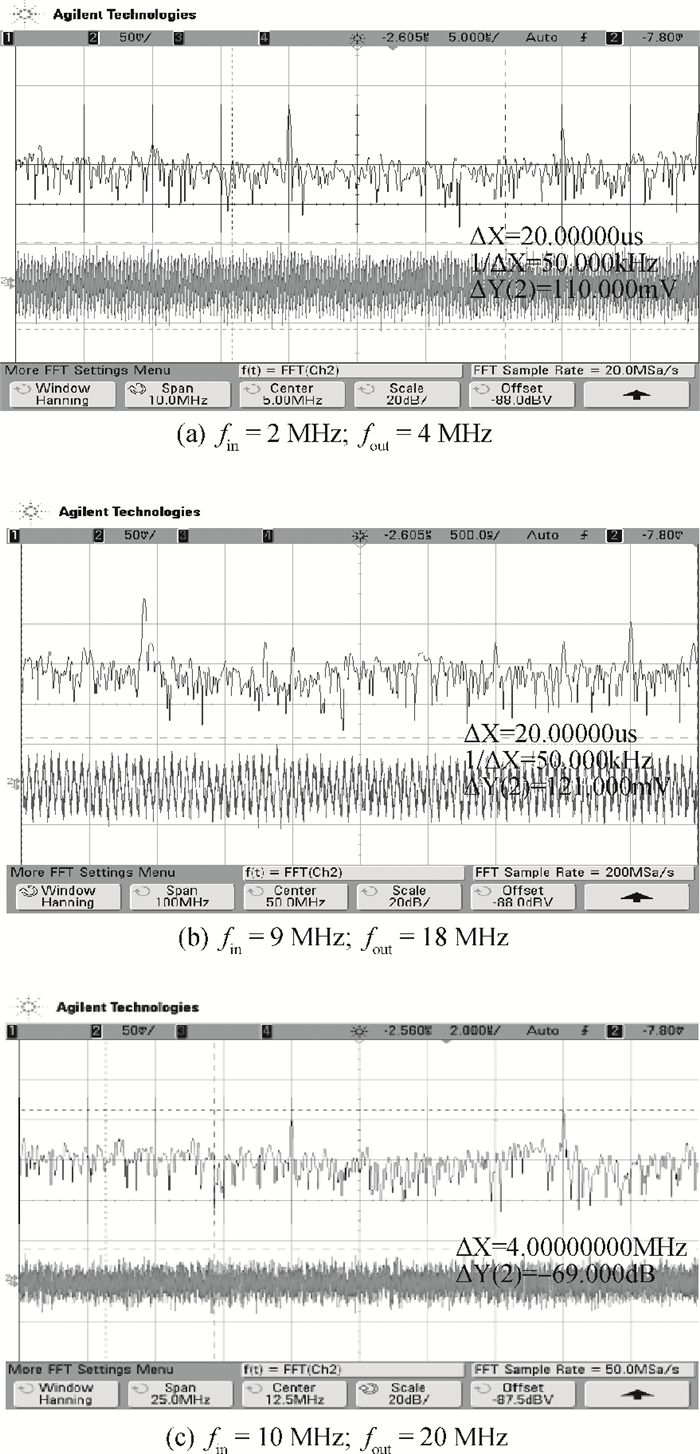
A novel I/Q mismatch calibration technique based on a digital baseband for a direct conversion transmitter is implemented in TSMC 0.13 μm CMOS technology. The proposed technique finishes a calibration task, which only needs a calibration chain to detect mismatches and then transmit them to the digital baseband. Simulation results show that the calibrated errors of the proposed technique are less than 7%. The measurement results indicate the function of the proposed technique is correct, but the performance should be improved further.-
Keywords:
- I/Q mismatch,
- direct conversion transmitter,
- calibration
-
References
[1] Zargari M, Nathawad L Y, Samavati H, et al. A dual-band CMOS MIMO radio SOC for IEEE 802.11n wireless LAN. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(12):2882 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.2005742[2] Hieu N T, Ryu H G, Wang C X, et al. The impact of the I/Q mismatching errors on the BER performance of OFDM communication systems. IEEE International Conference on Communications, 2007:5423 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4289569/keywords[3] Schenk T C W, Fledderus E R, Smulders P F M. Performance impact of IQ mismatch in direct-conversion MIMO OFDM transceivers. IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium, 2007:329 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4160718/authors[4] Horlin F, de Rore S, Lopez-Estraviz E, et al. Impact of frequency offsets and IQ imbalance on MC-CDMA reception based on channel tracking. IEEE J Selected Areas Commun, 2006, 24(6):1179 doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2005.864018[5] Brenna G, Tschopp D, Rogin J, et al. A 2-GHz carrier leakage calibrated direct-conversion WCDMA transmitter in 0.13μm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2004, 39(8):1253 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2004.831794[6] Vassiliou I, Vavelidis K, Georgantas T, et al. A single-chip digitally calibrated 5.15-5.825-GHz 0.18-μm CMOS transceiver for 802.11a wireless LAN. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(12):2221 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.819086[7] Hsieh Y H, Hu W Y, Lin S M, et al. An auto-I/Q calibrated CMOS transceiver for 802.11g. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(11):2187 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.857348[8] Mehta S S, Weber D, Terrovitis M, et al. An 802.11g WLAN SoC. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(12):2483 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.857418[9] Kang B, Yim J, Kim T W W, et al. An ultra-wideband transmitter with automatic self-calibration of sideband rejection up to 9 GHz in 65 nm CMOS. Int SoC Design Conf, 2010:332 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5682903/?reload=true&arnumber=5682903&contentType=Conference%20Publications -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: