| Citation: |
Wei Wang, Lu Zhang, Xueying Wang, Zhubing Wang, Ting Zhang, Na Li, Xiao Yang, Gongshu Yue. The combined effects of halo and linear doping effects on the high-frequency and switching performance in ballistic CNTFETs[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(11): 114004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/114004
****
W Wang, L Zhang, X Y Wang, Z B Wang, T Zhang, N Li, X Yang, G S Yue. The combined effects of halo and linear doping effects on the high-frequency and switching performance in ballistic CNTFETs[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(11): 114004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/114004.
|
The combined effects of halo and linear doping effects on the high-frequency and switching performance in ballistic CNTFETs
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/114004
More Information
-
Abstract
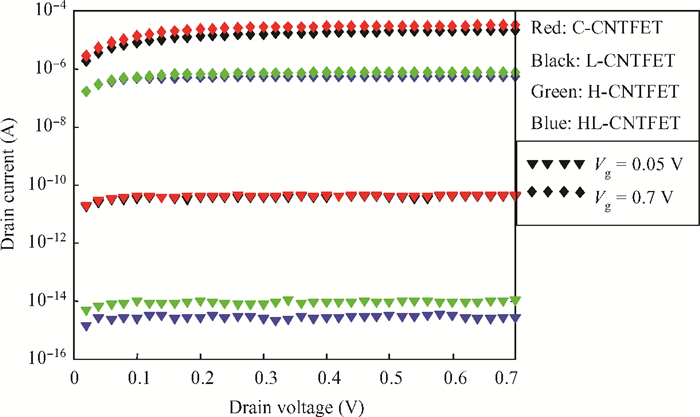
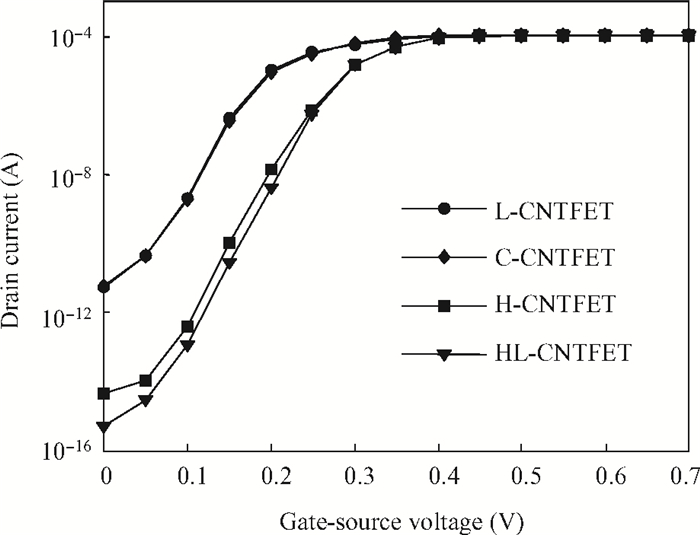
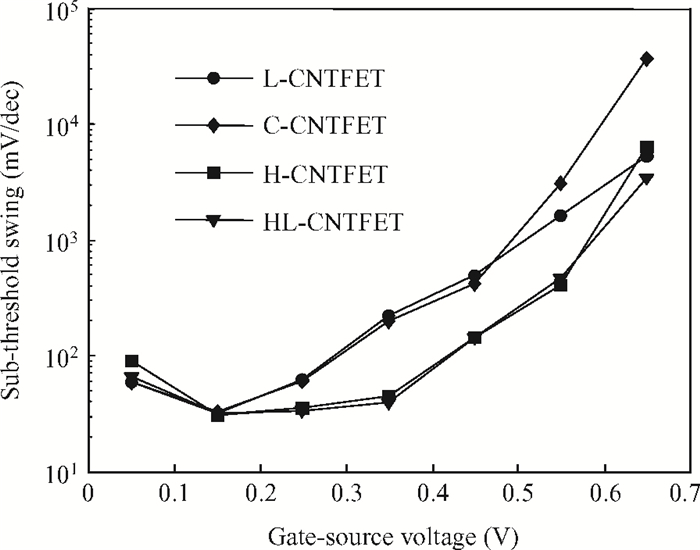
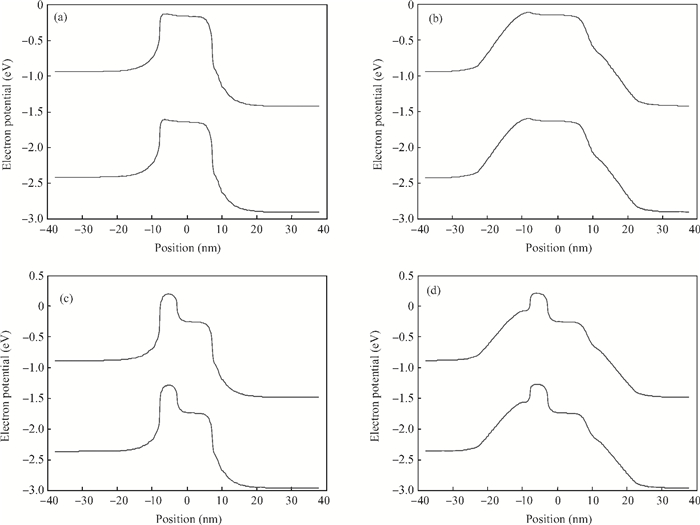
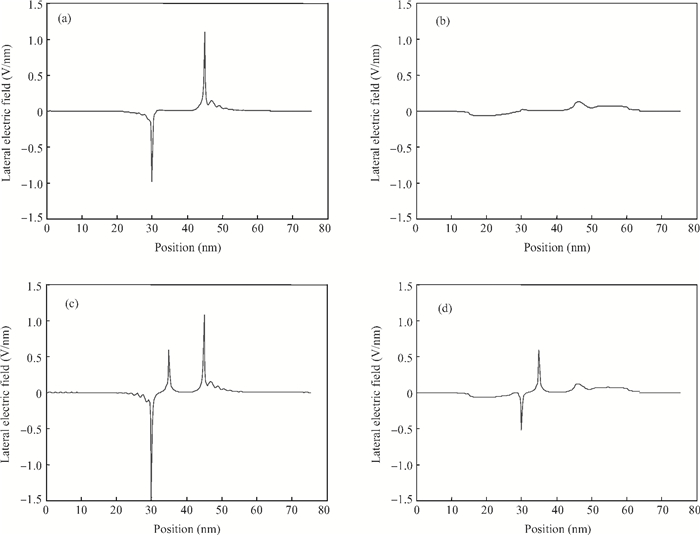
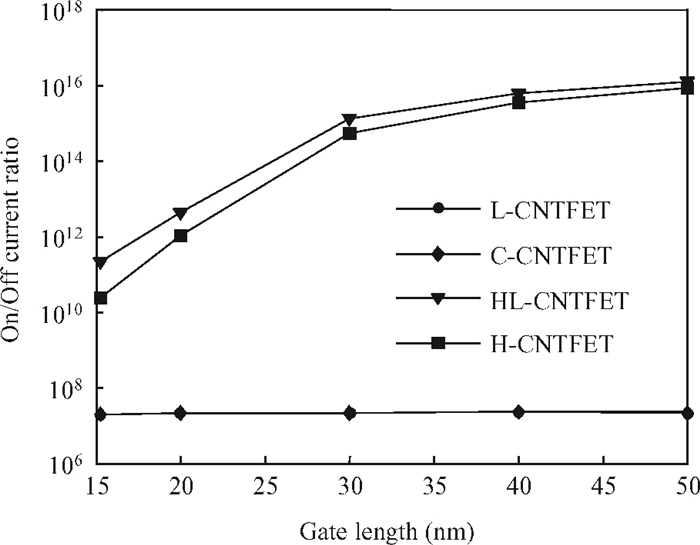
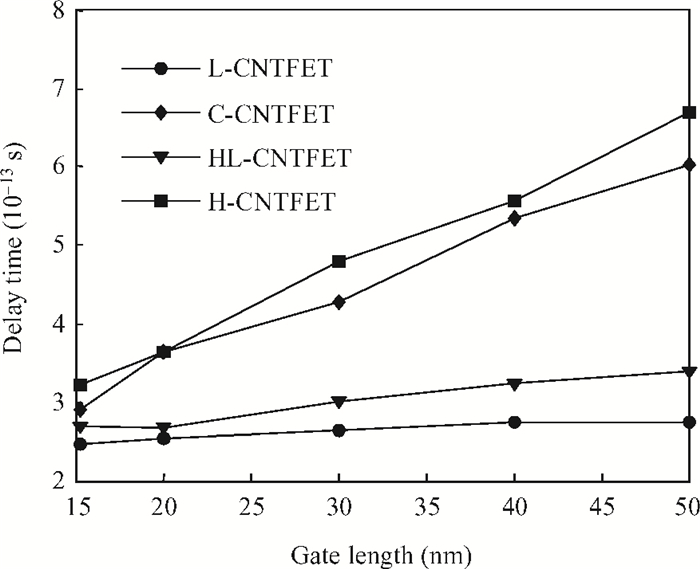
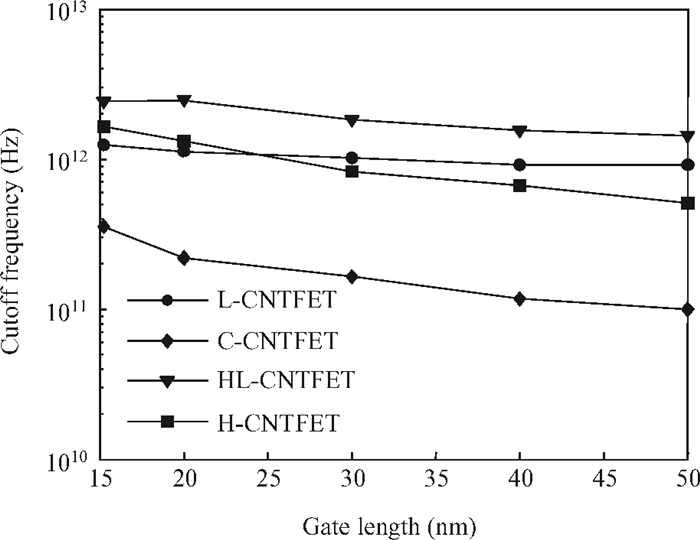
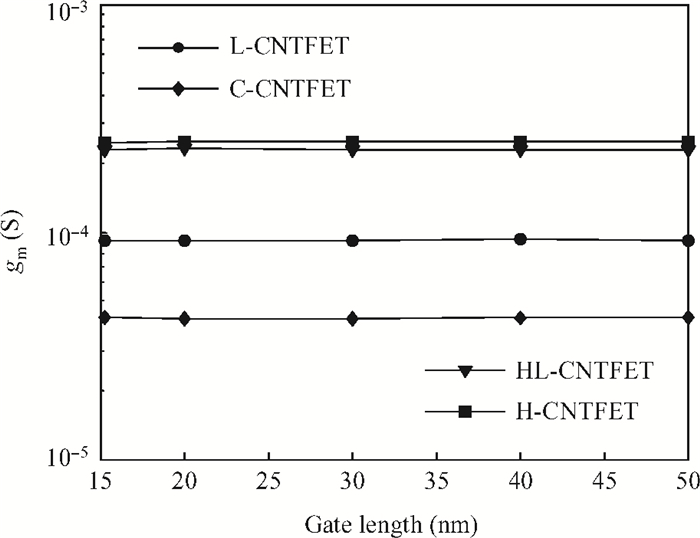
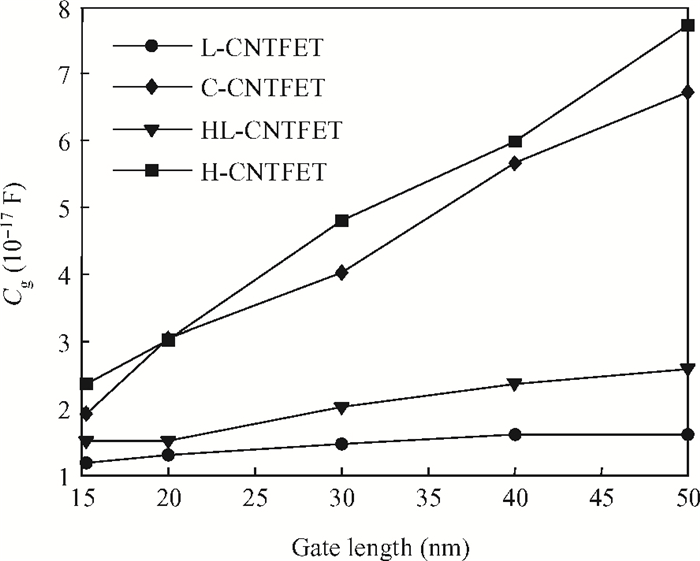
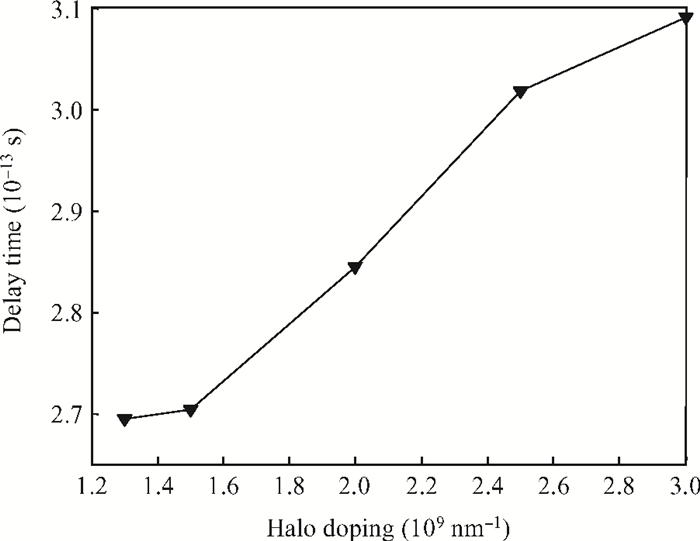
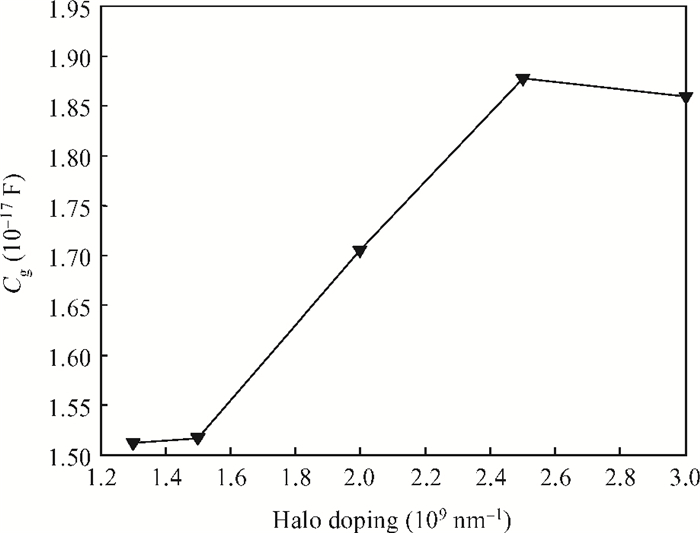
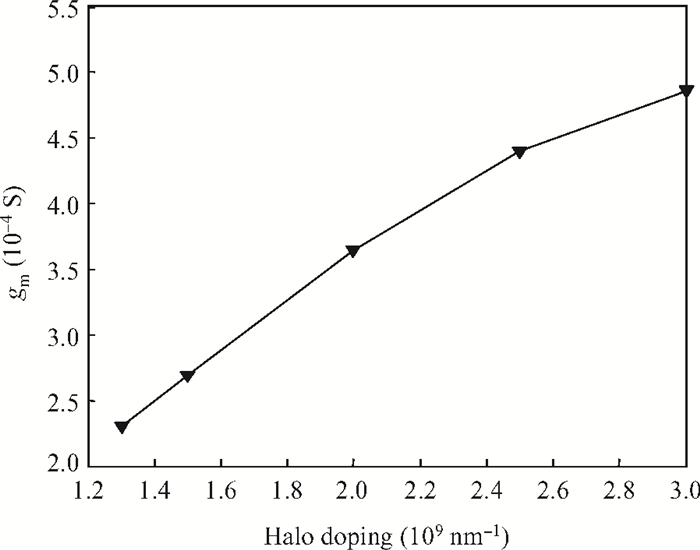
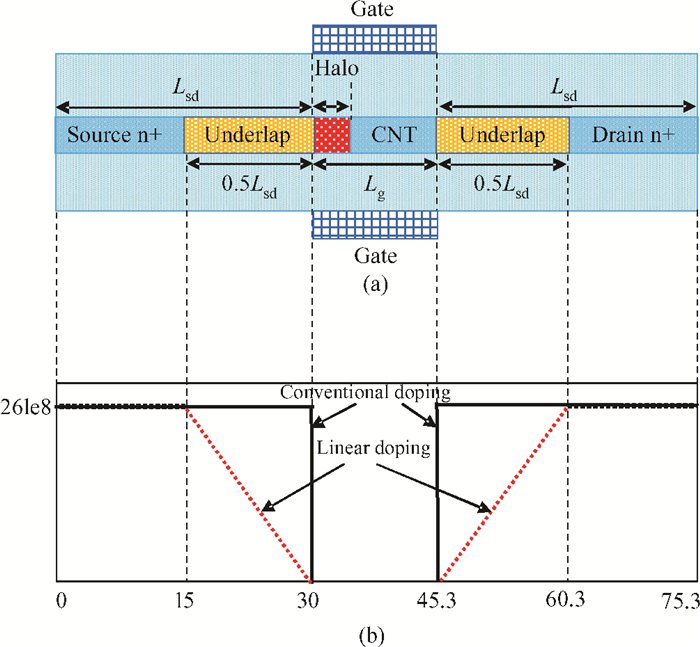
To overcome short-channel effects (SCEs) in high-performance device applications, a novel structure of CNTFET with a combination of halo and linear doping structure (HL-CNTFET) has been proposed. It has been theoretically investigated by a quantum kinetic model, which is based on two-dimensional non-equilibrium Green's functions solved self-consistently with Poisson's equations. We have studied the effect of halo doping and linear doping structure on static and dynamical performances of HL-CNTFET. It is demonstrated that a halo doping structure can decrease the drain leakage current and improve the on/off current ratio, and that linear doping can improve high-frequency and switching performance.-
Keywords:
- CNTFET,
- NEGF,
- Halo doping,
- SCE,
- linear doping
-
References
[1] Lu R F, Lu Y P, Lee S Y, et al. Terahertz response in single-walled carbon nanotube transistor:a real-time quantum dynamics simulation. Nanotechnology, 2009, 20(50):505401 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/20/50/505401[2] Kienle D, Léonard F. Terahertz response of carbon nanotube transistors. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 103(2):026601 http://www.tp1.physik.uni-bayreuth.de/de/publications/2009/Terahertz_Response_of_Carbon_Nanotube_Transistors/Terahertz_Response_of_Carbon_Nanotube_Transistors_Kienle__2009.pdf[3] Tans S J, Verschueren A R M, Dekker C. Room-temperature transistor based on a single carbon nanotube. Nature, 1998, 393(7):49 https://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v393/n6680/pdf/393049a0.pdf?foxtrotcallback=true[4] Shulaker M, Hills G, Patil N, et al. Carbon nanotube computer. Nature, 2013, 501(9):526 http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v501/n7468/full/nature12502.html[5] Shulaker M, Rethy J V, Hills G, et al. Experimental demonstration of a fully digital capacitive sensor interface build entirely using carbon nanotube FETs. Proc Int Solid State Circuits Conf, 2013:112 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6487660/[6] Hazeghi A, Krishnamohan T, Wong H. Schottky-barrier carbon nanotube field-effect transistor modeling. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2007, 54(3):439 doi: 10.1109/TED.2006.890384[7] Guo J, Lundstrom M, Datta S. Performance projections for ballistic carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 80(17):3192 doi: 10.1063/1.1474604[8] Fiori G, Iannaccone G, Klimeck G. A three-dimensional simulation study of the performance of carbon nanotube field-effect transistors with doped reservoirs and realistic geometry. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2006, 53(8):1782 doi: 10.1109/TED.2006.878018[9] Orouji A A, Arefinia Z. Detailed simulation study of a dual material gate carbon nanotube field-effect transistor. Phys E:Low-Dimensional Syst Nanostructures, 2009, 41(10):552 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1386947708003767[10] Liu X H, Zhao H L, Li T Y, et al. Improvement on the electron transport efficiency of the carbon nanotube field effect transistor device by introducing heterogeneous-dual-metal-gate structure. Acta Phys Sin, 2013, 62(14):147308 http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-WLXB201314064.htm[11] Arefinia Z, Orouji A A. Quantum simulation study of a new carbon nanotube field-effect transistor with electrically induced source/drain extension. IEEE Trans Device Mater Reliab, 2009, 9(2):237 doi: 10.1109/TDMR.2009.2015458[12] Xia T S, Register L F, Banerjee S K. Simulation study of the carbon nanotube field effect transistors beyond the complex band structure effect. Solid-State Electron, 2005, 49(3):860 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S003811010500064X[13] Guo J, Hasan S, Javey A, et al, Assessment of high-frequency performance potential for carbon nanotube transistors. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol, 2005, 4(6):715 doi: 10.1109/TNANO.2005.858601[14] Chen L, Pulfrey D L. Comparison of p-i-n and n-i-n carbon nanotube FETs regarding high-frequency performance. Solid-State Electron, 2009, 53(9):935 doi: 10.1016/j.sse.2009.05.006[15] Djeffal F, Meguellati M, Benhaya A. A two-dimensional analytical analysis of subthreshold behavior to study the scaling capability of nanoscale graded channel gate stack DG MOSFETs. Physica E:Low-Dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 2009, 41(10):1872 doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2009.08.002[16] Reddy G V, Kumar M J. A new dual-material double-gate (DMDG) nanoscale SOI MOSFET-two-dimensional analytical modeling and simulation. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol, 2005, 4(2):260 doi: 10.1109/TNANO.2004.837845[17] Alam K, Lake R. Role of doping in carbon nanotube transistors with source/drain underlaps. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol, 2007, 6(6):652 doi: 10.1109/TNANO.2007.908170[18] Kordrostami Z, Sheikhi M H, Zarifkar A. Influence of channel and underlap engineering on the high-frequency and switching performance of CNTFETs. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol, 2012, 11(3):526 doi: 10.1109/TNANO.2011.2181998[19] Sarvari H, Ghayour R. Design of GNRFET using different doping profiles near the source and drain contacts. International Journal of Electronics, 2012, 99(5):673 doi: 10.1080/00207217.2011.643496[20] Zhang Z, Song S C, Huffman C. Integration of dual metal gate CMOS on high-k dielectrics utilizing a metal wet etch process. Electrochem Solid-State Lett, 2005, 8(10):G271 doi: 10.1149/1.2030447[21] Zhou C, Kong J, Yenilmez E, et al. Modulated chemical doping of individual carbon nanotubes. Science, 2000, 290(5496):1552 doi: 10.1126/science.290.5496.1552[22] Datta S. Nanoscale device modeling:the Green's function method. Superlatt Microstruct, 2000, 28(4):253 doi: 10.1006/spmi.2000.0920[23] Wang W, Li N, Ren Y, et al. A computational study of the effects of linear doping profile on the high-frequency and switching performances of hetero-material-gate CNTFETs. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(12):124002 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/12/124002[24] Venugopal R, Ren Z, Datta S, et al. Simulating quantum transport in nanoscale CNTFETs:real versus mode-space approaches. J Appl Phys, 2002, 92(7):3730 doi: 10.1063/1.1503165[25] Wang W, Yang X, Li N, et al. Numerical study on the performance metrics of lightly doped drain and source grapheme nanoribbon field effect transistors with double-material-gate. Superlattices and Microstructures, 2013, 64(9):227 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0749603613003157 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: