| Citation: |
Xueli Ma, Kai Han, Wenwu Wang. Remote scavenging technology using a Ti/TiN capping layer interposed in a metal/high-k gate stack[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(7): 076001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/076001
****
X L Ma, K Han, W W Wang. Remote scavenging technology using a Ti/TiN capping layer interposed in a metal/high-k gate stack[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(7): 076001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/076001.
|
Remote scavenging technology using a Ti/TiN capping layer interposed in a metal/high-k gate stack
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/076001
More Information
-
Abstract
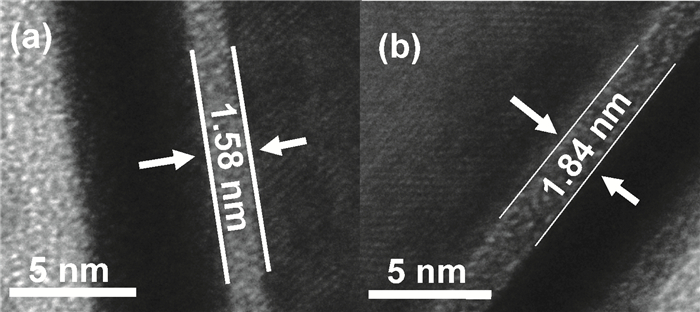
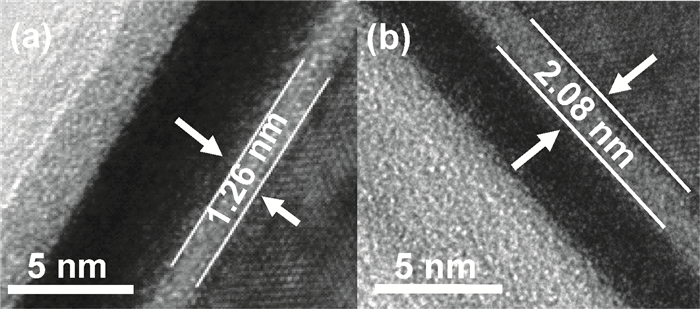
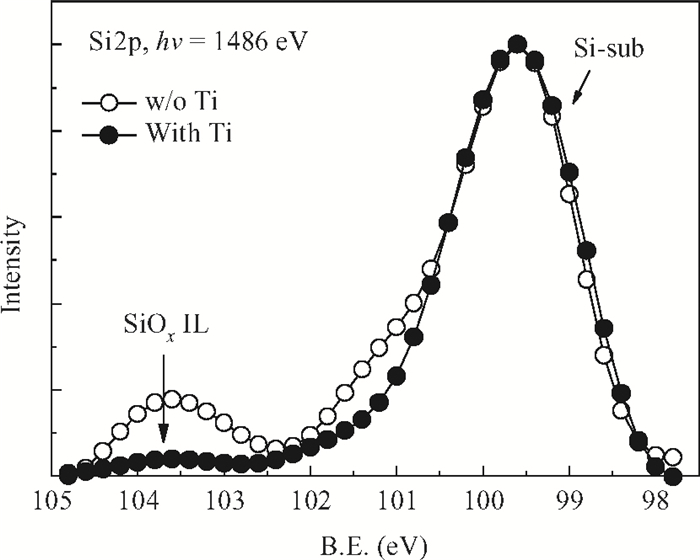
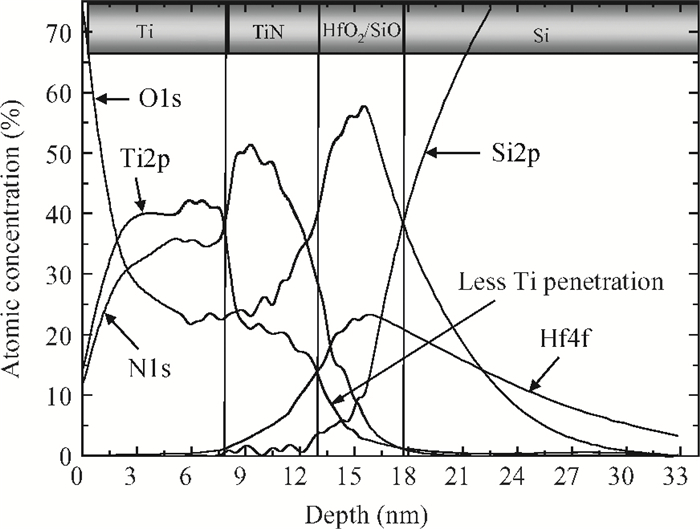
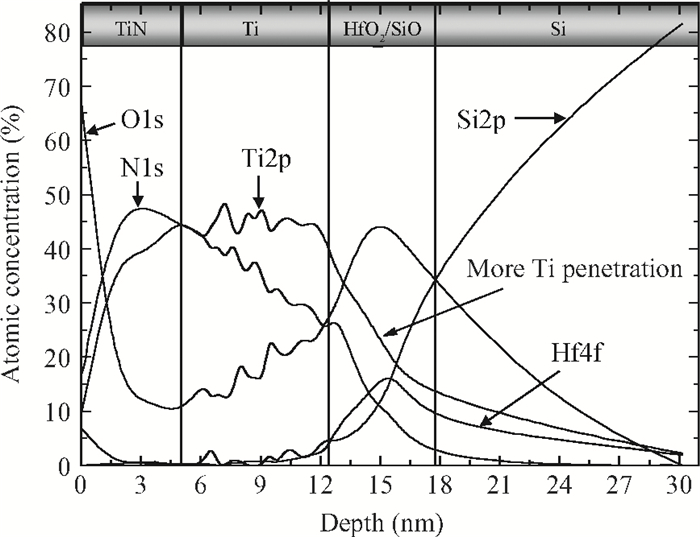
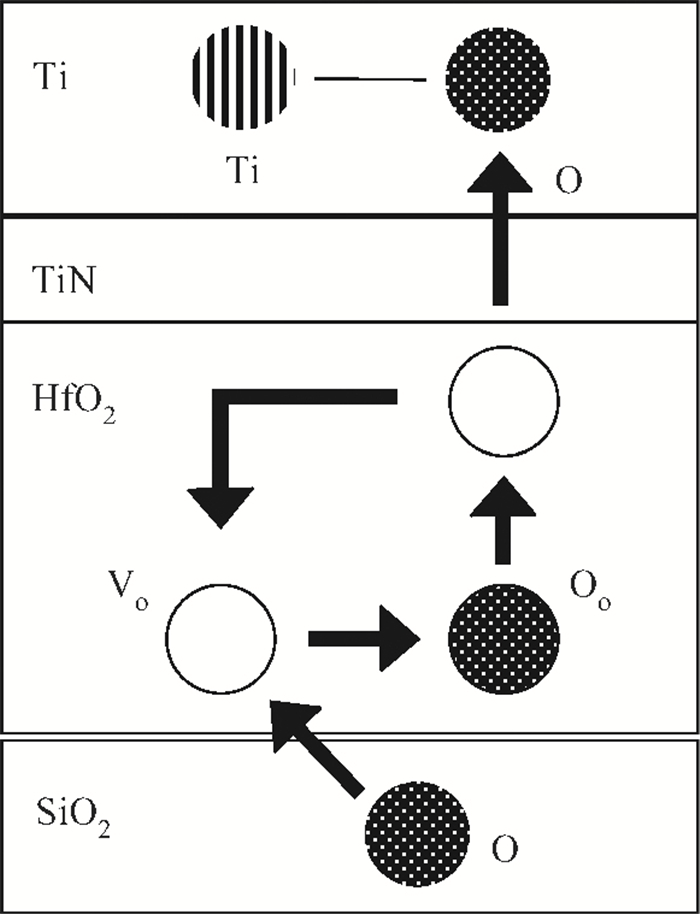
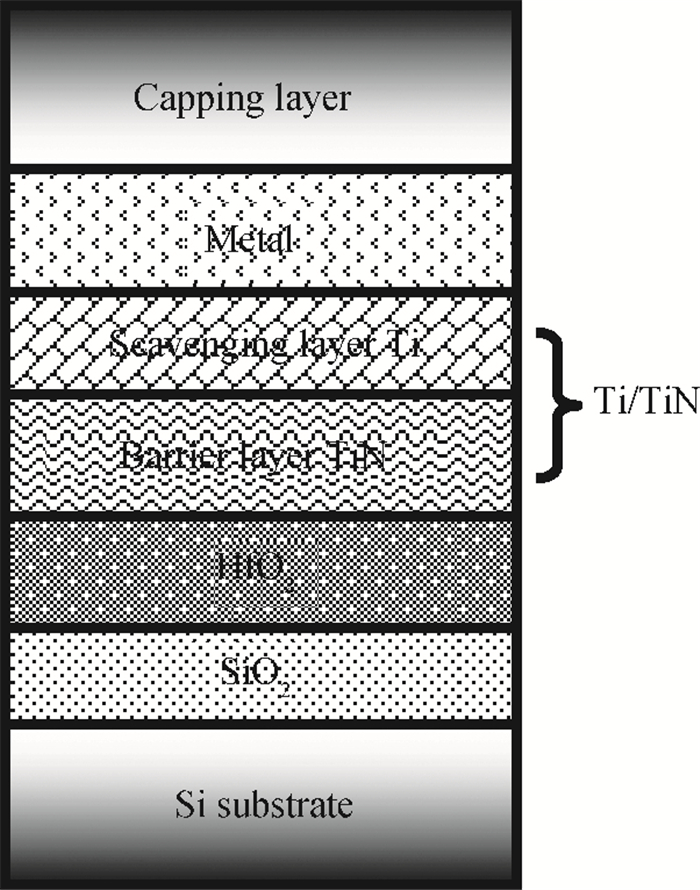
High permittivity materials have been required to replace traditional SiO2 as the gate dielectric to extend Moore's law. However, growth of a thin SiO2-like interfacial layer (IL) is almost unavoidable during the deposition or subsequent high temperature annealing. This limits the scaling benefits of incorporating high-k dielectrics into transistors. In this work, a promising approach, in which an O-scavenging metal layer and a barrier layer preventing scavenged metal diffusing into the high-k gate dielectric are used to engineer the thickness of the IL, is reported. Using a Ti scavenging layer and TiN barrier layer on a HfO2 dielectric, the effective removal of the IL and almost no Ti diffusing into the HfO2 have been confirmed by high resolution transmission electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.-
Keywords:
- scavenging technology,
- EOT,
- barrier layer,
- TEM,
- XPS
-
References
[1] ITRS.( http://public.itrs.net)[2] Changhwan C, Yong K C, Jong R S, et al. Fabrication of TaN-gated ultra-thin MOSFETs (EOT < 1.0 nm) with HfO2 using a novel oxygen scavenging process for sub 65 nm application. Proceedings of VLSI Technology Symposium, 2005:226 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1469277/?arnumber=1469277[3] Suzuki M, Tomita M, Yamaguchi T, et al. Ultra-thin (EOT=3Å and low leakage dielectrics of La-alminate directly on Si. Proceedings of IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2005:433 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1609371/?reload=true&arnumber=1609371&count=295&index=124[4] Choi K, Jagannathan H, Choi C, et al. Extremely scaled gate-first high-k metal gate stack with EOT of 0.55 nm using novel inter-facial layer scavenging techniques for 22 nm technology node and beyond. Proceedings of VLSI Technology Symposium, 2009:138[5] Huang J, Heh D, Sivasubramani P, et al. Gate first high-k metal gate stacks with zero SiOx interface achieving EOT=0.59 nm for 16 nm application. Proceedings of VLSI Technology Symposium, 2009:34[6] Misra V, Heuss G P, Zhong H. Use of metal-oxide-semiconduc-tor capacitors to detect interactions of Hf and Zr gate electrodes with SiO2 and ZrO2. Appl Phys Lett, 2001, 78(26):4166 doi: 10.1063/1.1380240[7] Kim H, McIntyre P C, Chui C O, et al. Engineering chemically abrupt high-k metal oxide/silicon interfaces using an oxygen-gettering metal overlayer. J Appl Phys, 2004, 96(6):3467 doi: 10.1063/1.1776636[8] Ⅲ Seo K, Lee D I, Pianetta P, et al. Chemical states and electrical properties of a high-k metal oxide/silicon interface with oxygen-gettering titanium-metal-overlayer. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89(14):142912 doi: 10.1063/1.2358834[9] Goncharova L V, Dalponte M, Starodub D G, et al. Oxygen diffusion and reactions in Hf-based dielectrics. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89(4):044108 doi: 10.1063/1.2221522[10] Wang W E, Kim Y S. A thermodynamic evaluation of the titanium-oxygen system from O/Ti=0 to 3/2. J Nucl Mater, 1999, 270:242 doi: 10.1016/S0022-3115(98)00780-6 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: